ARRT Radiography Exam Review
1/759
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
760 Terms
Study guide for the ARRT exam in radiography.
Anatomy and positioning are not covered in this study guide.
What is a tort?
A violation of civil law.
Torts are also known as ________.
Personal Injury Law
If a patient is apprehensive about being injured, or a radiographer causes fear in the patient, it is known as ________.
Assault
Unlawful touching or touching without consent, harm resulting from physical contact with the radiographer, and imaging the wrong body part or against the patients will is known as ________.
Battery
Unjustified restraint of a patient is known as ________.
False Imprisonment
Exposing confidential information, improperly exposing the patients body, inappropriately touching a patients body, or photographing a patient without their permission is known as ________.
Invasion of Privacy
Written information that results in defamation of character or loss of reputation is known as ________.
Libel
Orally spreading false information that results in defamation of character or loss of reputation is known as ________.
Slander
Respondeat Superior is a legal doctrine stating the employer is held liable for an employee's negligent act. Respondeat Superior means ________.
Let the master answer.
Res Ipsa Loquitur is a legal doctrine stating that the cause of the negligence is obvious. Res Ipsa Loquitur means ________.
The thing speaks for itself.
The ARRT Standards of Ethics consists of the ________ of Ethics and the ________ of Ethics.
1) Code
2) Rules
The ARRT ________ of Ethics serves as a guide for what radiographers aspire to become as professionals.
Code
The ARRT ________ of Ethics are mandatory, enforceable, and carry sanctions for violations.
Rules
Attempting to copy ARRT exam materials, disclosing exam questions, impersonating a test candidate, being convicted of a crime, engaging in unprofessional conduct, injuring a patient, misrepresenting CE units earned, violating state or federal narcotics and controlled-substance laws, and attempting to circumvent the certification and registration process are examples that violate the ARRT ________ of Ethics.
Rules
Acting in a professional manner, responding to patient needs, and supporting colleagues and associates in providing quality patient care, practicing technology founded upon theoretical knowledge and concepts, practicing ethical conduct appropriate to the profession and protecting the patient's right to quality radiologic care, and striving to improve knowledge and skills by participating in continuing education and professional activities are examples covered under the ARRT ________ of Ethics.
Code
In what order should radiographic exams be scheduled?
1) Fiberoptic (endoscopic) studies.
2) Radiography of the urinary tract.
3) Radiography of the biliary system.
4) Computed tomography studies.
5) Lower GI radiographic studies.
6) Upper GI radiographic studies.
Tachycardia is having a heartbeat of more than ________ beats per minute.
100
Bradycardia is having a heartbeat of less than ________ beats per minute.
60
Diastolic blood pressure greater than ________mm/Hg indicates an increasing level of hypertension.
90
Diastolic blood pressure less than ________mm/Hg gives some indication of shock.
50
The usual oxygen flow rate through a nasal cannula is ________ L/minute.
3 to 5
Loosing large amounts of blood or plasma may result in ________ shock.
Hypovolemic
When toxins are produced during massive infection causing a dramatic decrease in blood pressure, ________ shock is suspected.
Septic
________ shock is when blood pools in peripheral vessels.
Neurogenic
________ shock results from cardiac failure or other interference with heart function.
Cardiogenic
________ shock (or ________) is a reaction to foreign proteins after injections, and may follow injection of iodinated contrast media.
1) Allergic
2) Anaphylaxis
What are some symptoms of shock?
1) Restlessness and apprehension.
2) Accelerated pulse.
3) Pale skin.
4) Weakness.
5) Alteration in ability to think.
6) Cool, clammy skin.
7) Systolic blood pressure less than 30 mm/Hg.
What is the radiographer's response to shock?
1) Stop procedure.
2) Place patient in Trendelenburg position.
3) Call for help.
4) Determine blood pressure.
5) Administer oxygen.
6) Document time and occurrence of each symptom.
Contrast media ________ may occur in infants, or patients who have renal, cardiac or hepatic failure.
Overdose
What are some reactions to anaphylactic shock?
1) Flushing
2) Hives
3) Nausea
What are some reactions to cardiovascular shock?
1) Hypotension
2) Tachycardia
3) Cardiac Arrest
What are some other reactions that may be found as a result of contrast media injection?
1) Nausea/Vomiting
2) Sneezing
3) Sensation of Heat
4) Itching
5) Hoarseness of Voice
6) Coughing
7) Urticaria
8) Dyspnea
9) Loss of Consciousness
10) Convulsions
11) Cardiac Arrest
12) Paralysis
13) Change in Orientation
________ contains negatively and positively charged ions.
Iodinated Ionic Contrast Media
________ do not ionize into separate negative and positive charges.
Iodinated Nonionic Contrast Media
________ has a far lower incidence of contrast agent reactions because it is not ionized.
Iodinated Nonionic Contrast Media
What is the atomic number for iodine?
53
What is the atomic number for barium?
56
What is the atomic number for tungsten?
74
What letter represents the atomic mass number?
A
What letter represents the atomic number?
Z
In what order is venipuncture performed?
1) Wash hands.
2) Put on gloves.
3) Place tourniquet in place.
4) Select vein.
5) Cleanse area.
6) Remove air from syringe/tubing.
7) Insert needle.
8) Observe blood flow into catheter.
9) Remove tourniquet.
10) Begin injection.
When handling chemicals and they are exposed to skin, the area should be washed with cool water for at least ________ minutes.
5
When handling chemicals and they splash into the eyes, the eyes should be washed with cool water for at least ________ minutes.
15
This is used to define radiation exposure or radiation delivered to a specific point.
Air Kerma
Air kerma is measured in ________.
Gray (Gyᵃ)
This is sometimes used to measure exposure, but the preferred unit is air kerma.
Coulombs/Kilogram
This is used to define the amount of energy absorbed per unit mass of tissue.
Absorbed Dose
Absorbed dose is measured in ________.
Gray (Gyᵗ)
This is used to define the product of absorbed dose (Gy) times the radiation weighting factor (Wᴿ).
Equivalent Dose
________ takes into account the biologic impact of the type and energy of the radiation being used.
Radiation weighting factor (Wᴿ).
This is used to define the estimated risk present when various tissues are irradiated.
Effective Dose
Effective dose uses the ________, and takes into account the relative radiosensitivity of the irradiated organ or body part.
Tissue weighting factor (Wᵀ).
________ is the product of absorbed dose times the radiation weighting factor times the tissue weighting factor.
Effective Dose
________ is the unit of effective and equivalent dose.
Sievert (Sv)
The unit of radioactivity that is used to measure the quantity of radioactive material is the ________.
Becquerel (Bq)
Radiation exiting the x-ray tube is known as ________.
Primary Radiation
X-rays that emerge from the patient and strike the image receptor, and are composed of primary and scattered photons is known as ________.
Exit or Remnant Radiation
X-ray beams that contain photons of many different energies are known as ________.
Heterogeneous.
What are twelve properties of x-rays?
1) Highly penetrating, invisible rays.
2) Electrically neutral.
3) Liberate minute amounts of heat.
4) Polyenergetic, heterogenous.
5) Travel in straight lines.
6) Ionize matter.
7) Cause fluorescence of certain crystals.
8) Travel at the speed of light.
9) Affect photographic film.
10) Cannot be focused by a lens.
11) Produce chemical and biologic changes.
12) Produce secondary and scatter radiation.
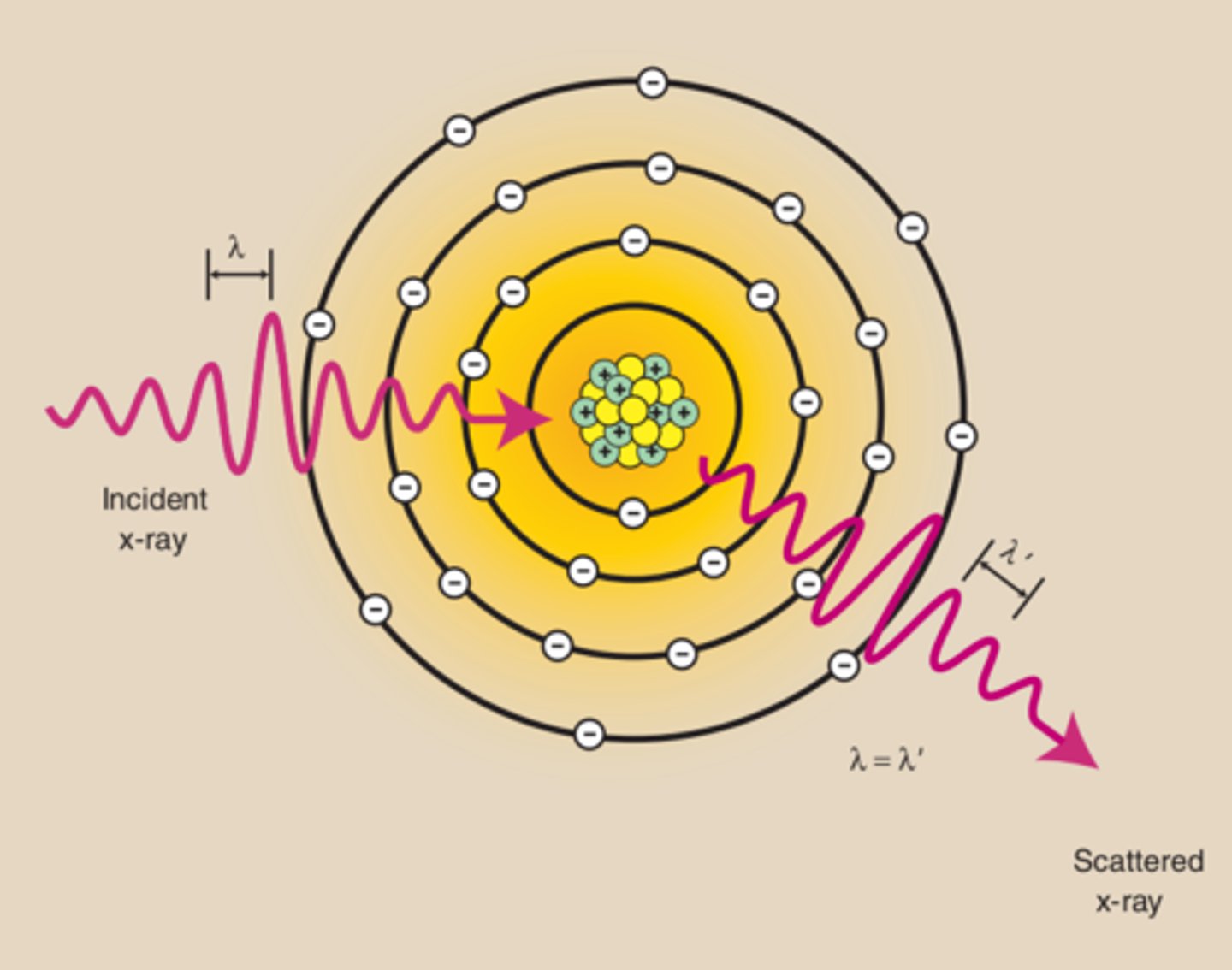
What occurs during Coherent Scattering?
The incident x-ray interacts with an atom causing it to become excited. The atom immediately releases this excess energy as a scattered x-ray having the same energy and wavelength as the incident x-ray, but in a different direction.
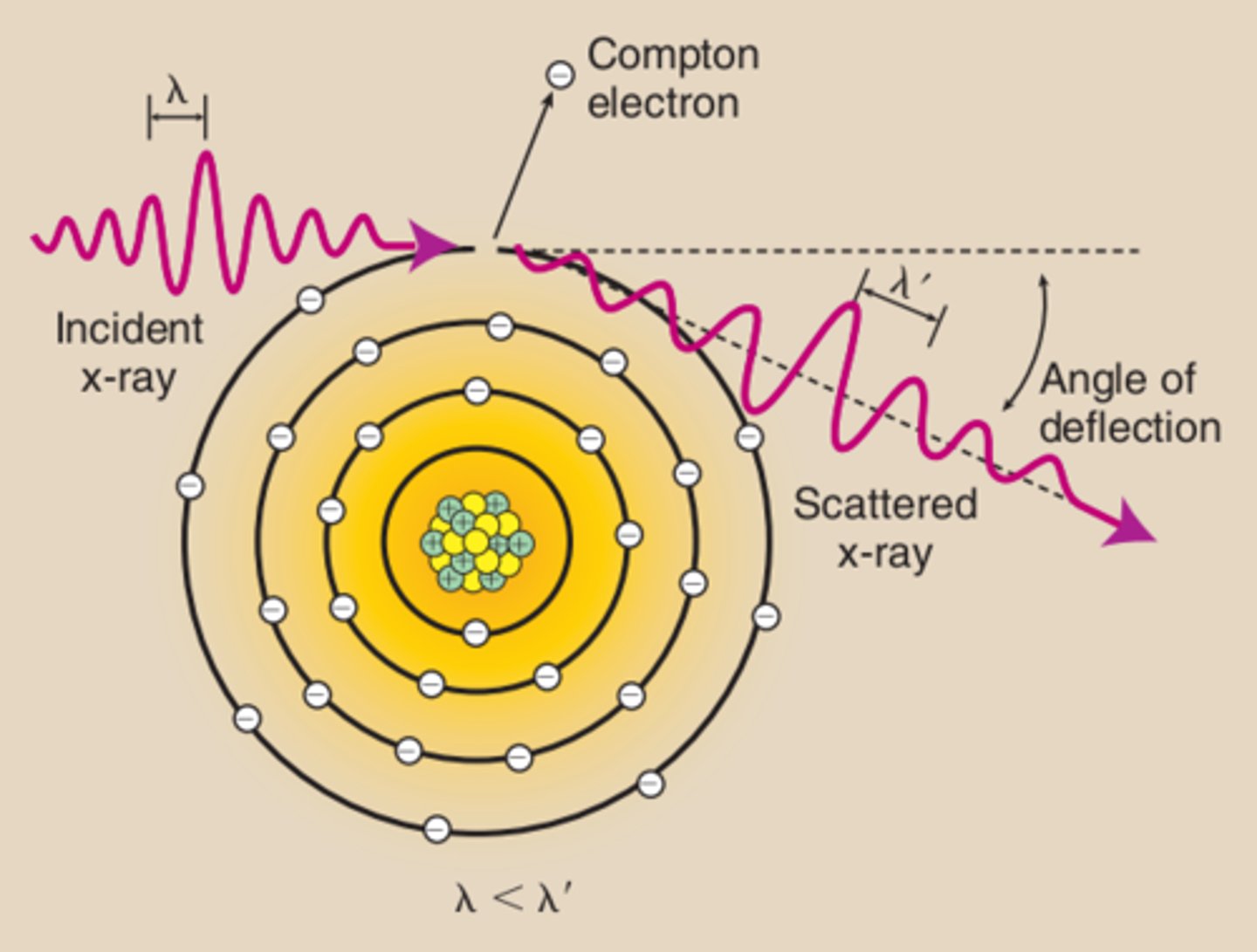
What occurs during Compton Scattering?
The incident x-ray interacts with an outer-shell electron and ejects it from the atom, ionizing the atom. The x-ray then continues in a different direction with less energy and a longer wavelength.
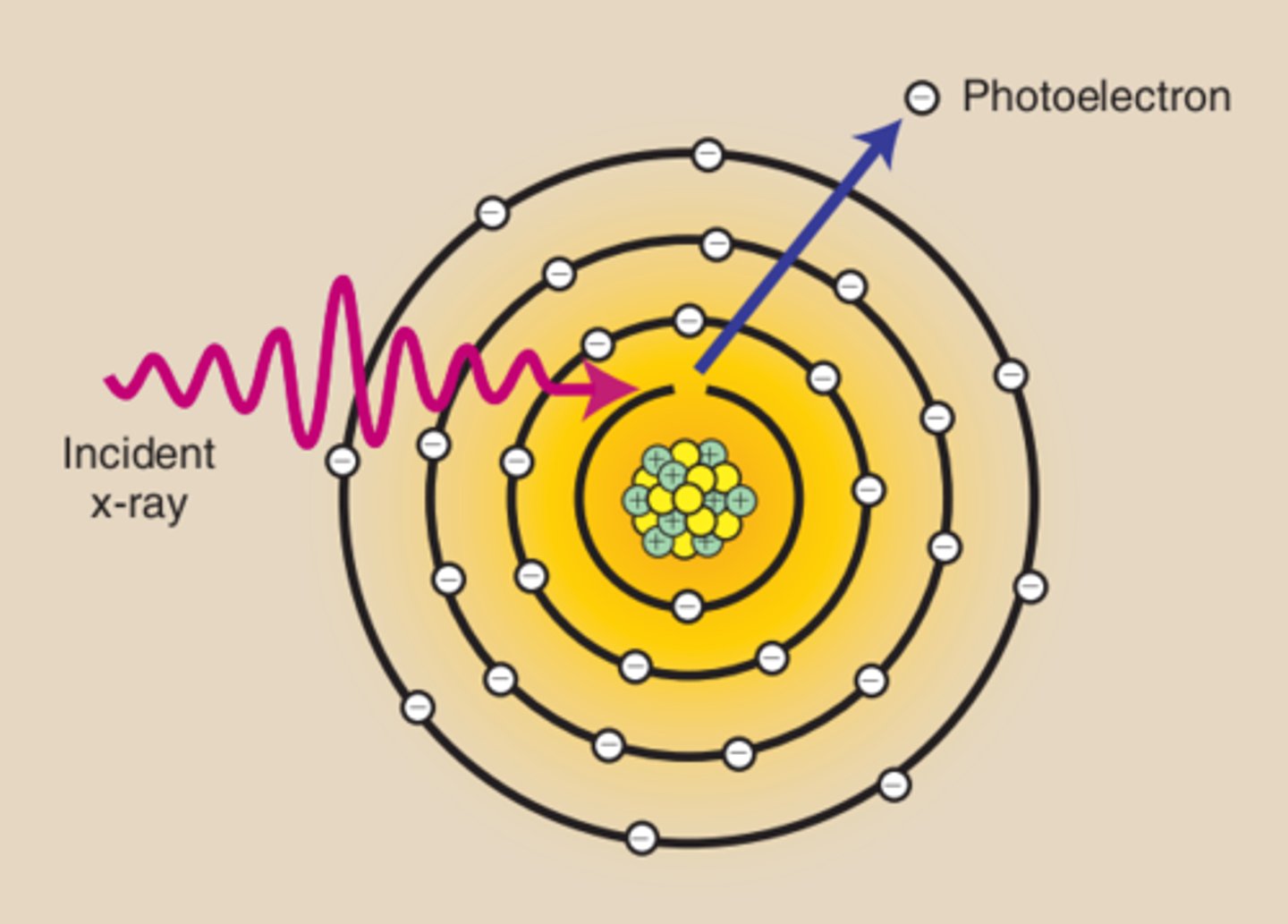
What occurs during the Photoelectric Effect?
The incident x-ray interacts with an inner-shell electron and ejects it from the atom, ionizing the atom. The x-ray is not scattered but totally absorbed, releasing all of its energy to the ejected electron. Characteristic x-rays are then produced as outer-shell electrons fill the void left by the inner-shell electron.
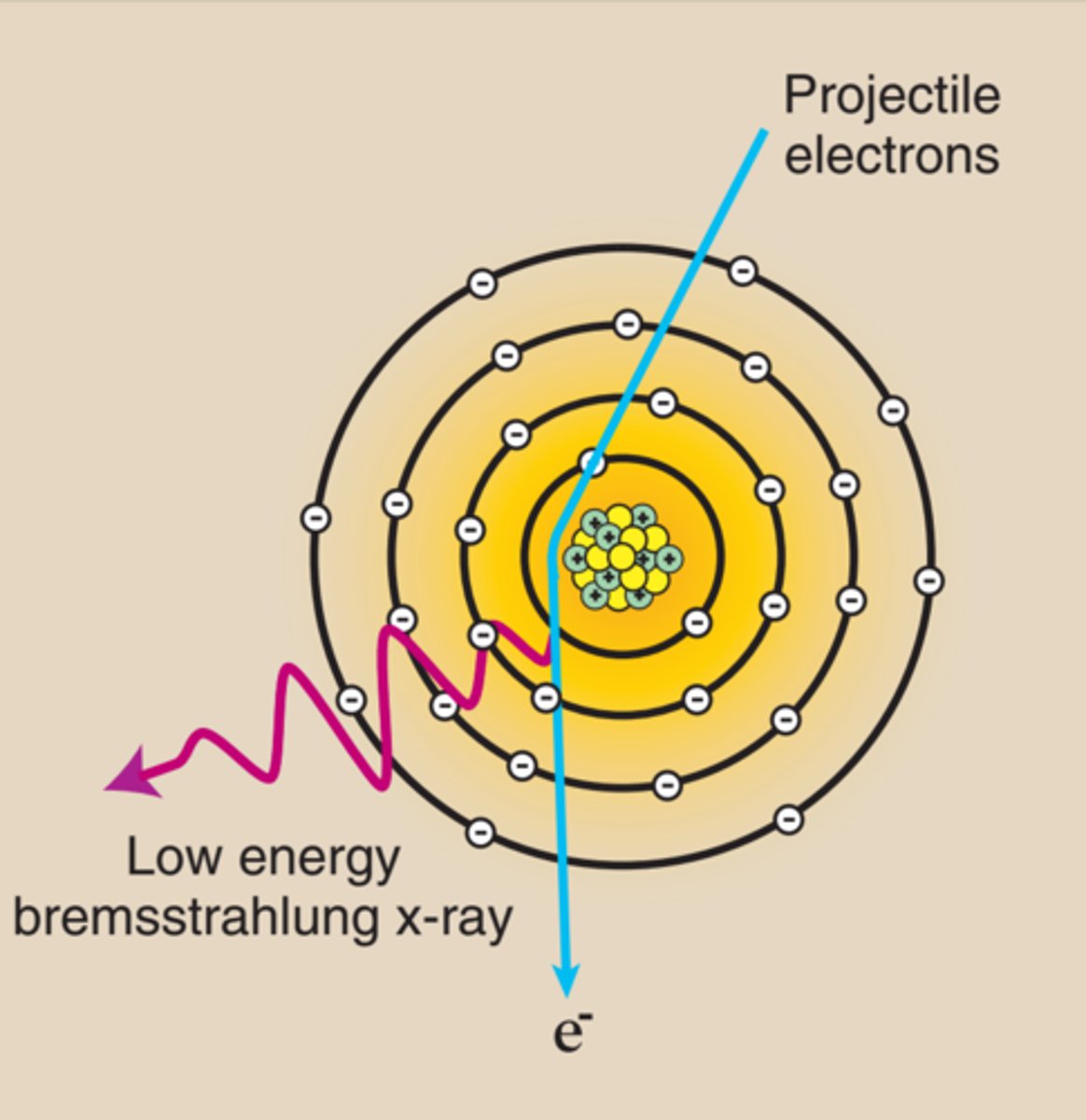
What is Bremsstrahlung Radiation?
Bremsstrahlung x-rays are produced when a projectile electron is slowed by the electric field of a target atom nucleus.
What is Characteristic Radiation?
When projectile electrons interact with inner-shell electrons of the target atom, rather than with an outer-shell electron.
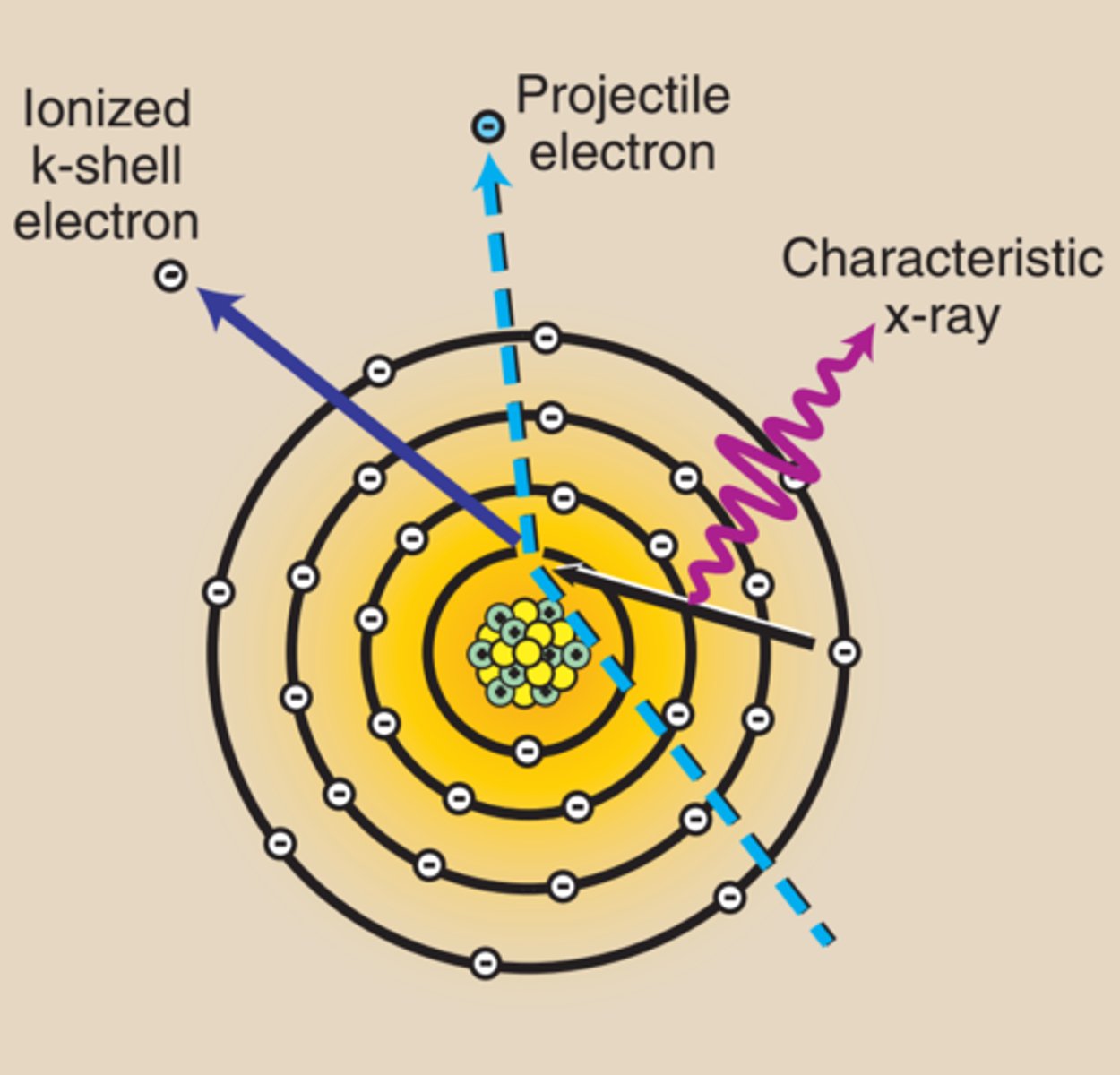
X-ray's have diagnostic wavelengths of ________ to ________, and travel as bundles of energy called photons.
1) 0.1 Å
2) 0.5 Å
The upper boundary dose that can be absorbed, either in a single exposure or annually, with a negligible risk of somatic or genetic damage to the individual, is known as ________.
Effective Dose
What is the annual effective dose limit for occupational exposure?
50 mSv
What is the annual equivalent dose limit for occupational exposure to the lens of the eye?
150 mSv
What is the annual equivalent dose limit for occupational exposure to the localized areas of the skin, hands and feet?
500 mSv
This is calculated by multiplying the radiographer's age in years times 10 mSv.
Cumulative effective dose limit.
The annual effective dose limit for students over the age of 18 is ________.
50 mSv
The annual effective dose limit for the general public, assuming frequent exposure is ________.
1 mSv
The annual effective dose limit for the general public, assuming infrequent exposure is ________.
5 mSv
The total equivalent dose to the embryo/fetus for the entire gestational period is ________.
5 mSv
The equivalent dose limit to the embryo/fetus per month is ________.
0.5 mSv
Effects that occur by chance and which may occur without a threshold level of dose, whose probability is proportional to the dose and whose severity is independent of the dose:
Stochastic Effects
Effects that have a threshold below which the effect does not occur. The threshold may be very low and may vary from person to person. However, once the threshold has been exceeded, the severity of an effect increases with dose:
Deterministic Effects
________ is somatic cell division that comprises of four phases. When division is complete, each new cell contains 46 chromosomes.
Mitosis
What are the four phases of mitosis?
1) Prophase
2) Metaphase
3) Anaphase
4) Telophase
________ is germ (sperm or ovum) cell division that halves the number of chromosomes in each cell so that the union of two germ cells produces a new cell with 46 chromosomes.
Meiosis
This occurs when radiation transfers its energy directly to the DNA or RNA.
Direct Effect
Because a cell contains mostly water, the probability that it will be struck by radiation is greater. This interaction is known as the ________ effect.
Indirect
________ of water occurs as radiation energy is deposited into the water of a cell.
Radiolysis
Cells are most sensitive to radiation when they are immature, undifferentiated, and rapidly dividing. This describes:
The law of Bergonie and Tribondeau.
If cells are more oxygenated, they are more susceptible to radiation damage. This describes:
Oxygen Enhancement Ratio (OER)
A whole-body dose of ________ will depress the blood count.
0.25 Gy
Somatic effects are evident in the ________ being exposed.
Organism
Doses causing somatic effects are much ________ than those received in general diagnostic radiography.
Higher
What are some examples of early somatic effects (acute radiation syndrome)?
1) Hematopoietic Syndrome
2) GI Syndrome
3) Central Nervous System Syndrome
What is hematopoietic syndrome?
It decreases the total number of all blood cells, and can lead to death.
What is GI syndrome?
It causes total disruption of GI tract structure, and function, and can result in death.
What is central nervous system syndrome?
It causes complete failure of the nervous system and results in death.
What are some examples of late somatic effects?
1) Carcinogenesis
2) Cataractogenesis
3) Embryologic Effects
4) Thyroid Function
5) Shortening of Life Span
What is carcinogenesis?
It causes cancer.
What is cataractogenesis?
It causes cataracts to form, following a nonlinear-threshold dose-response curve.
When are embryologic effects most sensitive?
During the first trimester of gestation.
What are late somatic effects of the thyroid?
Being a very sensitive organ, late somatic effects may manifest as cancer or cessation of function.
Shortening of lifespan ________ occur in modern radiation workers.
Does Not
A genetic effect is damage to the ________ molecule, which is then passed on to the next generation.
DNA