Public Health Engineering Random
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Hepatitis B
This virus commonly causes liver infection and is transmitted through blood and body fluids.
Inflammation of the liver
Hepatitis is best defined as:
Hepatitis A
Which virus is most commonly transmitted through contaminated food and water?
Hepatitis C
Which type of hepatitis is most likely to become chronic?
Sexual contact and blood exposure
Hepatitis B is mainly transmitted through:
Hepatitis D
Which hepatitis virus requires Hepatitis B virus to replicate?
Jaundice
A common symptom of acute hepatitis is:
Elevated ALT and AST
Which laboratory finding is most indicative of liver inflammation?
Hepatitis A and B
Which hepatitis virus has an effective vaccine available?
Hepatitis A
Which type of hepatitis is transmitted primarily through the fecal–oral route?
Hepatitis D
Which hepatitis virus requires another virus to replicate?
Hepatitis E
Which hepatitis virus is associated with high mortality in pregnant women?
Hepatitis C
Transmission through blood transfusion and shared needles is most common in:
Hepatitis D
Which hepatitis virus can cause severe disease as a superinfection in chronic Hepatitis B patients?
Hepatitis A
Which hepatitis virus usually causes only an acute, self-limiting illness?
Hepatitis C
Which hepatitis virus has no available vaccine and is often asymptomatic until late stages?
Cirrhosis and liver cancer
Chronic hepatitis may eventually lead to:
Adenovirus
This virus often causes respiratory infections
Influenza virus
This virus mutates frequently, and needs yearly vaccine.
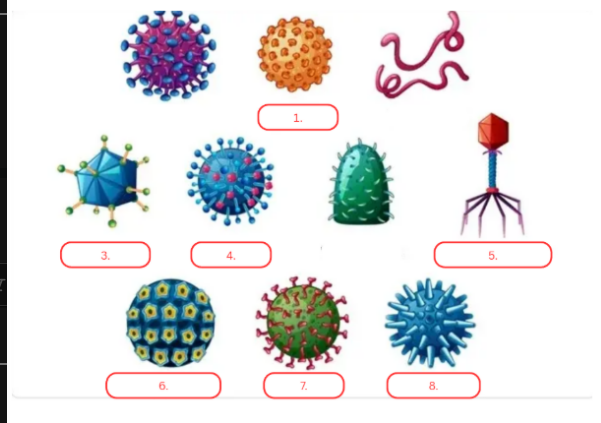
Bacteriophage
This virus infects bacteria
Rotavirus
This virus causes severe diarrhea in children and is common in pediatrics.
Papillomavirus
This virus causes warts and is linked to cervical cancer.
Rotavirus
This virus causes severe diarrhea in children and is common in pediatrics.
Herpes virus
This virus causes cold sores and genital infections, and can remain latent in nerves.
Protozoa
Malaria is caused by which type of organism?
HIV
The virus that commonly causes a decline in the immune system (AIDS) is:
Influenza virus
The virus most commonly associated with influenza (flu) is:
Ebola virus
The most common virus in Africa associated with hemorrhagic fever outbreaks is:
50 meters
Minimum safe distance of a potable water supply (deep well) from a cemetery is generally
Number of live births per 1,000 population per year
Crude Birth Rate (CBR) is defined as:
Giardia lamblia
A barangay reports multiple cases of children experiencing chronic diarrhea, weight loss, and greasy, floating stools. Investigation shows contamination of the spring water source by human and animal feces. The most likely causative microorganism is:
Pneumonia-like respiratory illness
Legionella bacteria typically cause:
Typhoid fever
Salmonella typhi causes:
Trematode
Schistosomiasis is caused by which parasite?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Walking pneumonia is commonly caused by:
A spore-forming bacteria
Anthrax infection is mainly caused by:
Spores enter breaks in the skin causing black eschar
How does Bacillus anthracis typically enter and cause cutaneous infection?
Releasing enzymes that destroy lung tissue
Mycobacterium tuberculosis damages lungs by:
Musty/earthy odor
What is the typical odor associated with Legionella contamination in water systems?
Archaea
In wastewater treatment, which microorganism produces methane?
A living organism that transmits disease
A disease vector is best defined as:
Microbial particles ≥0.3 microns
HEPA filters are used to remove:
*
Malaria
Which of the following diseases is transmitted by Anopheles mosquito?
Immediately shutdown and disinfect suspected water systems
In public health emergency response, what should be done FIRST when an outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease is suspected?
Data on births, deaths, marriages
Vital statistics primarily refer to:
Houses a collection of wild animals
A menagerie is a place that:
Vector
What do you call an organism that carries pathogens from one host to another?
Study of the causes of diseases
Which of the following best describes the word 'Etiology'?*
Parasite (Wuchereria bancrofti)
Which of the following is the causative agent of Filariasis?*
Aegypti
Which mosquito is primarily responsible for transmitting Chikungunya?
Leptospira bacteria
Leptospirosis*
Fever and joint pain
Which of the following happens when you are bitten by a tick carrying Lyme Disease?
Treponema pallidum
Syphilis*
Amoeba parasite (Entamoeba histolytica)
Which of the following causes Amoebiasis?*
Wuchereria bancrofti
Which of the following mosquitoes is not common in the Philippines?
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points
Which of the following best describes HACCP?
Culex mosquito
Which of the following is the primary vector for the transmission of Filariasis?
Mindanao
In which region of the Philippines is Filariasis most prevalent?*
President
When establishing communication during an emergency, which of the following is the least priority?
Randomized controlled trials > cohort studies > case-control studies
Which of the following best describes the hierarchy in epidemiological studies?
48 hours
Which of the following is the maximum time allowed to bury an unembalmed body according to PD 856: Chapter 21?
Camps and Picnic Grounds
Which of the following is the title of Chapter 10 of PD 856?
16
Which of the following is the minimum age of a minor prohibited from entering bars under Chapter 9 of PD 856?
80 dB
Which of the following is the maximum noise level (in decibels) that requires ear protection to be used?
Noise-cancelling mechanism
Which of the following describes the part of an ear protection device that cancels out noise?
Helminths
Which of the following is NOT considered a microfauna?*
Diseases caused by parasites in aquatic organisms
Which of the following best describes a 'Water-based disease'?*
a) Diseases transmitted through water
b) Diseases caused by lack of water for hygiene
c) Diseases caused by polluted water
d) Diseases that involve water in their treatment
Which of the following best describes a 'Water-washed disease'?
a) Diseases spread by insects in water
b) Diseases that are caused by contaminated water
c) Diseases transmitted through skin contact with water
d) Diseases related to drinking polluted water
Which of the following best describes a 'Water-borne disease'?
a) Diseases that are only waterborne
b) Diseases that can be contracted through swimming
c) Diseases related to the quality of water and water-based activities
d) Diseases caused by lack of water
Which of the following best describes a 'Water-related disease'?
a) Tinea capitis
b) Tinea pedis
c) Tinea cruris
d) Tinea versicolor
Which of the following does NOT belong to the group Tinea
a) Tinea Unguium
b) Tinea Capitis
c) Tinea Cruris
d) Tinea Pedis
Which of the following refers to a fungal infection commonly affecting the scalp?
a) Tinea Cruris
b) Tinea Capitis
c) Tinea Pedis
d) Tinea Unguium
Which of the following is a fungal infection that primarily affects the feet?
a) Tinea Cruris
b) Tinea Pedis
c) Tinea Unguium
d) Tinea Capitis
Which of the following refers to a fungal infection commonly found in the groin area?
a) Tinea Capitis
b) Tinea Cruris
c) Tinea Pedis
d) Tinea Unguium
Which of the following is the term for a fungal infection of the nails?
a) Amoeba
b) Entamoeba
c) Giardia
d) All of the above
Which of the following is classified as a protozoan?
a) Egg
b) Larva
c) Adult worm
d) Cyst
Which larval form of Hookworms penetrates the skin?*
a) To make cleaning easier
b) To prevent bacteria growth
c) To prevent food contamination
d) All of the above
Why should tiles in food preparation areas be smooth and non-absorbent?
a) For proper airflow
b) To prevent pests from hiding
c) For easier cleaning
d) To prevent food spillage
Why should there be a certain distance between the wall and the floor in food preparation areas?
a) It can mix with food
b) It can cause cuts on the skin where harmful substances may enter
c) It can cause contamination
d) All of the above
What is the effect of broken glass in food preparation?*
a) Egg
b) Rhabditiform larva
c) Filiform larva
d) Adult worm
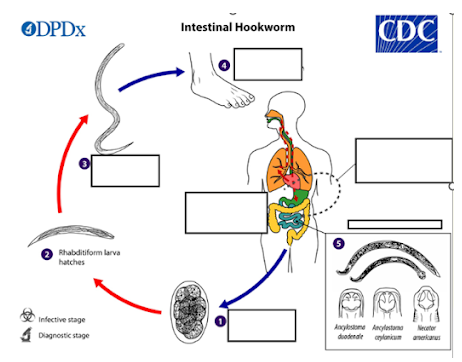
What is the infective stage of the intestinal hookworm lifecycle?
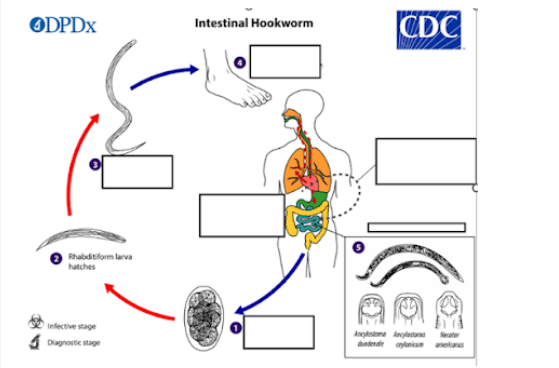
a) Mouth
b) Skin
c) Nose
d) Intestine
Through which part of the body does the filiform larva penetrate to enter the host?
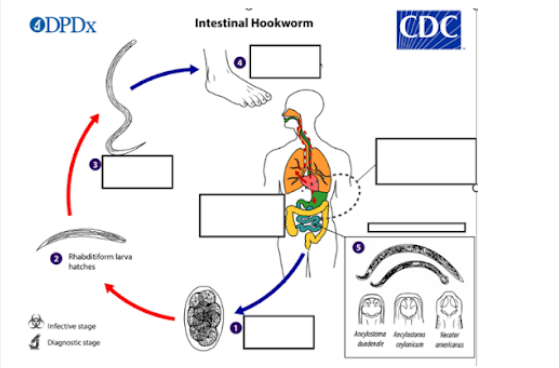
a) Stomach
b) Liver
c) Small intestine
d) Lungs
Where do adult hookworms reside in the human body?*
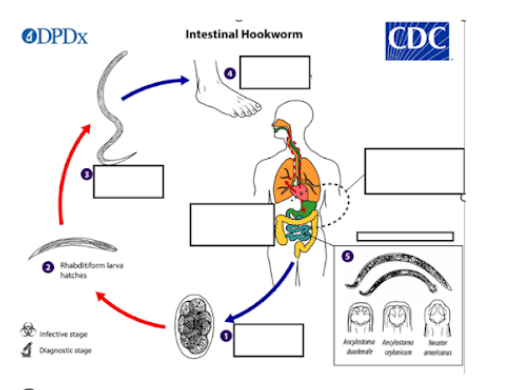
a) Rhabditiform larva
b) Filiform larva
c) Ancylostoma spp. larvae
d) Necator spp. larvae
What type of larvae can become dormant and later re-activate in the human body?
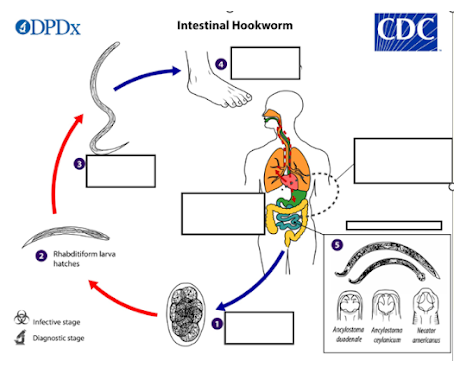
a) They are exhaled
b) They stay in the lungs
c) They die off
d) They are coughed up and swallowed
After reaching the lungs via circulation, what happens to the hookworm larvae?
a) Fertilized egg
b) Unfertilized egg
c) Embryonated egg with L3 larva
d) Adult worm
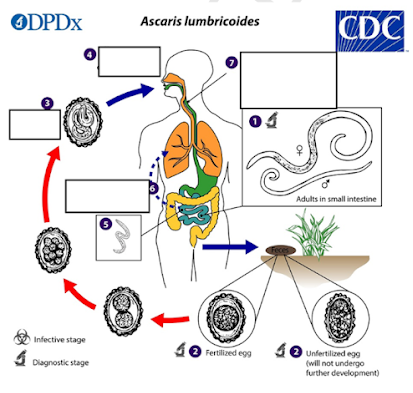
What is the infective stage of Ascaris lumbricoides?
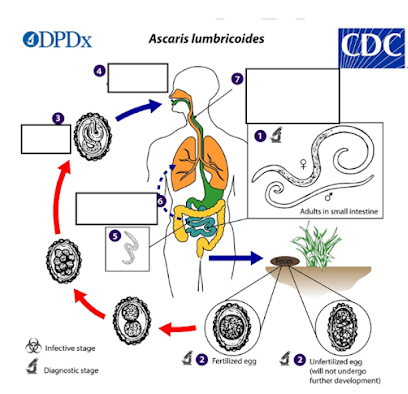
a) Skin penetration
b) Inhalation of larvae
c) Ingestion of embryonated eggs
d) Blood transfusion
How do humans become infected with Ascaris lumbricoides?
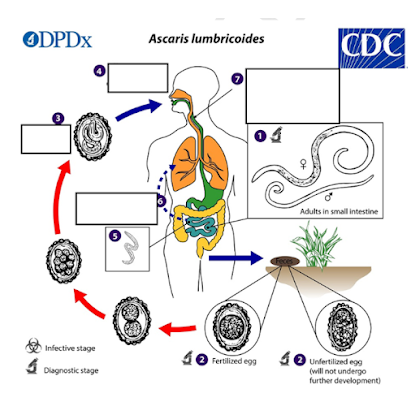
a) Liver
b) Heart
c) Lungs
d) Stomach
Aside from the intestine, where else do Ascaris larvae migrate and partially mature during their life cycle?
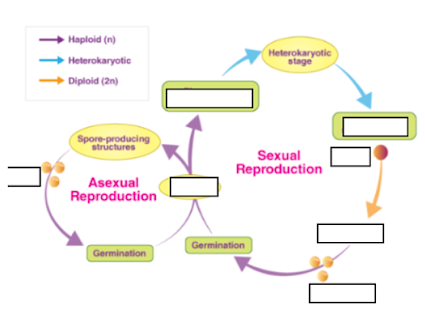
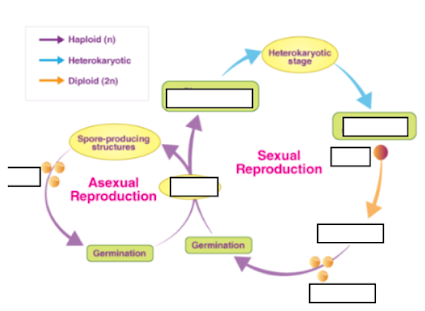
a) Plasmogamy
b) Germination
c) Meiosis
d) Spore production
What process occurs right after the zygote is formed during sexual reproduction?

a) Zygote
b) Spores
c) Mycelium
d) Gametes
What is produced at the end of both asexual and sexual reproductive cycles in fungi?
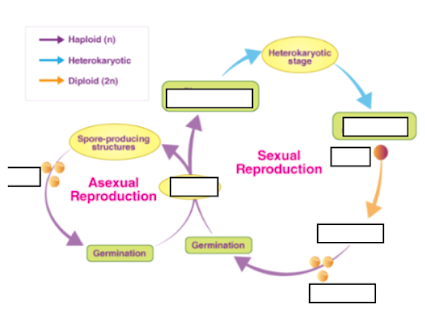
a) Karyogamy
b) Meiosis
c) Plasmogamy
d) Germination
What specific process involves the fusion of the cytoplasm of two fungal cells?
a) Zygote
b) Mycelium
c) Spores
d) Sporangia
What is formed by the fusion of nuclei during the sexual reproduction of fungi?
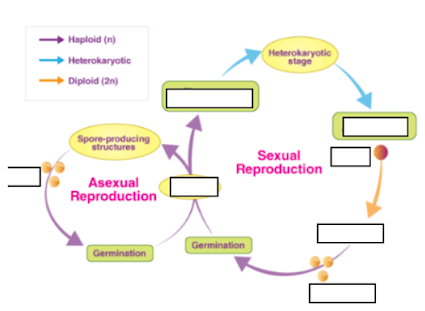
a) Zygote
b) Mycelium
c) Gametes
d) Zygospore
What structure forms from the germination of spores and gives rise to both sexual and asexual reproductive structures
a) Culex mosquito
b) Rats
c) Anopheles mosquito
d) Humans
Which of the following is considered an indirect vector for the transmission of Leptospirosis?
a) Descriptive epidemiology focuses on identifying the cause of disease, while analytical epidemiology focuses on disease distribution.
b) Descriptive epidemiology examines disease patterns and trends, while analytical epidemiology seeks to identify the causes and determinants of disease.
c) Descriptive epidemiology uses experimental data, while analytical epidemiology only uses observational data.
d) Descriptive epidemiology only studies chronic diseases, while analytical epidemiology studies infectious diseases.
Which of the following best distinguishes descriptive epidemiology from analytical epidemiology?
a) Malaria
b) Yellow fever
c) Dengue
d) Filariasis
Which of the following is transmitted by the Aedes mosquito?*
a) 60°C
b) 75°C
c) 100°C
d) 121°C
At what temperature is sterilization typically achieved using the method of autoclaving?
b) Fungi
c) Protozoa
d) Virus
e) Plant
Which of the following is NOT a type of microorganism?*
a) Sulfur dioxide
b) Ozone
c) Carbon dioxide
d) Sodium thiosulfate
Which of the following chemicals is commonly used to dechlorinate water?