CH. 4 | Heat and Temperature
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Thermodynamics
Study of macroscopic processes involving heat, mechanical, and other forms of energy
All energy forms can be converted to heat
Applications:
Systems with energy inputs and outputs, heat engines, heat pumps, refrigerators
Based upon but not concerned with microscopic details
Picture
Cohesion v. Adhesion
Cohesion
Attractive forces between like molecules (solids and liquids)
Adhesion
Attractive forces between unlike molecules
→ Water wetting skin
→ Glue mechanism: adhesives
Interactions can also be repulsive
Water beading on wax
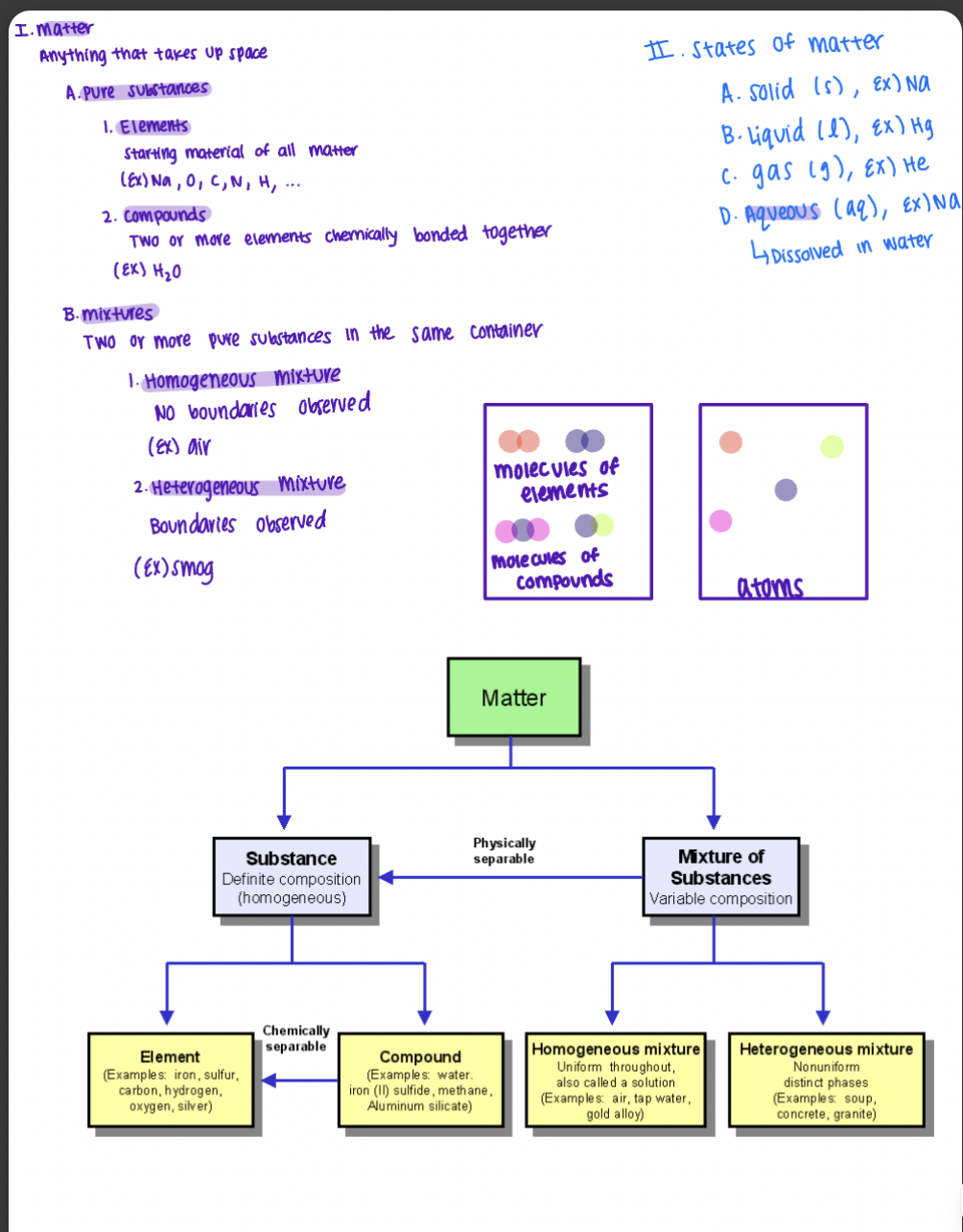
Phases of Matter (SOLID)
Definite shape and volume
Rigid 3-D structure
Atoms / Molecules bonded in one place
Allowed motions restricted to vibration in place only
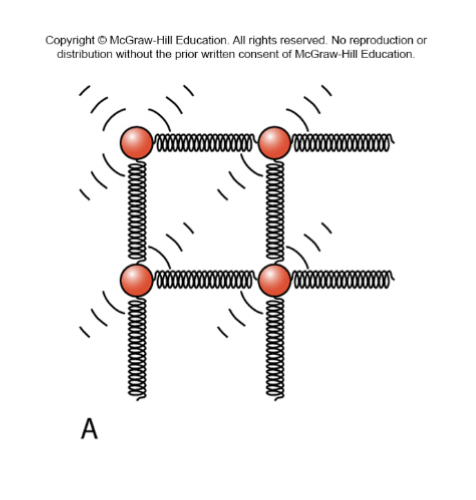
Phases of Matter (LIQUIDS)
Definite volume, indefinite shape
Only weak cohesive bonds between component molecules
Constituent molecules mostly in contact
Allowed motions
Vibrations
Bonds within molecule stretch/bend
Rotations
Molecule spins around center of mass
Limited translation
Entire molecule moves towards a specific direction
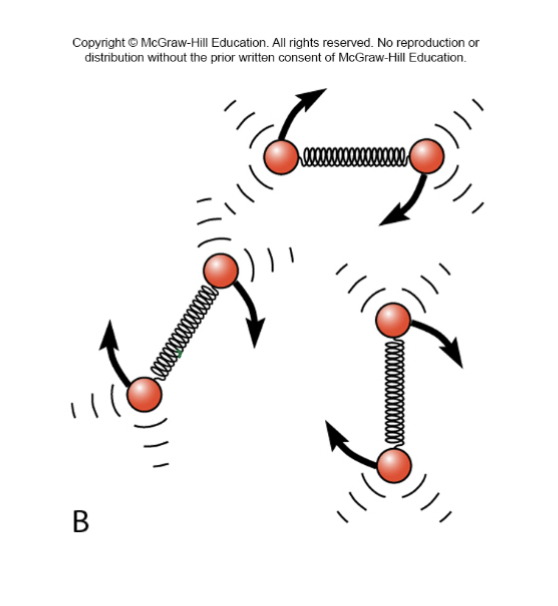
Phases of Matter (GASES)
Indefinte volume and shape
Molecules mostly not in contact
Allowed motions
→ Vibration & Rotation (molecules with more than one atom)
→ Translation on random, mostly free paths
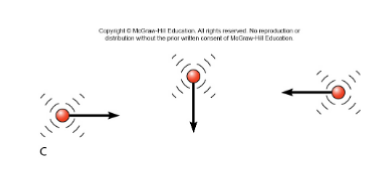
Molecular Motions
Characterized by average kinetic energy in a large sample
Temperature
Measure of average kinetic energy on the molecules making up a substance
Proportional to average kinetic energy
Evidence
Gases diffuse quickly at higher temperatures
Expansion / contraction with increasing / decreasing temperature
Temperature Conversions
Fahrenheit to Celsius
Celsius to Fahrenheit
Celsius to Kelvin

Temperature
A measure of the internal energy of an object
how hot or cold something is
Thermometers
Used to measure temperature
Rely on thermometrics properties
→ bimetialic strips and thermostats
Heat
A form of energy between two objects
External energy
Total potential and kinetic energy of an object that you can measure directly
Internal energy
Total potential and kinetic energy of the molecules
→ temperature , density , heat, etc
External energy can be transferred to internal, resulting in a temperature increase
Temperature v. Heat
Temperature
A measure of hotness or coldness of an object
Based on average molecular kinetic energy
Heat
Based on total internal energy of molecules
Doublng amount at same temperature doubles heat
2 Heating Methods
1) Temperature difference:
Energy always moves from higher temperature regions to lower temperature regions
2) Energy-form conversion:
Transfer of heat by doing work
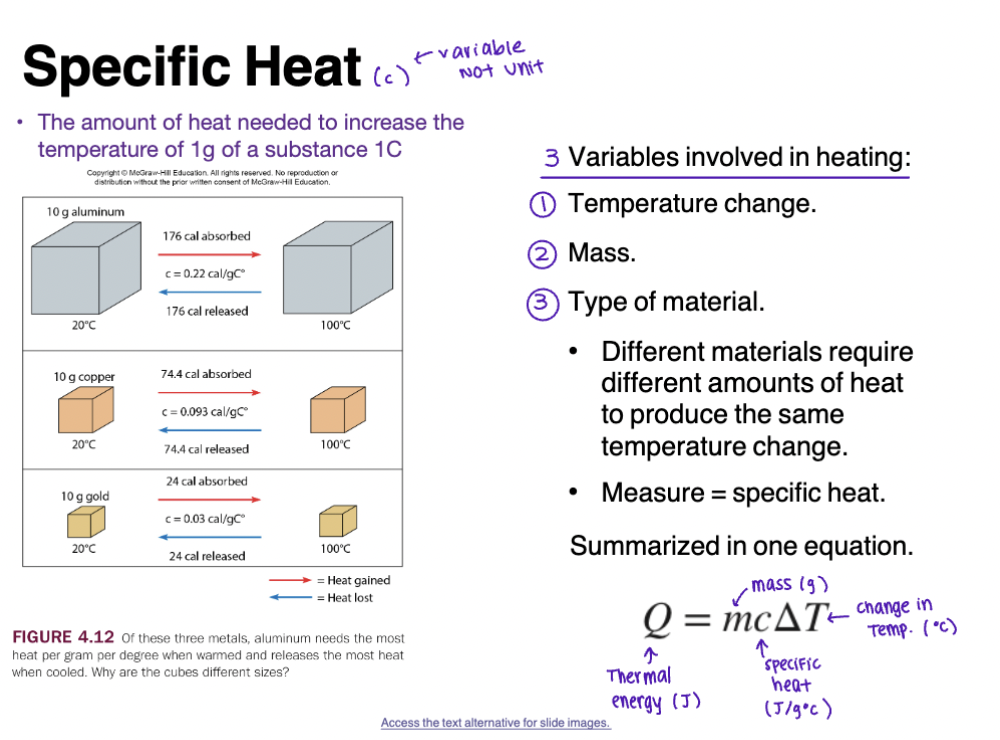
Specific Heat
The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of 1g of a substance 1C
3 Variables involved in heating
Temperature change
Mass
Type of material
Different materials require different amounts of heat to produce the same temperature change
Measure = specific heat
Summarized in one equation
Heat Flow
3 Mechanisms of heat transfer due to a temperature difference
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
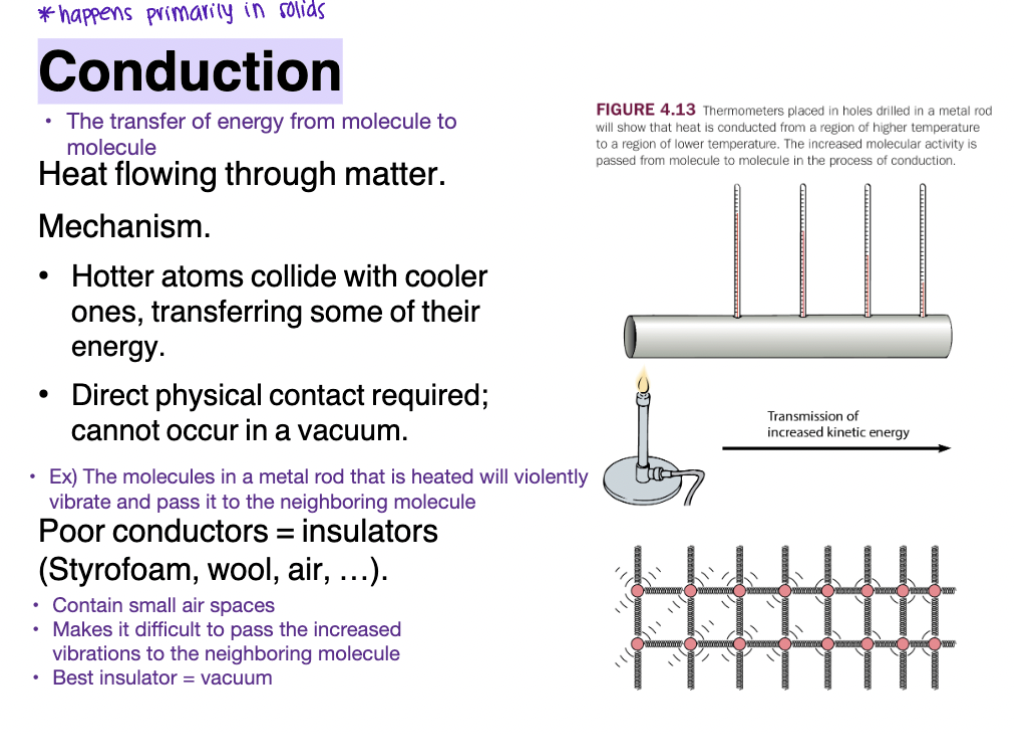
Conduction
The transfer of energy from molecule to molecule
Happens primarily in solids
Heat flowing through matter
increased KE from molecule to molecule
Mechanisms
Hotter atoms collide with cooler ones, transferring some of their energy
Direct physical contact required; cannot occur in a vacuum
Convection
Energy transfer through the bulk motion of hot material
happens only in liquids and gases
high KE molecules are moved from place to place
Examples
Space heater
Gas furnace (forced)
Natural convection mechanism - “hot air rises”
Radiation
Radiant energy
Energy associated with electromagnetic waves
→ Can operate through a vacuum
→ All objects emit and absorb radiation
Temperature determines
Emission rate
Intensity of emitted light
Type of radiation given off
Temperature determined by balance between rates of emission and absorption
→ global warming
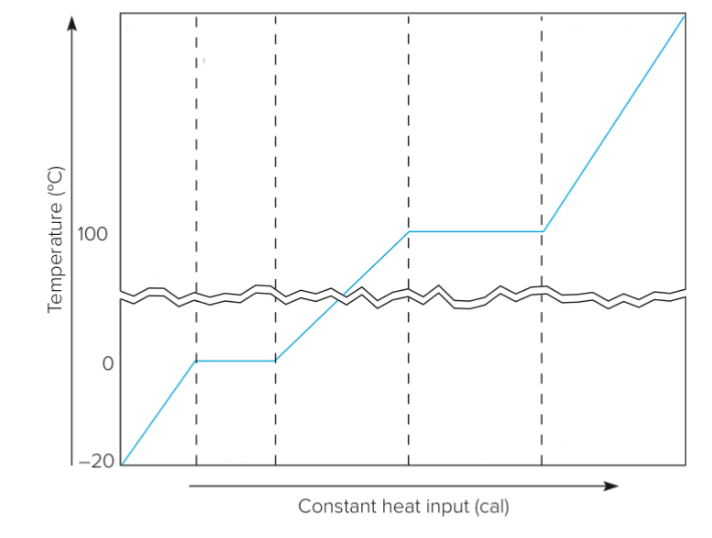
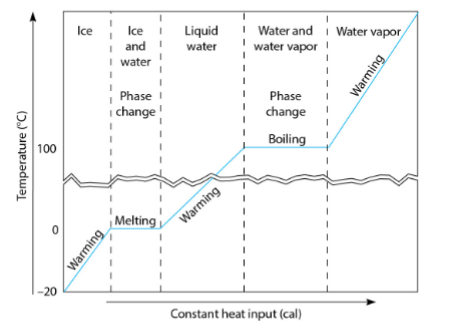
Phase Change w/ Heating
Phase change at constant temperature
Related to changes in internal potential energy
Latent heat
Cont. (Diagram)
Evaporation v. Condensation
Individual molecules can change phase at any time
Evaporation
Energy required to overcome phase cohesion
Higher-energy molecules near the surface can then escape
Condensation
Gas molecules near the surface lose kinetic energy to liquid molecules and merge

Thermodynamics
The study of heat and its relationship with mechanical and other forms of energy

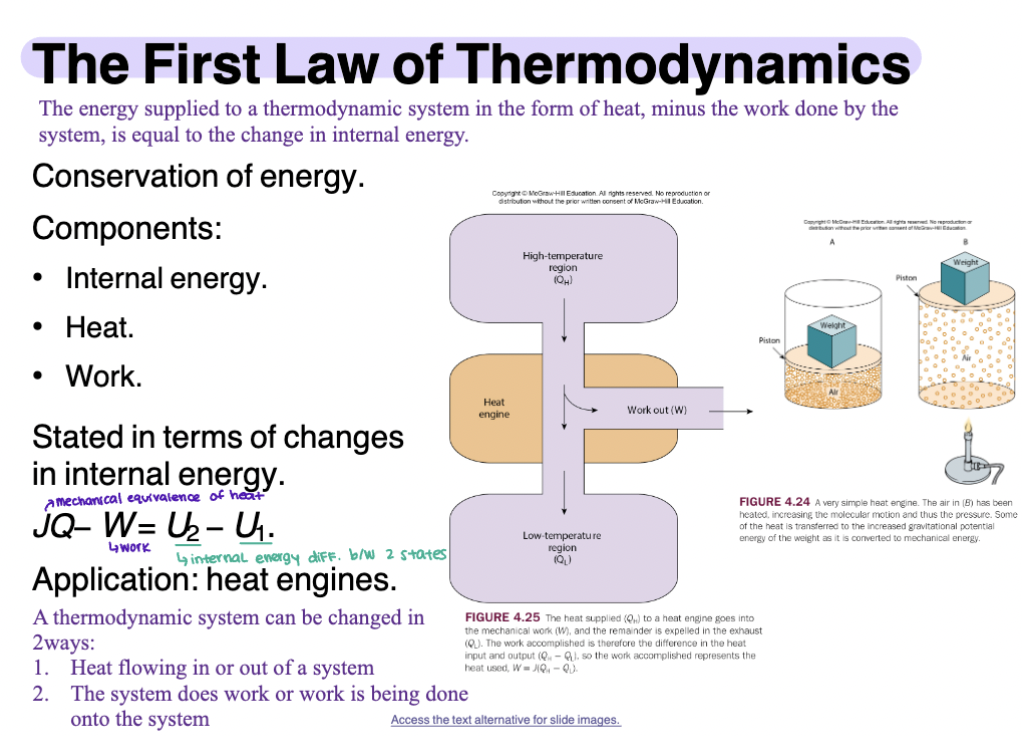
1st Law of Thermodynamics
The energy supplied to a thermodynamic system in the form of heat, minus the work done by the system, is equal to the change in internal energy
Conservation of energy
Components include, internal energy, heat, and work
Stated in terms of changes in internal energy
Application: heat engines
Cont.
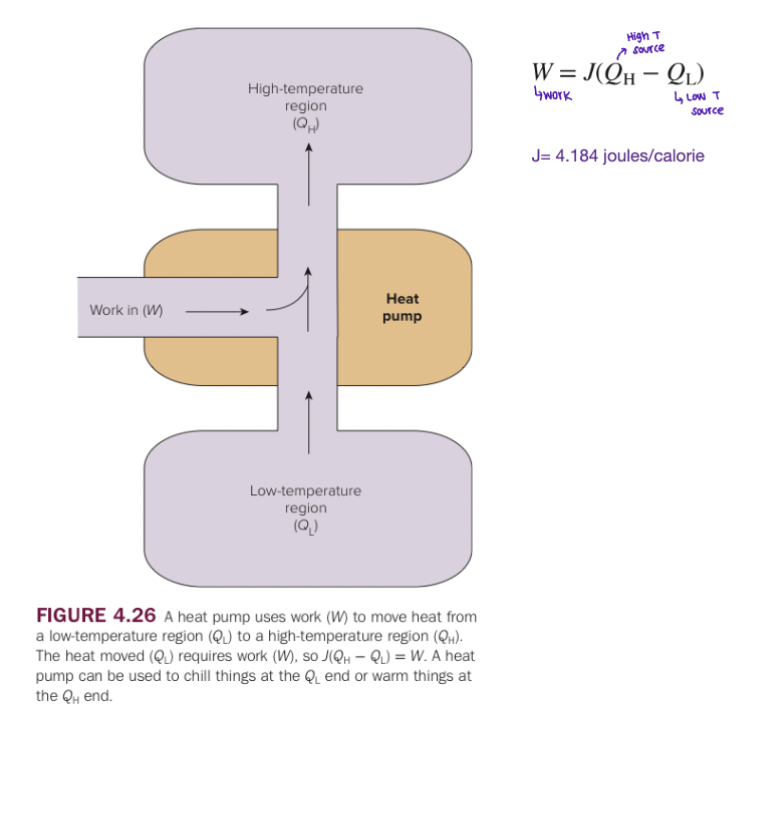
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Heat flows from objects with higher temperature to objects with cooler temperatures
Must use energy
Can be seen as entropy
Entropy = thermodynamic measure of disorder
clean office → messy office