Modern Architecture: Transformations and Key Figures
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
modern architecture
(adj.) relating to the present or recent times as opposed to the remote past.
modern
(noun) a person who advocates or practices a departure from traditional styles or values.
Modernism
Although some say it is rooted in the Period of Enlightenment, it is mostly a 20th century construct.
Modernist Architecture
Single most important new style or philosophy of architecture and design of the 20th century.
Modernist Architecture
Rejecting ornament and embracing minimalism (functionalism).
Cultural Transformations
New societal needs = new building types.
Territorial Transformations
Changes in the geographical and political landscape affecting architecture.
Structural Transformations
Innovations in building techniques and materials that influence architectural design.
Neoclassicism
Growing nationalistic fervor (due to independence) leading architects to establish unique national identities.
Rococo and Baroque
Styles that symbolized excess, artifice, and corruption.
A Rational Architecture
Architecture needs to go back to its essential elements, freed of deceptive overlay.
Enlightenment Rationalism
Basis of architecture should be science (as opposed to reverence for and emulation of archaic traditions and beliefs).
Marc-Antoine Laugier's "primitive hut"
A concept emphasizing pure, uncorrupted meanings in architecture.
Boullee's proposed Cenotaph a Newton (1784)
An architectural proposal that embodies Enlightenment Rationalism.
Education of the Architect
Teaching responsibilities of design: the duty of the architect or other educated person as a citizen.
Peter Behrens
An influential architect of the early 20th century known for his modernist designs.
Walter Gropius
A key figure in modern architecture and founder of the Bauhaus school.
Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe
A prominent architect known for his minimalist style and the phrase 'less is more'.
Le Corbusier
A pioneering architect who contributed significantly to modern architecture and urban planning.
Mass production
The manufacturing of goods in large quantities, influencing the design of factories and commercial buildings.
Transportation and communication
Infrastructure developments such as trains, newspaper presses, post offices, and telegrams.
Government buildings and facilities
Structures designed to serve the administrative functions of a state.
Commercial buildings
Structures designed for business purposes, including multi-level department stores.
Post-Renaissance Period
A historical period marked by revolutions and a search for new meanings in architecture.
Historical references
Roots for the establishment of national architectural styles during the Revivalism period (1800-1850).
Classical order
Architectural styles strongly associated with government buildings.
Age of Enlightenment
A period that emphasized reason and science in the development of architecture.
Architectural period
A time frame in which certain styles and philosophies dominate architectural design.
History and Theory of architecture
Became part of an architect's education.
Grand Tours
Trips to Greece and Rome where styles were noted, measured, and codified.
Vitruvius
Early ideas of a perfect architecture that were being challenged.
Territorial Transformations
New political states leading to volatile growth.
Industrial population
Drop in mortality due to medical advancements resulting in an increase in population.
Congested environments
Characterized by inadequate standards of light, ventilation, open space, poor sanitary facilities, and primitive drainage systems.
Rise in epidemics
Led to reforms in housing systems.
Streatham Street Flats
Designed by Henry Roberts, stacking apartments in pairs with a common staircase.
Society for Improving the Conditions of the Labouring Classes
Erected the Streatham Street Flats.
Streatham Street Flats capacity
Could fit 48 families.
Working-class architecture
Early example represented by the Streatham Street Flats.
Georges-Eugène Haussmann
Tasked to give Paris air and open space, connect and unify different parts of the city, and make it more beautiful.
Haussmann's impact on Paris
Converted Paris into a regional metropolis, linking opposite cardinal points and districts.
General Plan for Riverside
Designed by Frederick Law Olmstead in 1869, inspired by the winding Des Plaines River.
Curvilinear streets
Created a series of streets that wound across each other, resulting in tiny triangular mini-parks.
Garden City Diagram
Presented by Ebenezer Howard, idealized a city housing 32,000 people on a site of 3,600 ha.
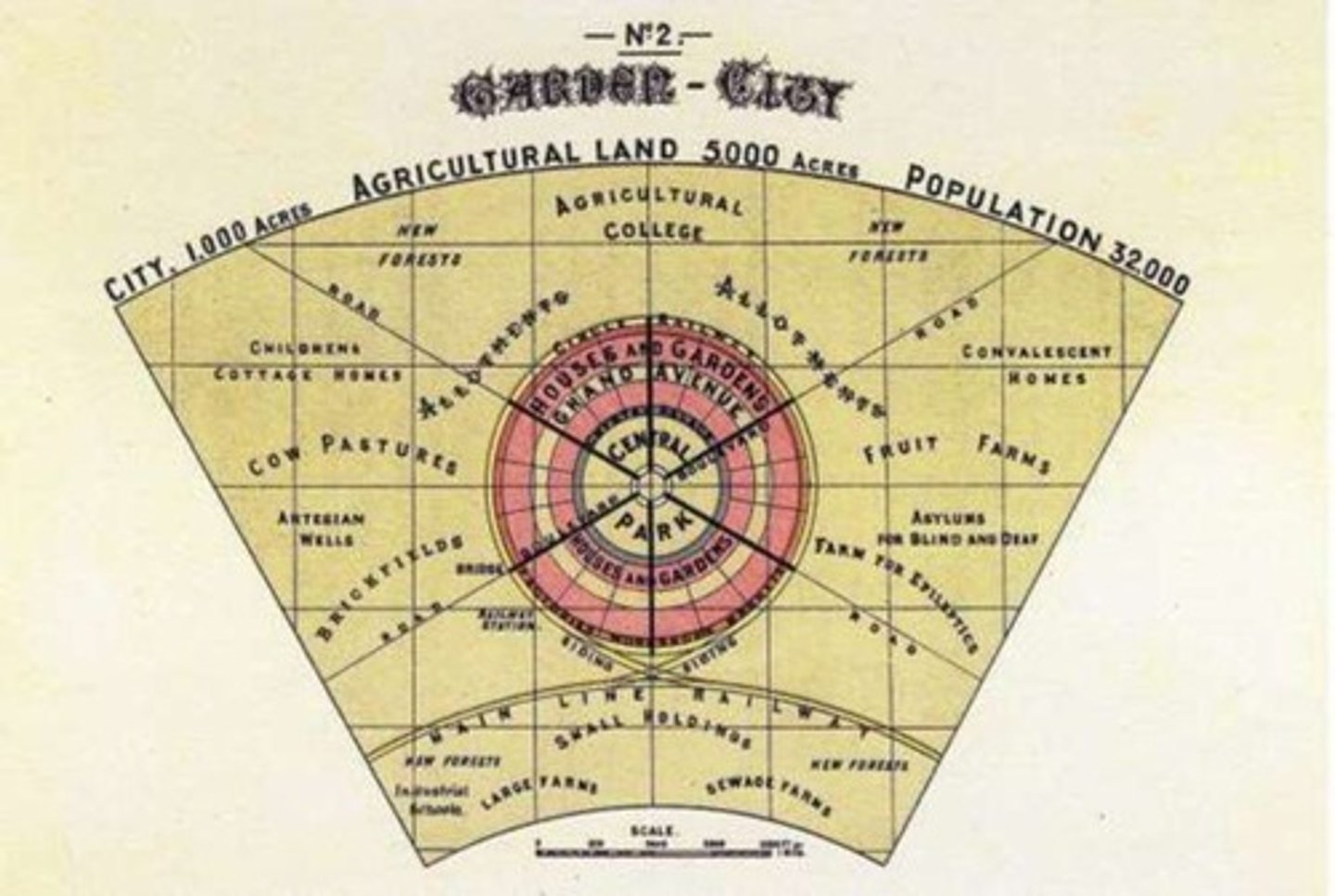
Howard's city design
Featured concentric patterns with open spaces, public parks, and six radial boulevards, 120 ft (37 m) wide.
Structural Steel
Replaced cast iron as a primary structural material, enabling skyscrapers and long-span structures.
Reinforced Concrete
Concrete with steel reinforcement, patented by François Hennebique in the late 19th century.
Precast Concrete Elements
Allowed for faster and more efficient construction.
Glass Innovations
Larger, uniform glass panes influencing modern facades.
Safety Glass
Laminated glass, patented in 1903, increased safety in windows and doors.
Aluminum
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, ideal for decorative elements and later, curtain walls.
Asphalt and Bitumen
Used for paving roads and roofing material, widely available due to advances in petroleum refining.
Skyscraper Construction
Utilizes steel framing and reinforced concrete.
William Le Baron Jenney
Built the Home Insurance Building in 1884.
Curtain Wall Systems
Non-load-bearing facades used in buildings like the Hallidie Building (1918) by Willis Polk.
Suspension Bridges
Advances in steel cable-making allowed for longer-span suspension bridges.
Brooklyn Bridge
Completed in 1883, an example of a suspension bridge.
Elevators
Hydraulic and electric elevators perfected in the late 19th century made tall buildings more practical and accessible.
Elisha Otis
Inventor known for developing the safety elevator.
Structural Transformations
Changes in building techniques from load-bearing masonry to steel frames.
Load-Bearing Masonry
Traditional construction method using heavy masonry walls.
Steel Frames
Lightweight structural system allowing for greater design flexibility.
Prefabrication
Construction method using pre-made components for efficiency.
Modular Systems
Construction approach using standardized components for consistency.
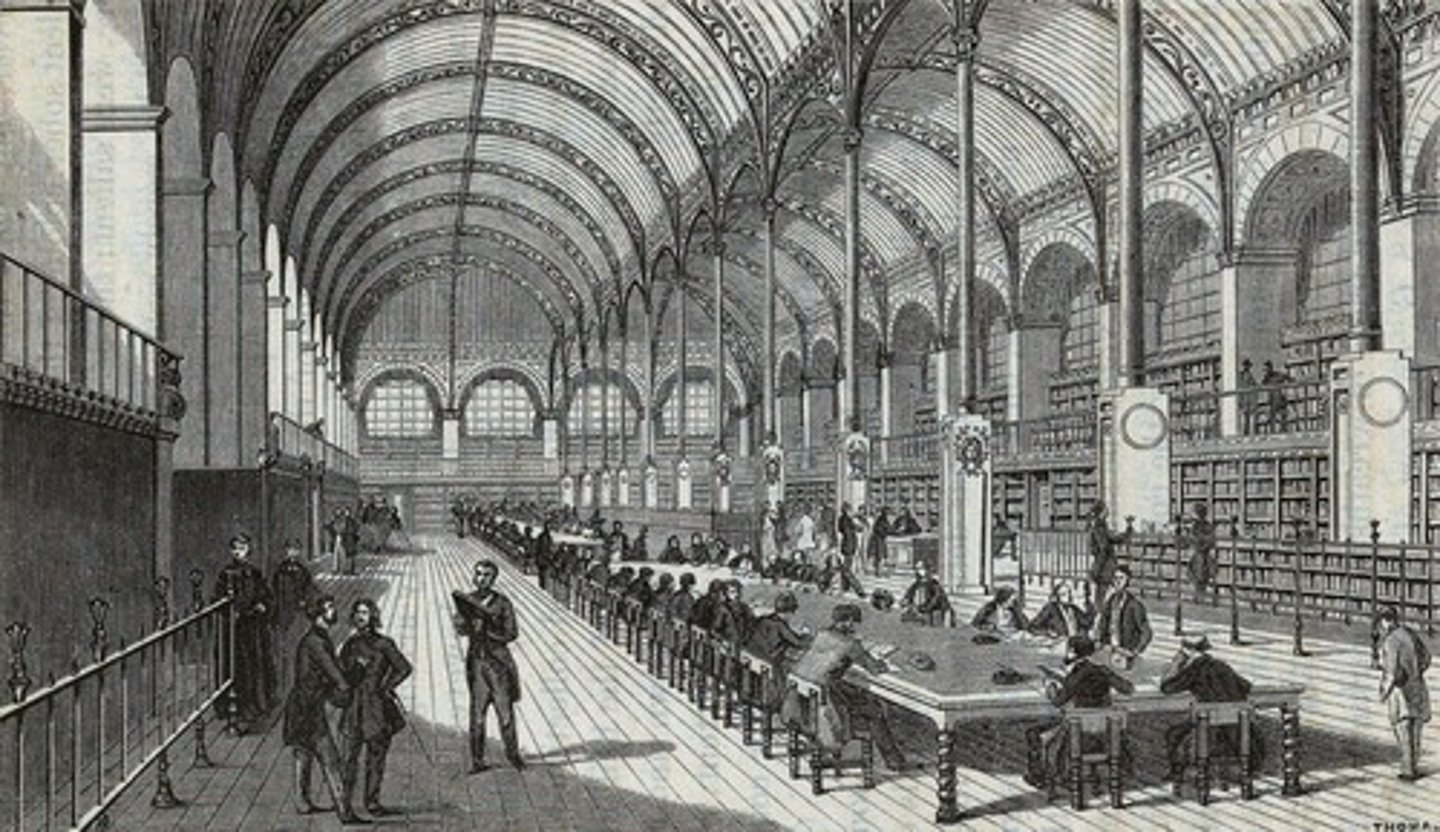
Bibliotheque Sainte-Genevieve
Library in Paris designed by Labrouste, showcasing innovative architecture.

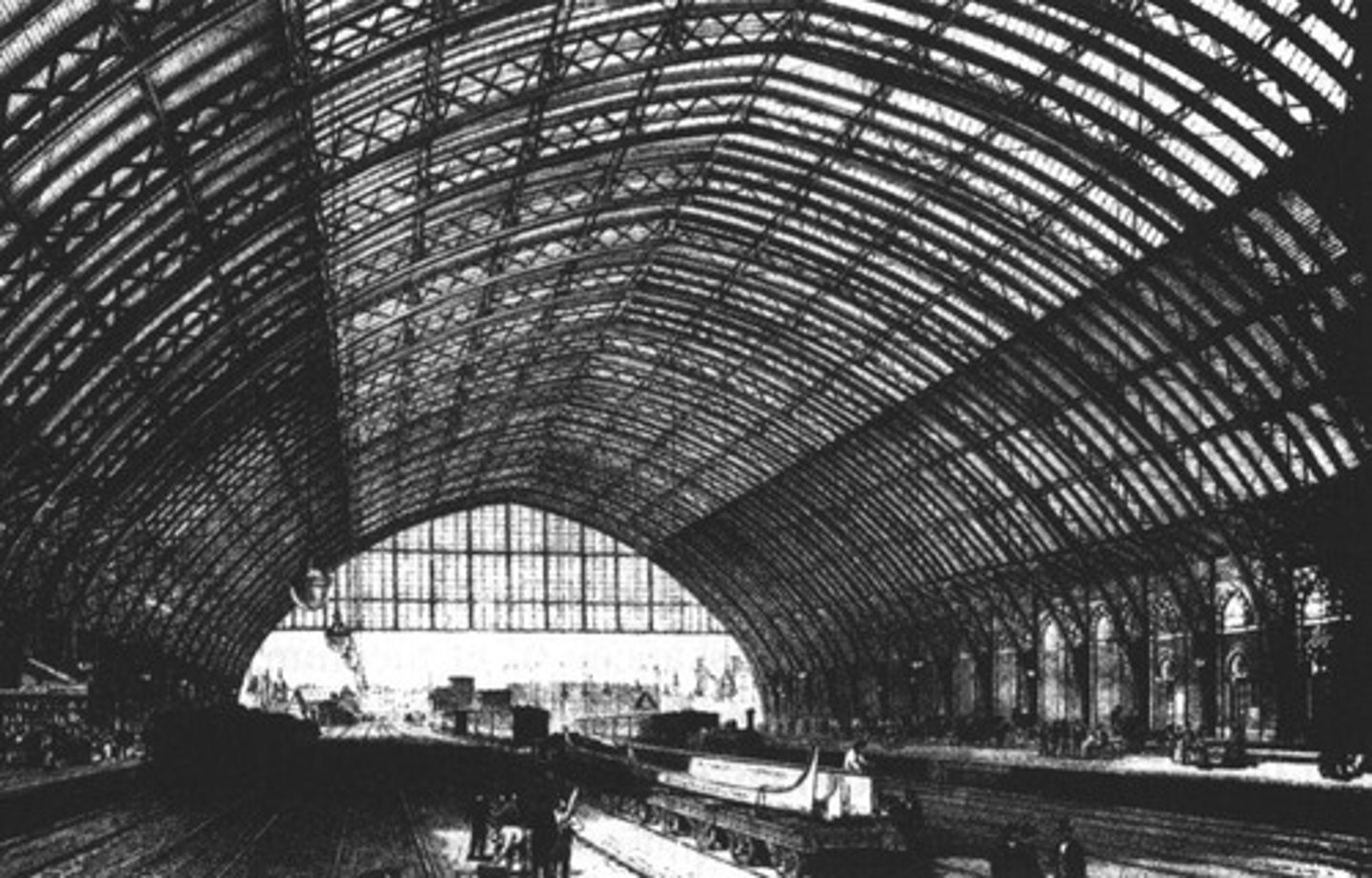
St. Pancras Station
London station with a clear span of 71.3 meters, built in 1863.

Palais des Machines
Exhibition hall in Paris with a span of 115 meters, built for the 1889 Exposition.

Heinrich Wofflin
Art historian who emphasized the structural logic in architecture.
Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe
Architect known for his minimalist and functional design principles.
Walter Gropius
Founder of the Bauhaus, advocating for the unity of arts and industrial production.
Primacy of Function and Utility
Design principle prioritizing the function of a building over aesthetics.
Peter Behrens
Architect and designer influential in the development of modern industrial architecture.
Jugenstil
Art movement in Munich characterized by youthful and abstract geometrical forms.
Deutsche Werkbund
Organization of architects and designers promoting the integration of art and industry.
AEG Turbine Factory
Factory designed by Behrens, showcasing clarity of form through function.
Fagus Shoe Factory
Building designed by Gropius, inspired by Behrens' AEG Turbine Factory.
Bauhaus
School founded by Gropius focusing on the unity of architecture, painting, and sculpture.
Normative Industrial Standards
Guidelines established for industrial production and design practices.
Bauhaus Schools
Institutions located in Weimar, Dessau, and Bernau focusing on modern design education.
Training at the Bauhaus
Duration of 1/2 to 3 years focusing on theory of forms, colors, and building construction.
Großgarage Süd
Innovative building in Halle (Saale) completed in 1929, featuring advanced elevator technology.
Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe
An architect known for his modernist designs and principles, including 'Less is more.'
Lake Shore Drive Apartments
A residential building designed by Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe in Chicago, completed between 1948-51.

Werkbund Housing Exhibition
An exhibition held in Stuttgart, Germany in 1927 showcasing the best in housing design and avant-garde architecture.
Barcelona Pavilion
The German pavilion designed by Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe for the 1929 Barcelona international trade fair, known for its single space delineated into subsidiary spaces.
Irony of Barcelona Pavilion
The pavilion required hand-assembly to achieve its apparent mechanical simplicity.
Mies Van Der Rohe's design principles
Principles that emphasize creating architecture from the nature of the task, the people, and the time.
Le Corbusier
An influential architect known for his theories on socially responsive architecture and modernist design.
L'Esprit Nouveau
A journal published by Le Corbusier containing theories of socially responsive architecture.
Vers Une Architecture
A book by Le Corbusier published in 1923, advocating for a new approach to architecture based on functionality.
The house is a machine for living in
A famous quote by Le Corbusier emphasizing the functional nature of residential architecture.
Le Corbusier's 5 points of architecture
A set of principles proposed by Le Corbusier that outline modernist architectural design.
Pilotis
A grid of slim reinforced concrete pylons that assume the structural weight of a building, freeing the ground floor circulation.
Open plan
The absence of load-bearing partition walls allowing greater flexibility in design and use of living spaces.
Free design of the façade
The principle that the exterior of a building is free from conventional structural restrictions, allowing for a lighter and more open façade.
Horizontal ribbon windows
Windows that light rooms equally, increasing the sense of space and seclusion.
Roof garden
Flat roofs with garden terraces that serve both harmonic and domestic utility.
Social and technological transformations
Changes in society and technology that influence architectural design and principles.
Rise of industrial production
The increase in industrial manufacturing that influenced the design principles of architects like Mies and Le Corbusier.
Digital production
The use of digital technology in architecture that influences design and production today.