AP CSA REMEMBER
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Autoboxing
the automatic conversion of primitive data types into their corresponding wrapper class objects. For example, converting an int to an Integer.
collaborator class
in Java refers to a class that works together with another class to achieve a common goal through collaboration and interaction.
composition relationship
is a "has-a" relationship where one class contains an object of another class as a part of its state. It represents a strong relationship where the child object cannot exist independently of the parent object.
concatenation operator
is "+", used to combine two strings or add strings to other data types. Example: "Hello" + "World" outputs "HelloWorld".
control structure
a block of programming that analyzes variables and chooses a direction in which to go based on given parameters. It determines the flow of execution in a program. Types include sequence, selection (if-else), and iteration (loops).
Downcasting
the process of converting a reference of a superclass to one of its subclasses. It is done explicitly and may result in a ClassCastException if the object being downcasted is not an instance of the subclass.
Encapsulation
the mechanism that binds the data (variables) with the methods (functions) that manipulate the data, ensuring data hiding and access control. It helps in achieving data abstraction and security in Java programming.
equals
is a method used to compare the contents of two objects for equality. It is commonly used to compare strings or objects to check if their values are the same.
==
This returns true if both the operands are referring to the same object, otherwise false.
checked exception
a type of exception that must be either caught or declared in the method signature using the throws keyword. It is checked at compile time to ensure proper handling.
compile time error
in Java occurs when the code does not conform to the syntax rules of the language during compilation, preventing the program from being successfully compiled.
run time error
occurs during the execution of a program. It is caused by conditions that occur when a program is running, such as division by zero or accessing an invalid memory address. Runtime errors can lead to program crashes or unexpected behavior.
syntax error
occurs when code violates the rules of the programming language, making it unable to compile. It is a mistake in the syntax of the code that prevents the program from running.
unchecked error
exceptions that occur at runtime and do not need to be declared in a method's signature. They are subclasses of RuntimeException and Error.
arithmetic exception
occurs when an exceptional condition has occurred in an arithmetic operation, such as division by zero. It is a runtime exception that can be handled using try-catch blocks.
array out of bounds exception
thrown when a program attempts to access an element at an index that is outside the bounds of the array. This typically occurs when a program tries to access an element at an index that is less than 0 or greater than or equal to the length of the array
concurrent modification exception
generally occurs when working with Java Collections. The Collection classes in Java are very fail-fast and if they are attempted to be modified while a thread is iterating over it, a ConcurrentModificationException is thrown
index out of bounds exception
a common runtime exception that occurs when you try to access an element at an index that is outside the valid range of a data structure, such as an array or a list.
null pointer exception
you are trying to access a part of something that doesn't exist. For example, in the code below we call . length() on myString , which would usually return the length of the string. In this case, the string doesn't exist (we set it to null ),
string out of bounds exception
a runtime exception when you try to access a character in a String at an invalid index. Attempting to access a character at an index that is either negative or outside the range of the String's length causes this exception to be thrown.
polymorphism
having a superclass called 'Animal' and two subclasses 'Dog' and 'Cat'. If we have a method drive() in Animal class, the same method can be used differently in the dog and cat classes.
insertion sort
a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time by comparisons
merge sort
an efficient, general-purpose, and comparison-based sorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, which means that the relative order of equal elements is the same in the input and output.
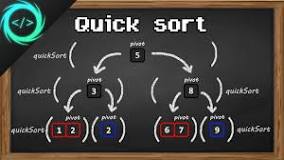
quick sort
a sorting algorithm that uses a divide-and-conquer strategy to sort an array. It does so by selecting a pivot element and then sorting values larger than it on one side and smaller to the other side, and then it repeats those steps until the array is sorted. It is useful for sorting big data sets
recursive sort
to sort a large list assuming you can recursively sort a smaller part of the list.
selection sort
an in-place comparison-based sorting algorithm that is known for its simplicity over other sorting algorithms. The technique involves choosing the array's smallest element and swapping it with the array's first element (if sorting in ascending order).