POCUS -Heart, Lung, Pulm
1/50
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the 4 cardiac imaging views?
Parasternal long axis, Parasternal short axis, subxiphoid, apical 4 chamber
What preset is used for viewing the heart?
abdominal
How should the pt be positioned for heart PSLAX & PSAX?
left lateral decubitus
How should the probe be placed for heart PSLAX?
left parasternal border w/ probe indicator at 4 o'clock
What cardiac view provides the best view of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve used to estimate the ejection fraction?
Parasternal long axis (PSLAX)
What cardiac view provides the best view to look for the D-sign of pericardial tamponade?
Parasternal short axis (PSAX)
What helps get a clearer view of the heart if there is a lot of lung interference?
have pt breath in and ask them to hold their breath after expiration
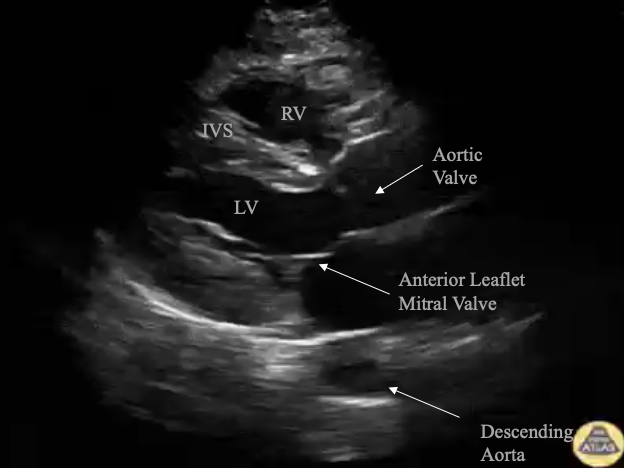
What view is this?
Parasternal long axis
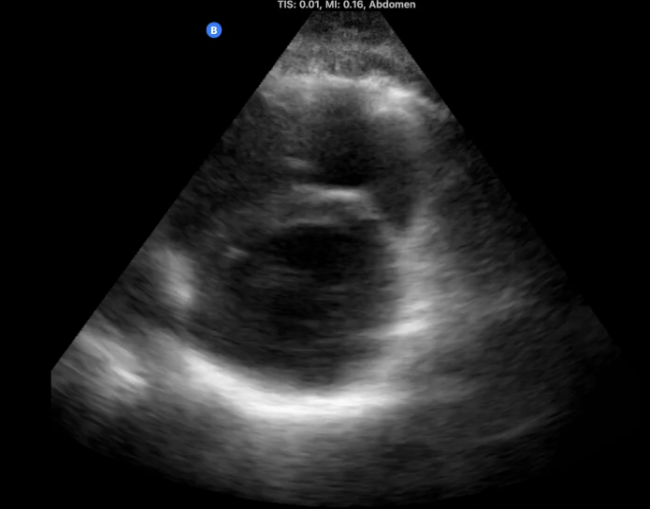
What view is this?
Parasternal short axis
How is the probe positioned for heart PSAX?
rotate the probe 90 degrees from the PSLAX position w/ probe indicator at 8 o'clock, slightly fan anteriorly
What is the big circle (donut) seen in PSAX?
LV
What needs to be included in the view of PSAX and PSLAX?
descending aorta posteriorly
What is the crescent shape seen on the left side of the screen in PSAX?
RV
What cardiac view provides an excellent view of overall left ventricle wall motion abnormalities?
Parasternal short axis (PSAX)
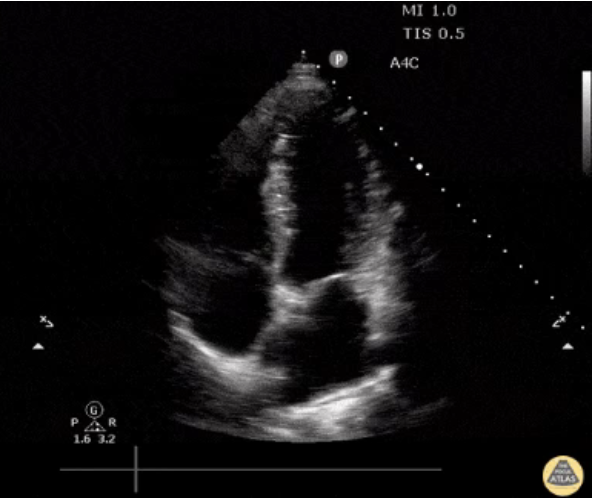
What view is this?
Apical 4 chamber
How should the pt be placed for heat A4C?
left lateral decubitus w/ left arm over pt head
*position is KEY
What probe is used to view the heart?
phased array
How should the probe be positioned for heat A4C?
apex of heat (PMI) w/ indicator facing pt’s right side
alt: start in PSLAX, slide down to apex and rotate probe 90 degrees, fan anteriorly
What side is the RV on in A4C?
left side of the image (will be narrower than LV)
*if it is on the other side, indicator is not in correct position
How should the pt be positioned for heat subxiphoid?
supine w/ arms to the side
How should the probe be placed for heart subxiphoid?
just below xiphoid process angle toward pts left nippe w/ indicator pointing to pts right
alt: start at umbilicus at 10 degree angle and move up
What cardiac view provides the best view to see a pericardial effusion and cardiac standstill?
Subxiphoid view
What can help obtain the best A4C view?
pt bend their legs to relax stomach muscles, breath in and hold breath, dec gain
What cardiac view is great for global cardiac function but a hard view to obtain?
Apical four chamber view (A4C)
What is the Trampoline sign?
beat-to-beat collapse of the right ventricle on US
What does the trampoline sign indicate?
tamponade
How does fine V fib show on US?
quivering
What lung conditions can US help dx?
PNA, pleural effusion, pneumothorax
What is B mode?
brightness mode
*DEFAULT mode
What is M mode?
motion mode
*capture motion, not the image along vertical axis
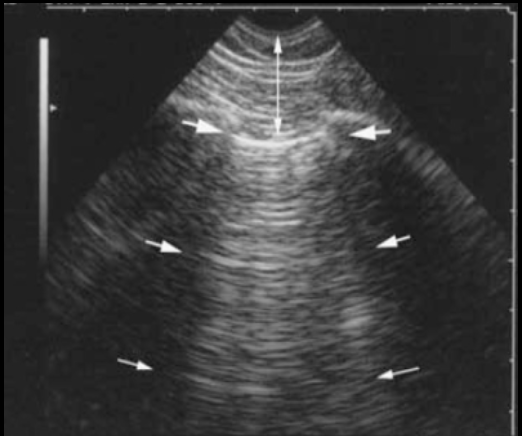
What type of artifact looks like a series of hyperechoic horizontal parallel line at regularly spaced intervals?
A-line artifact - “Bat sign'“
What does A-line artifact mean?
normal, means lungs are filled with air
A mirror image artifact is commonly seen with what body structures?
liver & diaphragm
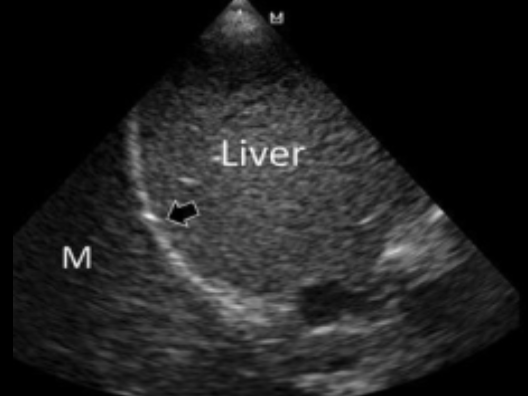
What does mirror image air artifact mean?
normal, if not present = lung pathology
What mode is good for pneumothorax or lung sliding?
M mode
What mode shows vascular flow?
Color doppler
What would you not see the lung was collapsed?
lung sliding
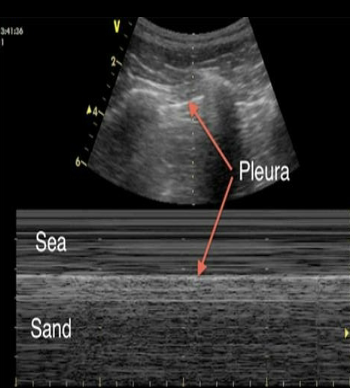
What does the Seashore sign mean?
*seen in M-mode
normal, indicates lung sliding is present → r/o pneumothorax
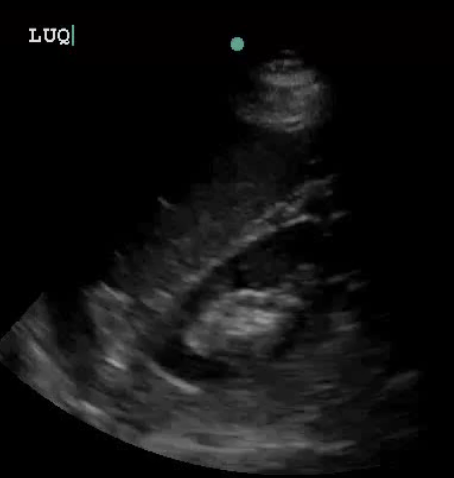
What does the curtain sign mean?
normal, seen when A-line pattern is moving in/out of the field of view w/ respiration temporarily obscuring the diaphragm and liver
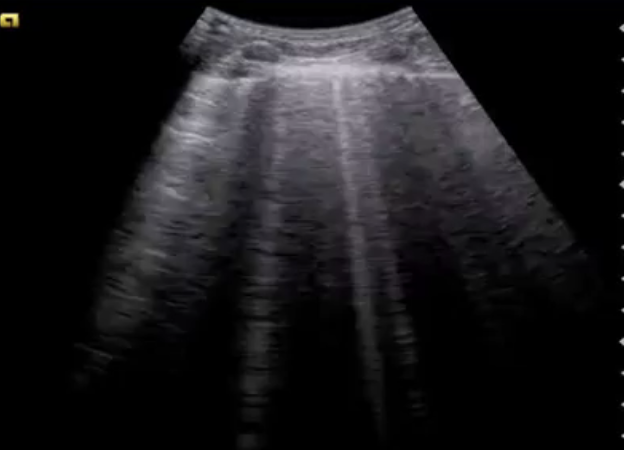
What type of artifact looks like vertical hyperechoic lines?
B-lines
What do B-lines mean?
pathological -d/t inc fluid in septa = pulm edema, CHF, fluid overload
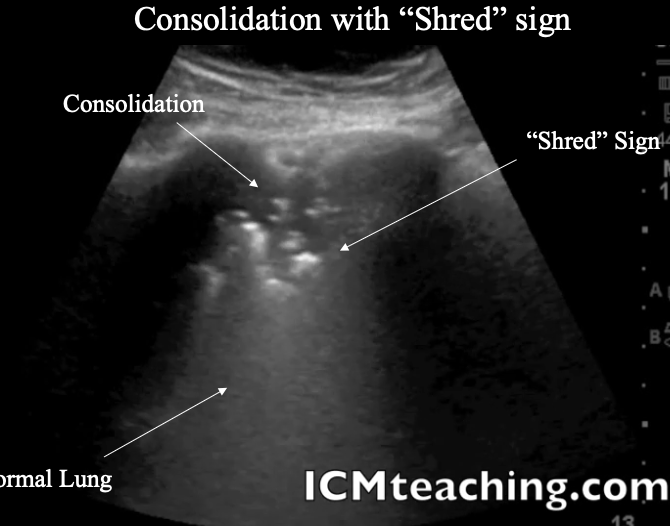
What is a Shred sign?
pathological -rough irregular border between consolidation and pleural effusion
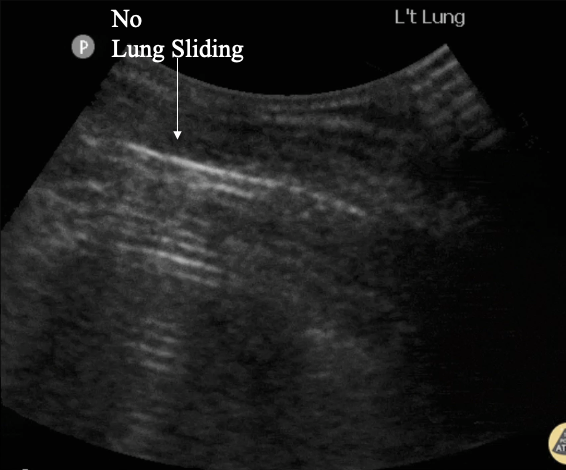
How does Lung sliding appear on POCUS?
visualized shimmering and movement of the pleura with respiration caused by the visceral pleura moving against the parietal pleura
What does consolidation indicate?
*post. lat. alveolar and/or pleural syndrome (PLAPS)
pathological, pleural effusion, consolidation of lung, ± air bronchograms
What US findings indicate a Pneumothorax?
no lung sliding, + lung point, ± A lines
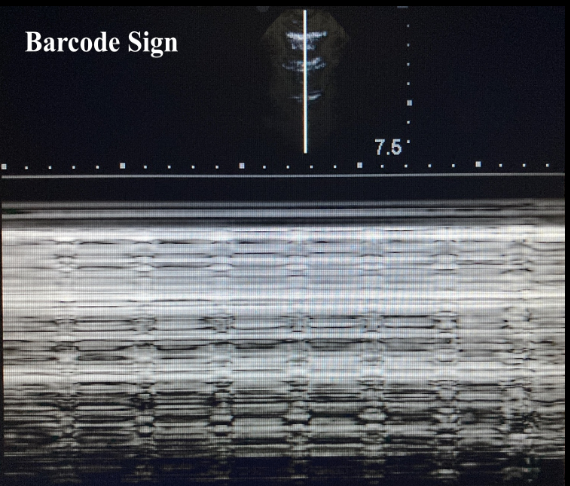
What does the barcode sign indicate?
*seen in M mode
pathological, pneumothorax
What is the Lung point sign?
M-mode finding of the exact point where the "seashore sign" changes to the "barcode sign" = EXACT location of pneumothorax
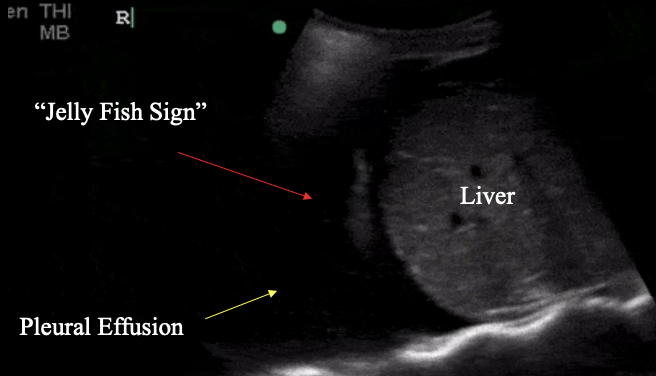
What is the Jelly fish sign?
pathological, collapsed lung floating w/in fluid collection = pleural effusion
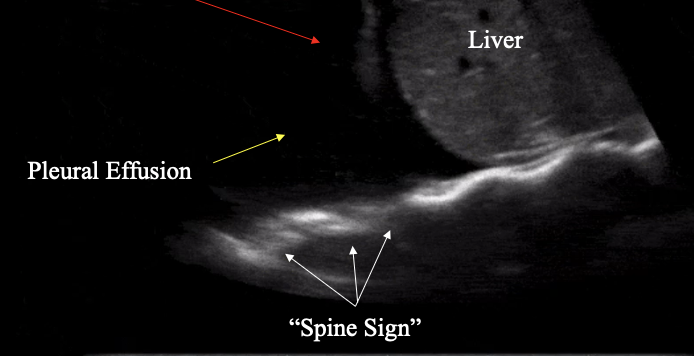
What is the spine sign?
pathological, spine visible posterior to fluid collection = pleural effusion
What US findings indicate pleural effusion?
anechoic free fluid above diaphragm, absent mirror image artifact, + spine sign, + jelly fish sign
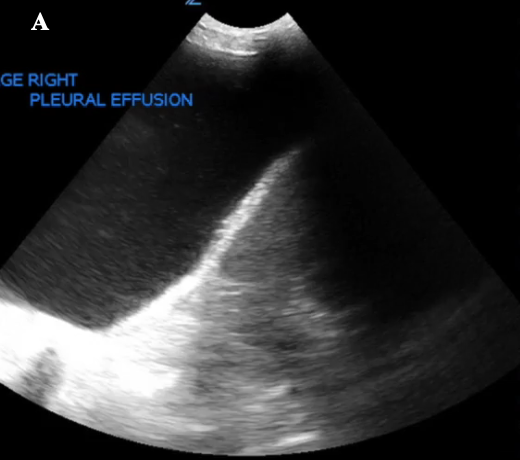
What is Plankton sign?
pathological, swirling echogenic material w/in effusion → suggest exudate = exudative pleural effusion