Joints (Ch 9)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
joints
where rigid elements of the skeleton meet at or articulations
what greek root means joint?
arthro
functional classification
based on amount of movement
synarthroses—immovable
amphiarthroses—slightly movable
diarthroses—freely movable
structural classification
based on material that binds bones together
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
fibrous joints
immovable or slightly movable
types of fibrous joints
sutures
syndesmoses (tibiofibular joint)
gomphoses
suture
occur between bones of the skull
gomphoses
tooth in a socket
syndesmoses
interosseous membrane between radius and ulna
synovial joints
most movable type of joint; fluid-filled joint cavity
what do synovial joints contain?
articular cartilage
joint (articular) cavity
reinforcing ligaments
sensory nerves
articular cartilage
type of hyaline cartilage covering the ends of opposing bones; absorbs compression
joint (articular) cavity
holds synovial fluid
reinforcing ligaments
thickened parts of the fibrous layer; job is to attach bone to bone
bursa (in the synovial joints)
a flattened fibrous sac lined by a synovial membrane; “pillow”
tendon sheath (in the synovial joints)
an elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon
bursae and tendon sheaths help with?
reducing friction
angular movements
increase or decrease the angle between bones
flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, circumduction
rotation
movement around a bone’s long axis
atlas and axis, hip and shoulder

elevation
lifting a body part superiorly
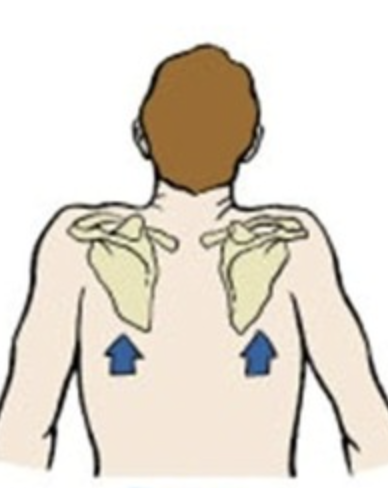
depression
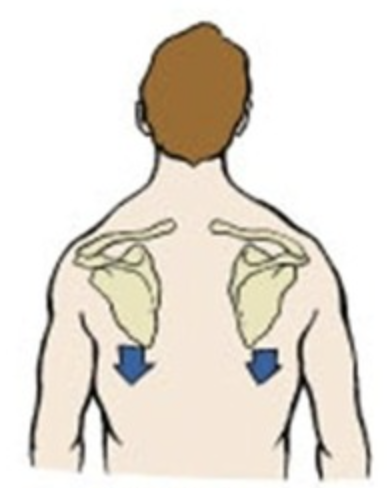
moving the elevated part inferiorly
protraction
nonangular movement anteriorly; move forwards and out

retraction
nonangular movement posteriorly

supination (arm)
forearm rotates laterally, palm faces anteriorly “serving soup”
pronation (arm)
forearm rotates medially, palm faces posteriorly
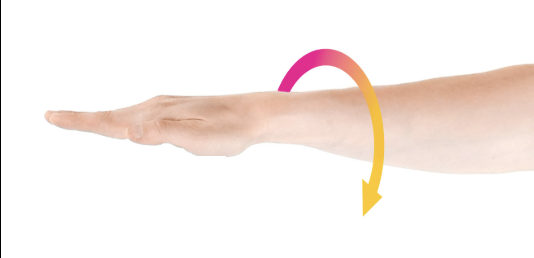
opposition
thumb moves across the palm to touch the tips of other fingers
inversion (feet)
turns sole medially
eversion (feet)
turns sole laterally
dorsiflexion (feet)
lifting the foot so its superior surface approaches the shin
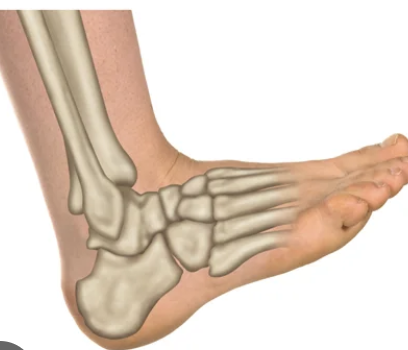
plantar flexion (feet)
depressing the foot, elevating the heel
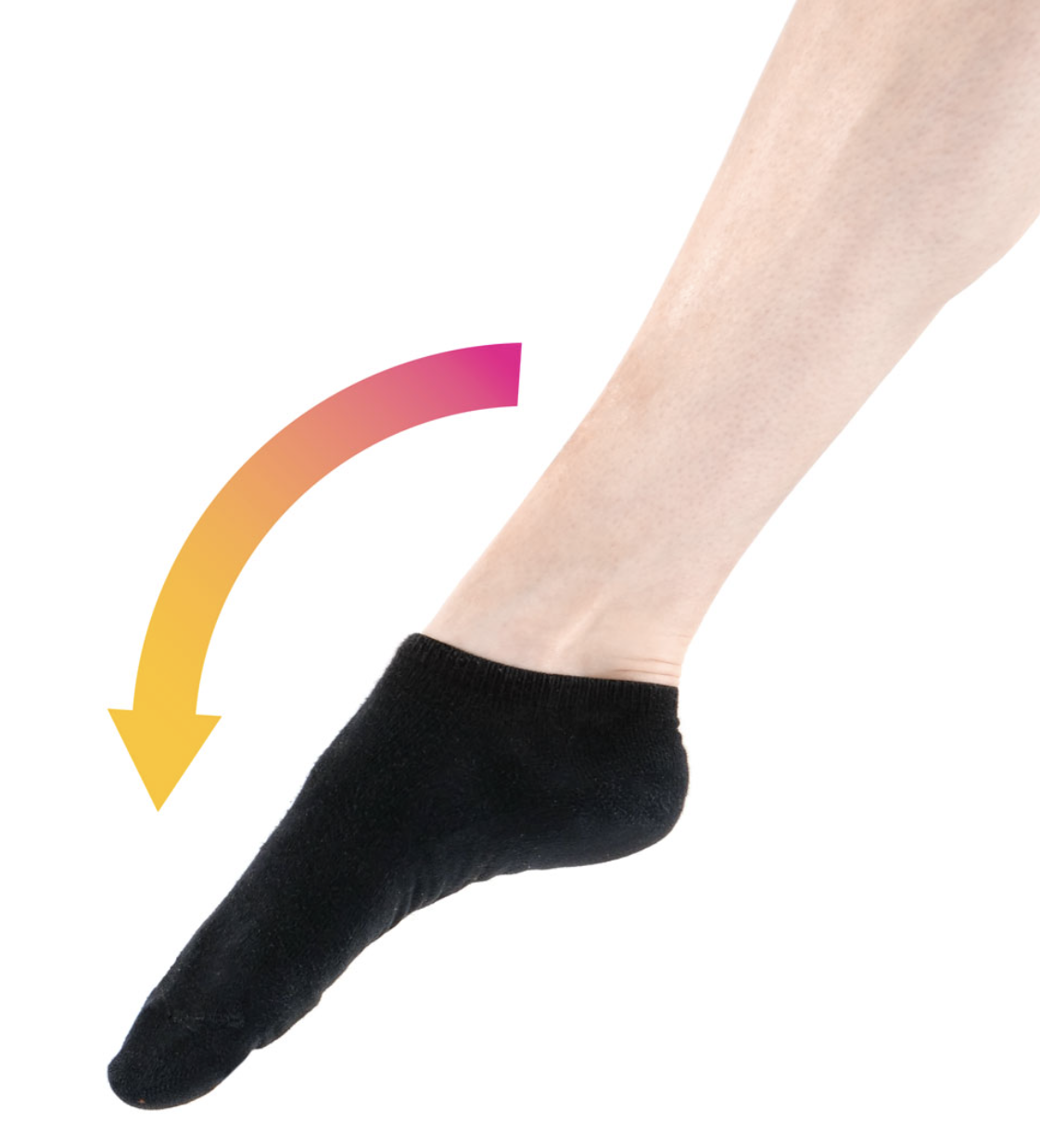
rotation
turning a bone around the longitudinal axis
flexion
decreasing the angle between two bones, usually in the sagittal plane

extension
increasing the angle between bones, usually in the sagittal plane
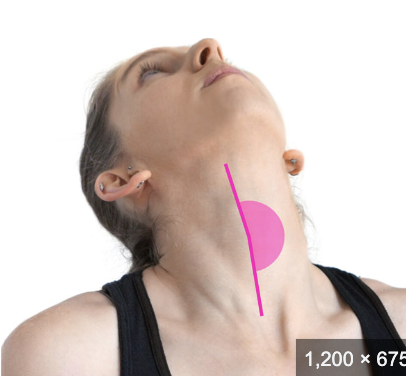
abduction
moving a limb away from the body midline in the frontal plane
adduction
moving a limb toward the body midline; “adding to the body”
circumduction
moving a limb or finger so that it describes a cone in space
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
in front of the knee joint; prevents anterior sliding of the tibia
posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
in the back of the knee joint; prevents posterior sliding of the tibia
locking the knee
stabilizes the knee joint without tiring the extensor muscles
joint tradeoff
more movable = less stable
less movable = more stronger
cartilaginous joints
bones are united by cartilage
what do cartilaginous joints contain?
synchondroses
symphyses
synchondroses
immovable joint between bones united by hyaline cartilage
symphyses
fibrocartilage unites bones; resists tension and compression (intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis)