5. Ecophysiology of stress
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
stress
when environmental change results in the decrease in the rate of a physiologically process, which can lead to a decrease in survival, growth, or reproduction deal with stress thru avoidance and tolerance
Stressors that animals and plants face
Temperatures
water
salinity
pH
nutrients availability
presence of toxins
Tolerance
confirm: just deal with unstable conditions
regulate: change body to deal with unsuitable environment
avoidance
migration
metabolic shutdown: hibernation/torpor, or resting stages (seeds, spores, cysts)
Temperature
Thermal tolerance curves
its effects cascade to higher levels of organization
ii. Effects of temperature on higher levels of organization
Rates of biochem reactions → organization-level performance traits → life history and cycle traits → fitness: reproduction and survival
Ways animals can manage temperature
dormacy
hiding, burrowing, shelter
migrating or moving to better conditions
modifying energy balance
panting , sweating
insulation
vasoconstruction, vasodilation
behavior (bathing, activity levels, etc)
Ectotherms
animal regulates body temperature thru energyexchange with its external environment
Ectotherms: cost vs benefits
Benefits
lower cost of doing business
larger fraction of energy goes to growth and reproduction
more competitive than endotherms when in optimal conditions
Costs:
dependence on environmental conditions
limited activity in cold temperature
endotherms
animal that regulates its body temperature thru internal metabolic heat generation
endotherms: costs vs benefits
Benefit
can be active for longer periods (stamina)
gain more access to temporal and geographic niches
increase speed with faster metabolism
optimal enzyme activity
Cost
need more energy to operate
need constant supply of food for energy for constant thermoregulation
Surface area to volume ratios and relationship to heat loss and water loss
higher ratio= smaller size animal= loses heat more quickly due to all of the S.A.= higher BMR per unit mass= lose water more quickly due to all of the S.A.
lower ratio= bigger sized animal= retain heat better= lower BMR per unit mass= hold H2O better
Hyperosmotic
more saline than organism’s cells or blood
isoosmotic
similar salinity to organism
hypoosmotic
environment has less salinity than organisms
Water potential and flow of water
a measure of water’s free energy and its tendency to move from one location to another and water always flows from high to low water potential
Water balance in animals
structure
fish (gillings)
humans (kidneys)
rectal/nasal salt glands
water exchanges: water loss vs water gain
water loss: respiratory evaporative water loss, cutaneous evaporative water loss, urinary and fecal water loss
water gain: ingested water, metabolic water production
Solute exchanges
salt and nitrogen wastes; change concentration = change water salt intake, dilute/concentrate urine
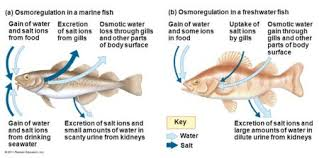
Different water balance strategies in freshwater and marine fish
Why do plants need to regulate water potential?
to maintain turgor pressure (avoid wilting), avoid air bubbles in xylem, and maintain stomatal conductance (open stomata) for photosynthesis
How do plants maintain water balance?
open/close stomata, increase hydraulic resistance in plant tissues (harder for water to flow thru), osmoregulation using solutes, increase amount of roots to take up more water
Strategies for dealing with high temperatures (desert)
creating/using microclimates: burrowing
locomotion that avoids S.A. contact (fly instead of walking)
diel patterns of behavior= be more active at dawn/dusk
seasonal patterns of behaviors= balance energy over the course of the week instead of day
physiological acclimation= have lowered metabolic rates, have special enzyme isoferms for enhanced heat tolerance
color change= light colored surfaces to reduce heat load during the day
Strategies for dealing with water loss (desert)
low water permeabilities
hyperosmotic urine= retain more water
burrowing=thermal buffering and humidity buffering
low SA/Vol ratio= lose water less quickly ( be big)
Nasal turbinates
increase S.A. of nasal cavity
drier environment= larger nasal turbinates
Avoidant strategies for extreme cold
more suitable microclimates locally → burrowing, huddling, bask in sun
find macroclimate (migrate)
remain inactive during coldest time of year (hibernate/ torpor)
Tolerating strategies for extreme cold
overcoming ice crystal formation because can pierce thru cells by
freezing point depression= using osmotic solutes to prevent freezing by lowering the temperature at which freezing occurs
supercooling= using antifreeze peptides
Regulating strategies for extreme cold
insulation (fur)
shunt blood from the surface and extremities
higher BMR
shivering thermengenesis
brown adipose tissue
Marine life challenges
food tends to be located in cold water, so avoidance is not an option
water has much greater heat capacity and thermal conductivity than air
solutions: lower body temperature, decrease SA/Vol ratio (be large), increase metabolism, use insulation (fur or blubber)