Chemistry Unit 4 AOS1 - Organic Reaction Pathways
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
oxidation (primary alcohol)
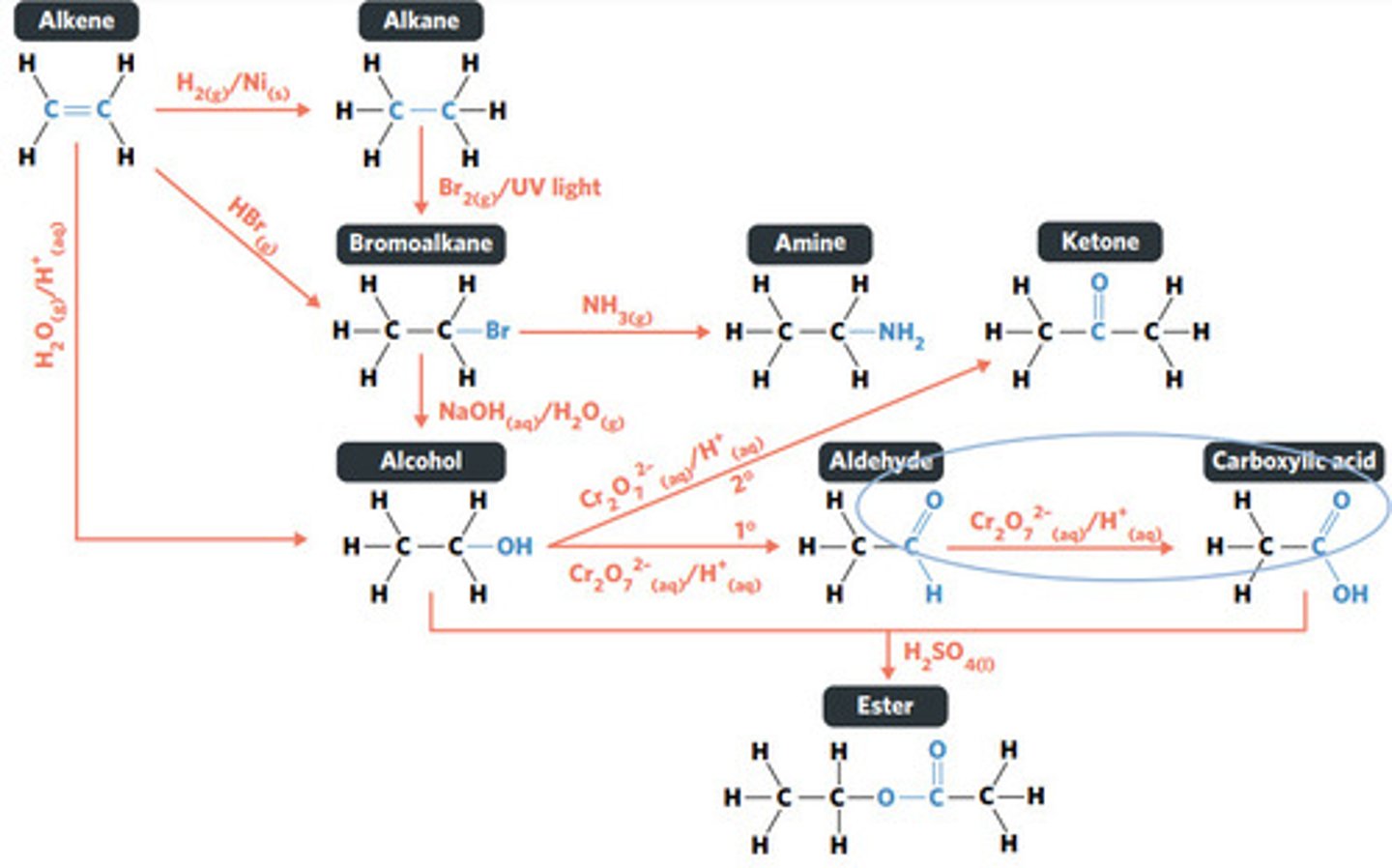
concentrated H2SO4 (sulphuric acid)
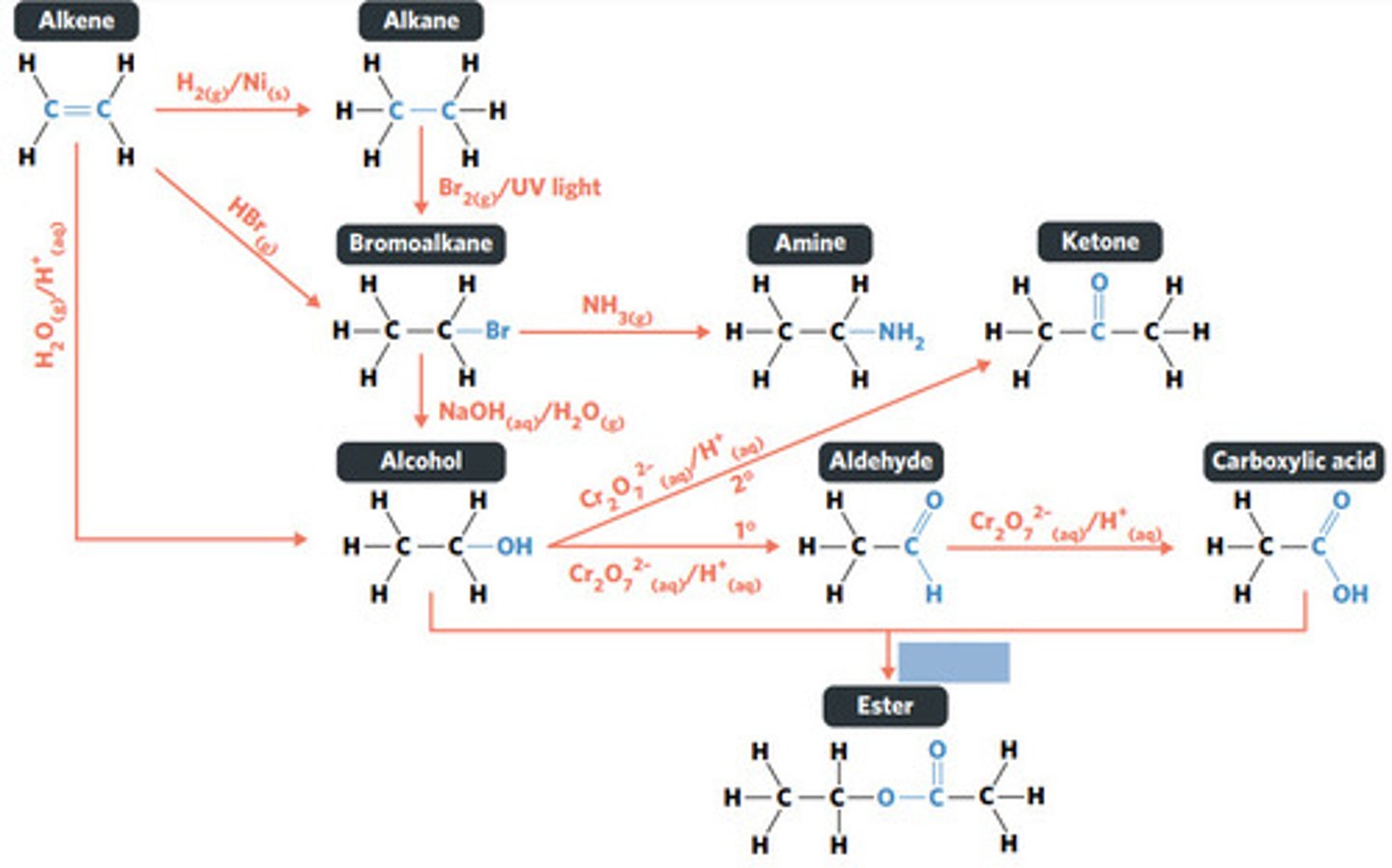
esterification: condensation reaction between organic compounds that forms at least one ESTER AS A PRODUCT
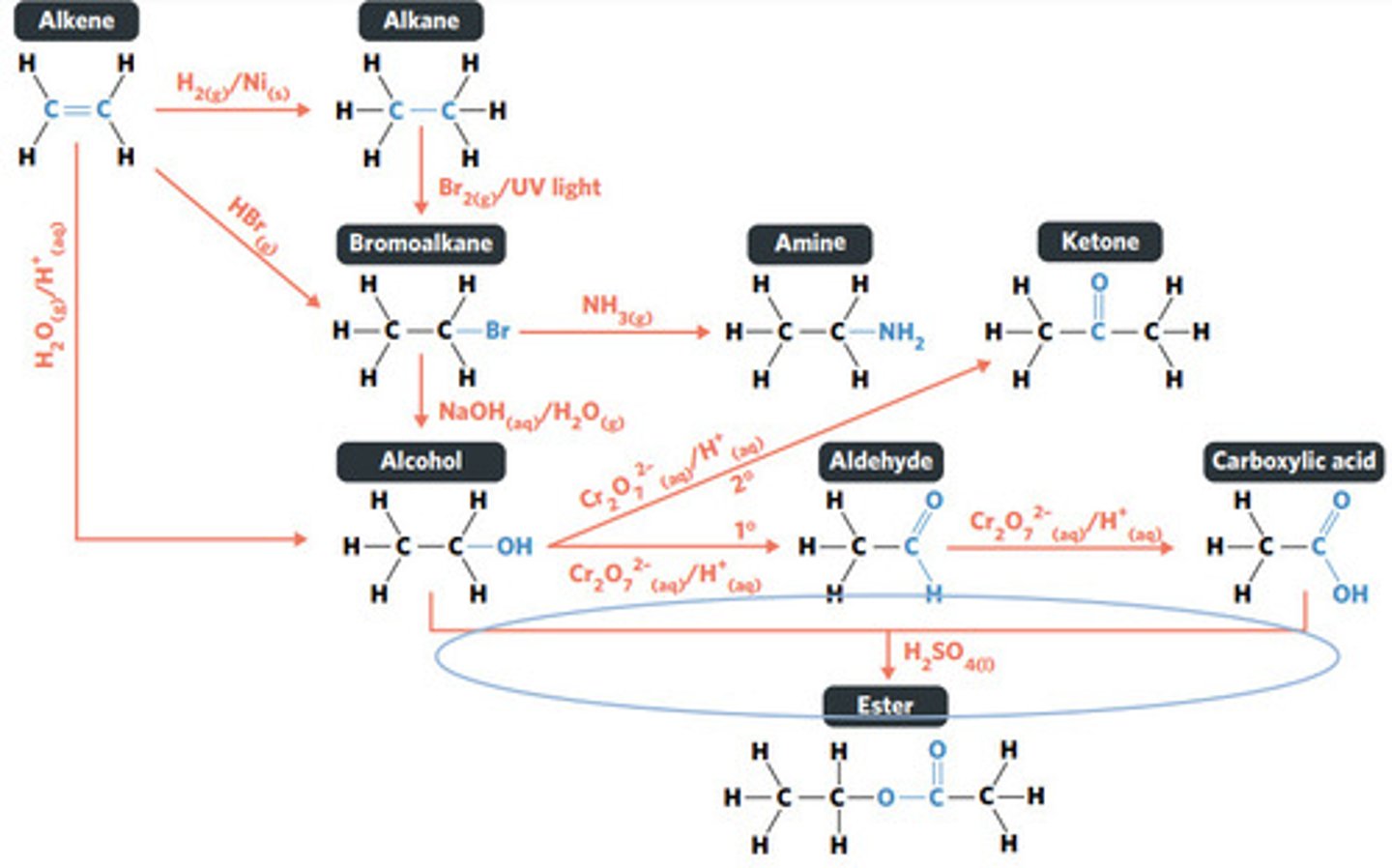
Cr2O7^2-(aq)/H+ (acidified)
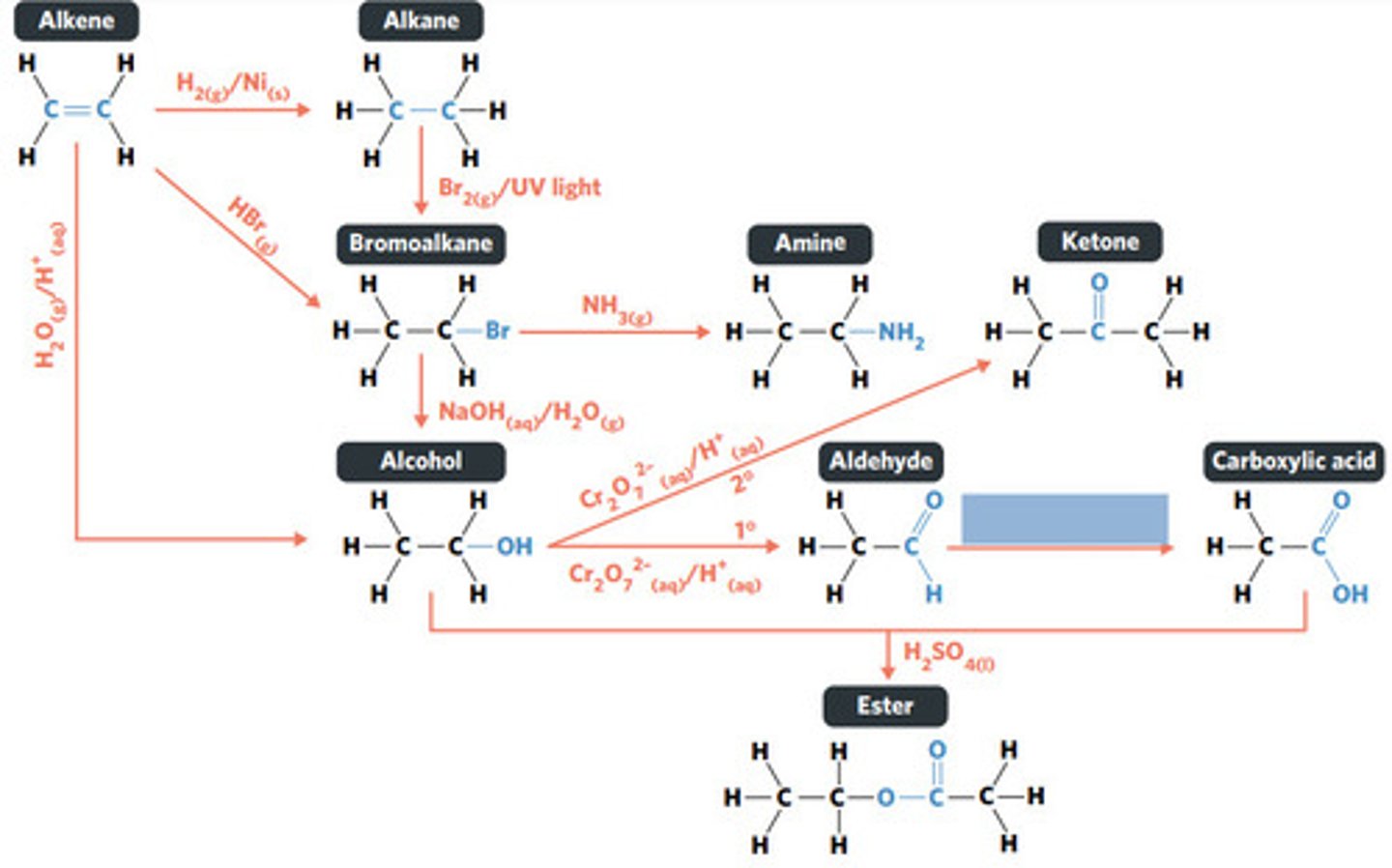
oxidation (primary alcohol)
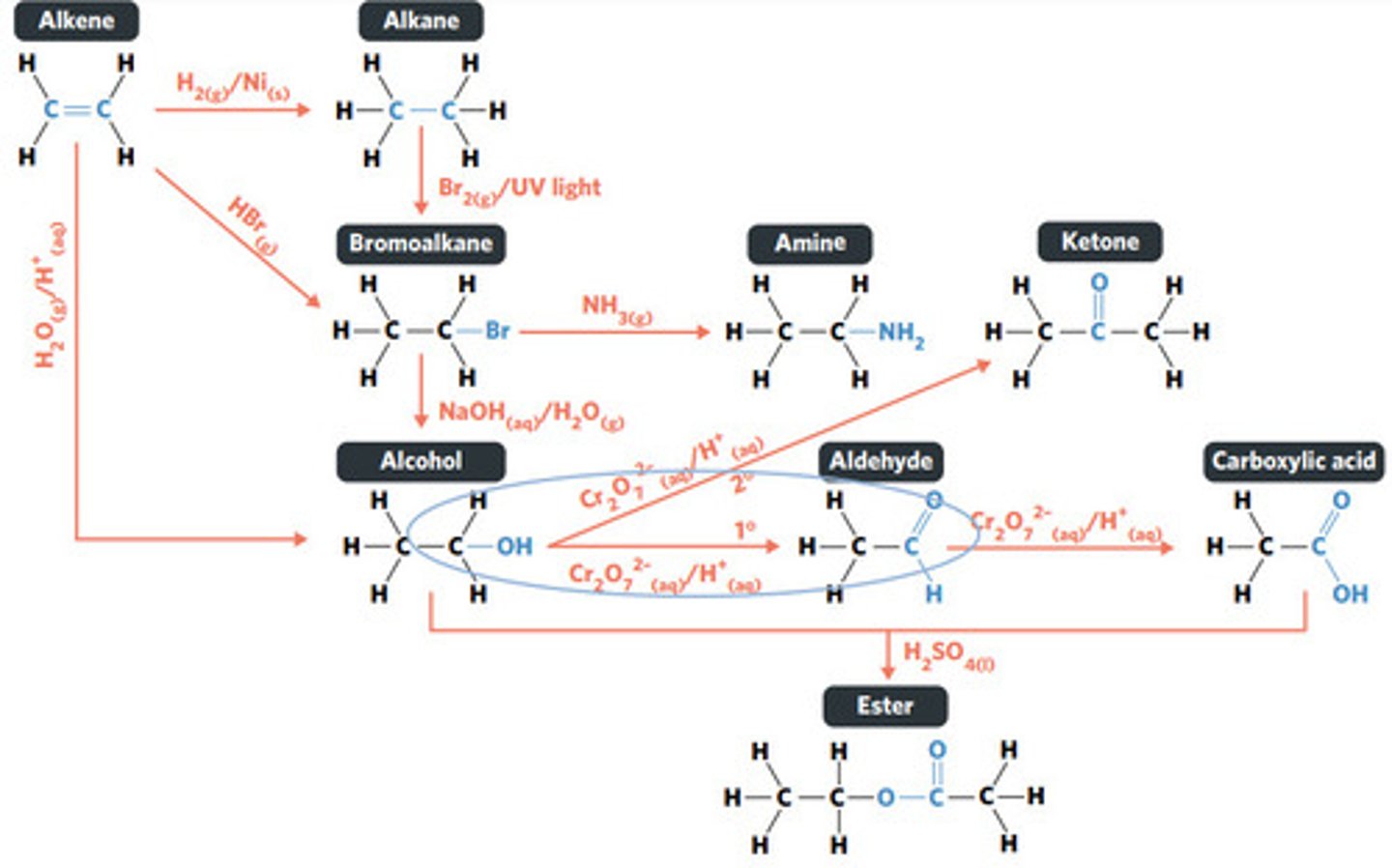
oxidation (secondary alcohol)
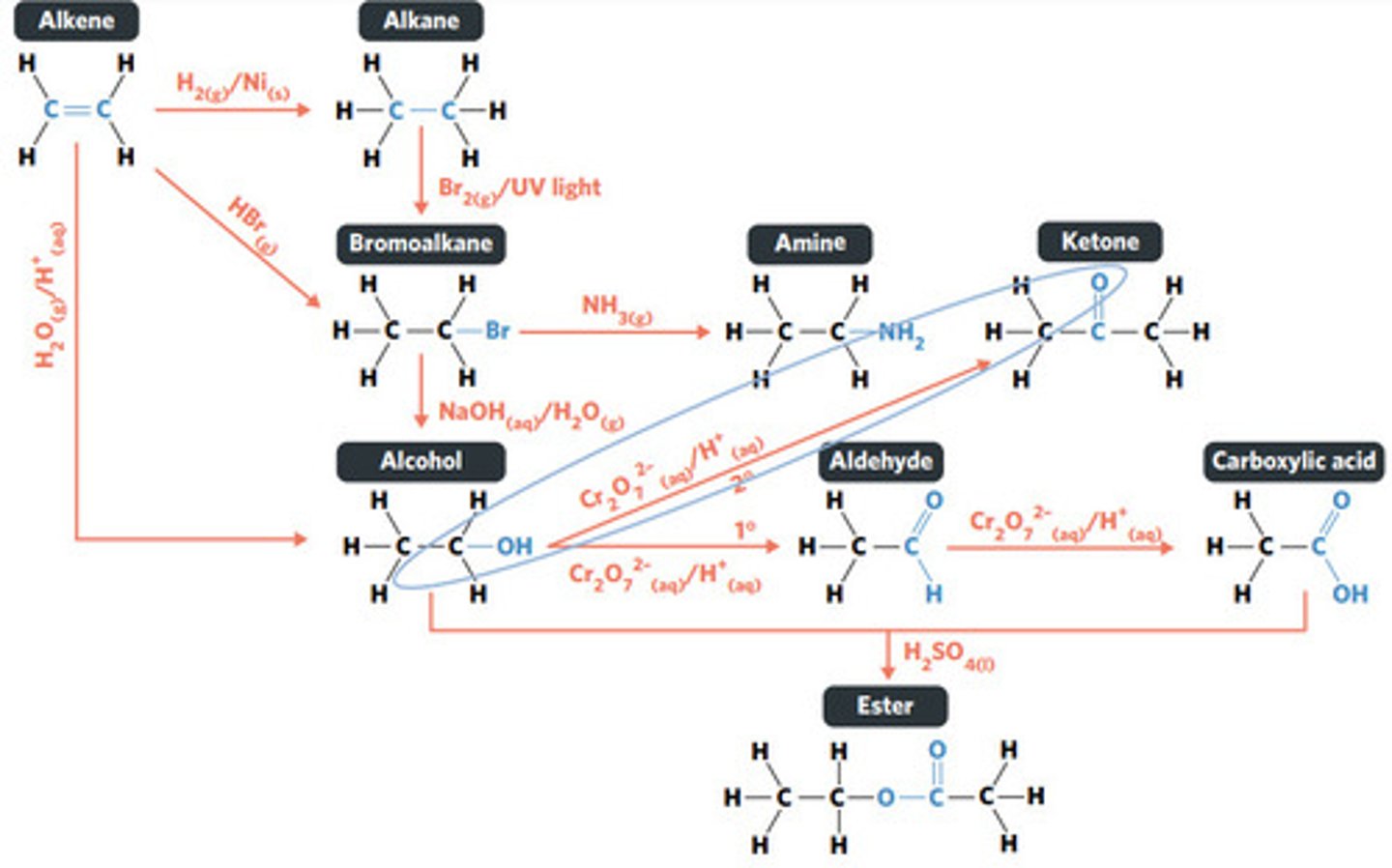
Cr2O7^2-(aq)/H+ (acidified)
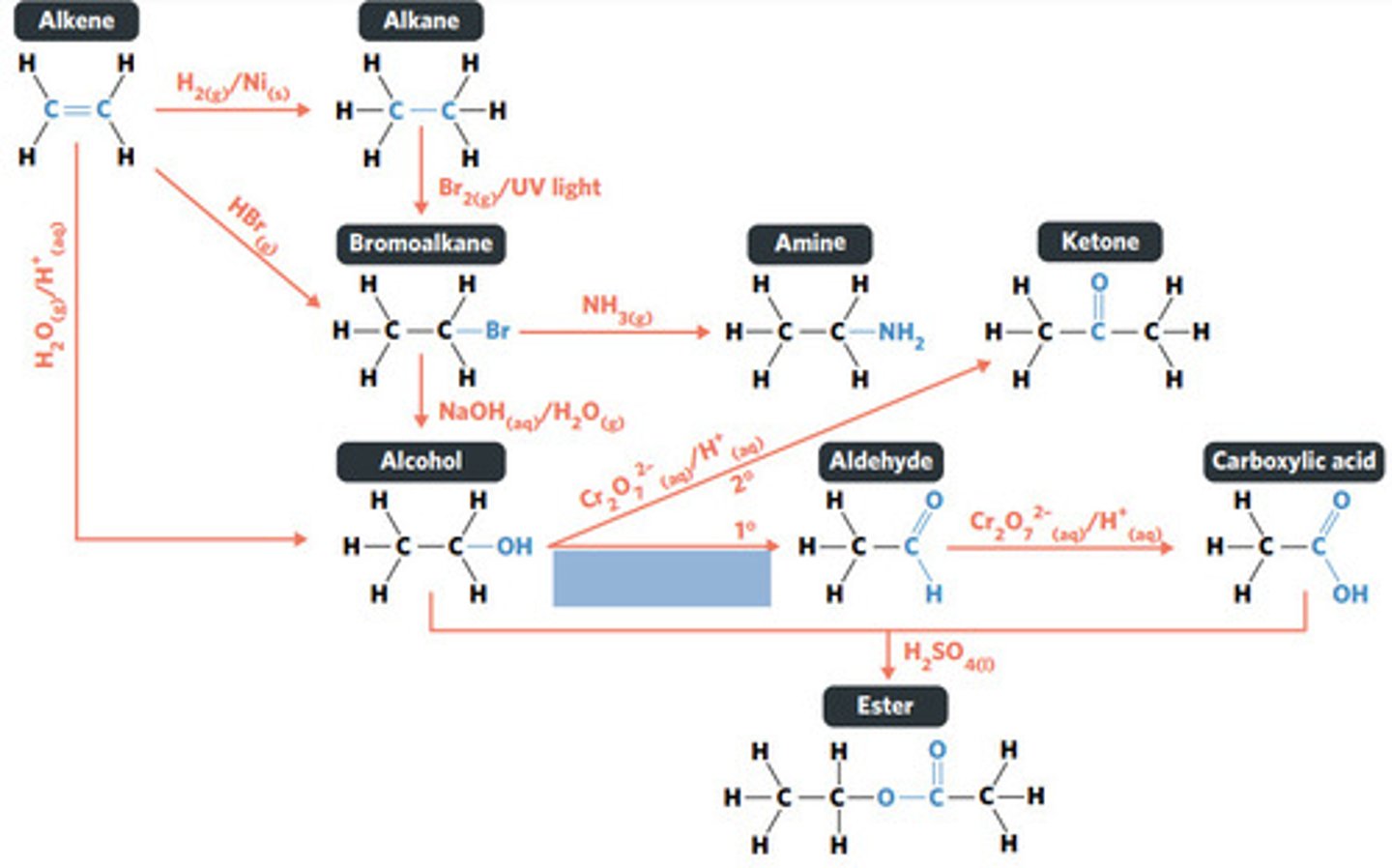
Cr2O7^2-(aq)/H+ (acidified)
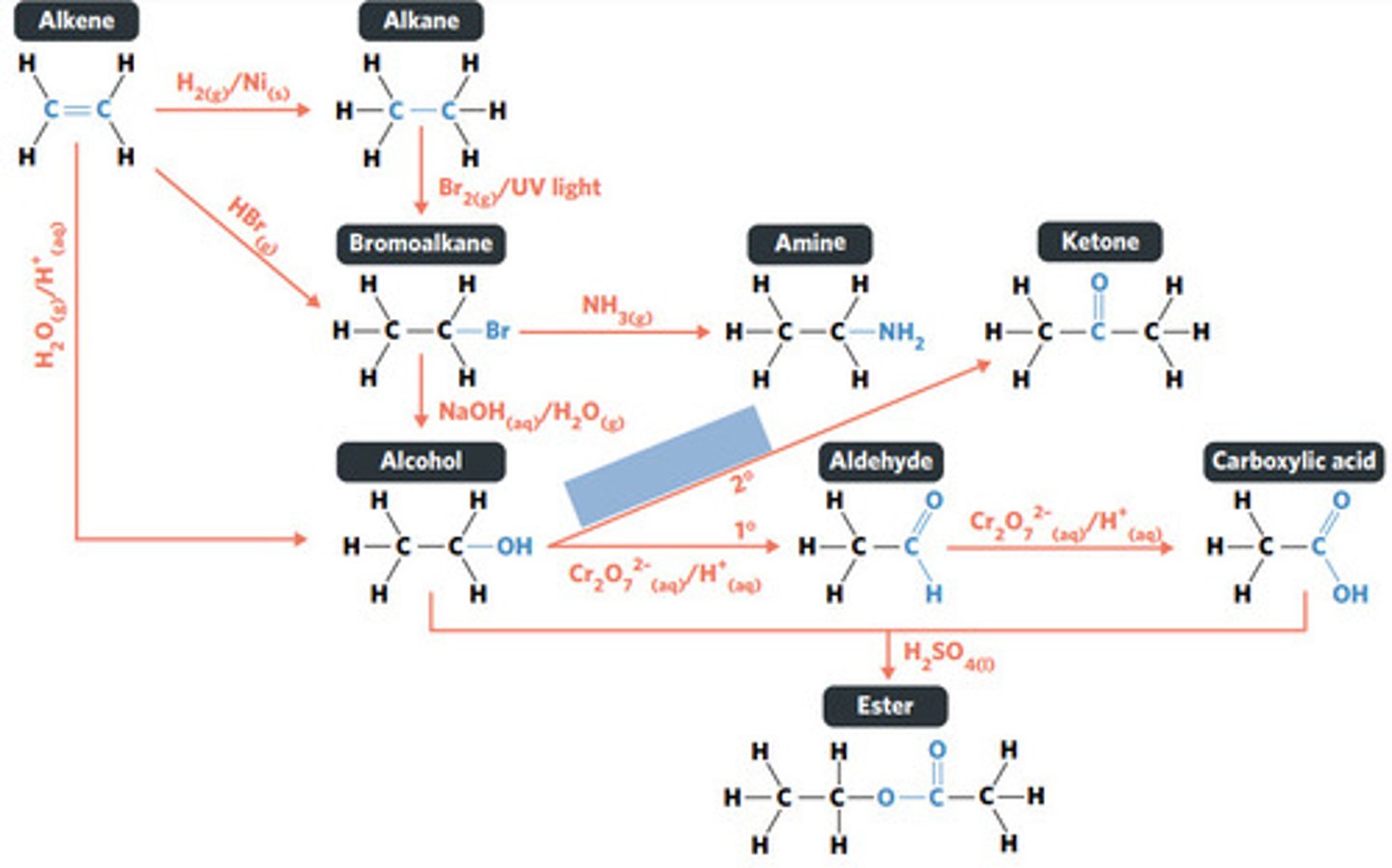
substitution reaction
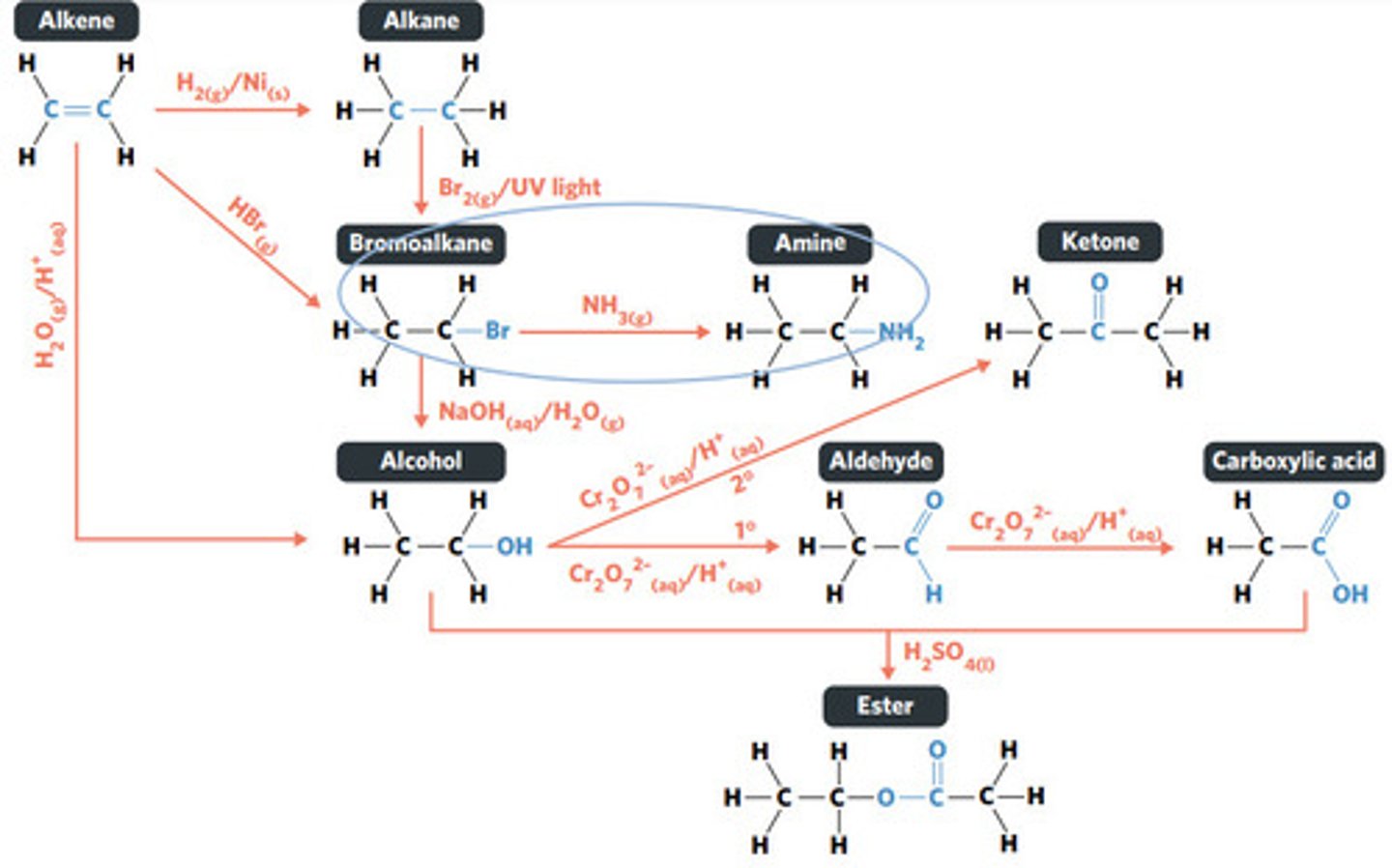
substitution reaction
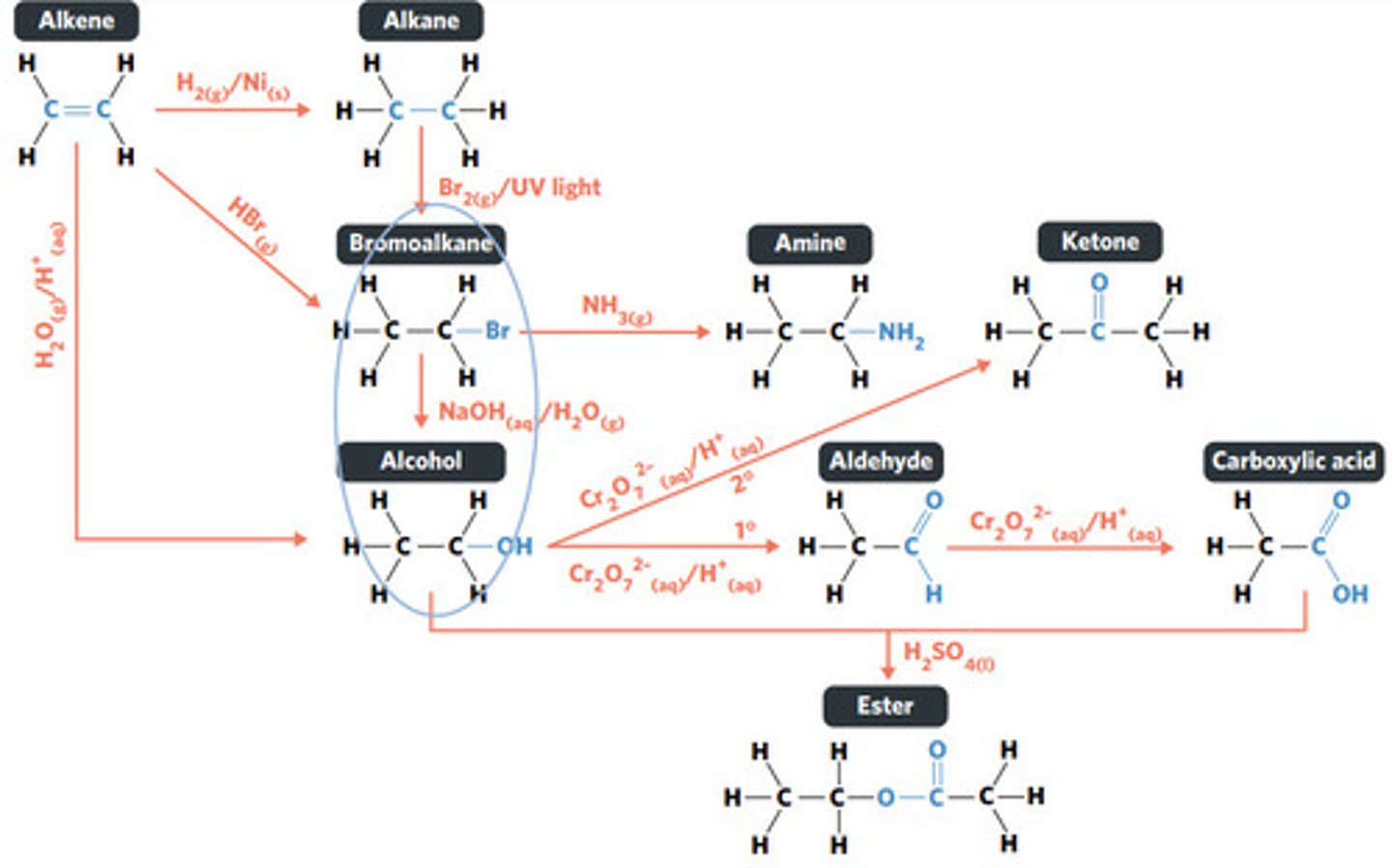
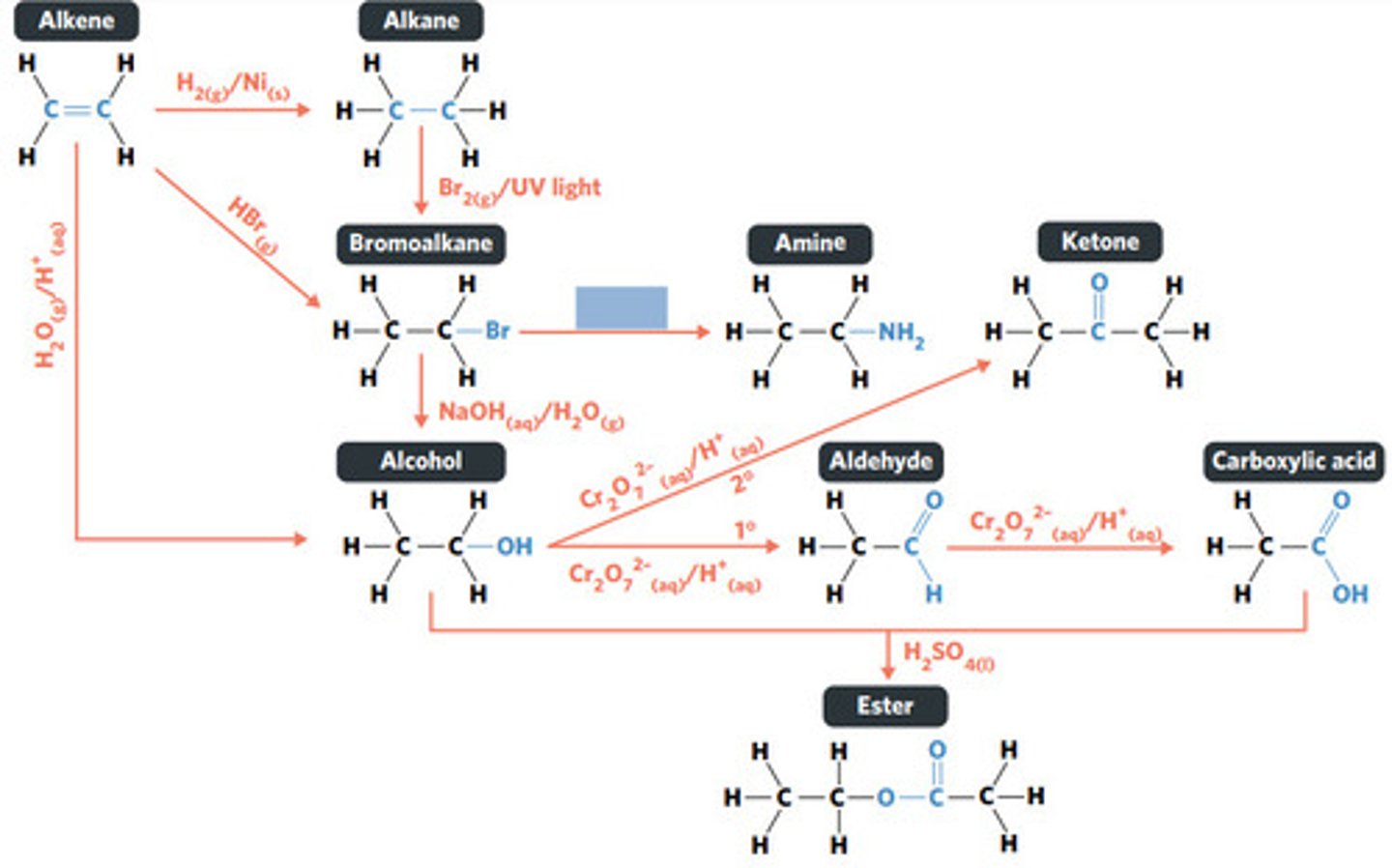
NH3 (g)
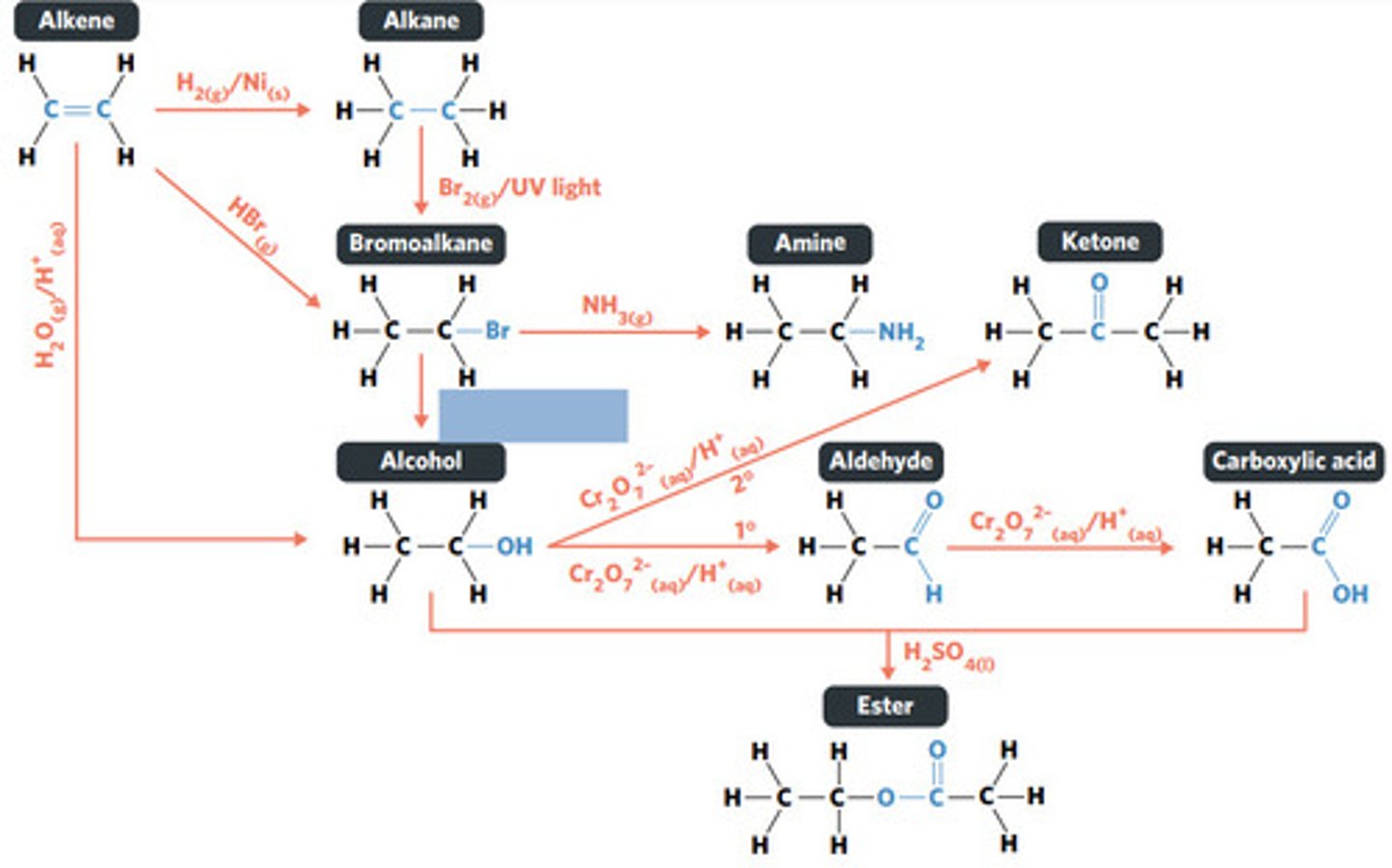
NaOH (aq)
substitution reaction
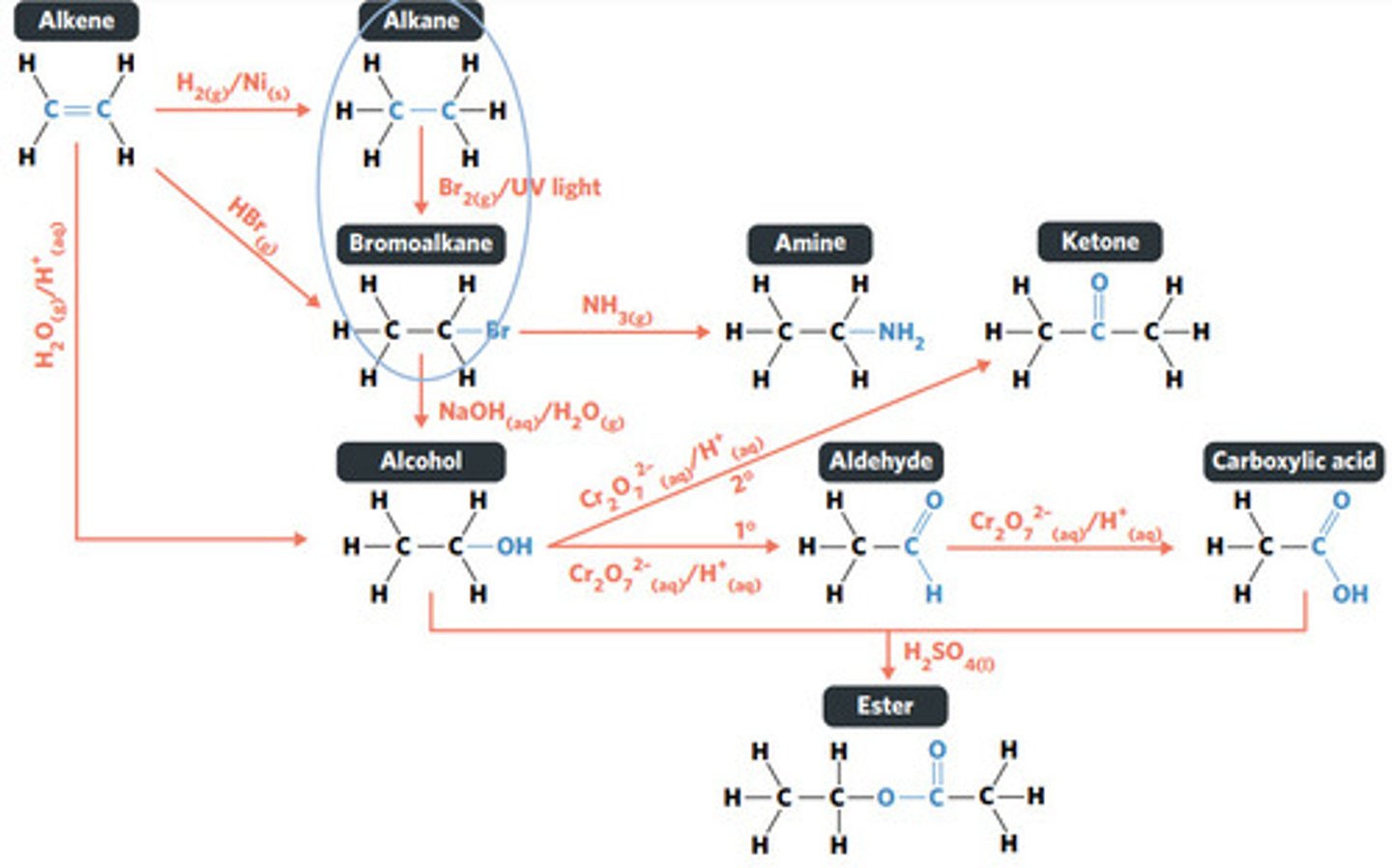
Br2 (g) / UV light
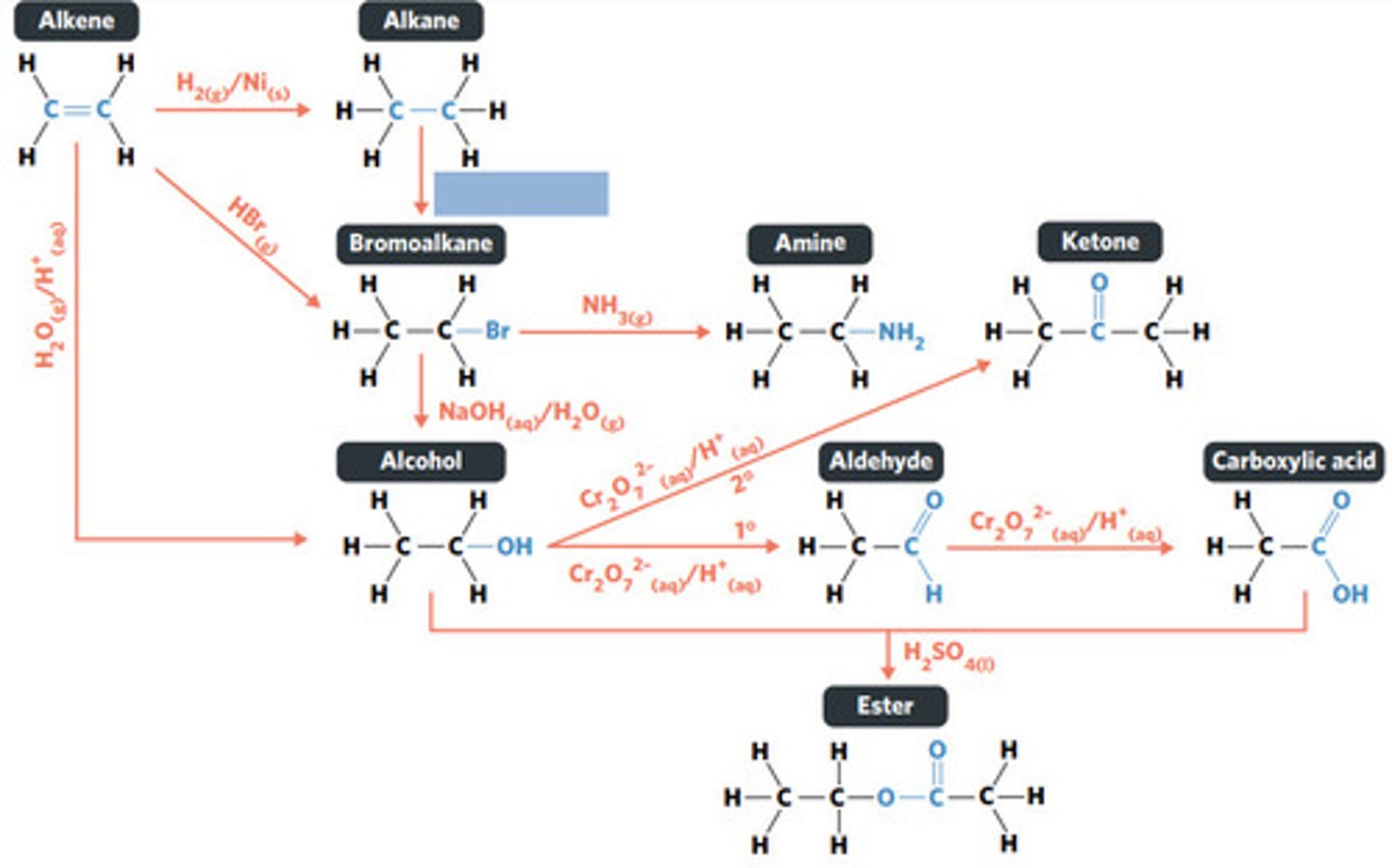
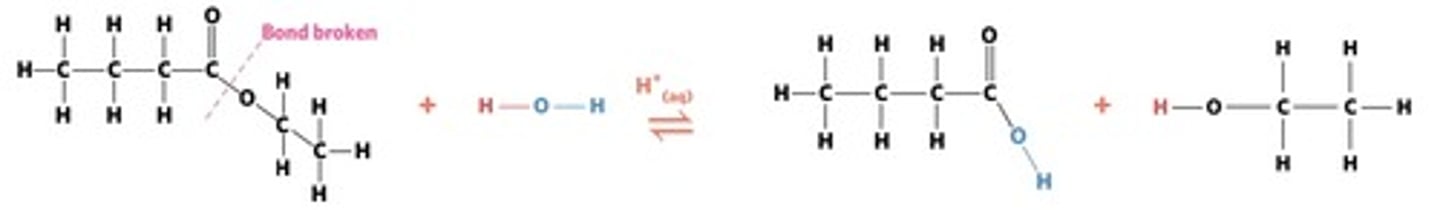
hydrolysis: addition reaction where WATER IS USED to BREAK THE BONDS of a substance
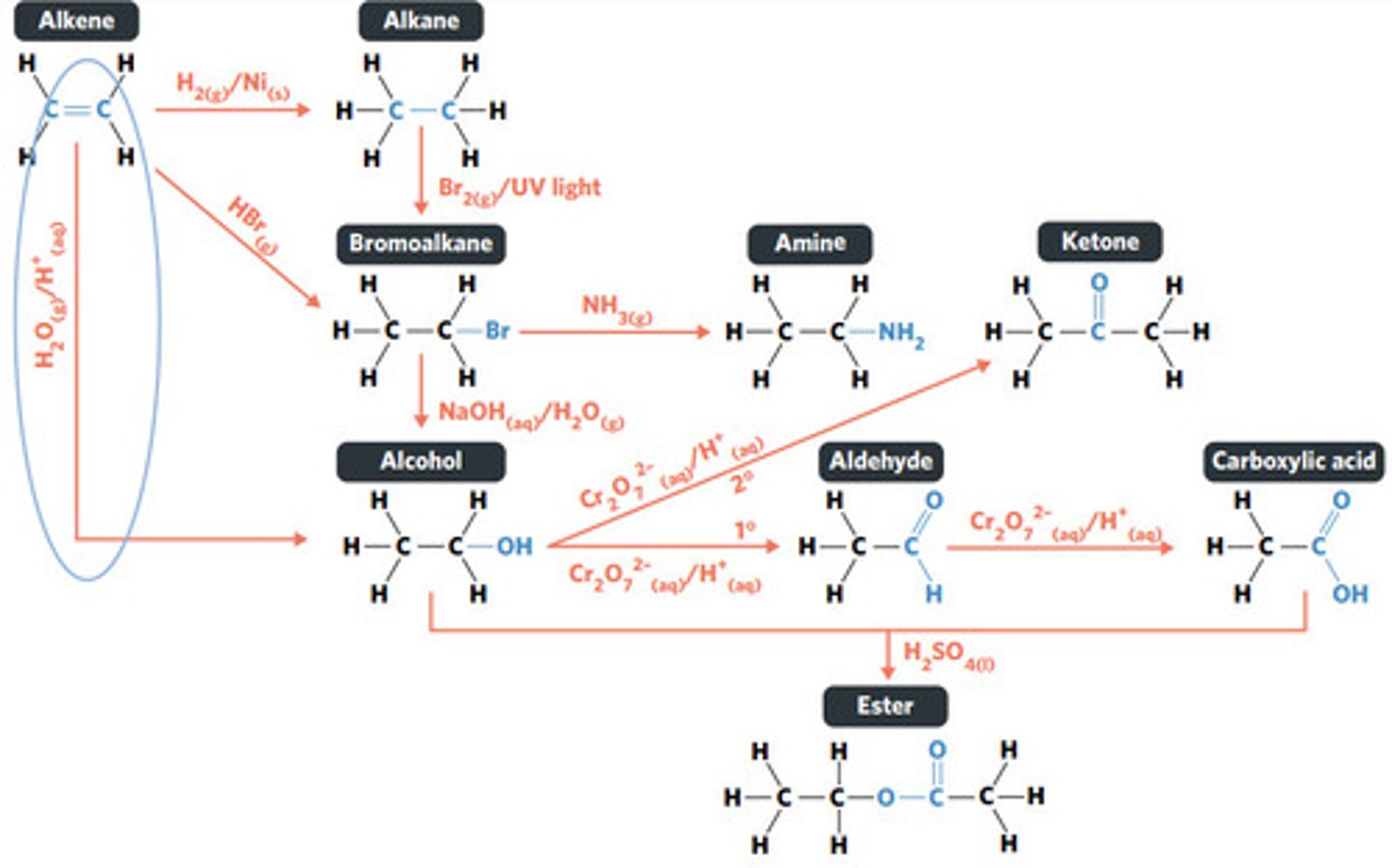
hydrolysis of an ester into a carboxylic acid and primary alcohol
addition reaction
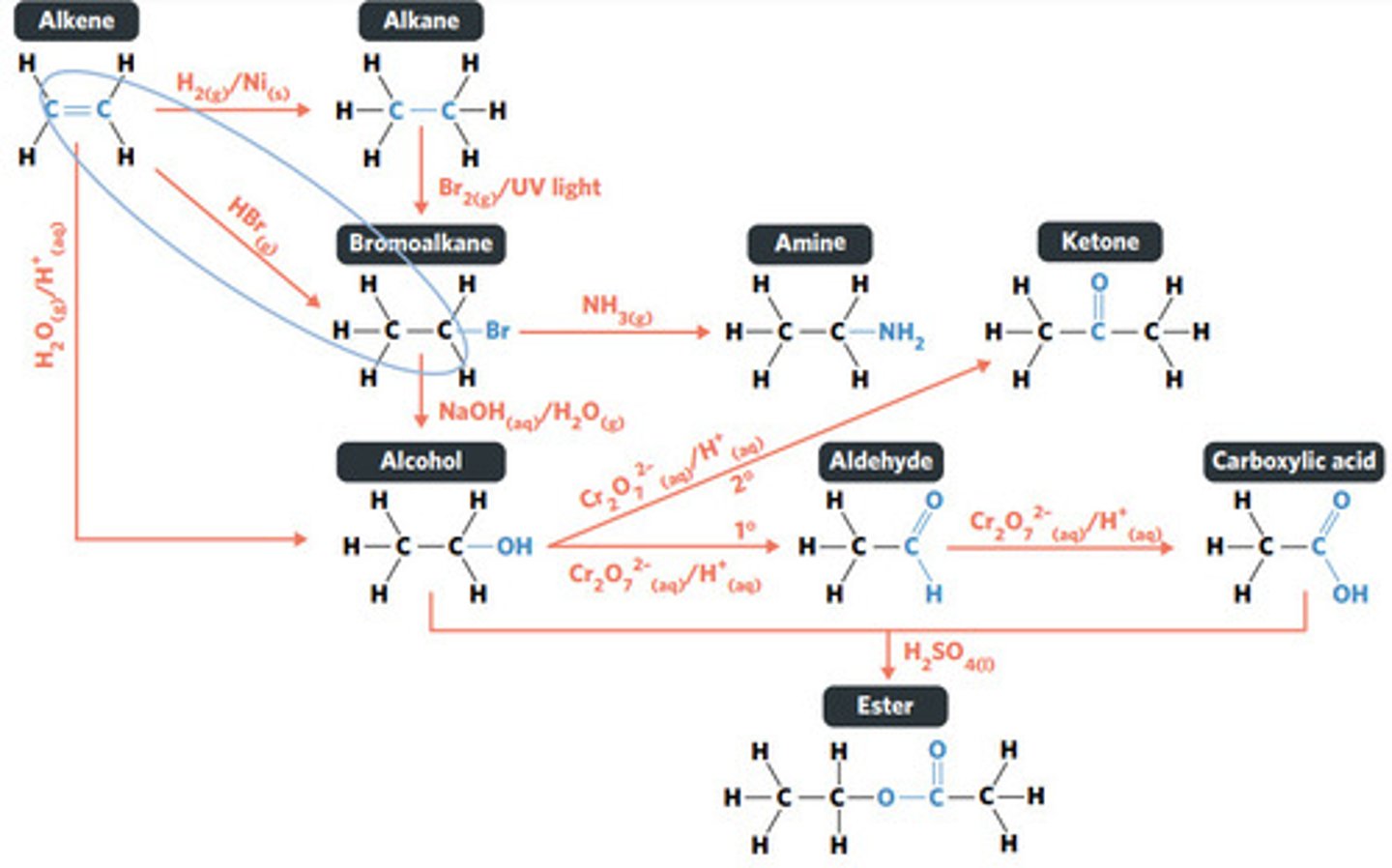
H2O (g) / H3PO4 (aq)
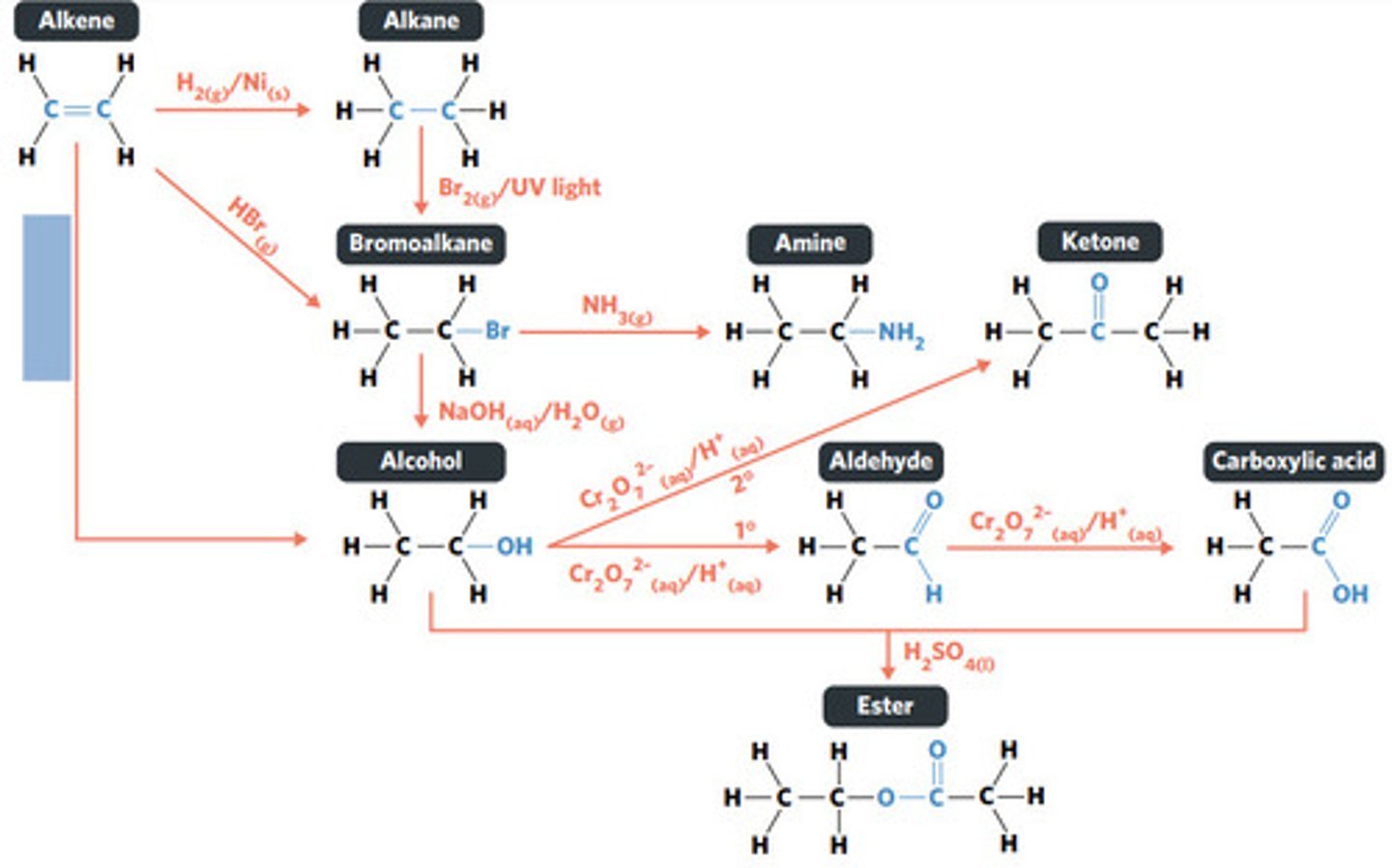
HBr (g)
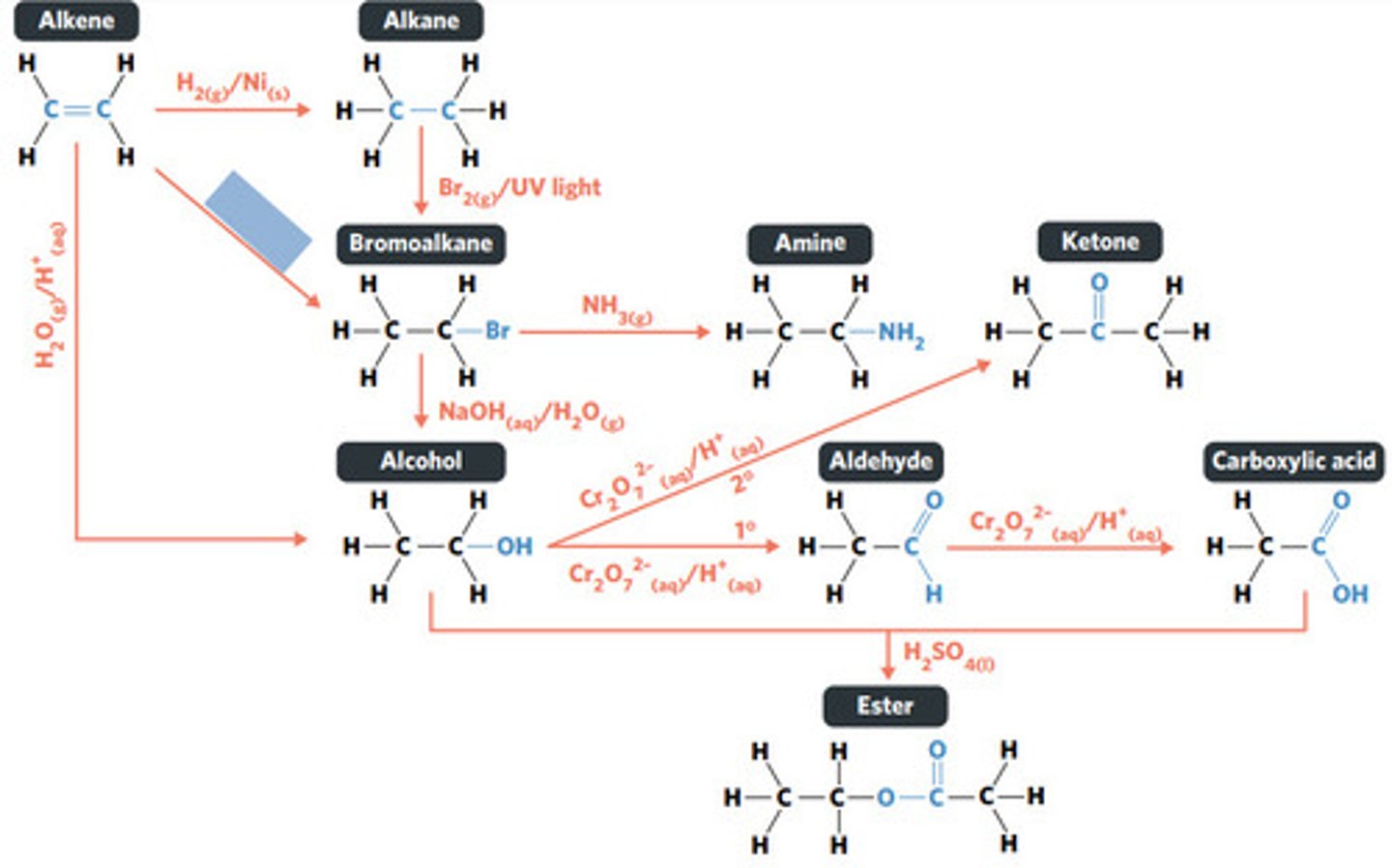
addition reaction (hydrogenation)
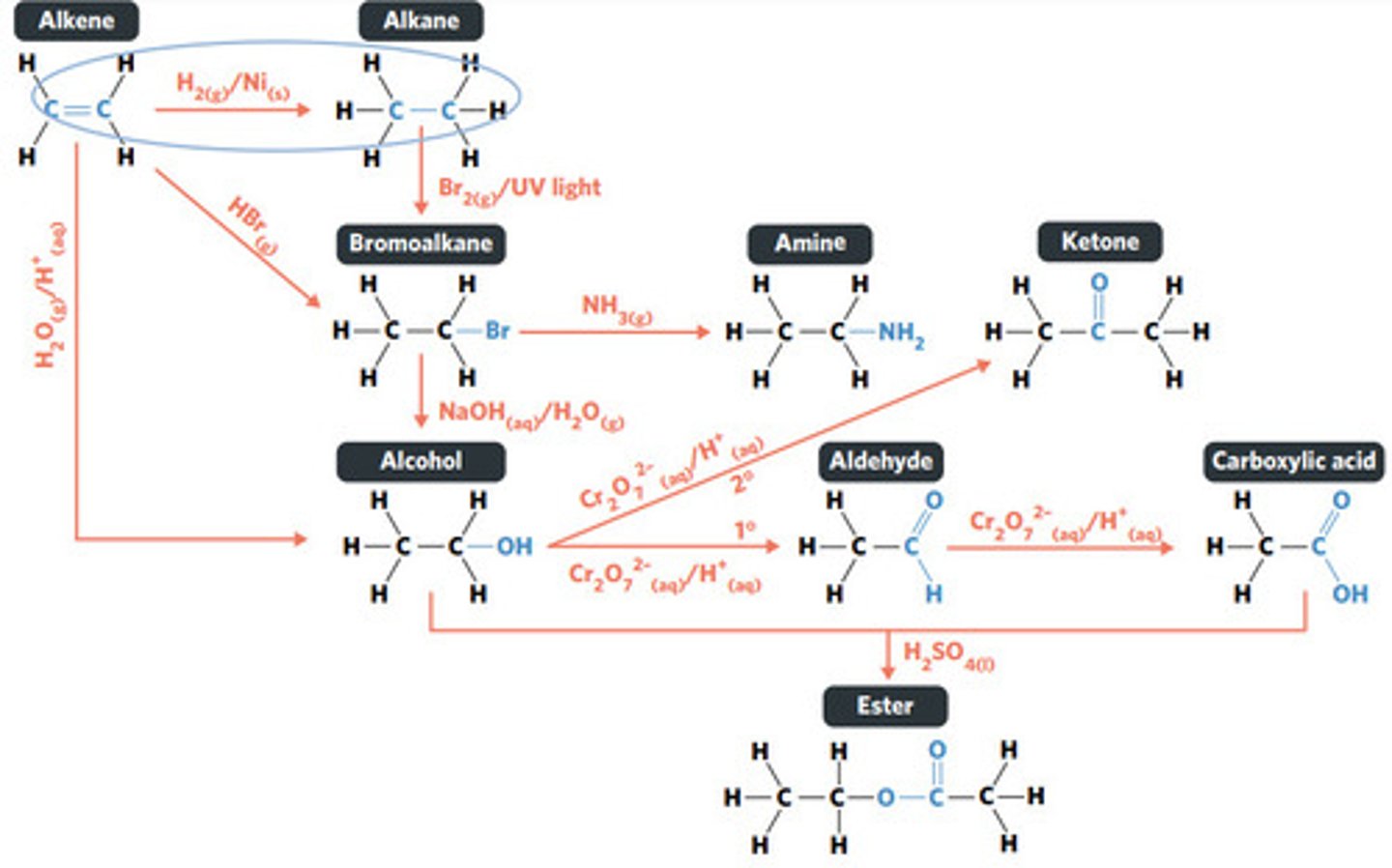
H2 (g) / Ni (s)
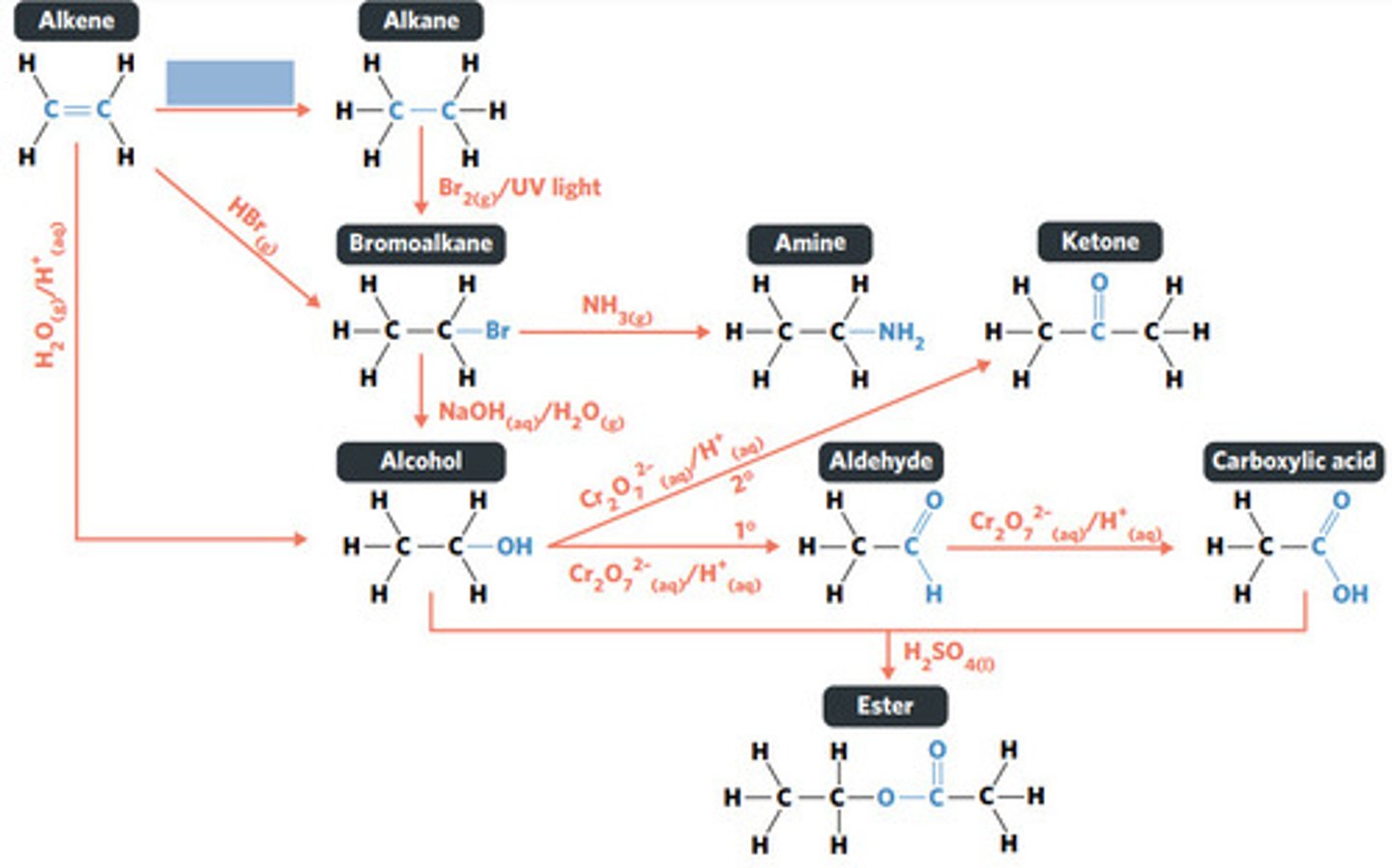
reaction where two molecules combine with each other to form a LARGER MOLECULE with NO OTHER PRODUCTS (alkene to alkane, alkene to alcohol, alkene to haloalkane)
addition reaction
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
What sort of hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions?
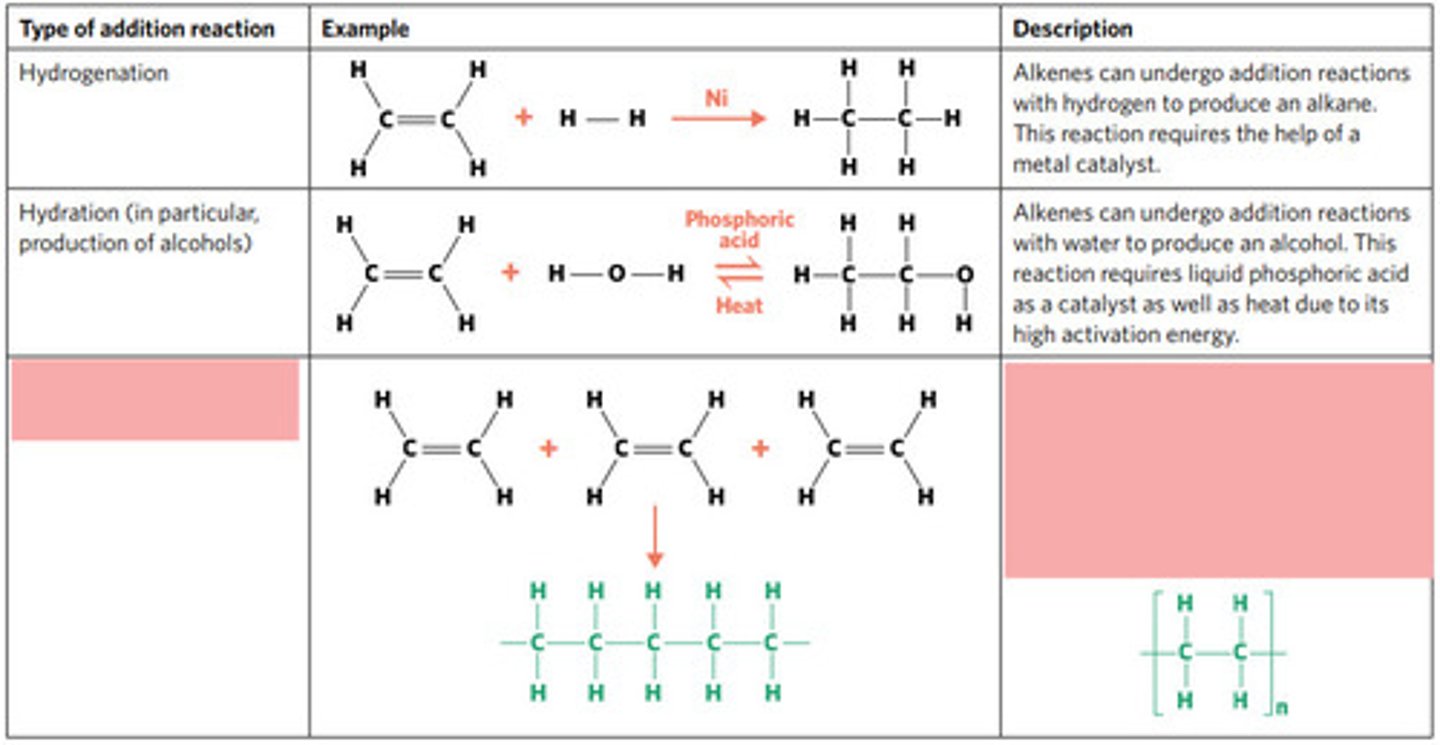
hydrogenation: alkenes react with hydrogen to produce an alkane, with help of metal catalyst
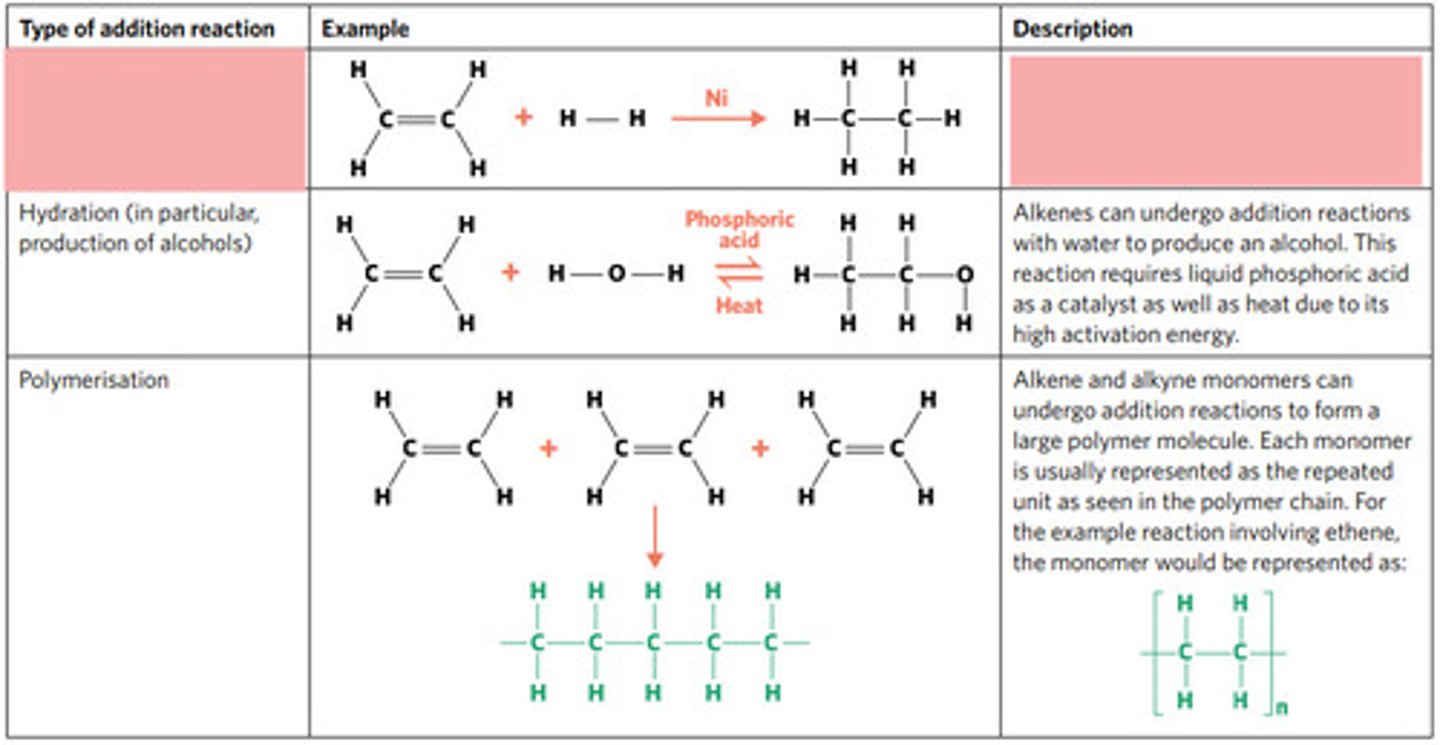
hydration: alkenes can react with water to produce an alcohol, with liquid phosphoric acid and heat as catalyst
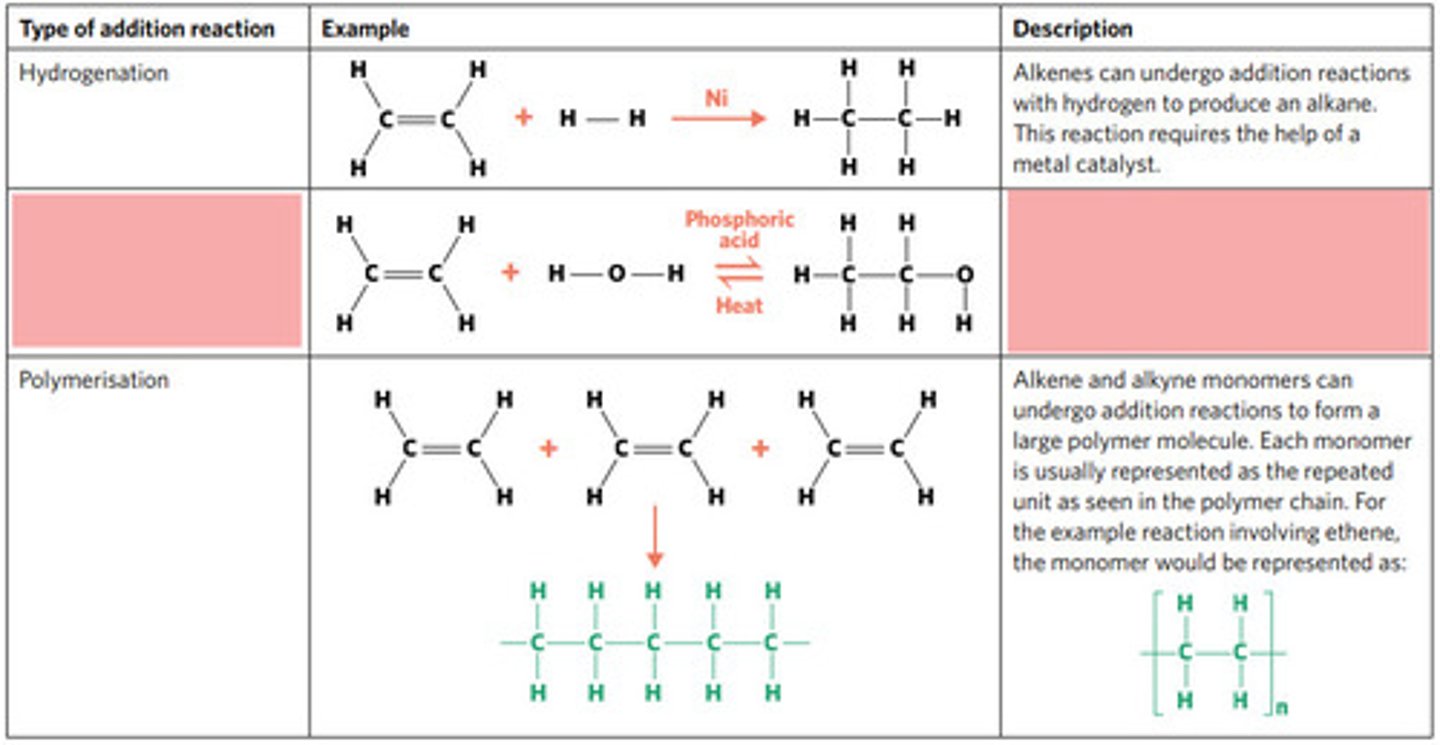
polymerisation: alkene/alkyne monomers undergo addition reactions to form a large polymer molecule (represented as repeated units)
SECONDARY ALCOHOLS (primary alcohols form aldehydes and carboxylic acids)
What sort of alcohol can be oxidised to produce a ketone?
dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) and permanganate ions (MnO4-)
What catalysts are commonly used as oxidising agents?
a HYDROGEN must be BONDED TO THE HYDROXYL CARBON
What must be present on an alcohol for oxidation to occur?
LIMITING the TEMPERATURE and OXIDISING AGENT available, and REMOVING THE ALDEHYDE as it being produced
How can the production of an aldehyde (rather than a carboxylic acid) be maximised from the oxidation of a primary alcohol?
reaction where two molecules combine with the release of a WATER MOLECULE (carboxylic acid to primary amide, esterification reaction)
condensation reaction
condensation of carboxylic acid to primary amide

reaction where an atom (or group of atoms) in a compound are REPLACED by another atom (or group of atoms) (eg. alkane to haloalkane, haloalkane to alcohol, haloalkane to amine)
substitution reaction
atom economy: extent to which the reactants are used to make the desired product
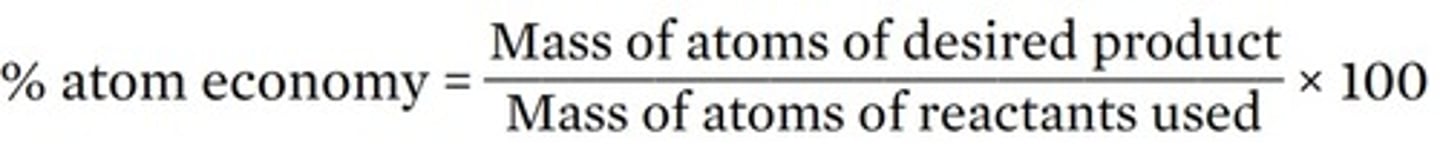
reactants/products lost in experimental process, equilibrium reacts don't proceed to completion, slow rate of reaction (incomplete)
Why do reactions rarely give 100% yield?
percentage yield
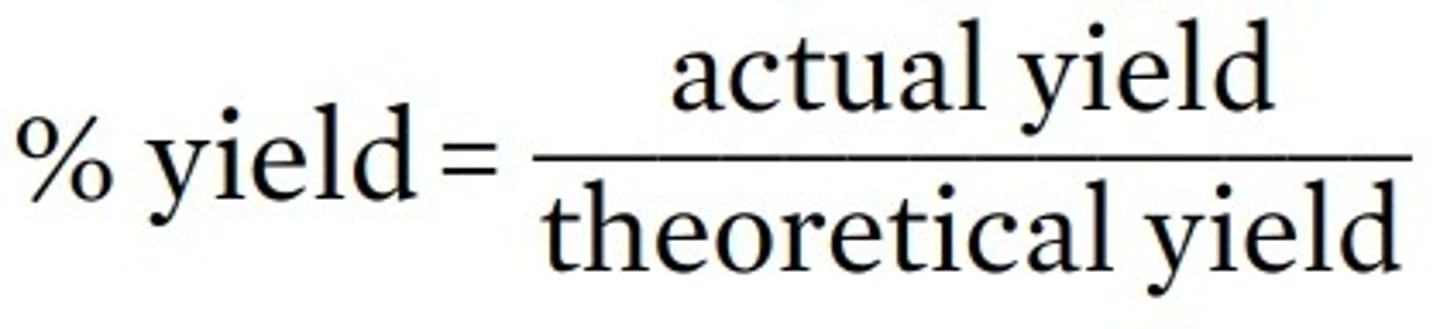
BROMINE is a dark red-brown liquid, but ALKENES and BROMOALKANES are COLOURLESS (so adding bromine to alkene solution and the solution becoming colourless indicates production of a bromoalkane)
decolourisation reaction
carboxylic acids act as WEAK ACIDS, so tests can include BASE NEUTRALISATION, COLOUR CHANGE OF LITMUS PAPER, react with CARBONATE to produce CO2, or a METAL to produce H2 (pop test)
How can it be tested that the product of the oxidation of an alcohol is carboxylic acid?