Exam 9: Unit 06 Chapter 11 Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
You and your colleagues are constructing a pedigree for a boy with cystic fibrosis. The individual's younger brother has also been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. How would these brothers be represented in a pedigree?
Both would be represented as completely shaded squares.
A person has a non-normal set of sex chromosomes but is obviously female. Her cells show two Barr bodies. Which condition accounts for these observations?
XXX
A man heterozygous for blood type A marries a woman heterozygous for blood type B. The chance that their first child will have type O blood is ____.
25%
A series of plants, produced through vegetative propagation, have been planted at different altitudes. The researcher observes that the higher the altitude, the shorter the plant will grow. Please make a hypothesis to explain the results.
Higher altitudes decrease the expression of genes that promote height.
On of the advantages of sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction is an increase in genetic variation in a population. Which does not contribute to genetic variation?
mitosis
A man carrying the allele for Huntington's disease marries a woman who is homozygous recessive for the allele. What is the probability that their offspring will develop Huntington's disease?
50 percent
A large difference between the concordance rates of fraternal and identical twins shows _____________.
a strong genetic influence.
An individual has type AB blood. His father has type A blood and his mother has type B blood. What is the individual's phenotype an example of?
codominance
Which disorder prevents sufficient chloride ions from entering cells?
cystic fibrosis
Why is Down syndrome called trisomy 21?
The syndrome results from an extra chromosome 21.
Figure 11-6This pedigree shows the transmission of a rare disease that is debilitating but not lethal. Carriers are not shown.
Which type of heredity does the pedigree in Figure 11-6 demonstrate?
X-linked recessive
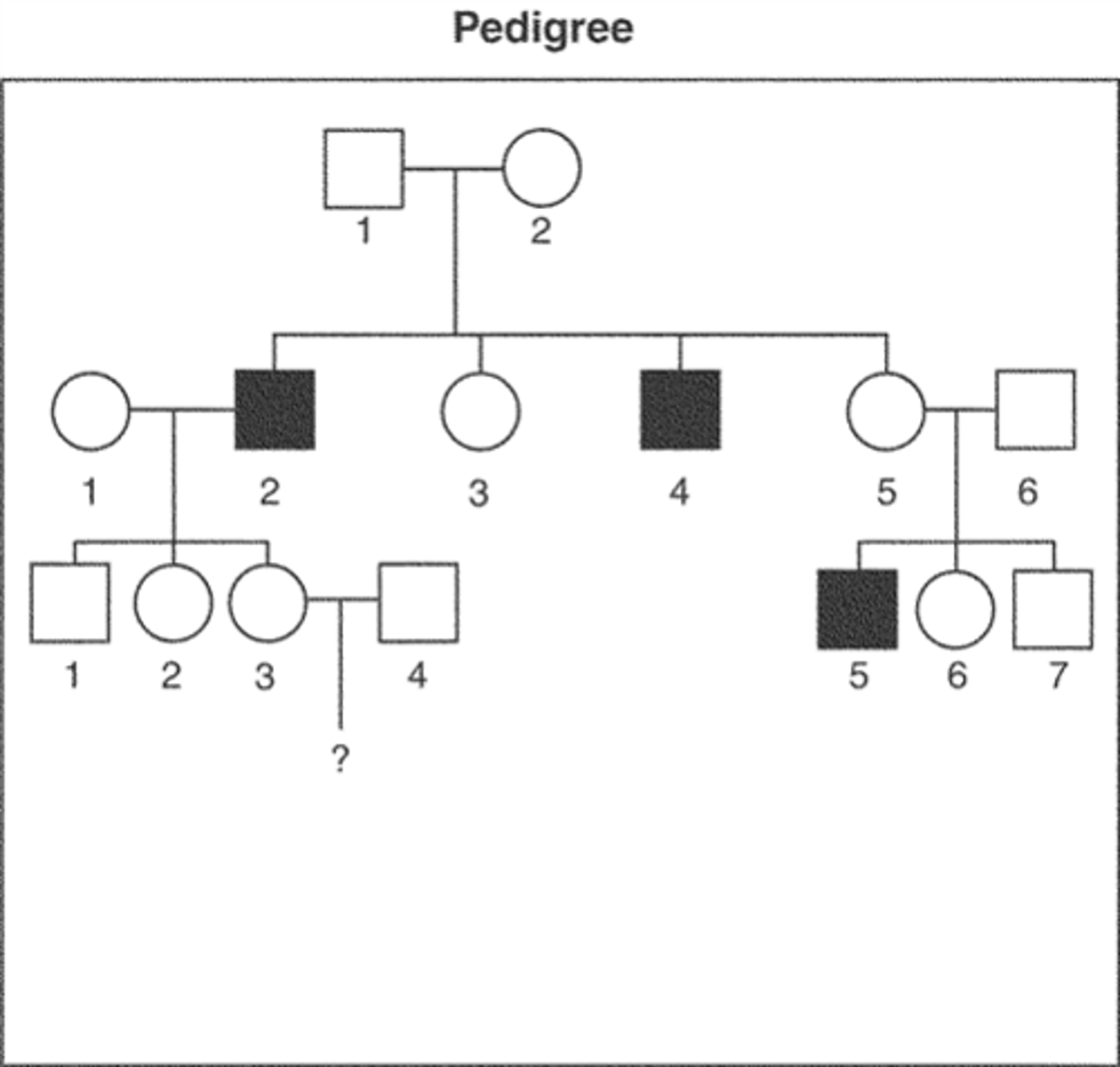
Which does NOT play a role in determining an individual's sex?
autosomes
Which defines an organism that is homozygous for a trait?
has two of the same alleles for a trait
Isabel and Dan were studying meiosis in their science class and its significance to sexual reproduction. They were asked to summarize how meiosis and sexual reproduction increase genetic variation in a population over time. They brainstormed a number of answers shown below. Which does not have an impact on genetic variation during meiosis?
random combination of gametes
Lilly did a presentation to her science class explaining the crossover of homologous chromosomes and the resulting genotypes. She used the diagram of homologous chromosomes shown below and asked the class to select the correct prediction of the genotypes that would occur after crossing over from the list shown. Which combination of genotypes is correct?
The gamete genotypes would be AB, Ab, ab, and aB.
Which is a dominant genetic disorder?
achondroplasia
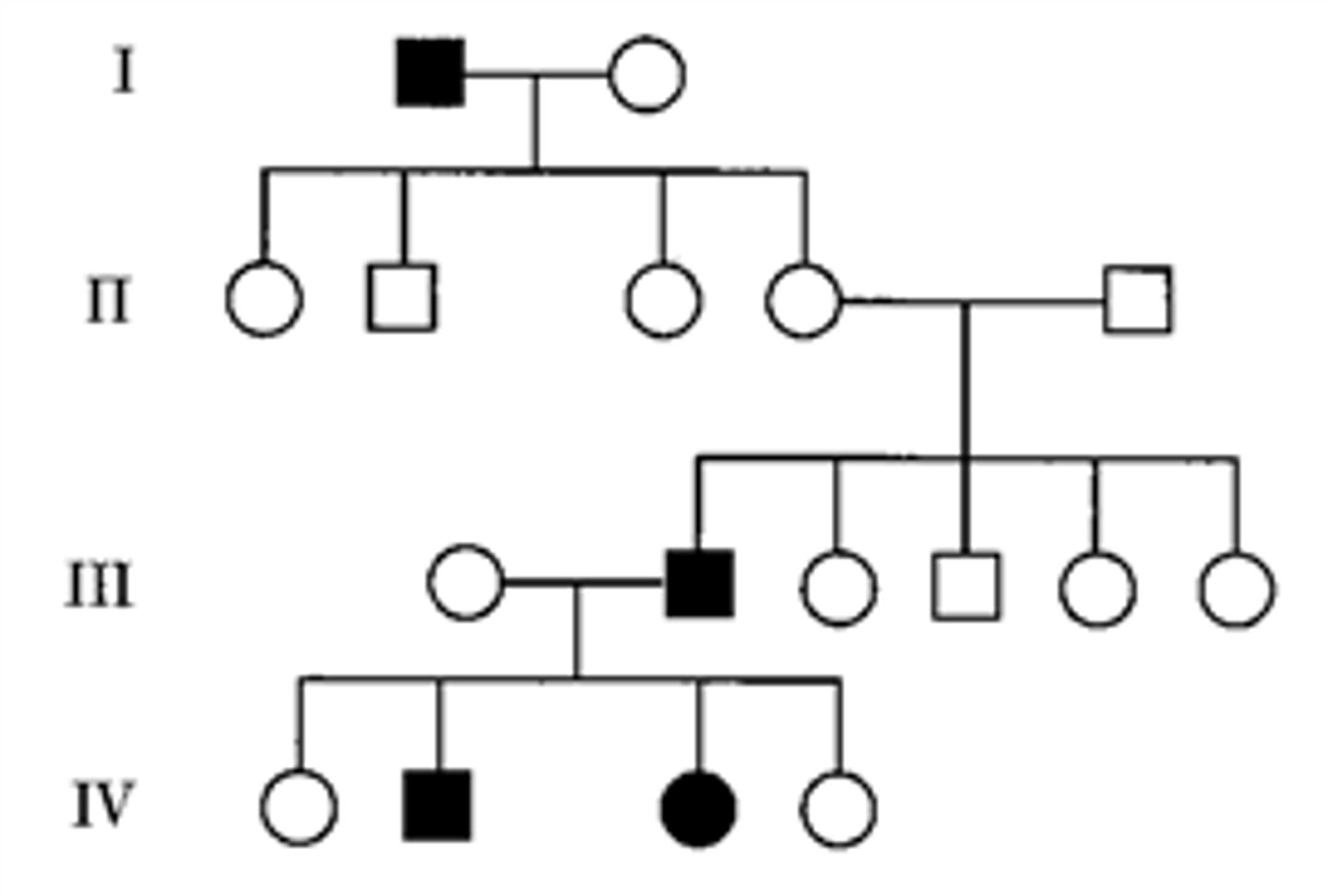
Figure 11-2
What is the probable mode of inheritance for the normal trait in Figure 11-2?
sex linkage
Which of the following could only be a result of nondisjunction during meiosis of sperm formation and not egg formation?
XYY
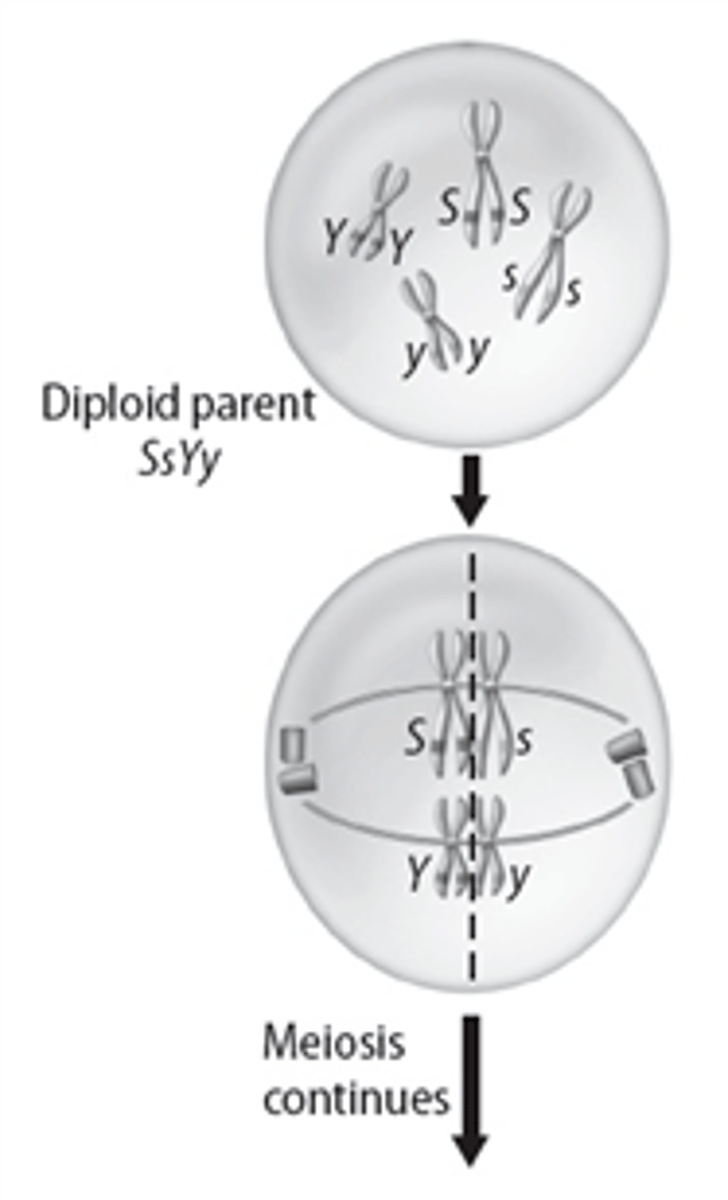
Miriam used the diagram below to help explain the significance of meiosis to her friend Karla. She was trying to show Karla why the process of meiosis resulted in increased genetic diversity in sexual reproduction. Miriam first asked Karla to predict all the potential types of the haploid gametes formed using the diagram below. Which of Karla's answers below is correct?
haploid gametes could be SY, sY, Sy, sy
A man's grandfather on his father's side had galactosemia. Assuming that his mother was not a carrier, what is the probability that this man is a carrier for the disorder?
0.50
What is the effect of sickle-cell anemia?
inefficient oxygen transportation
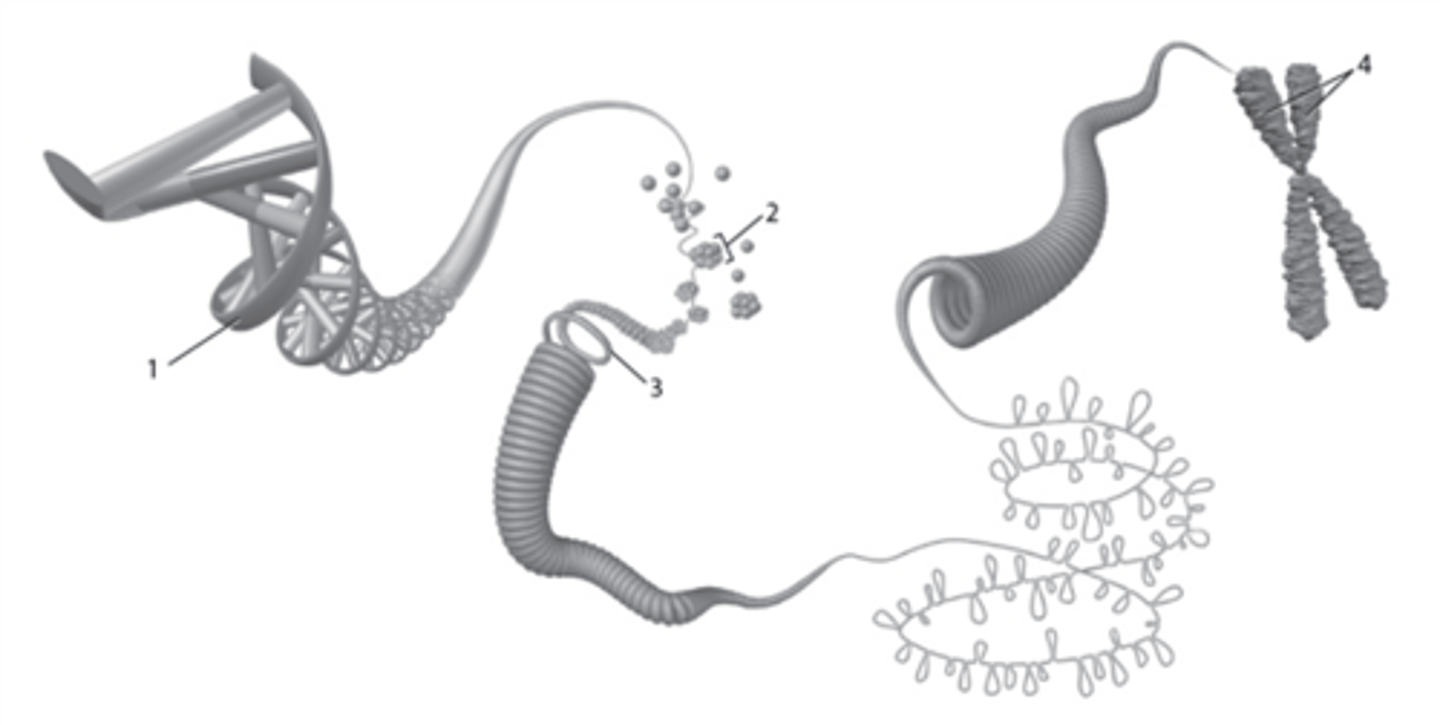
Gideon was trying to explain the difference between genes and chromosomes to Avery, his fellow classmate and showed Avery a picture of the DNA coiling to form a chromosome. Which label best represents a gene?
1
The gene for brown eyes (B) is dominant over the gene for blue eyes (b). Two brown-eyed people have a blue-eyed child. Which genotypes make this possible?
The mother and the father are both heterozygous brown-eyed (Bb).
When roan cattle are mated, 25% of the offspring are red, 50% are roan, and 25% are white. Upon examination, it can be seen that the coat of a roan cow consists of both red and white hairs. This trait is one controlled by ____.
codominant alleles
In humans, the sex-linked trait of normal blood clotting is dominant to hemophilia. Which of the following shows the genotype for someone who is considered to be a carrier for hemophilia?
A.) XH XH
B.) XH Xh
C.) Xh Xh
D.) XH Y
B