bio exam review
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/272
Last updated 5:46 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
273 Terms
1
New cards
* adhesion = water attracts to xylem walls
* cohesion = water attracts water
* cohesion = water attracts water
cohesion-adhesion
2
New cards
* xylem closer to stem centre
* phloem closer to outside
* vascular cambium separates xylem and phloem
* phloem closer to outside
* vascular cambium separates xylem and phloem
herbaceous stem
3
New cards
* DICOT ONLY
* grow thicker over time
* makes new xylem and phloem each year
* sapwood (young xylem) conducts minerals and water
* old xylem = hardens into heartwood
* bark protects woody stems
* tree rings determine climate and tree age
* grow thicker over time
* makes new xylem and phloem each year
* sapwood (young xylem) conducts minerals and water
* old xylem = hardens into heartwood
* bark protects woody stems
* tree rings determine climate and tree age
woody stem
4
New cards
structure performing specific functions in the cell
organelles
5
New cards
* contains and protects genetic material from cell
* double membraned for more selective permeability
* double membraned for more selective permeability
nucleus
6
New cards
* receives, modifies, packages and transport proteins made by ER
golgi apparatus
7
New cards
* makes spindle fibres
* helps separate and reorganize genetic material during mitosis
* helps separate and reorganize genetic material during mitosis
centrioles
8
New cards
* filled with enzymes and bounded by membrane
* enables digestion
* considered recycling centre of cell
* enables digestion
* considered recycling centre of cell
lysosomes
9
New cards
* found on ER surface
* protein synthesis
* floats in cytoplasm
* protein synthesis
* floats in cytoplasm
ribosomes
10
New cards
* transports materials throughout cells
vesicles
11
New cards
* store water and starch
* surrounded by tonoplast (membrane)
* surrounded by tonoplast (membrane)
vacuoles
12
New cards
* provides movement to certain cells
* made of fine protein fibres
* cilia = shorter, flagella = longer
* made of fine protein fibres
* cilia = shorter, flagella = longer
cilia + flagella
13
New cards
* gives cell energy from food molecules like glucose
* energy turns into ATP
* site of cellular respiration
* co2 from energy gets eliminated for cell
* energy turns into ATP
* site of cellular respiration
* co2 from energy gets eliminated for cell
mitochondria
14
New cards
* supportive network of fine protein fibres
* anchors organelles in place
* microtubules + microfilaments
* anchors organelles in place
* microtubules + microfilaments
cytoskeleton
15
New cards
* ONLY IN PLANTS! and certain protists
* contain chlorophyll
* makes carbs/sugars via photosynthesis
* contain chlorophyll
* makes carbs/sugars via photosynthesis
chloroplasts
16
New cards
* interior structure/lining of a tube
* ex: intestines have lumen
* ex: intestines have lumen
lumen
17
New cards
* large
* animal + plant cells
* membrane bound organelles
* reproduce by mitosis/meiosis
* double-stranded chromosomes in nucleus
* animal + plant cells
* membrane bound organelles
* reproduce by mitosis/meiosis
* double-stranded chromosomes in nucleus
eukaryotic cells
18
New cards
* smaller
* bacteria cells
* circular chromosomes
* no membrane bound organelles
* reproduce via binary fission
* bacteria cells
* circular chromosomes
* no membrane bound organelles
* reproduce via binary fission
prokaryotic cells
19
New cards
smooth:
* no ribosomes
* makes lipids (fats)
rough:
* protein synthesis
* has ribosomes
* no ribosomes
* makes lipids (fats)
rough:
* protein synthesis
* has ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
20
New cards
* process of traits passing from parents to offspring
* chromosomes carry genes
* important for cell reproduction/division
* chromosomes carry genes
* important for cell reproduction/division
heredity
21
New cards
specific location of gene on chromosome
locus
22
New cards
order of genetic info coding specific trait
gene
23
New cards
* made of nucleotides (subunits)
* pentose sugars (5 carbon sugars)
* nitrogen base
* phosphate base (PO4)
* pentose sugars (5 carbon sugars)
* nitrogen base
* phosphate base (PO4)
structure of nucleic acids
24
New cards
* deoxyribonucleic acid
* found in nucleus
* main components of genes
* sugars in nucleotides = deoxyribose sugars
* found in nucleus
* main components of genes
* sugars in nucleotides = deoxyribose sugars
dna
25
New cards
* found in nucleus
* instructs protein making
* nucleotides sugars = ribose sugars
* instructs protein making
* nucleotides sugars = ribose sugars
rna
26
New cards
purines
* large
* double ringed
* adenine + guanine
pyrimidines
* small
* single ring
* thymine + cytosine
\
* large
* double ringed
* adenine + guanine
pyrimidines
* small
* single ring
* thymine + cytosine
\
two types of dna nitrogen bases
27
New cards
adenine + thymine, guanine + cytosine
how do the dna nitrogen bases pair?
28
New cards
uracil + adenine, guanine + cytosine
rna nitrogen base pairings
29
New cards
rna = single helix
dna = double helix
* order of bases = acid individuality
dna = double helix
* order of bases = acid individuality
dna and rna helix
30
New cards
* new offspring made from single parent
* made from single parent cell division (no sex cells)
* clones, invariable generations
* made from single parent cell division (no sex cells)
* clones, invariable generations
asexual reproduction
31
New cards
* offspring from fusion of 2 sex cells
* offspring not identical to parents
* variable generations
* offspring not identical to parents
* variable generations
sexual reproduction
32
New cards
study of heredity and variation in genes
genetics
33
New cards
diploid = 2 sets of chromosomes (2n)
haploid = half the number of chromosomes
polypoid = 3+ sets
haploid = half the number of chromosomes
polypoid = 3+ sets
diploid, haploid, polypoid
34
New cards
variation of life in one area, divides into genetic, species and ecosystem
biodiversity
35
New cards
* sum of all different genes in species
* small differences = individual uniqueness
* allows better adaption to change
* small differences = individual uniqueness
* allows better adaption to change
genetic diversity
36
New cards
more vulnerable to disease/illness, climate changes or prey/predator changes
what happens with low genetic diversity?
37
New cards
* variety of species in one area
* more variety = healthier ecosystems
* more species = more complexity
* more variety = healthier ecosystems
* more species = more complexity
species diversity
38
New cards
* variety of habitats + organisms and their connections
* diverse ecosystems range in size/complexity
* diverse ecosystems range in size/complexity
ecosystem diversity
39
New cards
when organisms live in/on other organisms
walking ecosystems
40
New cards
grouping similar organisms together for specific reasons
classification in biodiversity
41
New cards
archea, bacteria, animalia, protists, plantae, fungi
6 kingdoms
42
New cards
* must be similar in structure
* must breed under natural conditions
* must be fertile
* must breed under natural conditions
* must be fertile
species requirements
43
New cards
* consumes living/dead organisms for energy
* unable to make their own food
* unable to make their own food
heterotroph
44
New cards
makes their own food using the sun
autotroph
45
New cards
main classification groups in hierarchy format going more and more specific
taxon
46
New cards
kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
taxon groups in order
47
New cards
archaea = only archaebacteria
eukarya = animals, plants, protists, fungi
bacteria = only eubacteria
eukarya = animals, plants, protists, fungi
bacteria = only eubacteria
domains
48
New cards
* one of 2 identical chromosome strands
* attached to each other by centromere
* attached to each other by centromere
chromatid
49
New cards
\
* found in eukaryotic cell nucleus
* carries genes
* found in eukaryotic cell nucleus
* carries genes
chromosome
50
New cards
* thread like structures
* made of dna and proteins
* found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells
* forms chromosomes
* made of dna and proteins
* found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells
* forms chromosomes
chromatin
51
New cards
g1: cell growth and preparing for duplication
s (synthesis): genetic info gets duplicated
g2: final prep for cell division
s (synthesis): genetic info gets duplicated
g2: final prep for cell division
name and describe stages of interphase (mitosis)
52
New cards
* “regular” cell division
* occurs in somatic cells
* when tissues must replace themselves
* parent cells divide and make 2 clone daughter cells
* occurs in somatic cells
* when tissues must replace themselves
* parent cells divide and make 2 clone daughter cells
what’s mitosis
53
New cards
* cells grows too big - surface area doesnt match volume
* too much volume = nucleus loses activity control and transport becomes too difficult
* allows organism growth
* maintains healthy cells
* too much volume = nucleus loses activity control and transport becomes too difficult
* allows organism growth
* maintains healthy cells
why does mitosis occur
54
New cards
PMAT - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telephase
prophase
* nuclear membrane dissolves
* centrioles move to poles + make mitotic spindle (microtubules)
* chromosomes condense and join at centromere
\
metaphase
* chromosomes line up along metaphase plate (cell equator)
* chromosomes condense and thicken
\
anaphase
* chromatid separate into single strands
* spindle fibres shorten + pull chromosomes to opposite poles
\
telophase
* chromosomes decondense
* spindles break down
* nuclear membrane forms
* animal cells = begin cleavage furrow (indenting cytoplasm)
* plant cells = form cell plate to divide cytoplasm
* cytokinesis = daughter cells form, cytoplasm divides
prophase
* nuclear membrane dissolves
* centrioles move to poles + make mitotic spindle (microtubules)
* chromosomes condense and join at centromere
\
metaphase
* chromosomes line up along metaphase plate (cell equator)
* chromosomes condense and thicken
\
anaphase
* chromatid separate into single strands
* spindle fibres shorten + pull chromosomes to opposite poles
\
telophase
* chromosomes decondense
* spindles break down
* nuclear membrane forms
* animal cells = begin cleavage furrow (indenting cytoplasm)
* plant cells = form cell plate to divide cytoplasm
* cytokinesis = daughter cells form, cytoplasm divides
name and describe the stages of mitosis
55
New cards
* same genes
* chromosome from male and female parent
* may be different variations
* arranged in same order in the dna chromosomes
* chromosome from male and female parent
* may be different variations
* arranged in same order in the dna chromosomes
homologous pairs
56
New cards
* cell division that makes gametes (sex cells)
* reduces number of chromosomes to half (haploid)
* only occurs in eukaryotes who can sexually reproduce
* only occurs in at least diploid organisms
* have TWO divisions
* 1 parent cell = 4 gamete cells
* each gamete holds different genetic info (not identical)
* reduces number of chromosomes to half (haploid)
* only occurs in eukaryotes who can sexually reproduce
* only occurs in at least diploid organisms
* have TWO divisions
* 1 parent cell = 4 gamete cells
* each gamete holds different genetic info (not identical)
whats meiosis
57
New cards
* interphase before meiosis
* dna replicates
* two identical copies of chromosome within homologous pair is made, attaches at centromere
* copy called sister chromatid
* dna replicates
* two identical copies of chromosome within homologous pair is made, attaches at centromere
* copy called sister chromatid
what’s premeiotic interphase
58
New cards
prophase 1
* homologous chromosomes pair together (synapsis)
* chromatids cross over to exchange genetic info at random points (chiasmata)
* pair becomes a tetrad (4 sister chromatids) held together via kinetochore
* centrioles move to opposite poles and spindle fibres appear
\
metaphase 1
* spindle fibres attach to kinetochore of tetrads
* tetrads line up at metaphase plate
* independent assortment happens
* chromosome pairs separate randomly
\
anaphase 1
* tetrad pulls apart, each chromosome moves towards opposite pole
* chromosome pulls apart at kinetochore
* sister chromatids are intact still
\
telophase 1
* chromosome reach poles
* nuclear membrane reforms
* spindle fibres dissolve
\
cytokinesis
* cytoplasm + organelles divide
* daughter cells = haploid
* one chromosome from each og homologous pair
* sister chromatid still exist
* homologous chromosomes pair together (synapsis)
* chromatids cross over to exchange genetic info at random points (chiasmata)
* pair becomes a tetrad (4 sister chromatids) held together via kinetochore
* centrioles move to opposite poles and spindle fibres appear
\
metaphase 1
* spindle fibres attach to kinetochore of tetrads
* tetrads line up at metaphase plate
* independent assortment happens
* chromosome pairs separate randomly
\
anaphase 1
* tetrad pulls apart, each chromosome moves towards opposite pole
* chromosome pulls apart at kinetochore
* sister chromatids are intact still
\
telophase 1
* chromosome reach poles
* nuclear membrane reforms
* spindle fibres dissolve
\
cytokinesis
* cytoplasm + organelles divide
* daughter cells = haploid
* one chromosome from each og homologous pair
* sister chromatid still exist
name and describe stages of meiosis 1
59
New cards
homologous chromosomes pair together
whats synapsis
60
New cards
the random points when chromatids cross over for exchanging genetic info
what’s chiasmata
61
New cards
no interphase/dna replication
* no crossing over
* chromosomes in daughter cells from meiosis 1 are formed as sister chromatids
\
prophase 2
* chromosome condense
* spindle fibres appear
* centrioles move to opposite ends
\
metaphase 2
* centromeres divide
* sets of chromatids move to equator
\
anaphase 2
* chromatids move to opposite poles
\
telophase 2
* chromosomes unwind, nuclear membrane forms
* makes 4 haploid cells (sperm or ova) after cytokinesis
* all genetically variable
* no crossing over
* chromosomes in daughter cells from meiosis 1 are formed as sister chromatids
\
prophase 2
* chromosome condense
* spindle fibres appear
* centrioles move to opposite ends
\
metaphase 2
* centromeres divide
* sets of chromatids move to equator
\
anaphase 2
* chromatids move to opposite poles
\
telophase 2
* chromosomes unwind, nuclear membrane forms
* makes 4 haploid cells (sperm or ova) after cytokinesis
* all genetically variable
meiosis 2
62
New cards
diploid spermatogonia → primary spermatocytes → 4 spermatids
sperm formation (spermatogenesis)
63
New cards
diploid oogonia → primary oocytes → 1 egg + 3 polar bodies
* polar bodies all die
* polar bodies all die
egg formation
64
New cards
mistakes during meiosis
\
trisomy
* fertilized cell has extra chromosome copy
* 3 chromosomes instead of 2
\
monosomy
* missing chromosome
* 1 chromosome instead of 2
\
trisomy
* fertilized cell has extra chromosome copy
* 3 chromosomes instead of 2
\
monosomy
* missing chromosome
* 1 chromosome instead of 2
nondisjunction
65
New cards
* chromosome fragment fails to reattach properly
* loss of chromosome segment
* usually deadly/serious disorder
* loss of chromosome segment
* usually deadly/serious disorder
deletion
66
New cards
segment reattaches to complete homologue
duplication
67
New cards
segment reattaches to correct homologue in reverse order
inversion
68
New cards
segment attaches to nonhomologous chromosome
translocation
69
New cards
* cells for testing collected from amniotic fluid
* occurs when fetus is larger
\
* occurs when fetus is larger
\
amniocentesis
70
New cards
* obtaining cells for testing via villi lining in uterus
chorionic villus sampling
71
New cards
* organism can only pass one of it’s two genes
* inherited traits determined by two alleles of a gene
* each offspring contains one allele from each parent
* inherited traits determined by two alleles of a gene
* each offspring contains one allele from each parent
law of segregation
72
New cards
* genes found on separate chromosomes are inherited independently of each other
law of independent assortment
73
New cards
dominant alleles will always mask recessive alleles
law of dominance
74
New cards
homozygous = two of same allele (both dom or both rec)
heterozygous = two different alleles (one dom + one rec)
heterozygous = two different alleles (one dom + one rec)
homozygous vs heterozygous
75
New cards
physical/psychological traits of organism
phenotype
76
New cards
genetic makeup/combination of alleles for given trait
genotype
77
New cards
different alleles expressed to produce an intermediate phenotypes
* ex: red x white flower = pink flower
\
* ex: red x white flower = pink flower
\
incomplete dominance
78
New cards
two expressed at the same time
* ex: red x white cow = red, white and roan (red and white hair)
* ex: red x white cow = red, white and roan (red and white hair)
codominance
79
New cards
two identically paired x chromosomes (XX)
female sex chromosomes
80
New cards
one x and one y (XY)
male sex chromosomes
81
New cards
evolutionary relationships between species
phylogeny
82
New cards
* diagram showing evolutionary relationships between organisms
* tips = species
* nodes = common ancestor
\
* tips = species
* nodes = common ancestor
\
phylogenic tree
83
New cards
taxonomic group including a single common ancestor + all it’s descendants
clade
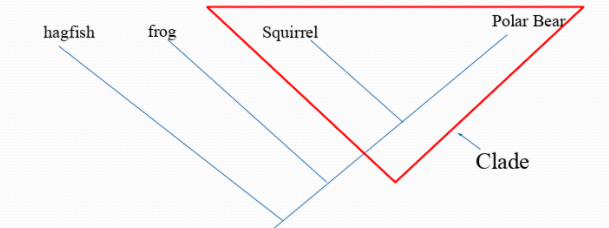
84
New cards
* dna profile of species in barcode format
* only 6000 species profiled currently
* only 6000 species profiled currently
iBOL method
85
New cards
* compare similarities in early embryotic stages of development
* similarities could indicate common ancestor
* similarities could indicate common ancestor
developmental similarities method
86
New cards
similar form, different function
homologous structure
87
New cards
similar form and function in different organisms
analogous structure
88
New cards
* archaea is “ancient”, found in extreme environments like hot springs or volcanos
* eubacteria found anywhere
* eubacteria gets people sick, archaea can’t
* eubacteria found anywhere
* eubacteria gets people sick, archaea can’t
archaea vs eubacteria
89
New cards
* prokaryotes
* cant get humans sick
* found in harsh environments
* first life on earth
* cant get humans sick
* found in harsh environments
* first life on earth
characteristics of archaea
90
New cards
* prokaryotic
* usually has cell wall
* can infect humans
* usually has cell wall
* can infect humans
characteristics of eubacteria
91
New cards
* heterotrophs
* sexual + asexual
* eukaryotes
* chitin cell wall
* mostly terrestrials
* can be parasitic
* saprobes → absorb food via decaying matter
* sexual + asexual
* eukaryotes
* chitin cell wall
* mostly terrestrials
* can be parasitic
* saprobes → absorb food via decaying matter
characteristics of fungi
92
New cards
* unicellular usually
* eukaryotic
* hetero and/or autotroph
* no cell wall
* swim with flagella
* aquatic habitats
* eukaryotic
* hetero and/or autotroph
* no cell wall
* swim with flagella
* aquatic habitats
characteristics of protists
93
New cards
* multicellular
* eukaryotic
* autotroph
* mostly sexual reproducers
* aquatic/terrestrial habitats
* chloroplasts, cell wall, cellulose
* static
* develop embryos protected by plant tissues
* eukaryotic
* autotroph
* mostly sexual reproducers
* aquatic/terrestrial habitats
* chloroplasts, cell wall, cellulose
* static
* develop embryos protected by plant tissues
characteristics of plants
94
New cards
* eukaryotic
* multicellular
* heterotroph
* sexual
* aquatic and terrestrial
* multicellular
* heterotroph
* sexual
* aquatic and terrestrial
characteristics of animals
95
New cards
tiny loop of dna in bacteria
plasmid
96
New cards
carbon source = CO2
energy source = light
energy source = light
photoautotroph
97
New cards
carbon source = CO2
energy source = inorganic chemicals
energy source = inorganic chemicals
chemoautotroph
98
New cards
carbon source = organic compounds
energy source = light
energy source = light
photoheterotroph
99
New cards
carbon source = organic compounds
energy source = organic chemicals
energy source = organic chemicals
chemoheterotroph
100
New cards
* aerobes = oxygen used
* obligate aerobes = oxygen necessary
* anaerobes = oxygen not necessary
* obligate anaerobes = oxygen kills
* facultative anaerobes = survive with/without oxygen
* obligate aerobes = oxygen necessary
* anaerobes = oxygen not necessary
* obligate anaerobes = oxygen kills
* facultative anaerobes = survive with/without oxygen
five classes of respiration