Embalming II 2405.2 - Exam 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
one-point injection
type of injection that embalmers hope to achieve; injection and drainage from a single location; customarily selected as the primary injection technique
- R common carotid artery and R internal jugular vein
- R femoral artery and R femoral vein
- R axillary artery and R axillary vein
the most frequently selected vessels for one-point injection include:
split injection
injection of solution from one site with drainage from a different site; this method reduces short-circuiting of the solution and establishes a uniform distribution
- right internal jugular vein (drainage)
- right femoral artery (injection)
the most frequently used combination of vessels in the split injection method:
multi-point injection
injections from two or more sites; an additional site is identified to supplement the primary injection site when arterial solution cannot reach a particular area or when the area is insufficiently preserved
multi-point injection
autopsied cases are always __________-_________ cases
restricted cervical injection
raising both right and left common carotid arteries for injection; allows for the head to be injected separately
restricted cervical injection
beneficial when swelling of the face is a concern
internal jugular vein
normally the _________ __________ vein is used for drainage during restricted cervical injection
sectional embalming
type of multi-point injection; different sections/regions of the body are embalmed separately using specific arteries
sectional embalming
beneficial for difficult cases (ex: decomp)
pressure
the action of a force against an opposing force; a force applied or acting against resistance
whatever pressure is necessary to overcome vascular resistance and properly distribute embalming solution to all areas of the body
the recommended pressure when embalming:
gravity injection
provides a slow, steady method of injection that allows the body to accept the embalming solution at a slower rate; historical/antequated method of injection
percolator
large glass reservoir that has a delivery hose attached to the bottom of the bowl
foot
approximately, one-half (0.43) pound of pressure is obtained for each ________ of height the device is raised above the injection point
.5
when estimating, used ____ pounds instead of the more precise .43 pounds
hand pump
this method is historical and consists of utilizing a hand-operated pump and tubing; this apparatus can be used for aspiration as well (but it would be very slow)
bulb syringe
historical method; the simplest form of injection apparatus; consists of a bulb-type rubber syringe and tubing (think of a baby’s nose sucker)
air pressure
works like a hand pump but is mechanical/electric; historically, these machines were very dangerous to use and difficult to operate; not commonly used in the US
centrifugal force machine/pump
the most commonly used method of creating injection pressure today; this is the modern embalming machine
- pulsating - fluid is injected in spurts
- non-pulsating (direct) - fluid is injected on a continuous basis
- automatic pressure control
three common types of centrifugal force pumps:
rate-of-flow
the speed at which fluid/solution is injected
ounce per minute
rate-of-flow is measured in:
potential pressure
indicated by the injector gauge needle when the embalming machine is running, and the rate-of-flow is closed (what you want the pressure to be)
actual pressure
indicated by the injector gauge needle when the arterial tube is open, and the arterial solution is flowing into the body (what the pressure actually is when you start injecting)
differential pressure
difference between potential and actual pressure
drainage
the other half of standard arterial embalming
1. drain tube
2. angular spring forceps
3. trocar (for heart tap)
the three drainage instruments:
(primary)
- alternate
- intermittent
- concurrent
(other/last resort)
- direct heart drainage
the four drainage methods:
alternate drainage
with this method, arterial solution is never injected while drainage is done; alternate between injecting and draining but never do both at the same time
intermittent drainage
injection is done continuously, but drainage is only taken at certain intervals; compromise between alternate and concurrent; helps prevent short circuiting
concurrent drainage (continuous)
injection and drainage proceed at the same time throughout the entire embalming procedure; the least effective drainage method
direct heart drainage (aka heart tap)
drainage method in which a trocar is inserted (from the normal entry point) directly into the right atrium of the heart and drainage is taken through the trocar; recommended only in special situations where a vein cannot be used for drainage
alternate drainage
the most effective drainage method:
• Select a large vein
• Select a large drainage instrument
• Use pre-injection when possible
• Use manual massage during injection
• Increase rate-of-flow and/or injection pressure
• Select an alternate drainage site if needed
• Use intermittent or alternate forms of drainage (restricting drainage is beneficial and creates vascular pressure)
7 ways to improve drainage:
blood, blood clots, interstitial fluid, lymphatic fluid, embalming solution
drainage is composed of:
- rigor mortis
- gas in the cavities
- contact pressure
- tumors and swollen lymph nodes
- bandages
- skeletal edema
extravascular influences affecting injection pressure include:
- condition of the vessels (normal/schlerotic)
- local congestion or coagulation of blood
intravascular influences affecting injection pressure include:
primary dilution
strength of the arterial solution mixed in the embalming machine
C x V = C^1x V^1
to determine strength of the primary dilution, we can use the equation:
unmixed arterial fluid in the bottle
the left side of the primary dilution equation represents:
mixed solution in the embalming machine
the right side of the primary dilution equation represents:
secondary dilution
decrease in concentration of arterial solution by vascular and interstitial fluids
concentration
the "C" variables stand for:
volume
the "V" variables stand for:
16
____ ounces in a standard embalming fluid bottle
128
_____ ounces in a gallon
3
most embalming machines hold ___ gallons
hypotonic solution
solution having a lesser concentration of dissolved solute than the solution to which it is compared
hypertonic solution
solution having a greater concentration of dissolved solute than the solution to which it is compared
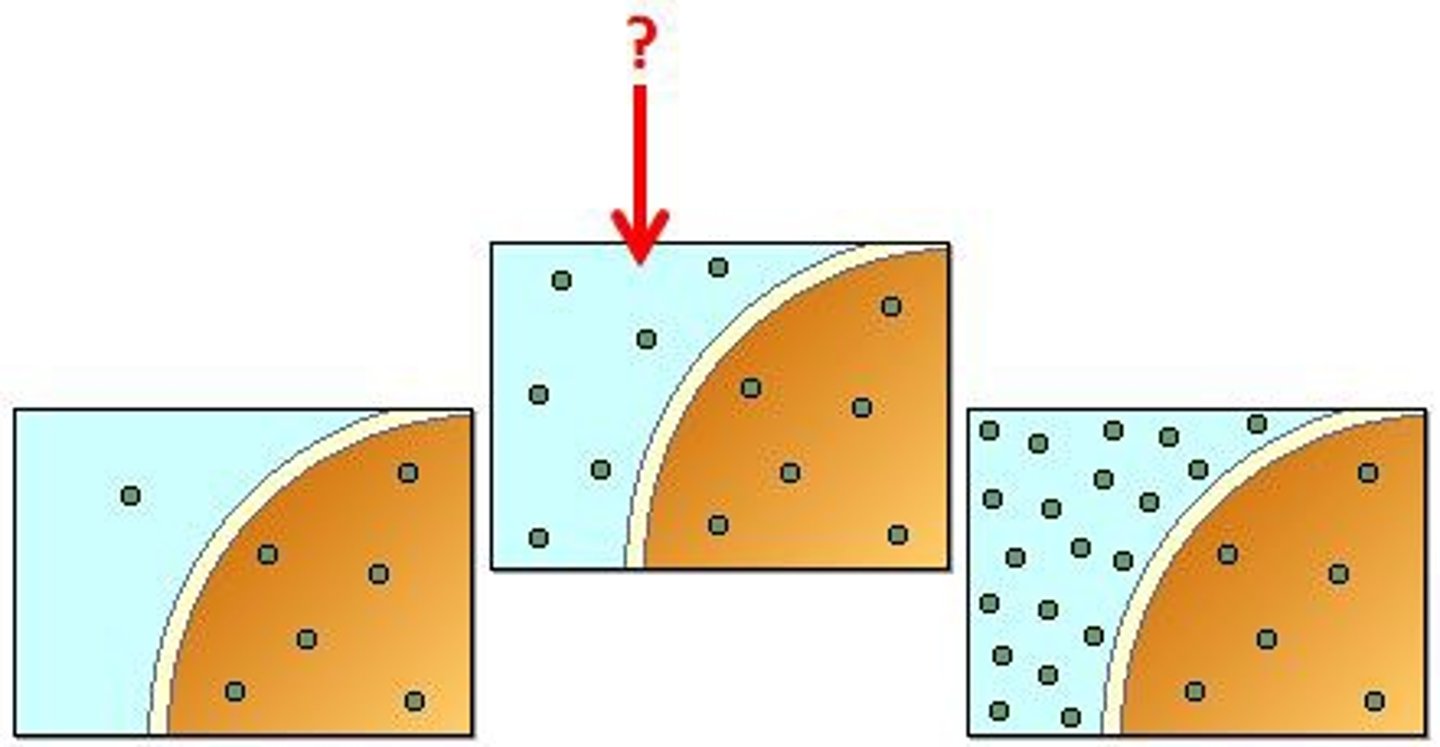
isotonic solution
solution having an equal concentration of dissolved solute as the solution to which it is compared
pressure filtration
passive transport system enabling the passage of arterial solution from the capillary to the tissue fluid; movement from an intravascular to an extravascular position
osmosis
passage of pure solvent from a solution of lesser concentration to one of greater solute concentration when the two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane
dialysis
separation of substances in solution on the basis of differences in their ability to pass through a semipermeable membrane
gravity filtration
extravascular settling of preservative fluids by gravitational force to the dependent areas of the body; occurs naturally and without action of the embalmer
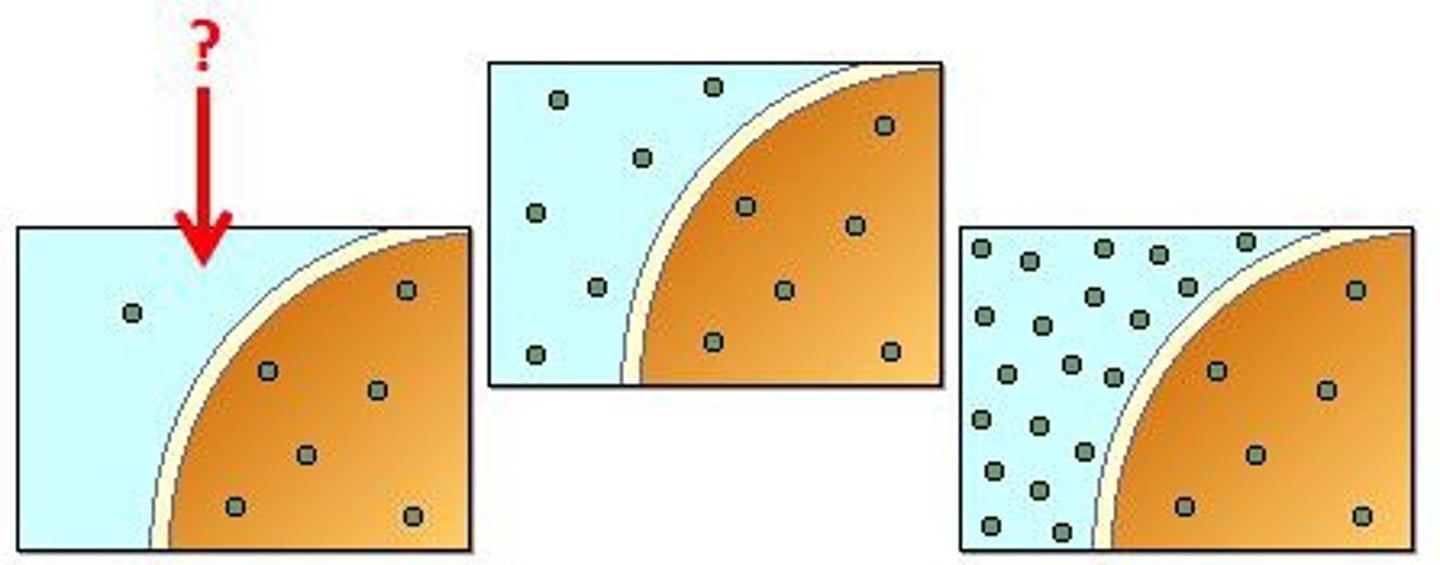
hypotonic
a _______________ solution will move toward the more concentrated solution – to try and create a state of balance/equilibrium between the two
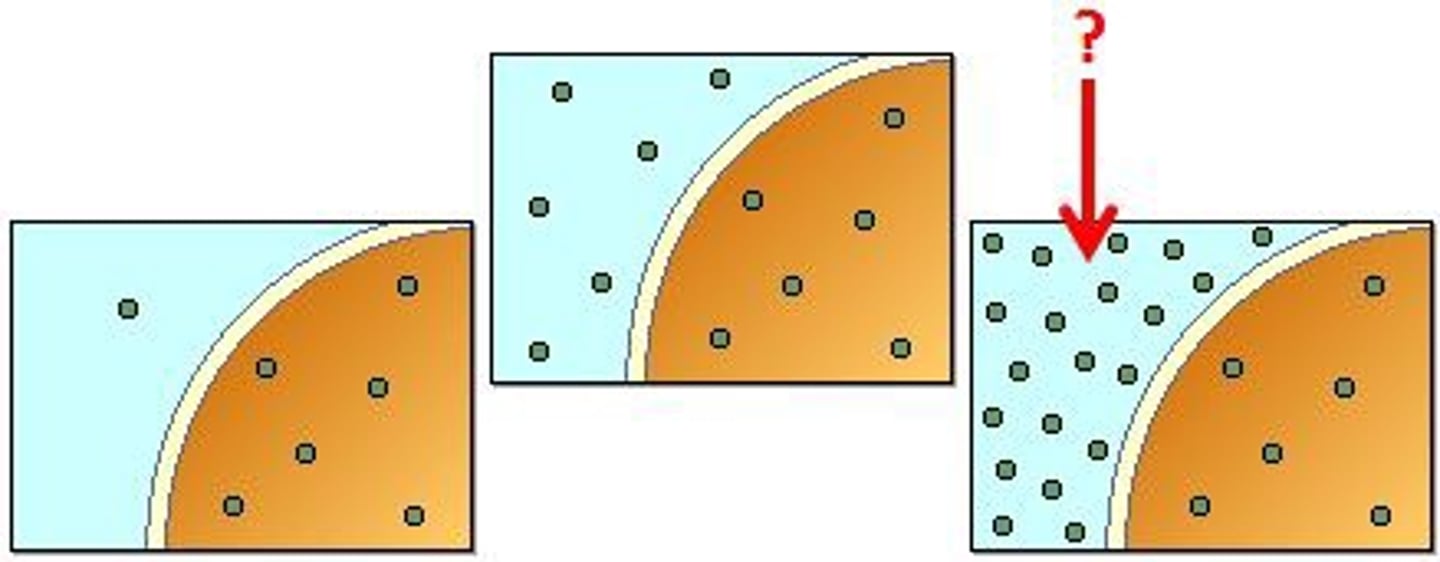
hypertonic
a ________________ solution will not move. Instead, the other solution will move toward it to create the balance/equilibrium
hypotonic
hypertonic
isotonic
• Distention of superficial vessels
• Large volume of blood drainage
• Reduction of intravascular blood discolorations
• Dye tracing (dye seen in tissues)
• Loss of tissue elasticity (firming)
• Drying of the tissues
• Rounding and distention seen in the lips, fingertips, and toes
• Bleaching/mottling of the tissues
(8) signs of distribution and diffusion:
• Increase rate-of-flow
• Increase injection pressure
• Inject using the pulse function
• Restrict drainage (to increase vascular pressure)
• Massage the body
• Inject a greater total volume of solution
• Relieve any extravascular pressure
(7) ways to improve distribution and diffusion:
distribution
the movement of embalming (arterial) solution from the point of injection throughout the arterial system and into the capillaries
diffusion
the movement of embalming (arterial) solution from within the vascular system through the capillary walls and into the tissue spaces