Bio Plants Unit
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Spermatophytes
Seed plants
Sister Clade to horsetails and ferns
Spermatophyte growth
Secondary and primary at Apical Meristems
Spermatophyte secondary meristems
Vascular Cadmium and cork cadmium
Vascular cambium and cork cambium
Vascular cambium makes secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem (inner bark)
Cork cambium makes waxy protective cells that become outer bark
Tree rings
Show age and Temperature and Precipitation have marked effect.
Can be used to predict historical things like tennis khan having favorable weather
Monilophytes
Ferns and horsetails
Sister clade to Spermatophytes
Gymnosperms
Clade of seed plants
Woody, and lack protective ovary outside seeds
No flowers or fruits
Only have tracheids so don’t make hard wood (softwood)
Cycads
Subtropical
Short woody trunks; leaves like palm cuz of conv. Evo. Of “pinnate” leaf structure
Many hunted to extinction
Cycads reproduction
Dioecious cones: Females with special seed bearing megasporophyll, males have pollen bearing microsporophyll
Sperm have flagella
Ginkgo
1 relic species
Motile sperm
Dioecious
May live >1000 years
Cultivated in china
Gnetoohytes
Was once thought to be sister to angiosperms cuz of fleshy cones and morphology
Ghetum
Trop. Evergreen trees shrubs and lianas
Can be dioecious or monoecious
Welwitschia
Dioecious
One relic species in naming desert of sw Africa
Insect pollinated
conifers
Outside tropics
Resins (prot. Chemicals)
Well branches and simple leaves
Conifers reproduction
Wind pollinated; seed dispersed by wind birds and mammals
Cones have megastrobilus and microstrobilus
Gametes have no flagella
Megastrobilus
Conifer seeds protected by woody scales
Ovulate cones
Microstrobilus
Conifer pollen bearing herbaceous scales
Microsporangiate cones
Megaspore mother cycle
Meiosis+mitosis makes 4 megaspore but 3 aborted
Develops into megagametophyte w/ megasporangium
Makes pollen chamber for fert.
Archegonia developed w/ hella megagametophyte
Becomes mature ovule
Microspore mother cell maturation
Meiosis 1 and 2 of mother cell make 4 microspores
Tetras of 4 haploid pollen cells
Maturation of these microspores make microgametophytes (pollen)
Fert.
Pollen enters archegonia w/ eggs
Makes zygote
Disintegrates archegonium and creates embryo
Uses megagametophyte as nutritive tissue
Becomes mature seed
Seed
Has 2n embryo
Nutritive tissue (n)
and Seed coat (2n) protective outer layer from sporophyte tissue
Photosynthate
Product of P.S
Source
Where photosynthate is made
Sink
Where photosynthate is being transported to
Source to sink
Sucrose active trans into sieve tube
Brings water from xylem thru osmo.
Pushes contents to sink w/ pressu.
Synthate unloaded and water back 2 xylem
Apoplastic path
Leave metoprolol cells into apoplast before sieve tube and selectively choose which to transport
Symplastic
Stays in simplest and doesn’t do selective trans
Turgor
Cell pressure from water
Turgid
Cells have turgor and cell wall makes it tall and rigid.
When dehydrated they wilt
Xylem pressure
Down when stoma open up when stoma closed
Water up xylem
Water leaves stoma
Pressure difference brings water from xylem
Tension and cohesion created brings up rest of water
Stoma opening
In light H+ leaves bringing in K+ and Cl- bringing in water
Tension increases and guard cell open
Opp. In absence of light
Open during day close at night
Tracheid
Water conducting elements in land plants w/out xylem and phloem
Developed into xylem phloem later
Allowed plant to grow toward light and have better spore dispersal
Rhyniophytes
No roots and anchored through rhizomes which absorbed water thru unicellular filaments rhizoids
Had aerial branches sporangia at leaves and dichotomous branching (2 equivalent branches at apex)
Lycophytes
Club misses and spike misses and quillworts
Sister group to other vasc. Plants
True roots
Dichotomous branching
Simpler vasc. Tiss. In stems than other
Microphylls (simple leaflike structures on stem arranged spirally)
Apical cell division
Sporangia in conelike strobilli (spore bearing microphylls at end of stem)
Vasc. Plant. Sporophyte
Branching independent sporophyte
Produces more spores and has complex development
Sporophyte is large obvious part of plant
Monilophytes
Not dichotomous branching
Reduced true leaves in circles around stem
True roots w/ irregular branching
Large sporophyte small gametophyte ind of eachother
Small short lives gametophyte
Sori (undersurface of leaves w/ sporangia)
Microphylls
Likely first leaflike structures to evolve in vasc plants
Euphyllophytes
Clade of Monilophytes and seed plants
Overtopping (growth pattern where one branch differentiates from and grows beyond others
Megaphyll (larger more complex leaf)
Developed photosynthetic tissue between members of overtop branches w/ greater S.A of branches
Male gametophyte
Heterospory
Microgametophyte
Sperm
Fertilization
Zygote
Embryo
Sporophyte
Microsporangium
Spore mother cell
Meiosis
Microsperm
Microgametophyte
Megagametophyte hetero
Heterospory
Megagametophyte
Egg
Fert
Zygote
Embryo
Sporophyte
Megasporangium
Spore mother cell
Meiosis
Megaspore
Megagametophyte
Homospory
Gametophyte
Archegonium (male) and antheridium (female)
Sperm (male) egg (female)
Fert
Zygote
Embryo
Sporophyte
Sporangium
Spore mother cell
Meiosis
Spore
Gametophyte
Hetero Microgametophyte
Sperm
Fert
Zygote
Embryo
Sporophyte
Microsporangium
Spore mother cell
Meiosis
Microspore
Microgametophyte
Heterospory
Allows for prod. Of many small microspores w/ easy transportation
Large megastores for nutrition and protection of embryo
Allows for long distance fert
Angiosperm
Seed plants w/ reproductive organs in flowers and seeds enclosed in fruits
Vascular plant
Clade sister to gymnosperms
Angiosperm synapomorphy
Xylem has vessels in addition to tracheids
Net venation in leaves
Flowers and fruits
Ovules and seeds enclosed in carpel
Germination of pollen on a stigma
Double fert
Nutritive tissue called endosperm
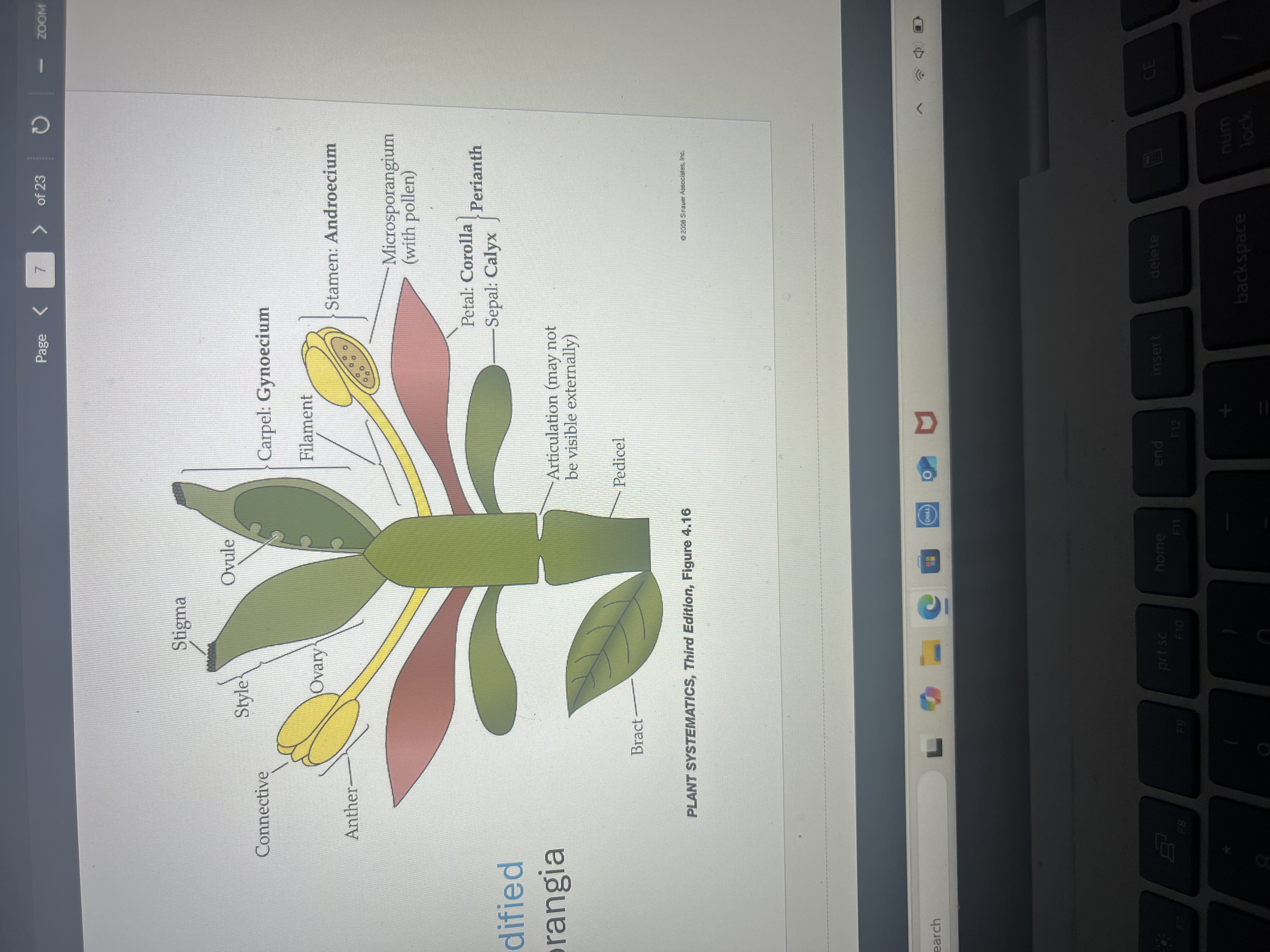
Flowers
A shoot with modified leaves
Some have sporangia
Sepals or calyx (leaves at base for prot. And attraction)
Petals or corolla for protection and attraction
Stamens (has male microsporangia)
Ovules and seeds enclosed by leaf called carpel
Pistil is fused carpel containing ovary
Style and stigma are in pistil and receive and transmit pollen to ovary
Pollination
Movement of pollen from anther to stigma
Angiosperm life cycle
Male and female separation and development
Double fertilization creates 2n zygote and 3n endosperm
Cotyledons around embryo
Seedling
Repeat
Antipodal and synergids
Accumulations of 6 cells
3 cells in the back of mature ovule is antipodal cells
3 at the opening of the cell is synergids
Pollen development
Each anther sac is microsporangium
2n mother cell undergoes meiosis 1 and 2 to make 4 microspores
Each goes thru mitosis. Making 2 cell pollen grain
One cell is a generative cell dividing by mitosis to make 2 sperm cells
Other is tube cell creating the pollen tube
Tube cell grows a pollen tube to reach ovule when it lands on a stigma
After double fert. Maturation of seed
Zygote becomes embryo w/ 1 or 2 cotyledons (seed leaves)
Cotyledons absorb endosperm or become photosynthetic when seed germinates
3 genetically diff. Individuals in angiosperm seeds
Embryo (2n)
Endosperm (3n) (2 polar nuclei and sperm)
Seed coat (2n) protective outer layer derived from diploid sporophyte tissue of previous generation
Monoecious
Mega and microsporangia in same plant
Dioecious
Mega and microsporangia in different plants
Selfing costs
Inbreeding depression (reduction in fitness because of unmasking of deleterious recessive mutations)
No genetic diversity
Mechanism to prevent selfing
Half of flower plants are genetically incapable of self fert. Because of S-locus proteins
Heterostyly also by producing Pin or thrum flowers w/ different length pistols and stamens
Benefits of selfing
Pass on advantageous traits
Can assure reproduction in a place with low pollinators or mates
Common in invasive plants
Chasmogamous (open) flowers
Flagrant to promote outside fertilization
Cleistogamous (closed) flowers
Small bud like flowers that are not open and are self compatible to produce later in season
Promotion of outcrossing
Mutualistic evolution for other animals to disperse pollen
Different flower structure is for different pollinations
Bee pollination
Blue purple or yellow
Radial or bilateral symmetry
Broad tube with nectar guides
Fly pollination
Pale flower with musky odor
Colored and strongly scented like decaying flesh
Moth pollination
Bloom in evening with pale color and rich fragrance
Hummingbird pollination
Bright colors
Shade of red
Tubular with hella nectar
No smell
Wind pollination
Scent less nectar less inconspicuous flowers
A lot of small dry lightweight pollen
Exposed feathery stigmas and protruding stamens
Causes allergies
Fruit
Mature ovary containing seeds
Berry
Single carpel or multiple fused carpels
Aggregate fruit
Multiple pistols and carpels fused or unfused (strawberries)
Multiple fruit
Fused mass of many individual flowers (pineapple)
Animal dispersal
Promote eaten by animal to be moved in they poop
Bird catcher tree sticks seeds on birds that land on it