A Level Biology Edexcel B
1/884
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
885 Terms
Features and function of the Nucleus
Present in all eukaryotic cells
Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope)
Membrane contains nuclear pores to allow movement of mRNA and ribosomes out of nucleus, and enzymes into nucleus
Stores genetic material as chromatin
nucleolus (site of ribosome production)
Where is the site of ribosome production?
Nucleolus
Features and Function of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Folds of membrane with it's surface covered in ribosomes
Folds and processes proteins made on the ribosomes
Features and Function of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Folds of membrane (no ribosomes)
Production, processing and storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
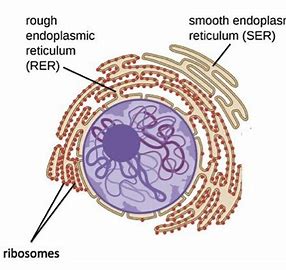
How to distinguish between smooth or rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Observe under electron microscope
If ribosomes present, it is RER
If ribosomes not present, it is SER
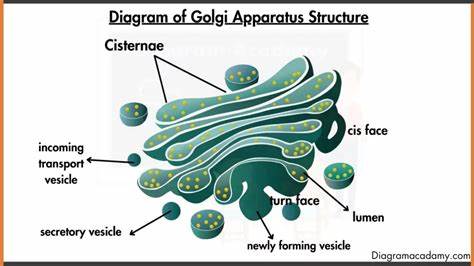
Features and function of Golgi Apparatus
Flattened Fluid filled curved sacs called cisternae
Sorts and modifies proteins and lipids before packaging them into vesicles to be transported.
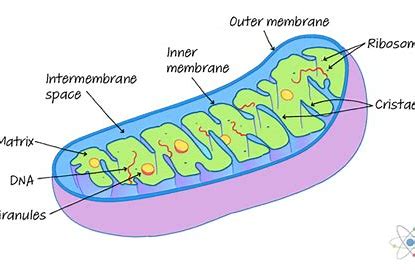
Features and function of mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration
Surrounded by a double membrane (envelope)
Inner membrane folded to form cristae
Matrix contains enzymes needed for aerobic respiration Also contains ribosomes and small pieces of DNA needed for replication of mitochondria before cell division
Features and function of centrioles
Not found in plant or fungi cells
Made out of hollow fibres called microtubules
Microtubules are filaments of a protein that is used to move substances inside the cell and supports shape of cell
Two centrioles at a right angle to each other form a centrosome
Organises spindle fibres during cell division
Features and function of 80s Ribsosomes
Found in eukaryotic cells only
Site of protein synthesis and translation
Made up of large 60s subunit, and small 40s subunit
Features and function of lysosomes
Bound by single membrane
Form of vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes
Used by cells of immune system for programmed cell death
Features and function of vacuole
Large and central in plants (animal cells may have one, but they are often small and temporary)
Fluid filled cavity surrounded by a membrane (tonoplast)
Helps maintain hydrostatic pressure and store cell sap
Features and function of plasmids
Small loops of DNA sometimes found in bacterial cells
Contain genes that can be passed between prokaryotes (antibiotic resistance)
Features and function of slime capsule
Help keep bacteria moist and prevent them from drying out
Help protect bacterial cells from attack of host organisms immune system cells
Features and function of Nucleoid
Area in which circular DNA is found
Genetic material in prokaryotic cells often found as single circular strands
Features and function of Pilus
Thread like structures found on cell surface membrane
Enables bacteria to attach to other cells and surfaces
Allows plasmids to be passed from cell to cell
Features and function of 70s Ribosomes
Large 50s subunit
Small 30s subunit
Site of protein synthesis
Features and function of cell wall (prokaryotic)
Made of peptidoglycan
Provides strength and support to the cell
Difference in structure of Gram negative and Gram positive bactera
Gram positive:
Thick layer of peptidoglycan
Inner plasma membrane
Gram negative:
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
Outer lipopolysaccharide membrane
Gram Staining Test Procedure + Results
Crystal violet solution for 1 minute, then wash with water
Iodine solution for 1 minute, wash with water.
Alcohol added for 1 minute (lipopolysaccharide soluble in alcohols so outer membrane dissolves)
Red safranin for 1 minute, then dried
Gram positive: Purple
Gran negative: Pink/Red
Resolution
Minimum distance between two objects where they can still be seen as two separate objects
Features of transmission electron microscope
Beams of electrons transmitted through the object, producing a 2D image.
Resolution 2000x better than light microscope
Features of Scanning electron microscope
Beam of electrons scans back and forth over the surface of the sample producing a 3D image
What type of staining is required for electron and light microscopes?
Electron microscopes - heavy metals (reflect electrons)
Light microscopes - methylene blue
Advantages of electron microscopy
Higher resolution and magnification
Disadvantages of electron microscopy
Sample must be placed in a vacuum, therefore not living
Expensive and not portable
Produces only black and white images
What is the protective coat of Nucleic acid in viruses called?
Capsid
Describe the lytic cycle of a virus
Attachment - virus attaches to the surface of the host
Penetration - viral DNA/RNA is inserted into the cytoplasm of host call
Biosynthesis - viral DNA replicated and viral proteins are made
Maturation - new viruses assembled
Lysis - Lysis of cell releases newly made phage (independent of host cell's genome)
Describe the lysogenic cycle of a virus
Virus attaches to surface of host cell and inserts DNA/RNA in the form of a provirus
Viral DNA integrates with host cell’s DNA
Enables viral DNA to be replicated through cell division of host cell.
Provirus can remain dormant if virus produces repressor proteins, inhibiting the transcription of the provirus.
Ethical implications to using untested drugs
Difficult to obtain informed consent
Unknown side effects
May not ending up being more effective than other existing alternatives/treatment
What are the 5 stages of mitosis?
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Describe interphase
G1, S, G2 - DNA replication and preparation for cell division - chromosomes and some organelles are replicated
Describe prophase
Chromosomes condense (2 sister chromatids joined by a centromere
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrioles move to opposite poles forming spindle network
Describe Metaphase
Chromosomes align along equator of the cell
Spindle fibres attach to chromosomes by centromeres
Describe Anaphase
Spindle fibres contract and pull chromatids to opposite poles of the cell
Centromere divides
Describe Telophase
Chromosomes uncoil and become chromatin
Nuclear envelope forms around two sets of chromosomes
Two nuclei that form are identical
Describe cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides
Produces 2 daughter cells
What is the main purpose of meiosis?
Production of haploid gametes
Maintenance of chromosome number
How is genetic variation acheieved?
Crossing over - exchange of sections of DNA between homologous chromosomes
Independent assortment - various combinations of maternal and parental chromosome arrangement
What is a translocation mutation?
Where 1 part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a completely different chromosome
What is a non-disjunction mutation
Homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate
What is polysomy? examples!
More than 2 chromosomes in a cell
Down's syndrome
What is monosomy? examples!
Less than 2 chromosomes in a cell
Turner's syndrome
Describe the process of Oogenesis in steps
Primordial germ cell divides several times by mitosis to form oogonia
Oogonia matures and continues to grow to form primary oocyte.
Primary oocyte undergoes mitosis to form 1 secondary oocyte and 1 polar body.
Secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis to form 1 haploid ootid and one more polar body.
First polar body produced undergoes meiosis to produce 2 polar bodies
Polar bodies die as ootid develops
Describe the process of spermatogenesis in steps
Primordial germ cell divides several times by mitosis to form spermatogonia.
Spermatogonia continues to grow the form primary spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes undergoes meiosis to form secondary spermatocytes
Secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosis to form spermatids
Spermatids differentiate and grow to form spermatozoa
Features of the ovum
Zona pellucida (protective coating to prevent polysomy (fertilisation by more than 1 sperm)
Cortical granules - release substances causing zona pellucida to harden
Follicle cells - protective coating
Features of spermatozoa
Many mitochondria to provide more energy for movement (rotation of flagellum)
Acrosome contains digestive enzymes to break through zona pellucida
Describe sexual reproduction in mammals in steps
Sperm head contacts zona pellucida and acrosome reaction occurs (acrosome fuses with cell membrane of sperm to release enzymes).
Sperm head fuses with cell membrane of egg to allow sperm nucleus to enter egg cell.
Cortical reaction occurs.
Nuclei fuse - full set of chromosomes is restored, forming diploid zygote.
How does a zygote form a blastocyst?
Zygote undergoes mitosis to form morula.
Morula continues to divide and undergo differentiation to form blastocyst
Describe pollen formation
Diploid microspore mother cells undergo meiosis to form 4 haploid microspores.
Haploid microspores undergo mitosis to form pollen grains
What two types of nuclei do pollen grains consist of?
Generative nucleus and pollen tube nucleus
Describe ovum formation
Diploid megaspore mother cells undergo mitosis to form an ootid and 3 polar bodies.
Ootid undergoes mitosis 3 times to form an embryo sac
Describe the process of fertilisation in plants
Pollen grain sticks to stigma and later germinates.
Pollen tube grows down style via secretion of digestive enzymes (digest surrounding tissue as a source of nutrients).
Pollen tube grows through micropyle into embryo sac.
Generative nucleus divides by mitosis to form 2 sperm cells which enter embryo sac.
Double fertilisation occurs:
one sperm cell fuses with female nucleus to form diploid zygote.
one sperm cell fuses with 2 polar body nuclei to form a triploid endosperm nucleus (served as nutrients for embryo).
Describe aseptic culture technique
- Decide on microorganism you want to culture and obtain the culture
- Provide microorganism with appropriate nutrients in sterile nutrient medium: either broth or agar (microorgnaisms that need very specific combination of nutrients can be grown in selective medium
- Inoculate the culture
- If broth used, swirl inoculating loop in culture
- If agar used, make streak or spread plate\
Describe methods of aseptic technique
All equipment should be sterile by flaming equipment with bunsen flame
Lids replaced as quickly as possible
Describe growth curve of microorganism in closed culture
- Lag phase
- Microorganisms slowly adapting to environment.
- Reproduction rate increases slowly
- Log Phase
- Microorganisms grow at maximum rate as long as ther eis sufficient nutrients
- Stationary phase
- Death rate = reproduction rate
- Buildup of waste products and lack of nutrients
- Death phase
- Death exceeds new cell population as conditions continue to deteriorate
Ways in which bacterial growth can be measured?
Cell count, Turbidimetry and Dilution plating
Describe process, and pros and cons of cell count
Haemocytometer
- Sample broth stained with trypan blue
- Useful because includes only counting living cells and is accurate
Cons:
- Slow
- Expensive equipment
Describe process, and pros and cons of turbudimetry
Form of colorimetry
As turbidity increases, transmission decreases
Use calibration graph to obtain cell count
Pros:
- Can be conducted in field & quick
Cons:
-Equipment is expensive
- Values affected by other variables
- Counts non-viable cells as well
- Calibration curve required
- Assumes density of cells is equal across the culture
Describe process, and pros and cons of dilution plating
Original culture serially diluted
Multiplied by dilution factor to obtain cell count
Pros:
- Doesn't require complex or expensive equipment
- Obtains direct cell count
Cons:
- Slow (incubation period)
- Dilutions required
What are endotoxins?
Lipopolysaccharides in outer lipid membrane of gram negative bacteria eg. Salmonella
Effects local to site of infection
Effects local to site of infection
What are exotoxins?
Soluble proteins produced and released by bacteria as they metabolise and reproduce eg. Staphylococcus
Spread around the body through blood and bodily fluids.
Spread around the body through blood and bodily fluids.
Host tissue invasion
Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)