Chapter_10_Alturism & Helping
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are prosocial behaviors?
Actions intended to benefit others
What is the evolutionary perspective?
How can humans survive? Survival of the genes
What is kin selection?
We are more likely to help genetic relatives than those not related to us
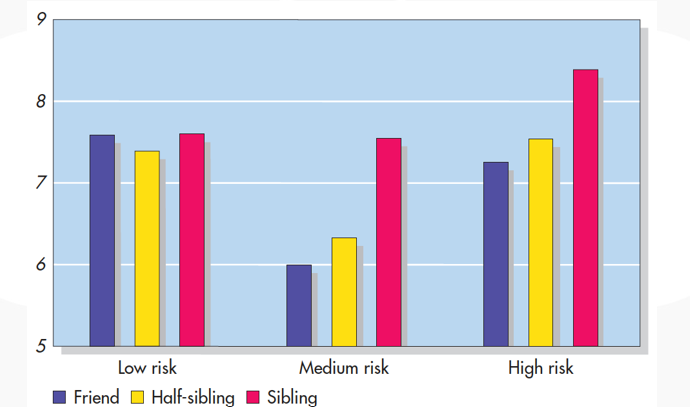
Why is the medium risk graph much lower than the high risk?
Low risk - Not bad
Medium risk - I have time to think about it, NO
High risk - Acting off instinct - no time to think
What is reciprocal altruism?
Altruism that involves an individual helping another (despite the immediate consequences) and becoming more likely to receive help from the other in return
We see this across species
Reciprocal Altruism
This is a transaction. The other person may FEEL like they have to help out
What is empathy?
Trying to understand their position and emotions
To the best of my ability to understand their emotions.
Trying to be in their shoes.
This goes deeper into how that person might be feeling.
To see other points of view
THIS IS ABOUT EMOTIONS
What is sympathy?
Recognizing that someone is going through something.
Recognizing that emotion.
THIS IS ABOUT THE SITUATION
Why do people commit prosocial behaviors?
1.) It feels good
2.) What I do for you, you do for me!
What is the negative state relief model?
The idea that people help others in order to counteract their own feelings of sadness
Courageous resistance
Providing sustained and deliberate help in the face of potentially enormous costs (immediate or long term)
EX. Firefighters have higher rates of cancer.
EX. We still have a good feeling when taking care of someone very ill (don’t worry, caretaker stress is a real thing)
What does altruistic mean?
Motivated by the desire to improve another’s welfare.
What is the empathy-altruism hypothesis?
The empathy creates altruistic motives for helping
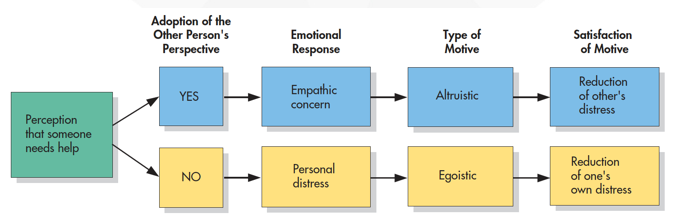
People who have __ empathy tend to help people whether or not they will forget or remember the person.
People who have HIGH empathy tend to help people whether or not they will forget or remember the person.
•Acting fast, on instinct, often produces (more/less) helping and cooperative behaviors than when there is time to consider the costs and benefits of their actions.
MORE
What is the bystander effect?
The presence of other people inhibits helping
Fear
Someone will do something, it doesn’t have to be me
Similar to loafing: If we don’t think our contributions will do anything, we won’t contribute.
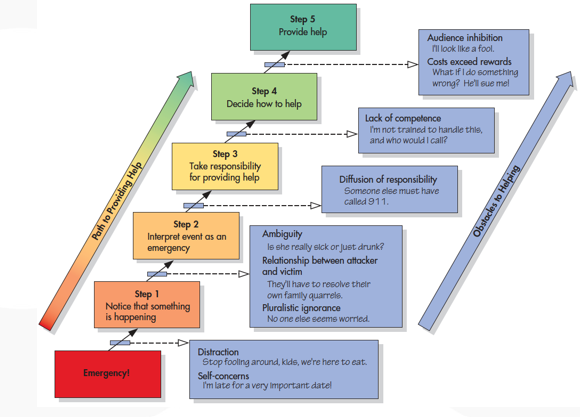
When is intervention more likely to occur / bystander effect less likely to occur
1.) When the bystanders know and feel connected to each other
2.) Effective helping would require multiple helpers
3.) People feel they will be scorned for failing to help
If you need help, how do you get other people to help you?
Make eye contact
Point at them
Make a direct request
(This makes the person feel like they are the only people to help)
Research shows that people who are in good moods are …
More likely to help people.
When the cost of helping is high and we have time to think about it, what are people more likely to do?
NOT HELP
When our good mood makes us want to party with our friends but the party coincides with helping other people, we are going to…
Mostly likely party with our friends.
Our motivation to engage in this social activity may prevent us from taking the time to notice or take responsibility for helping someone in need.
When are negative moods more likely to make us help us?
1.) If we feel guilty (you have to have good insight)
2.) If we focus on other people
3.) If we think about our personal values that promote helping (“I really shoudn’t act like such a jerk next time, I have to be nicer.”)
When our negative moods make us less likely to help others.
1.) If we blame others for our bad moods
2.) If we become very self-focused (If I can’t help myself, how can I help other people?)
3.) If we think about our personal values that do not promote helping.
When people have less insight, people have a harder time…
… regulating their emotions/behaviors.
Even when you have insight, you need to process it..! Insight is not enough.
Our mind and body can only hold so much before we have to…
Lash out
Tell someone
People who tend to be more helpful are more likely to…
Be more agreeable
Honest and humble
Have advanced moral reasoning
Exhibit more empathetic concerns for the suffering of a stranger
“The relationship between individualism or collectivism and prosocial behavior, however, is quite mixed.” What does Dr. B think about this?
Do we define the prosocial behaviors for other cultures that they do not know? Are we using American language to define behavior that is not popular or known as collectivist cultures?
People are more likely to offer help to others who are…?
Physically attractive
Not perceived as being responsible for the situation they are in
A lot of marginalized groups are seen to get the blame from our culture
People are usually more helpful to people who…
1.) They know and care about
2.) Who are similar to themselves
3.) Who are in their group
What is identity fusion?
A strong sense of connection to a group that you share an identity with. You are more likely to help these people in your group.
Sports teams
Gender and helping - __ are less likely than women to receive more help.
MEN
__ are more likely to provide social support
WOMEN
True or false? There does not seem to be a general and consistent gender difference in who is more likely to help others.
True
Certain cultures prevent people from asking and receiving help. What is an example?
Asian and Asian American people struggled more psychologically and physiologically.
Asking for help can be seen as bad in some cultures.
This is hard because this requires people to be VULNERABLE
Helping requires people to…
Recognize that the people who need help are human. We are all human. We are all in the group of being human.
We are all affected by all the actions of people.