A7 - Lower Extremity
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
- AP pelvis
- Frog-leg pelvis
State the standard bilateral pelvis projections
AP pelvis
ID standard bilateral pelvis projection
Frog-leg pelvis
ID standard bilateral pelvis projection
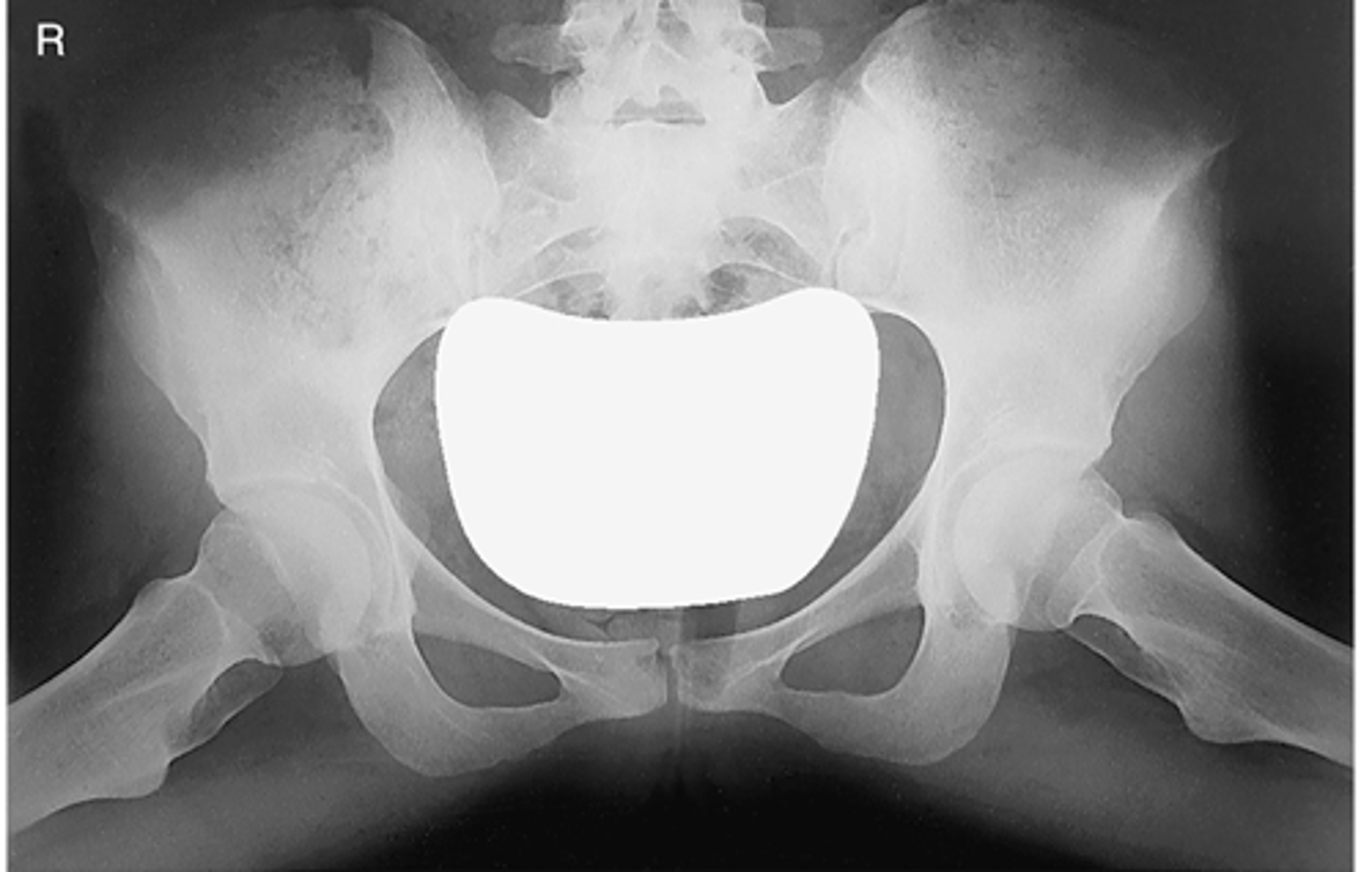
No
Are there any supplementary bilateral pelvis projections?
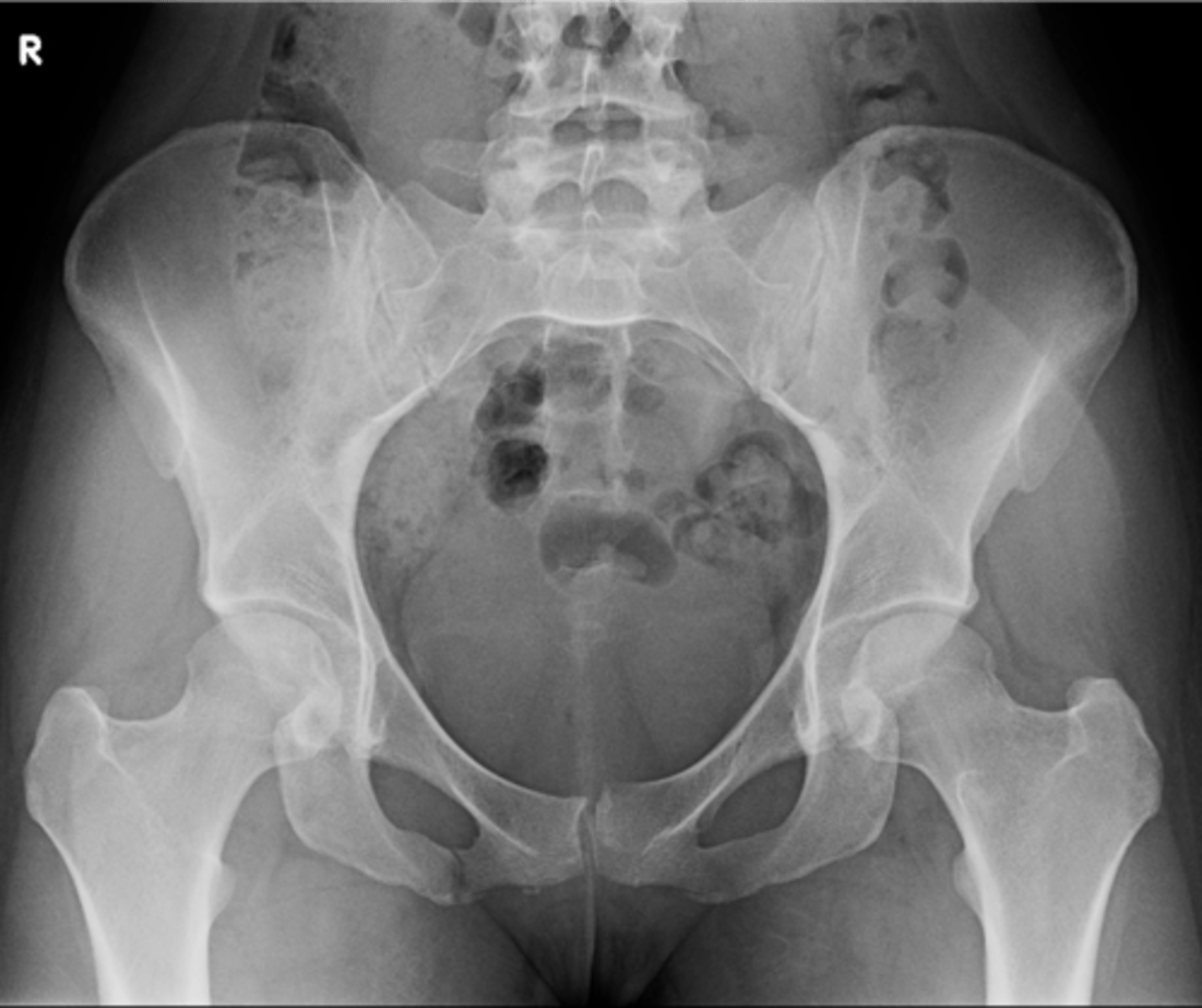
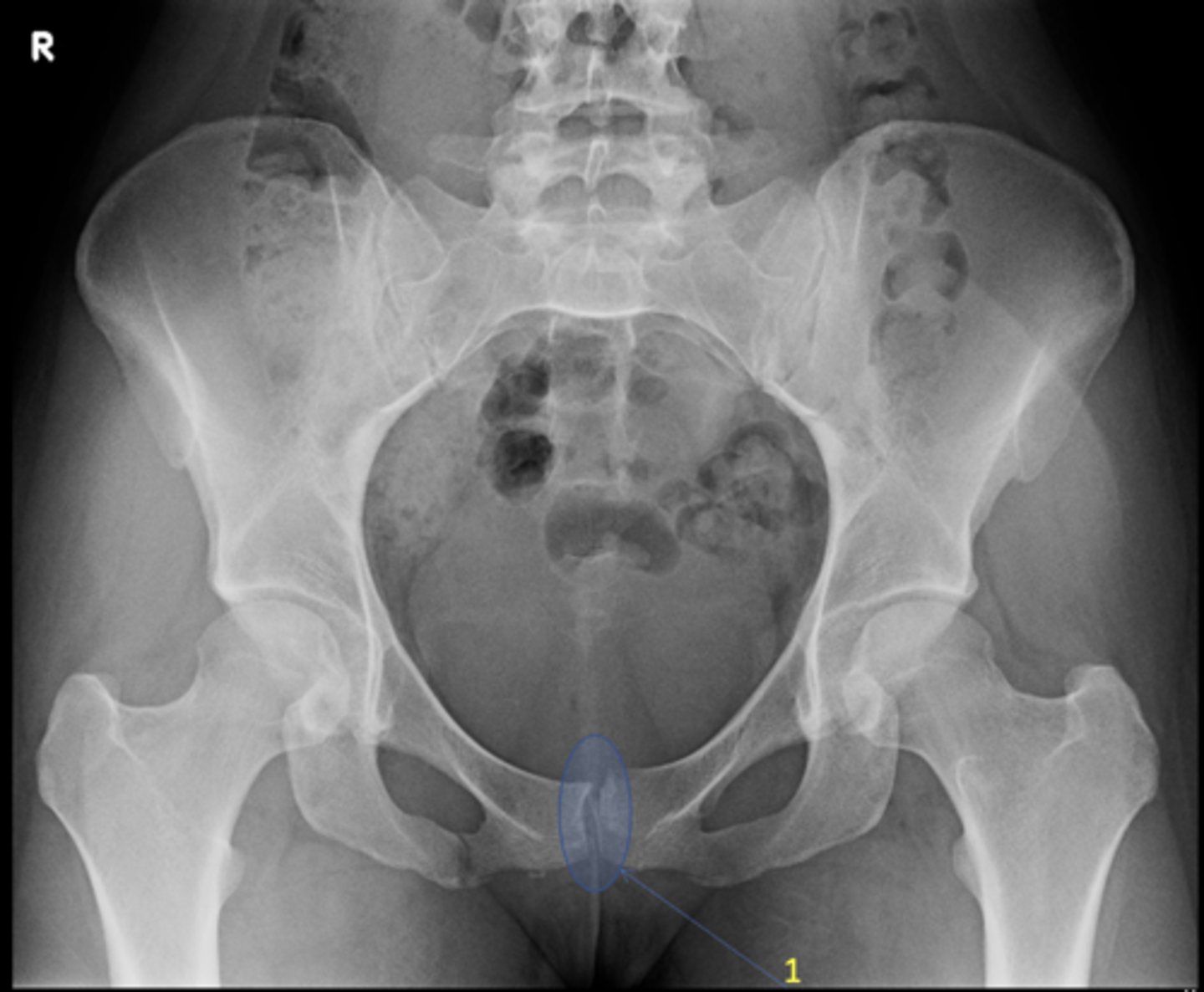
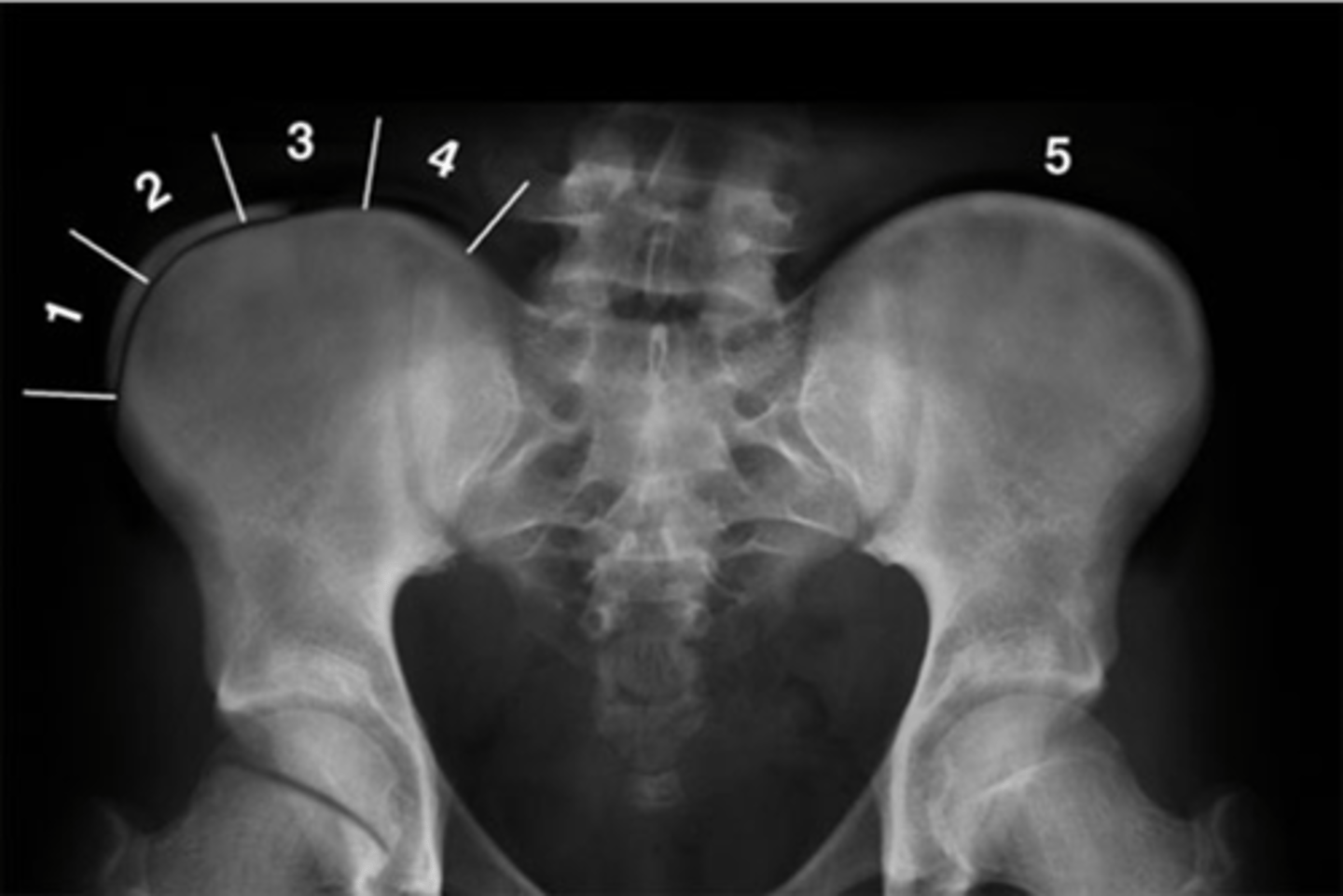
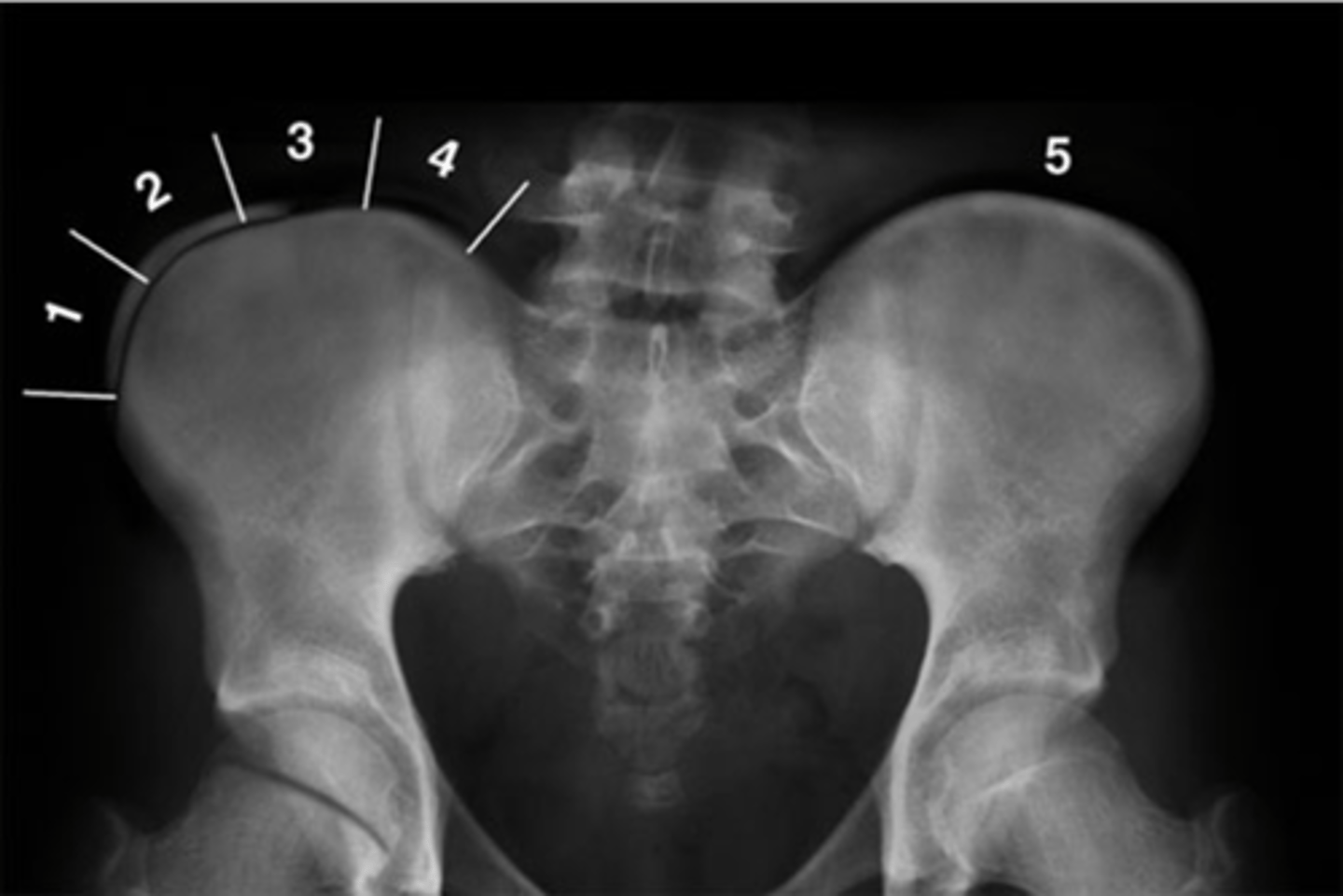
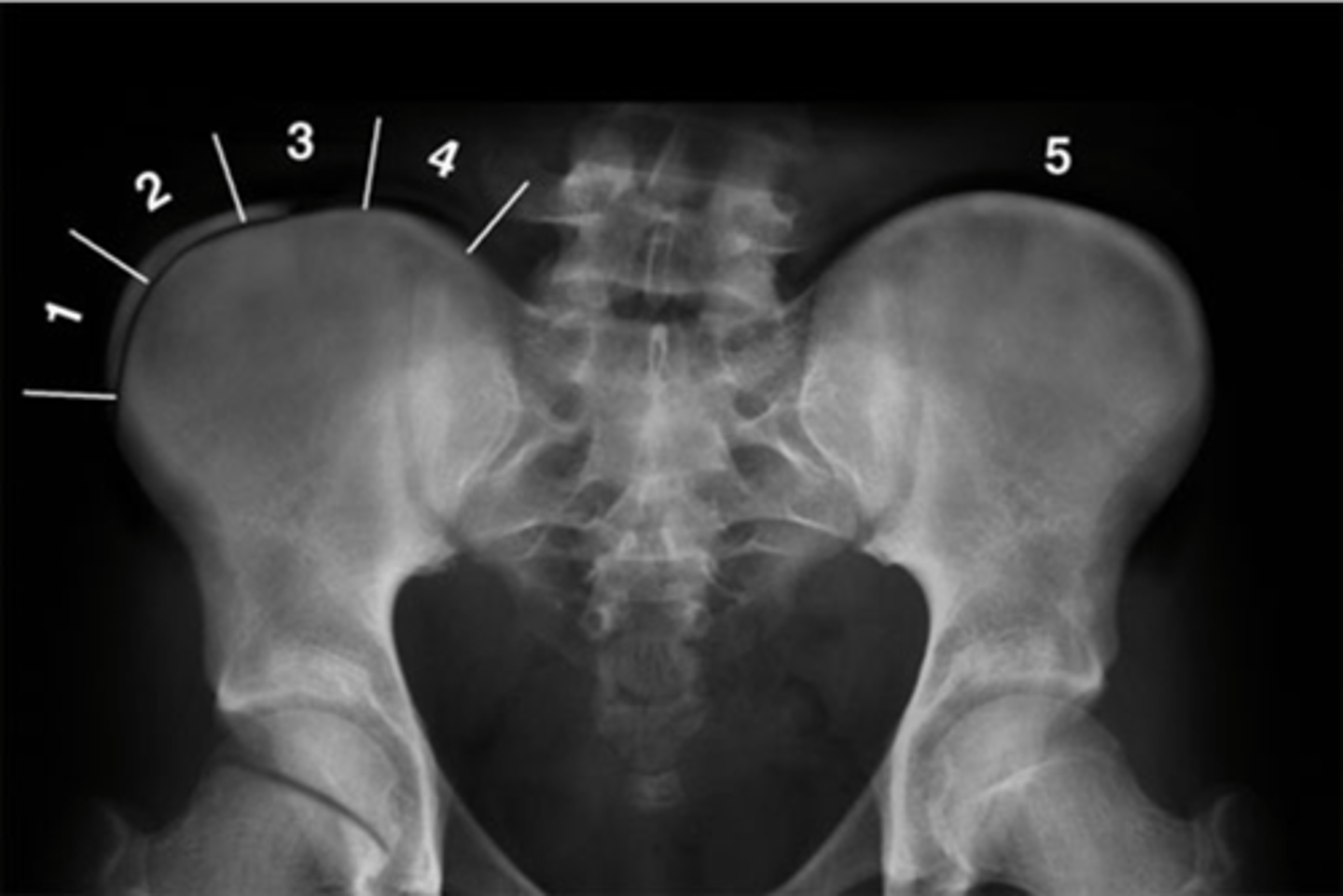
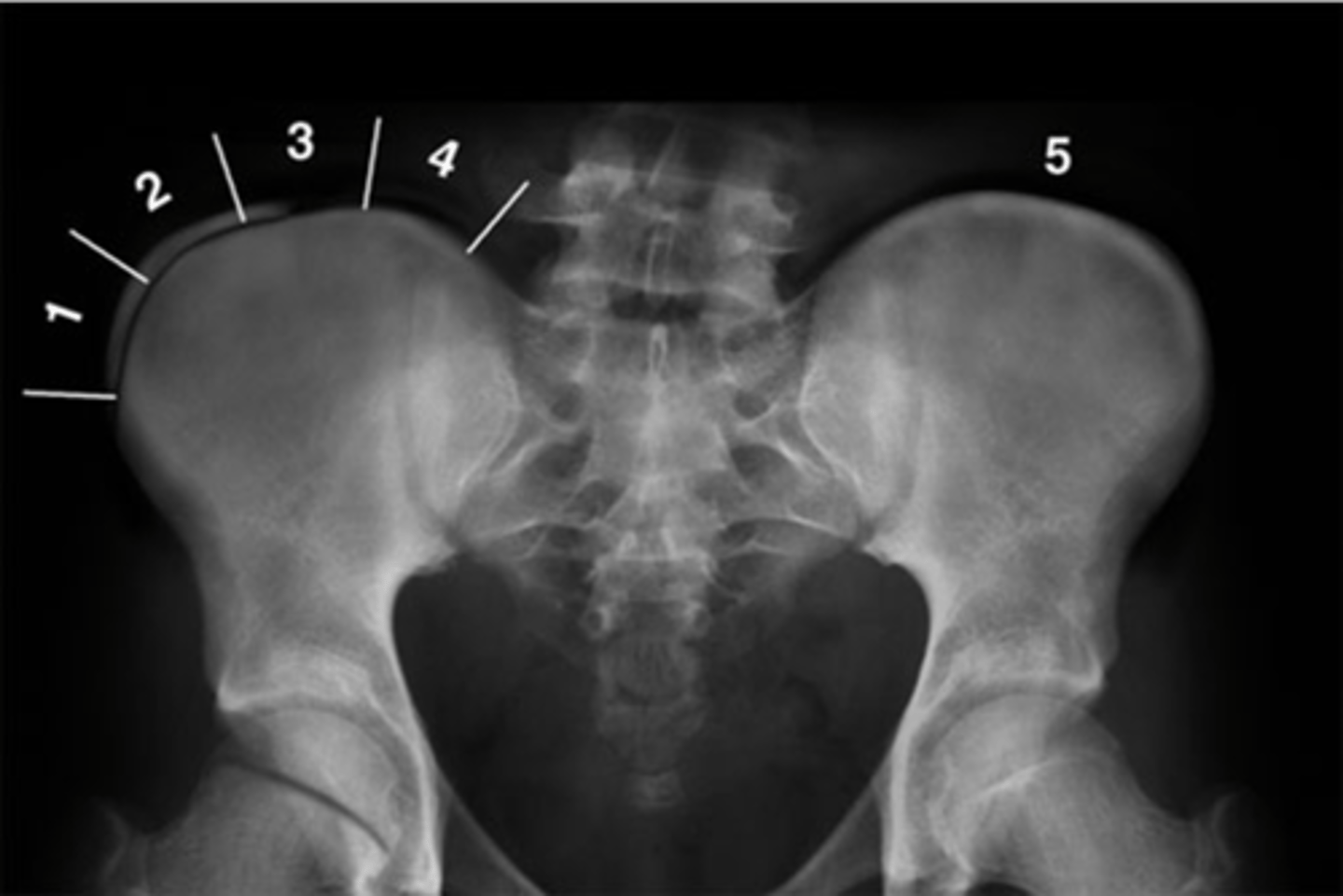
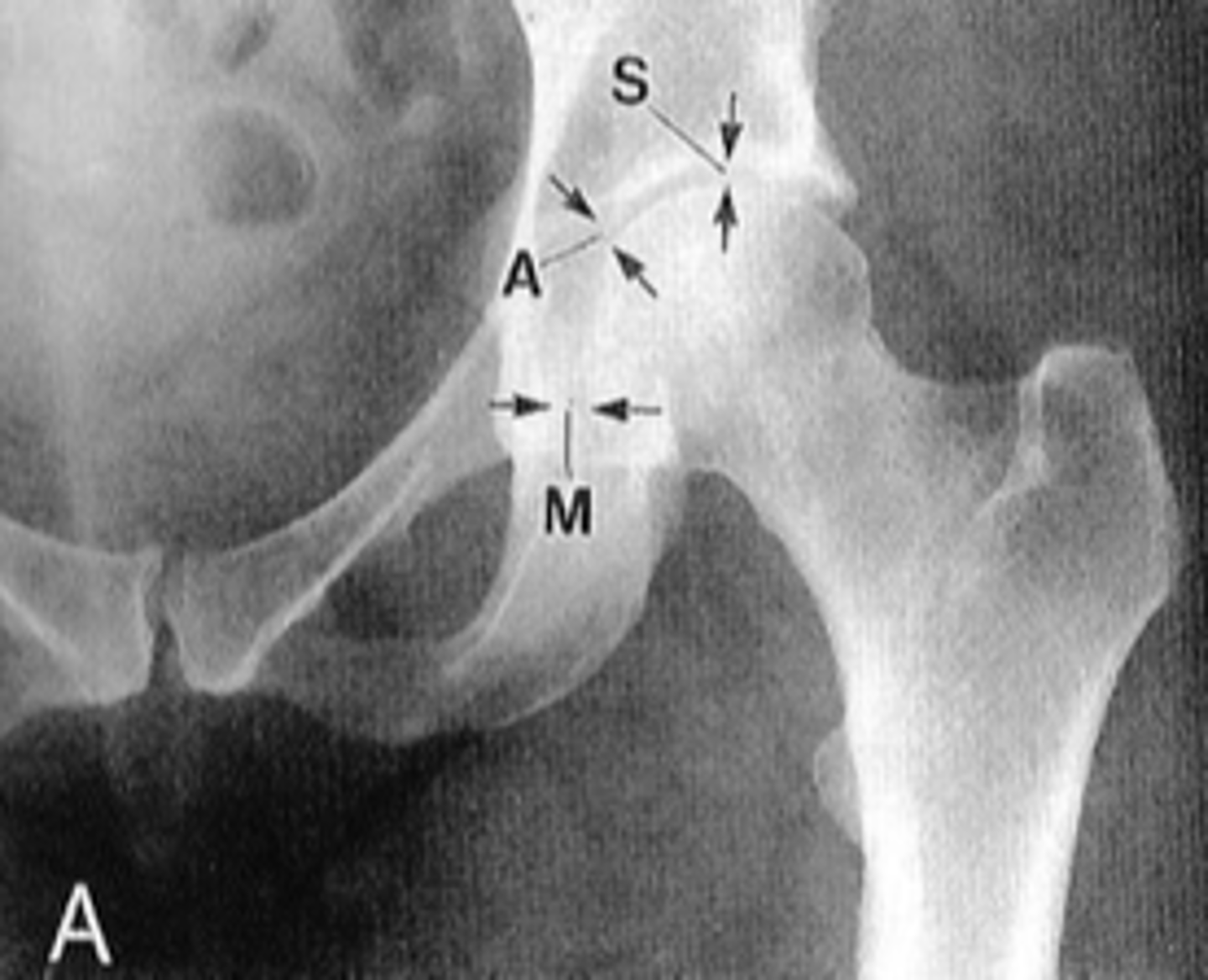
Pubic symphysis
ID 1
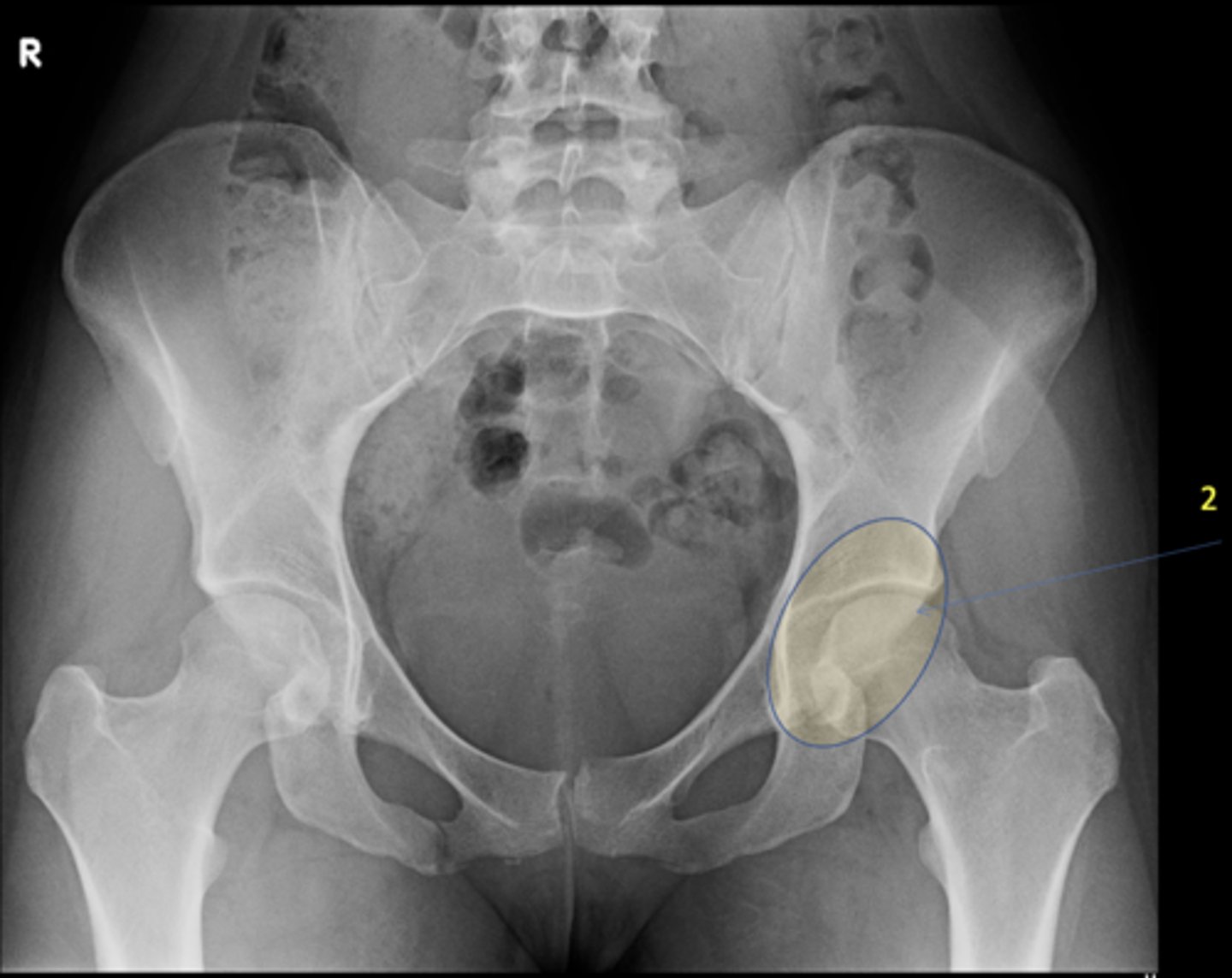
Left femoroacetabular joint
ID 2 (joint)
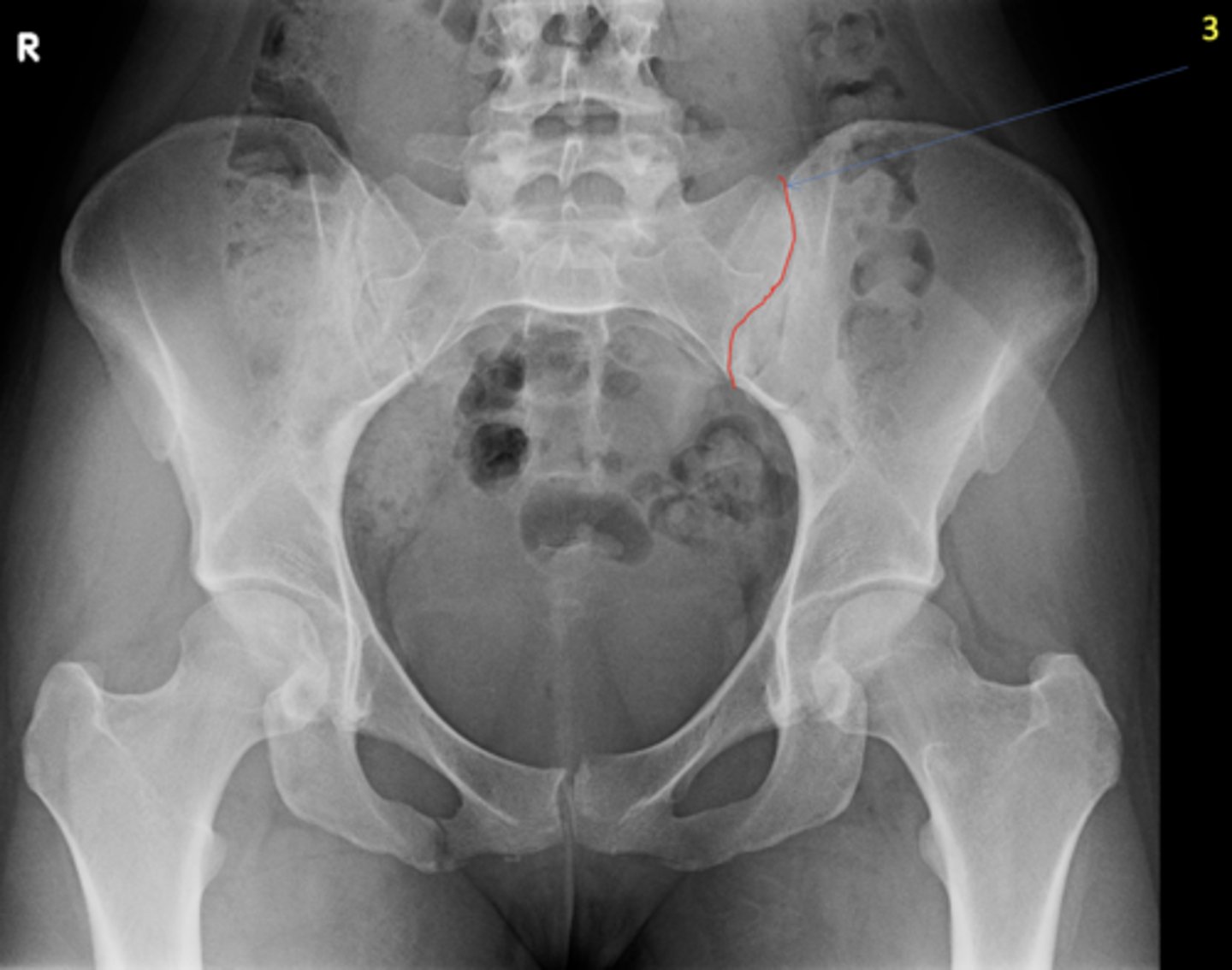
Left posterior sacroiliac joint
ID 3 (joint)
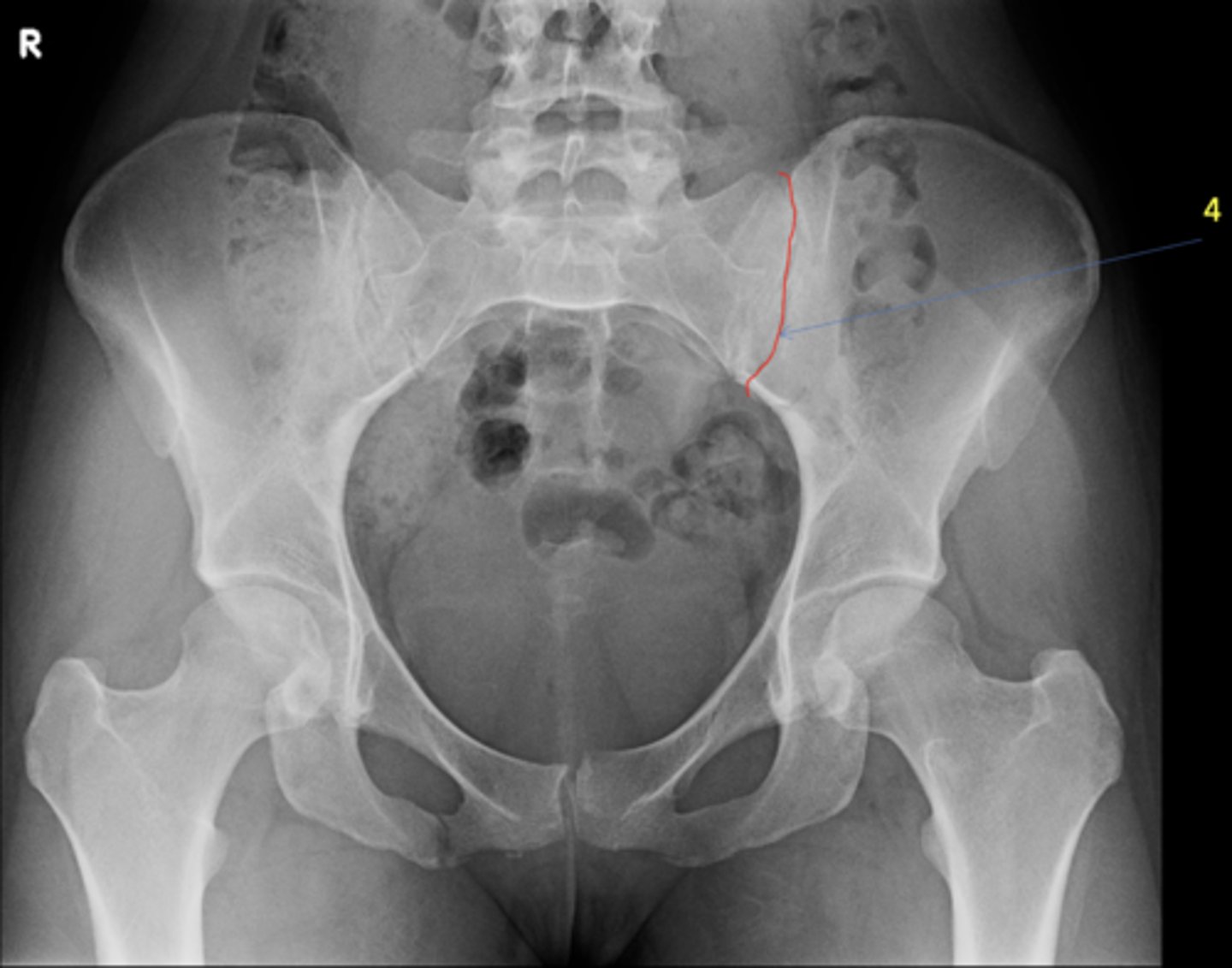
Left anterior sacroiliac joint
ID 4 (joint)
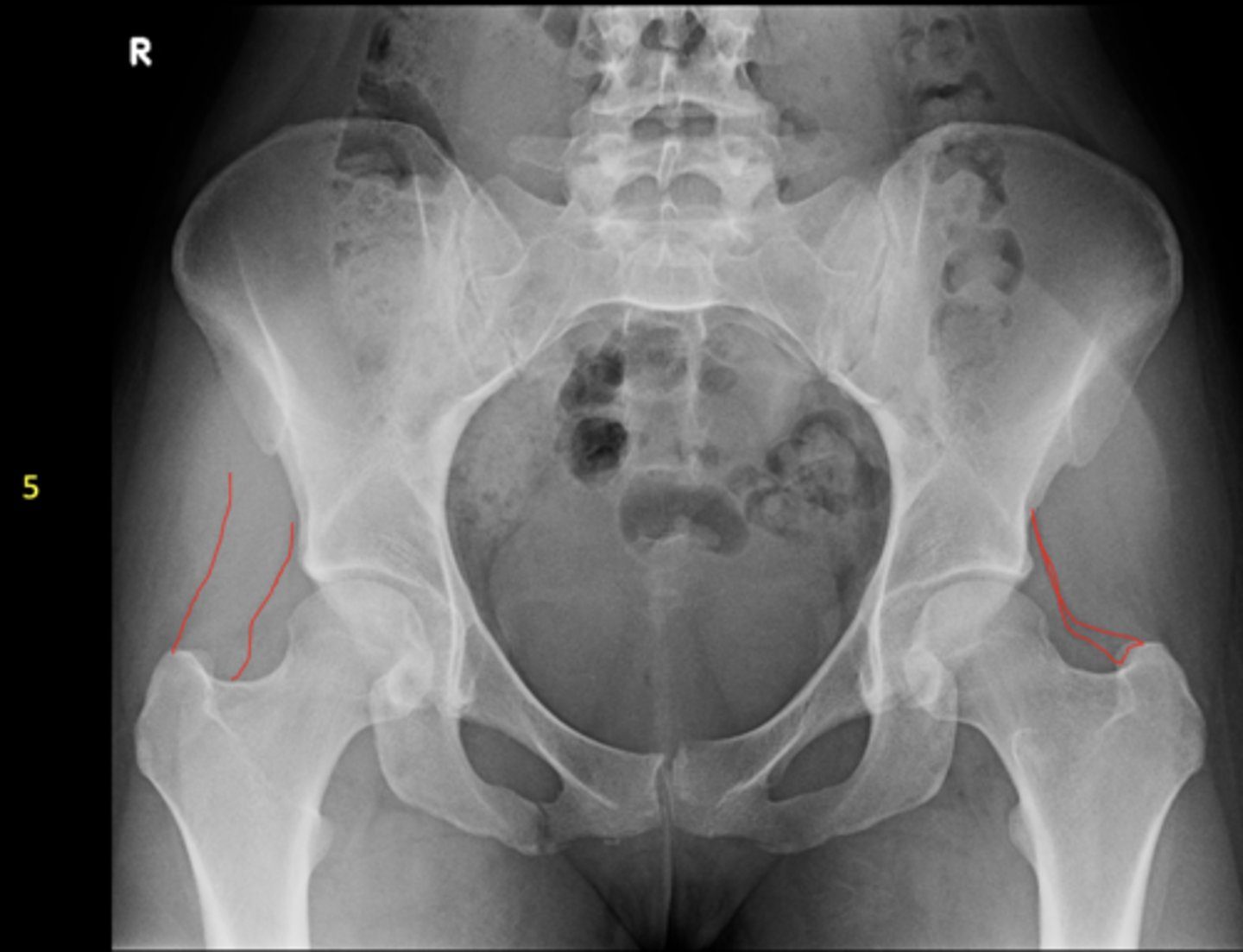
Right: gluteus medius
Left: gluteal fat stripe
ID 5
- AP hip
- Frog-leg (lateral) hip
State the standard unilateral hip projections
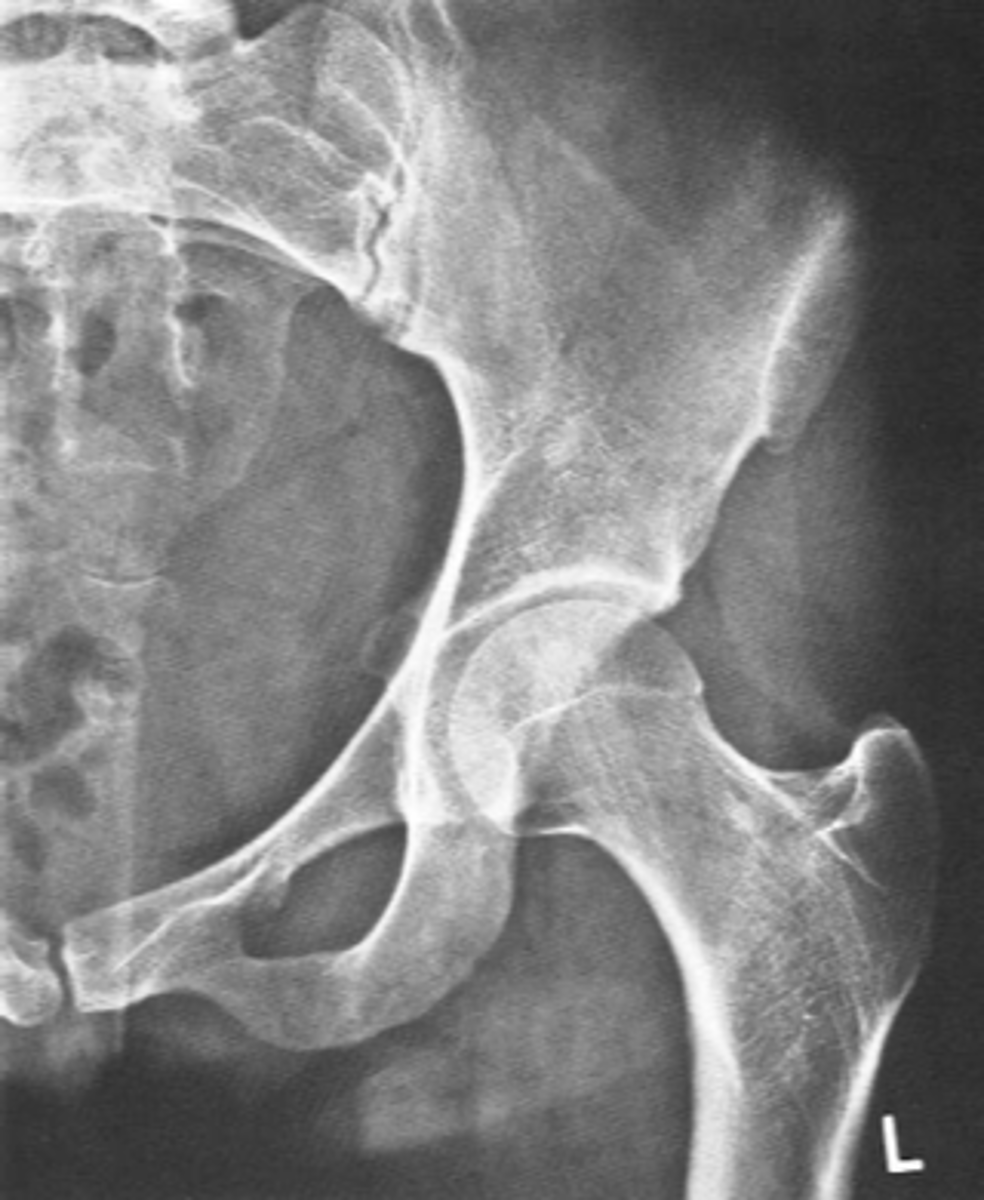
Unilateral AP hip
ID standard unilateral hip projection
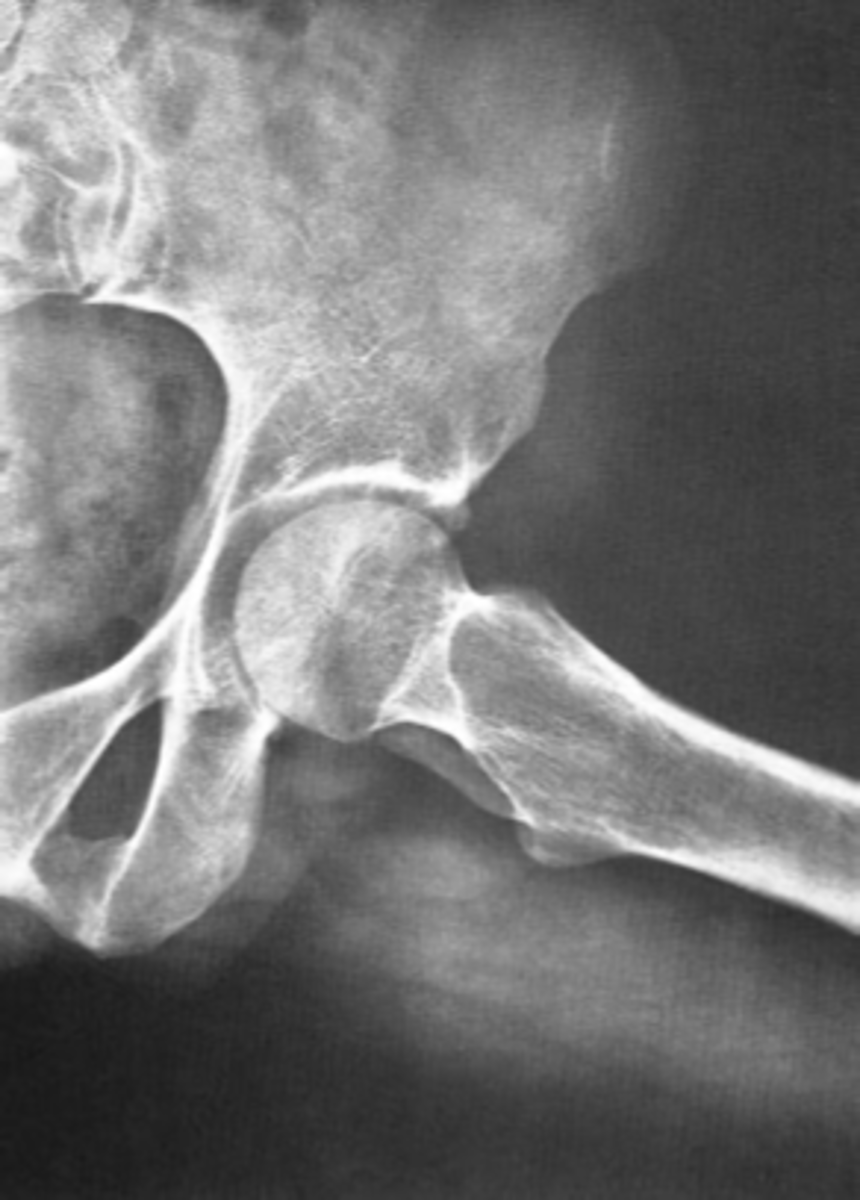
Frog-leg (lateral) hip
ID standard unilateral hip projection
No
Are there any supplementary unilateral hip projections?
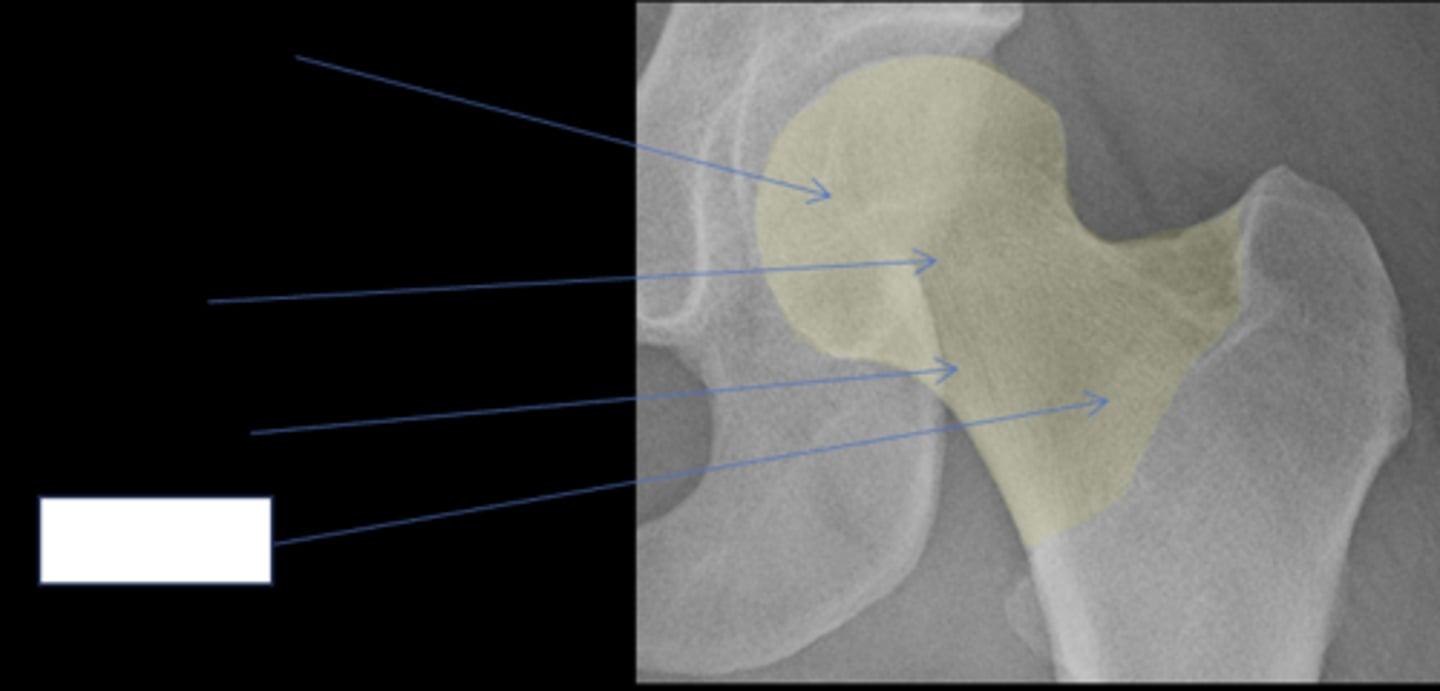
- Femoral head
- Femoral neck
State the parts of the hip that are intracapsular
Femoral head
ID anatomy
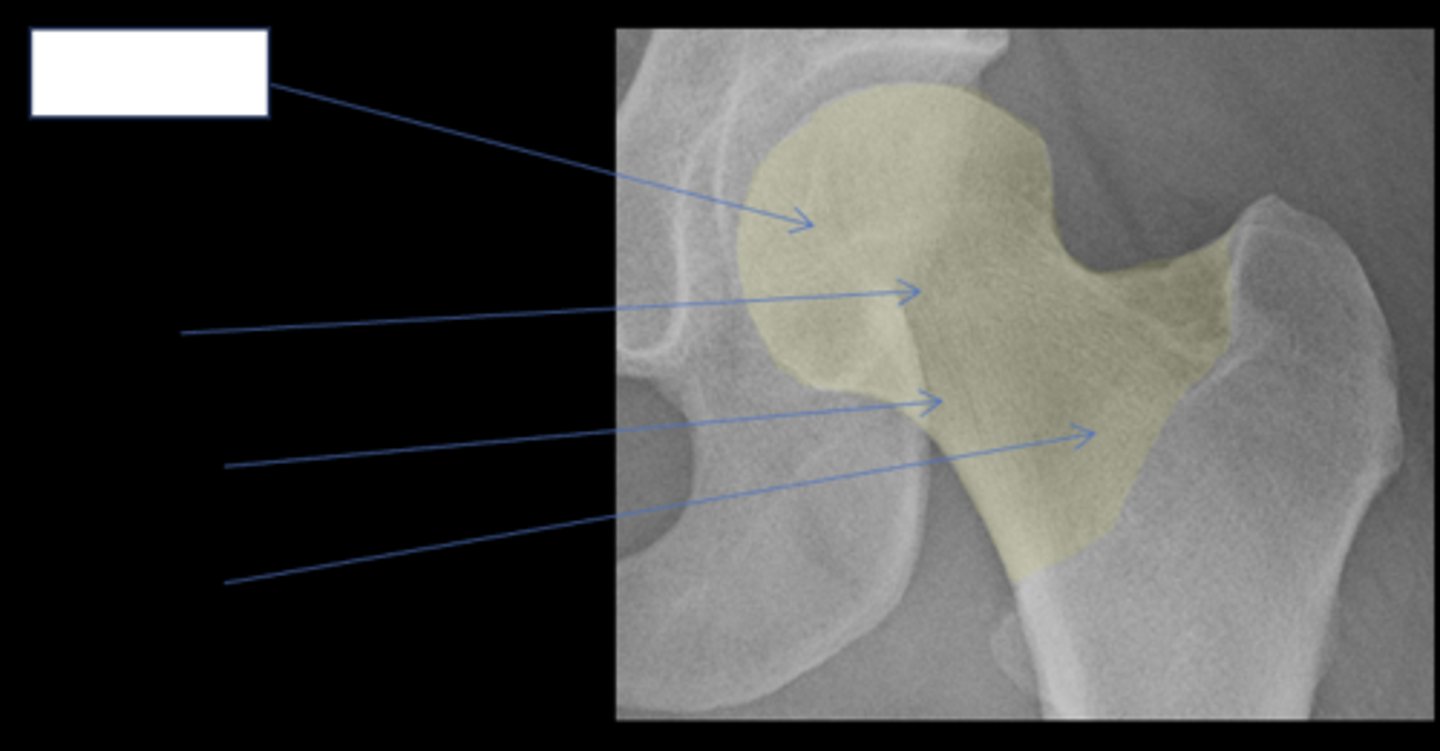
Subcapital
ID anatomy
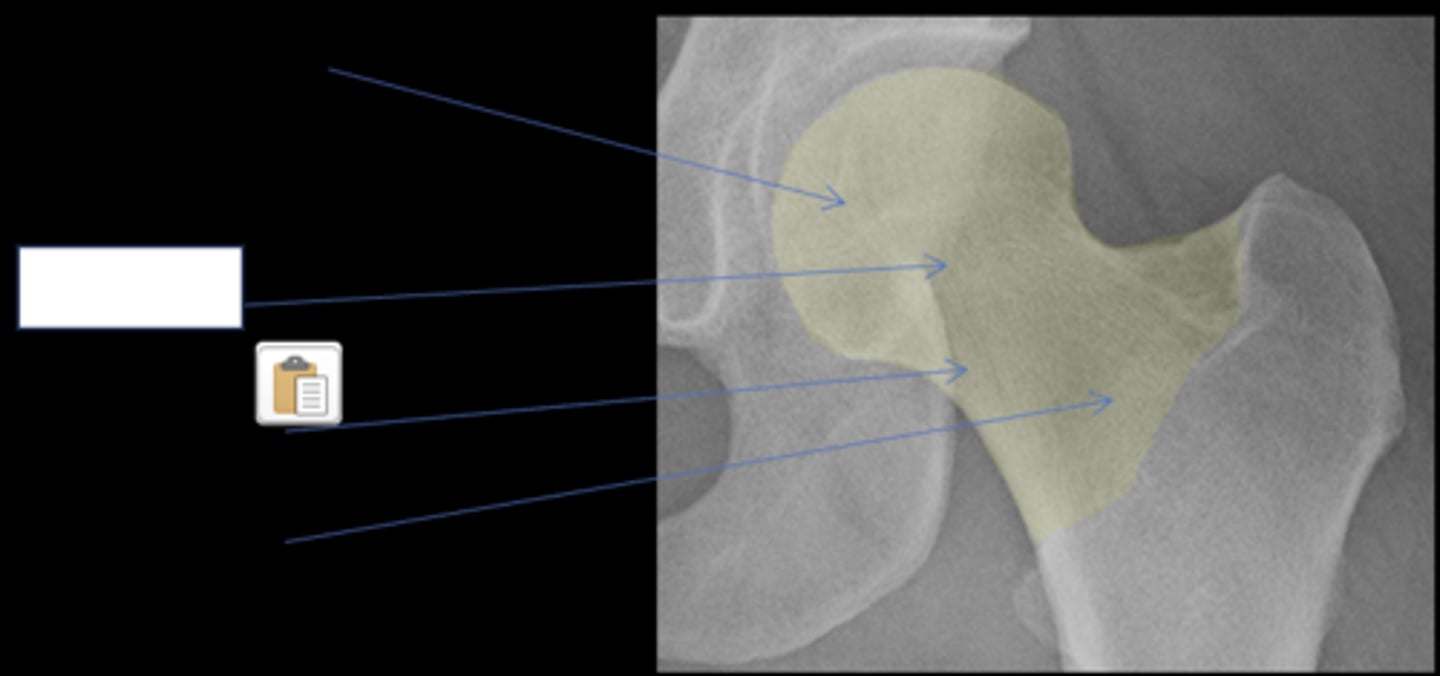
Mid-cervical
ID anatomy
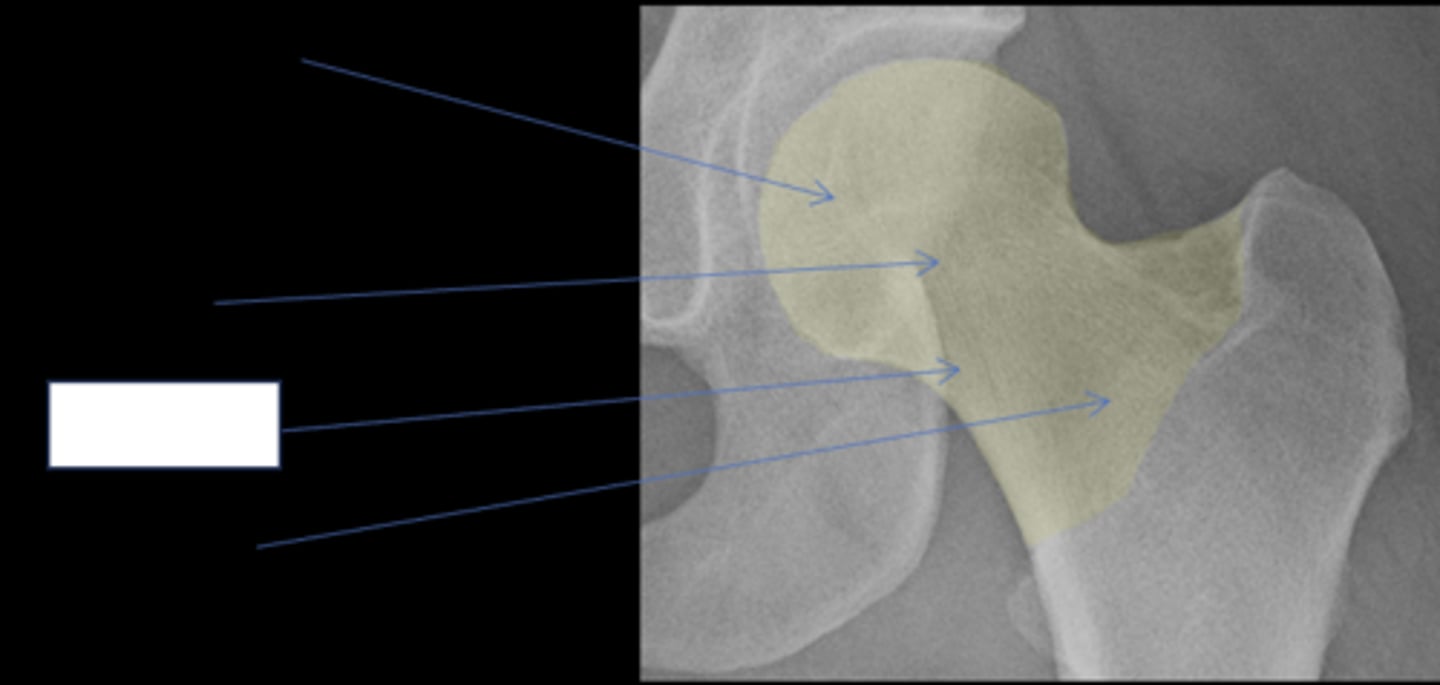
Basicervical
ID anatomy
Appearance of lesions and their ability to heal is different when intracapsular
Importance of intracapsular hip
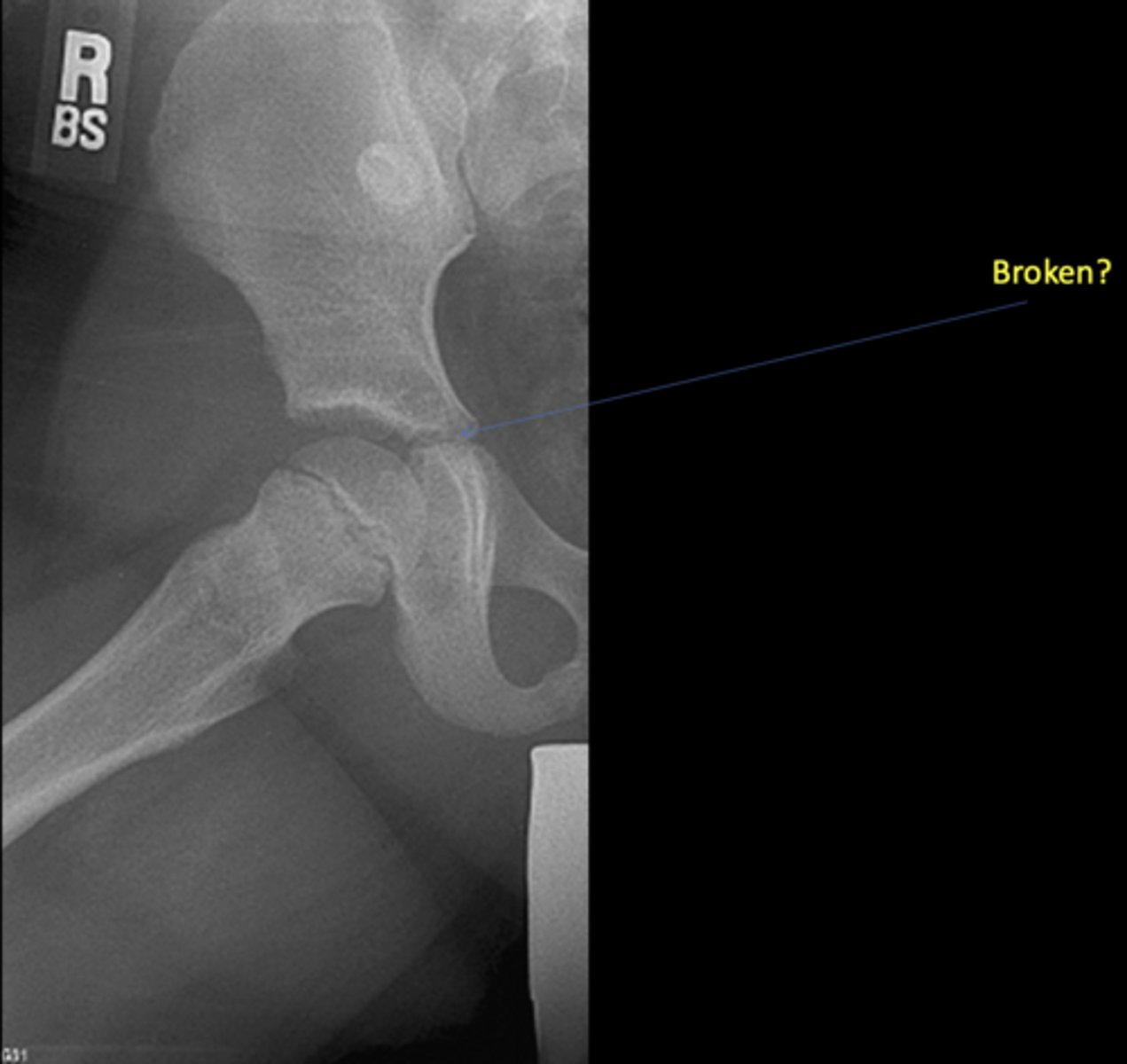
No - growth plate in a child
Broken?
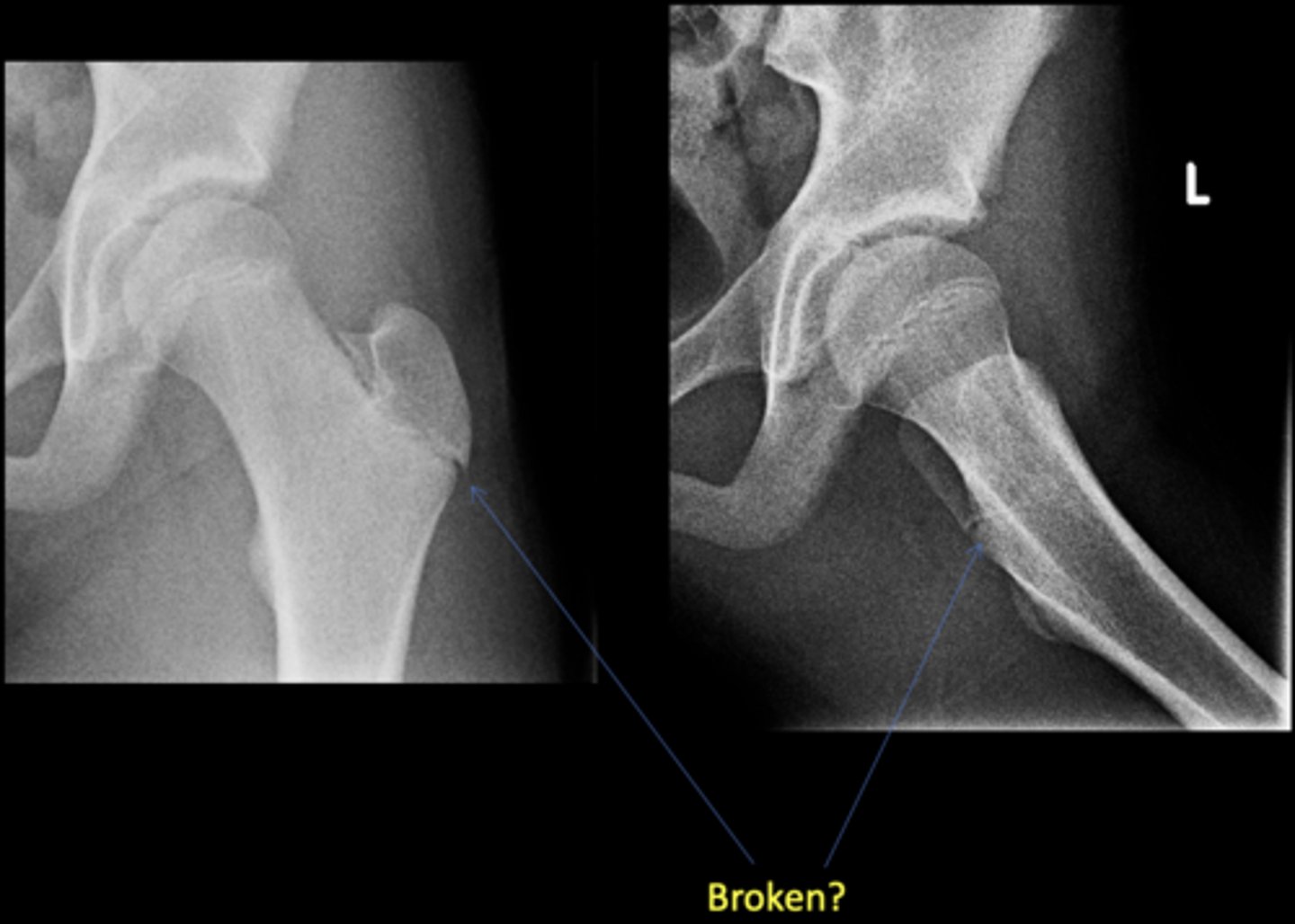
No - growth plate in a child
Broken?
AP hip
View on left?
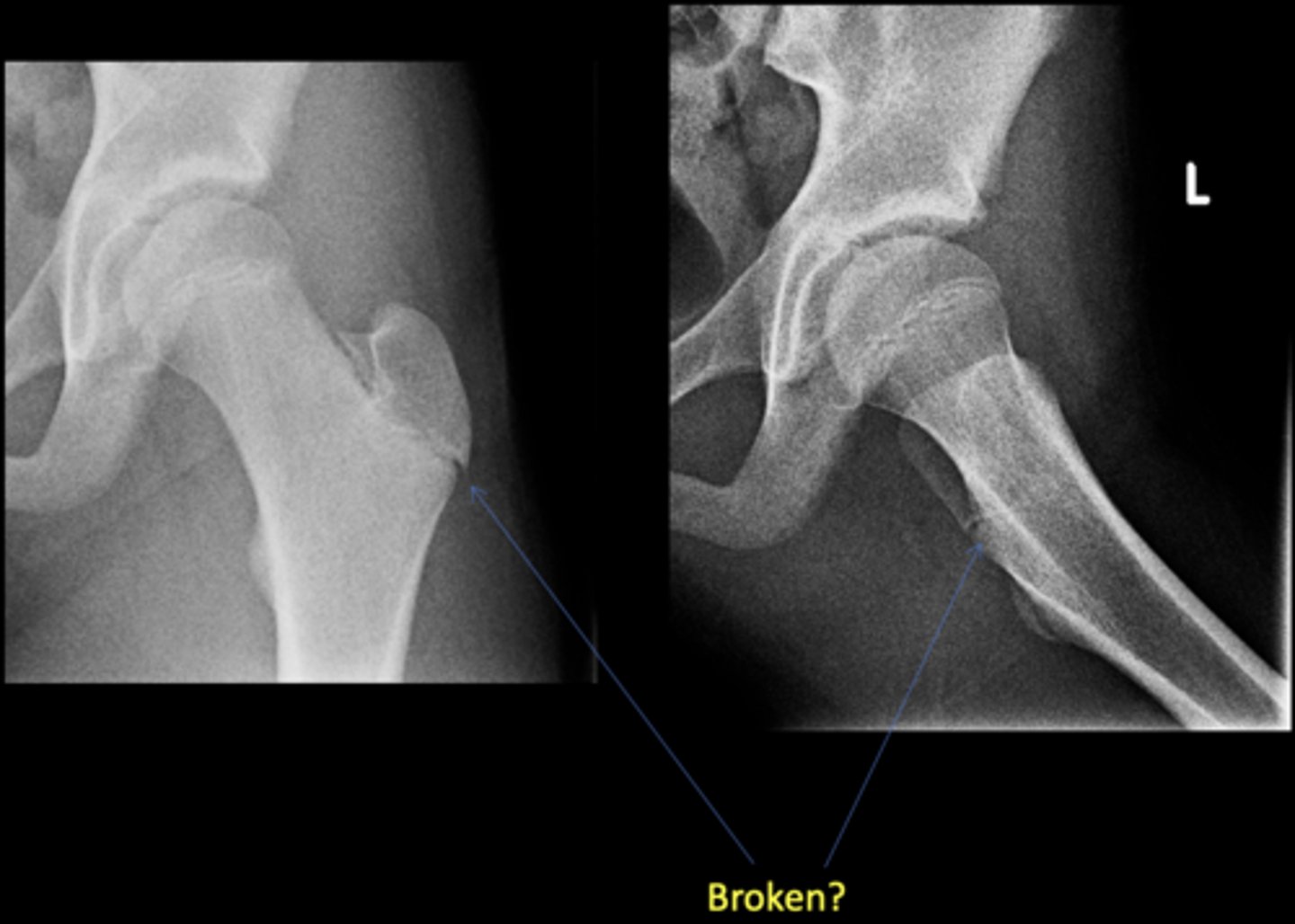
Frog-leg hip
View on right?
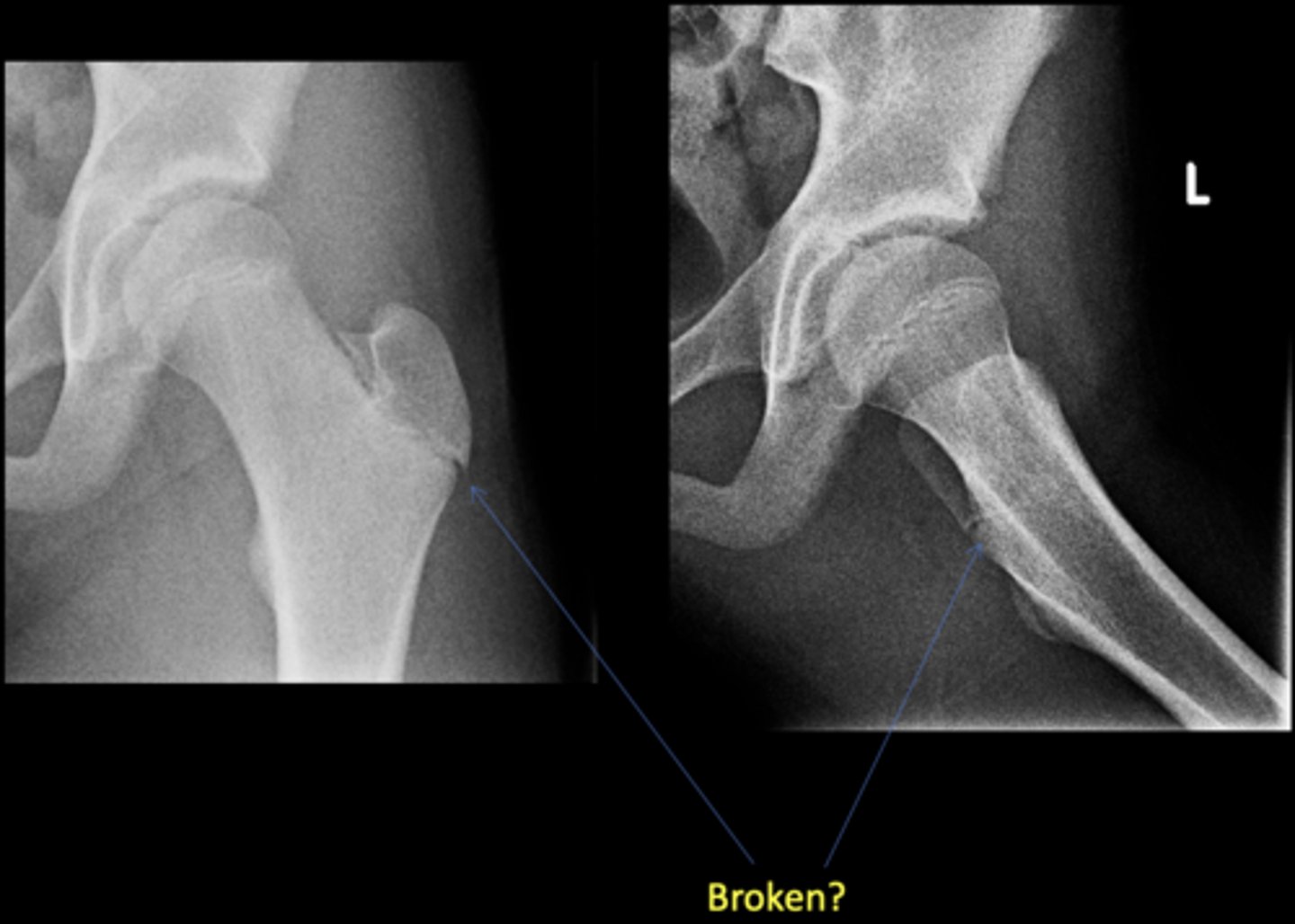
0
Risser's Classification Stage _____: no ossification center at the level of iliac crest apophysis
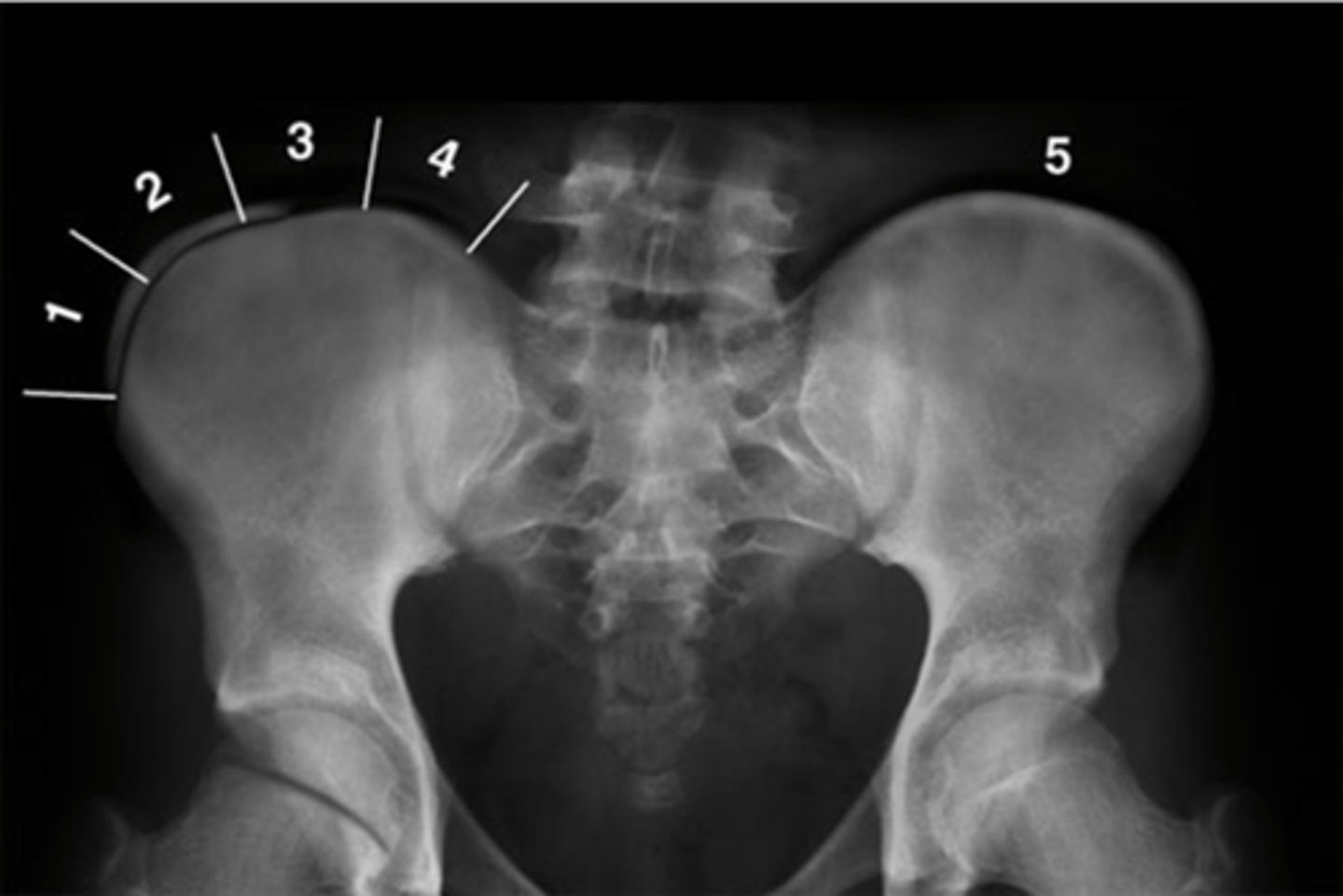
1
Risser's Classification Stage _____: apophysis under 25% of the iliac crest
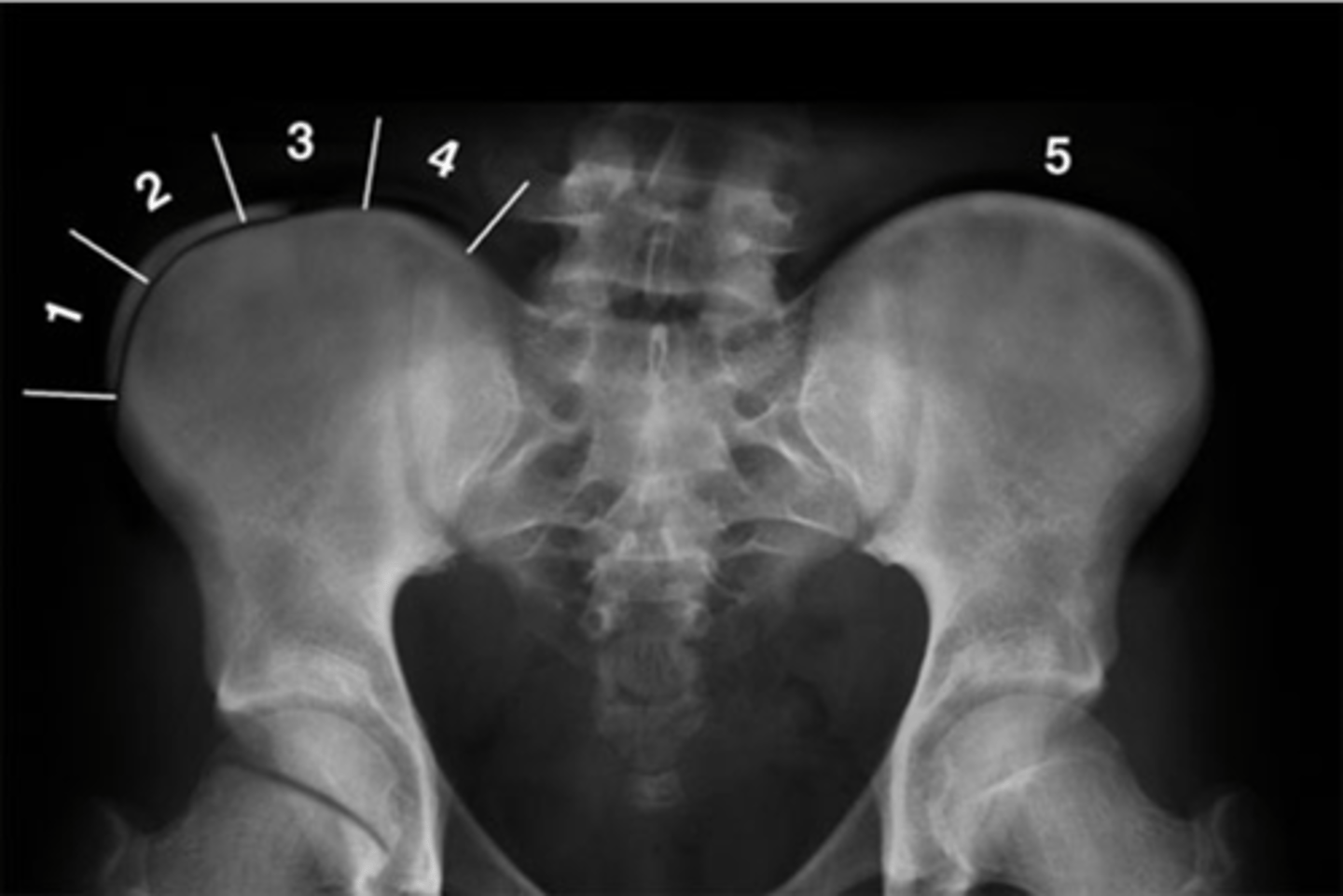
2
Risser's Classification Stage _____: apophysis over 25-50% of the iliac crest
3
Risser's Classification Stage _____: •apophysis over 50-75% of the iliac crest
4
Risser's Classification Stage _____: apophysis over >75% of the iliac crest
5
Risser's Classification Stage _____: complete ossification and fusion of the iliac crest apophysis
Ischial apophysis
ID
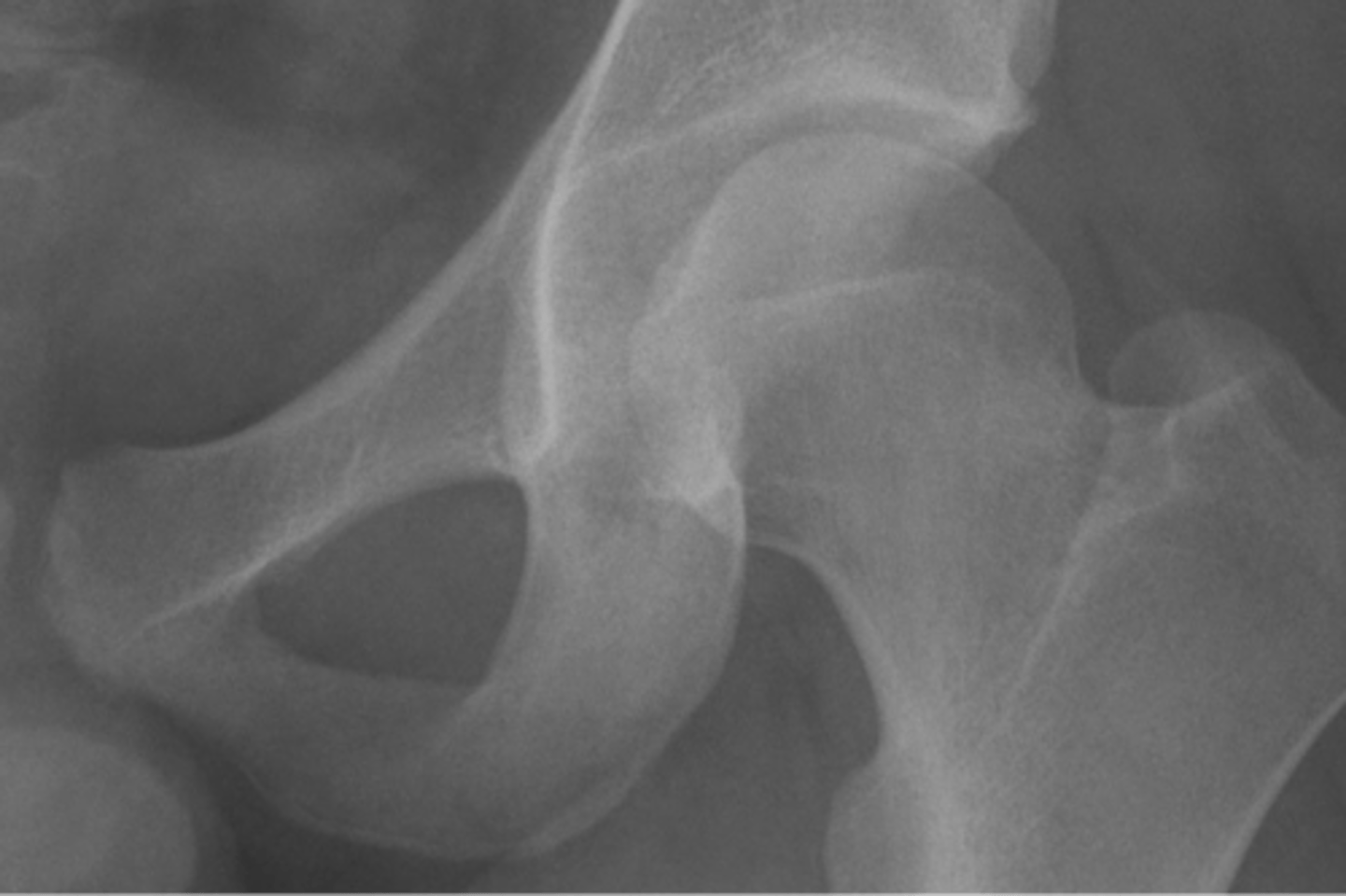
Ischiopubic synchondrosis
ID
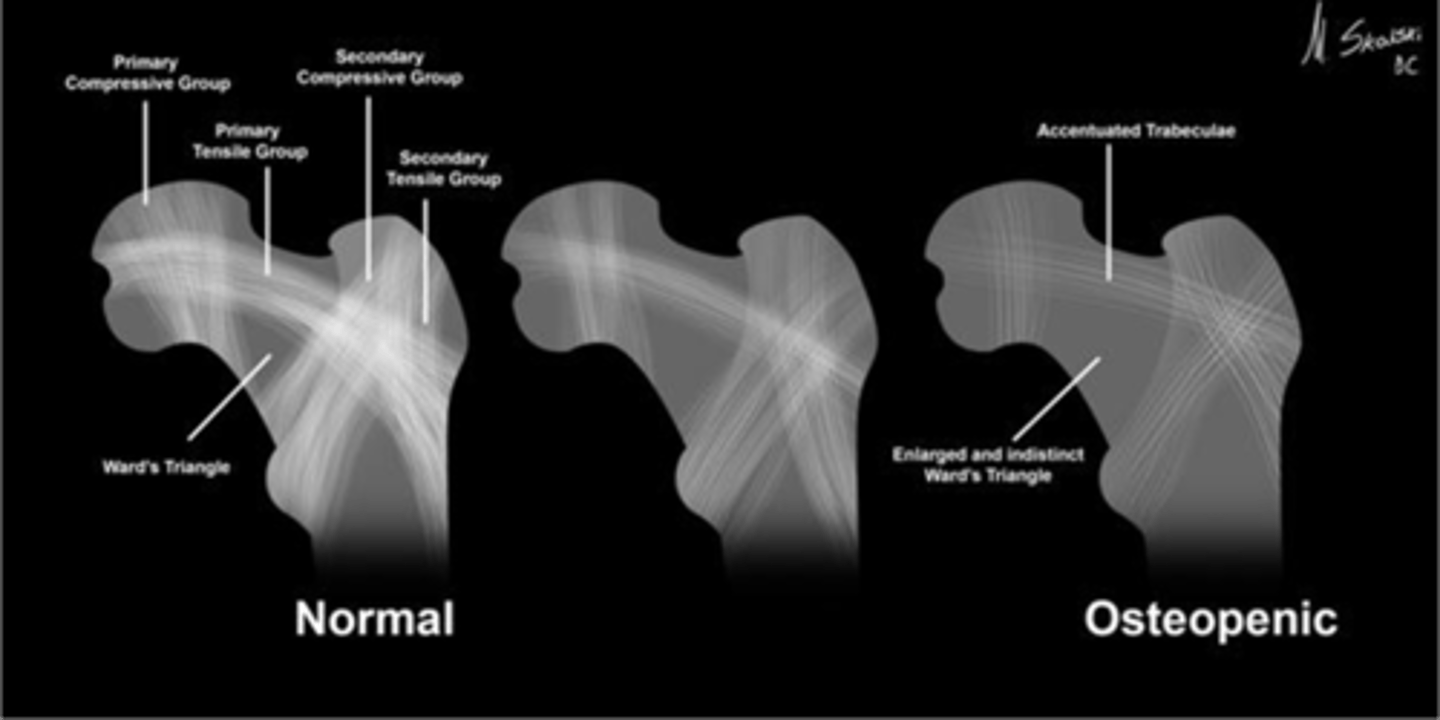
Wards triangle
An area that appears more radiolucent because it is surrounded by an abundance of trabeculae. The 1˚ and 2˚ compressive and tensile groups of the proximal femur leave a small region to appear more lucent
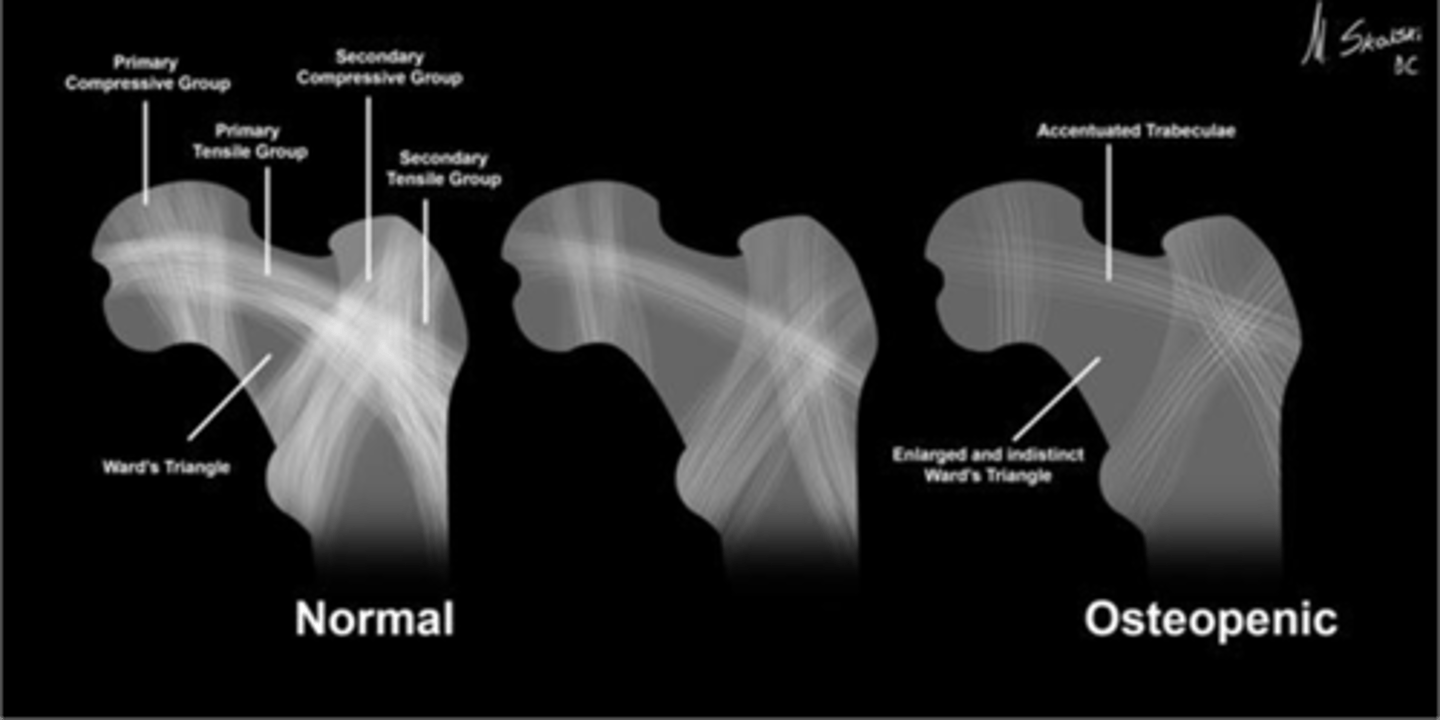
Osteopenia
Wards triangle becomes enlarged as bone density reduces, signifying _____
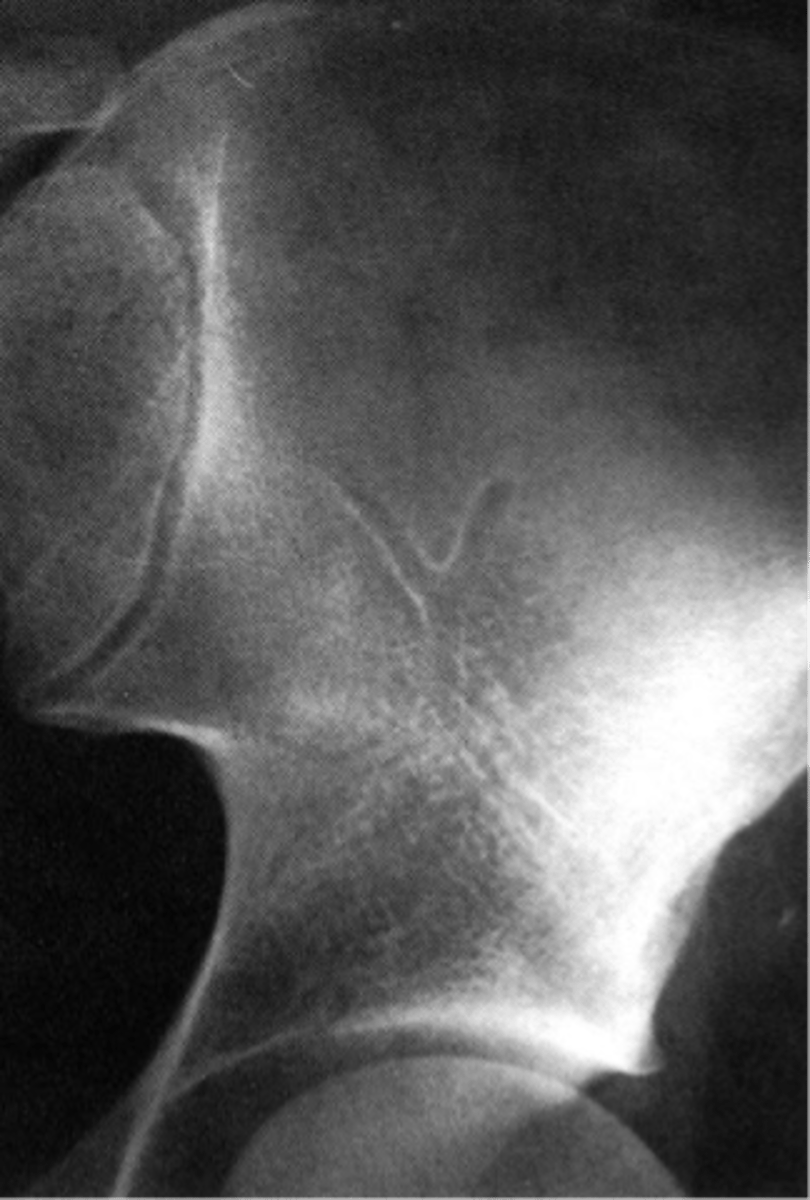
Normal vascular channel
ID
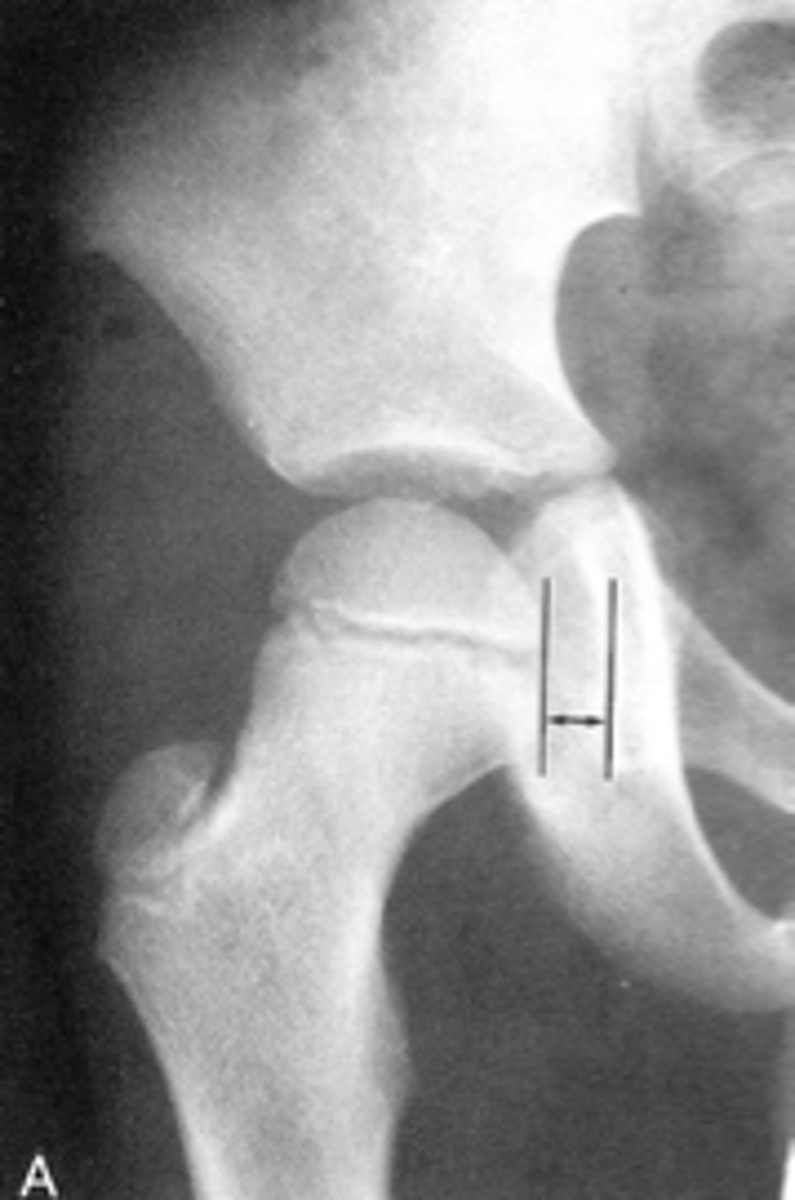
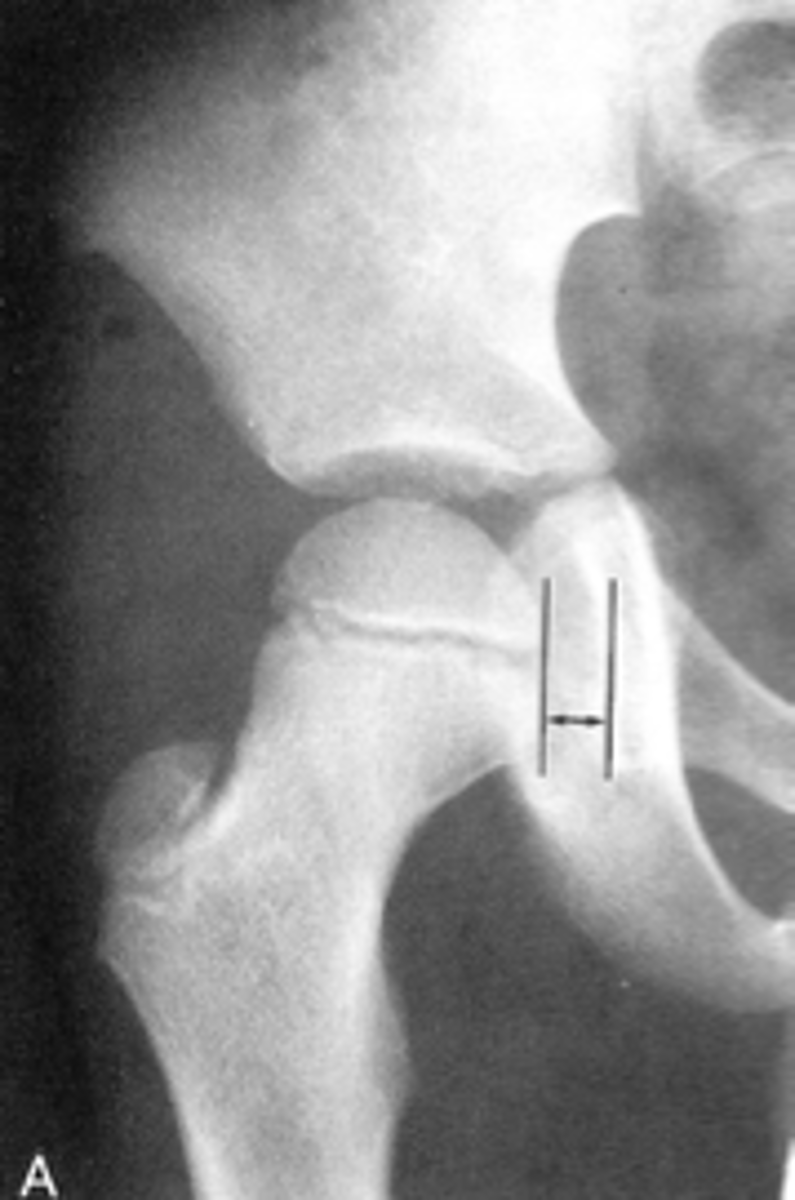
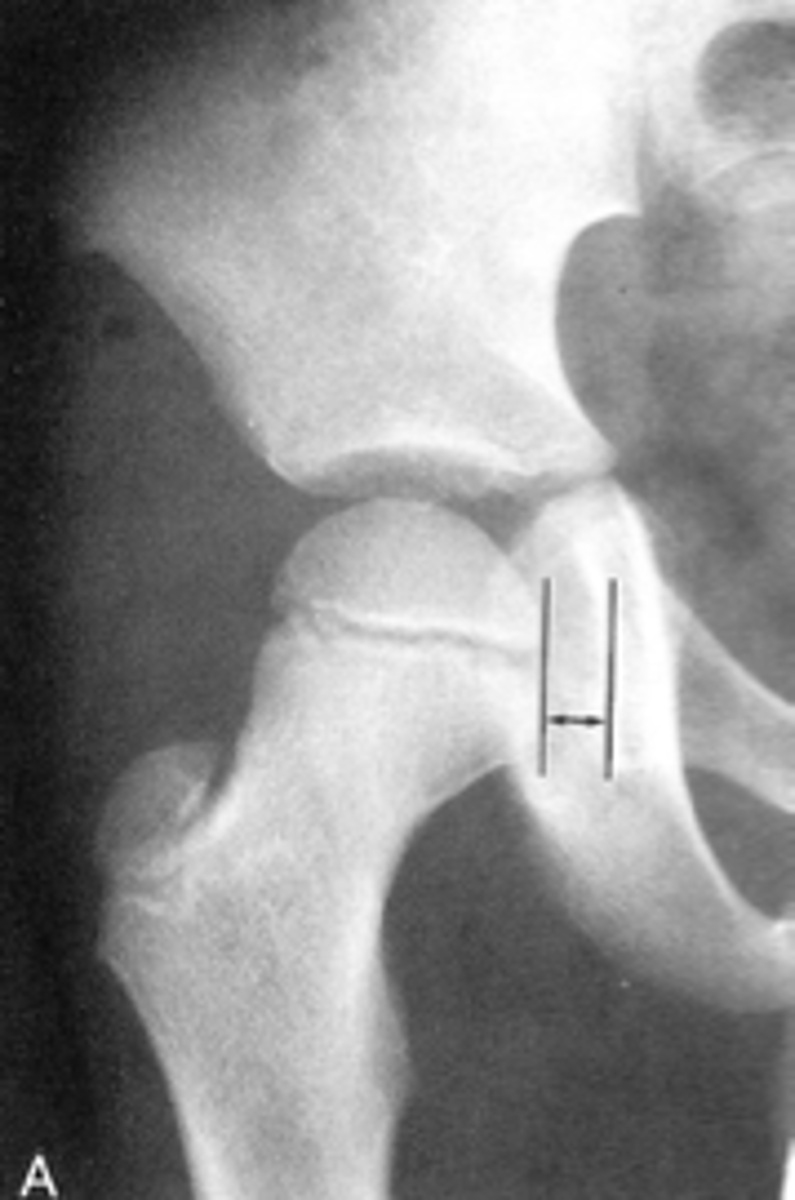
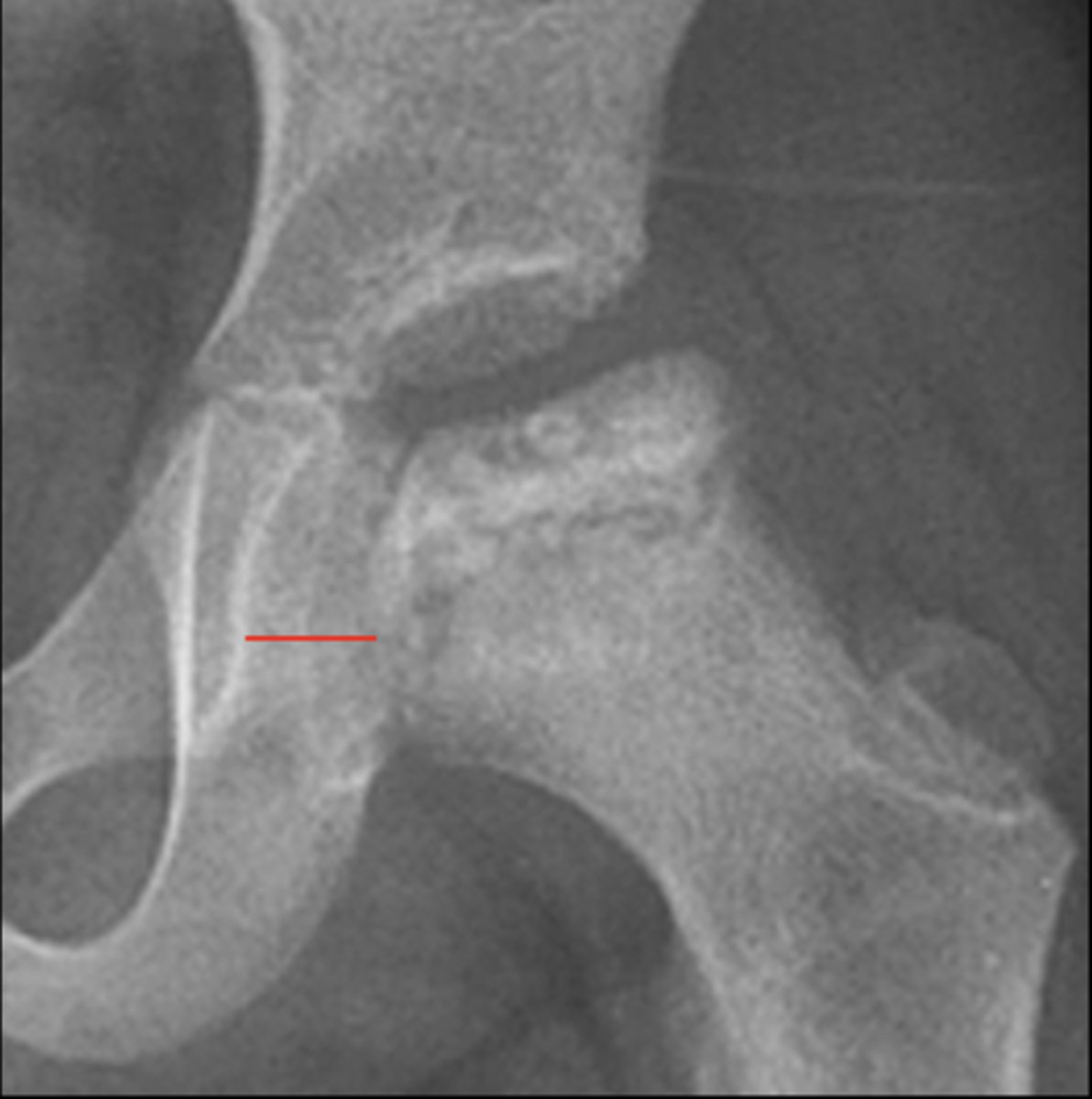
Kohler's teardrop distance
ID measurement line
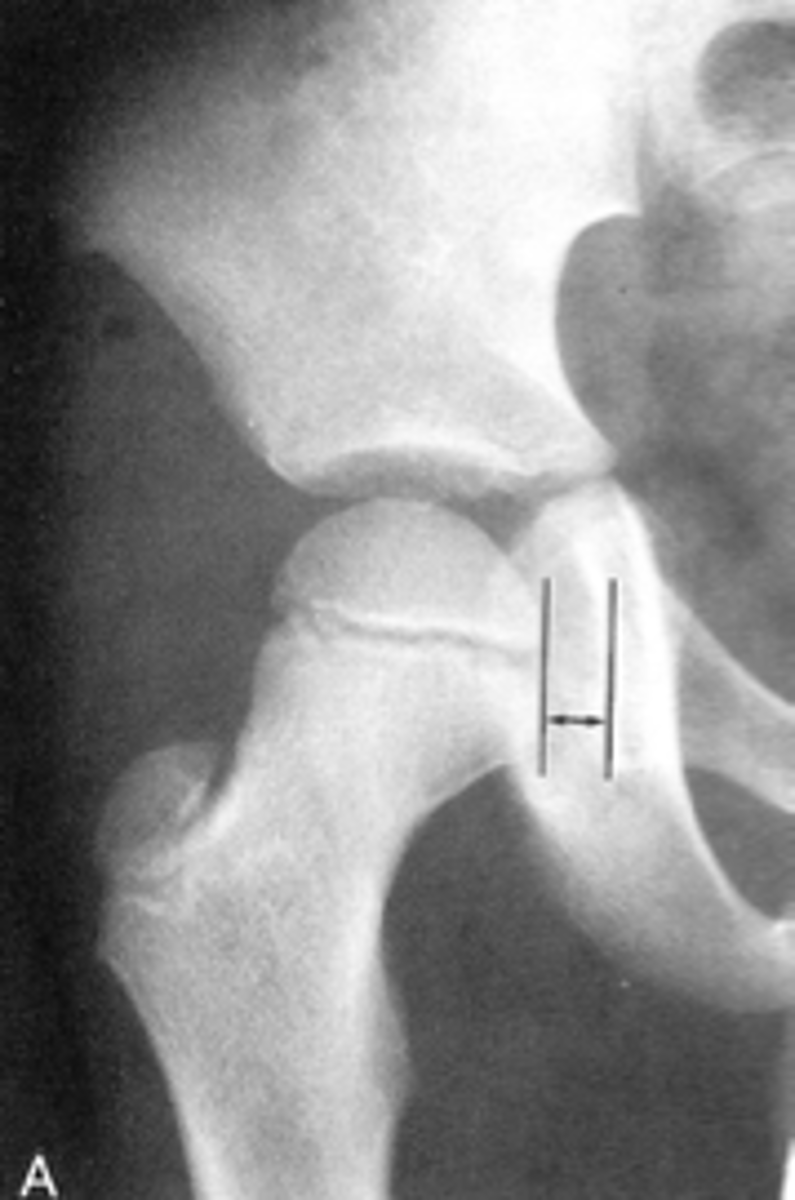
- AP pelvis
- AP hip
What views are needed to see Kohler's teardrop distance?
- Medial margin of femoral head
- Lateral border of teardrop
Kohler's teardrop distance landmarks
6-11 mm
Normal Kohler's teardrop distance measurement
2 mm
The normal Kohler's teardrop distance is 6-11 mm, and there should be no greater than a _____ difference when comparing to the contralateral side
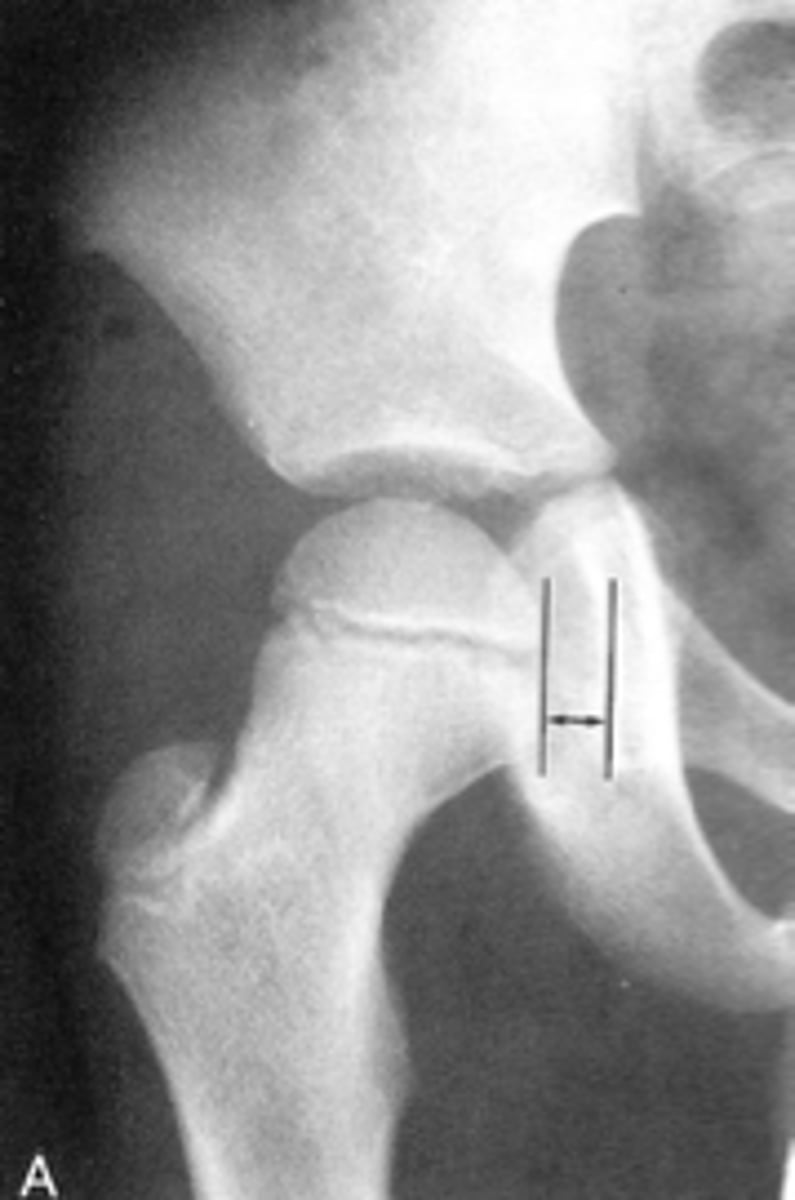
Hip joint effusion
Clinical significance of an enlarged Kohler's teardrop distance
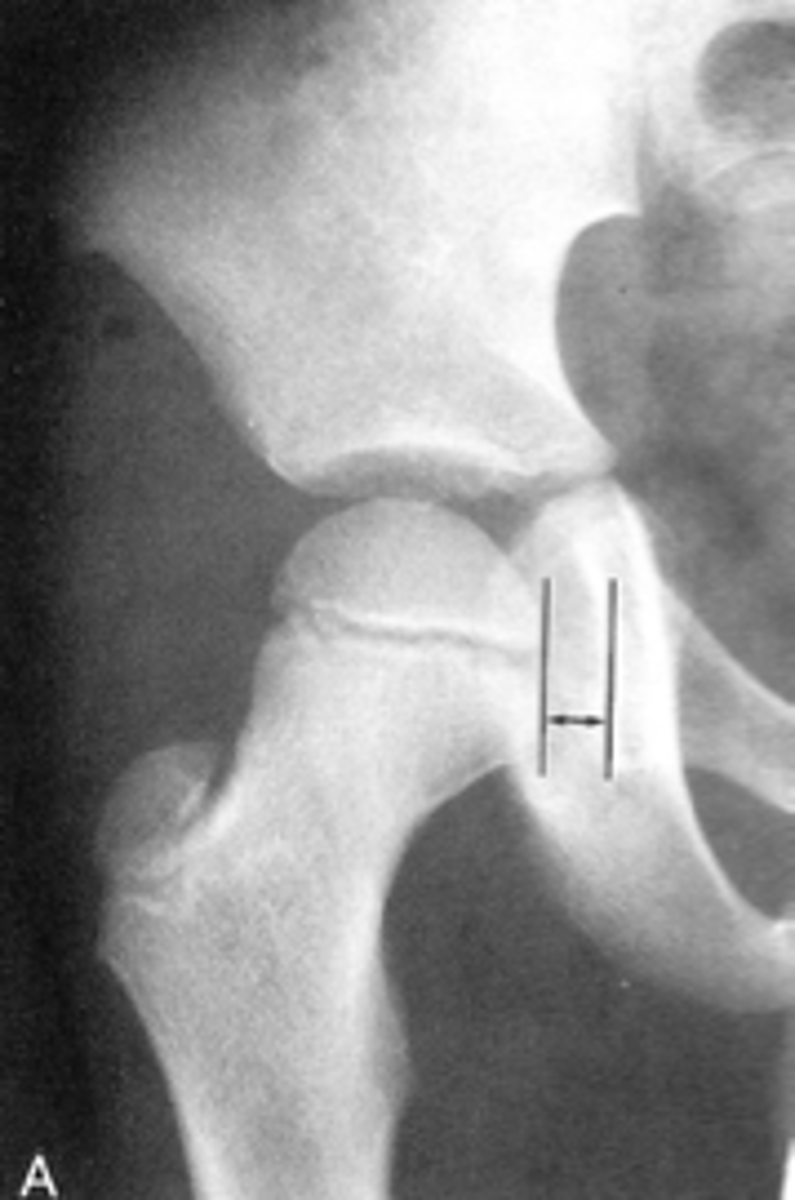
Waldenstrom's sign
What sign indicates an enlarged Kohler's teardrop distance?
- Accentutation of the normal limits
Intracapsular swelling/joint effusion
Waldenstrom's sign is usually an indication of _____
Inflammatory arthritis
Clinical significance of a small Kohler's teardrop distance
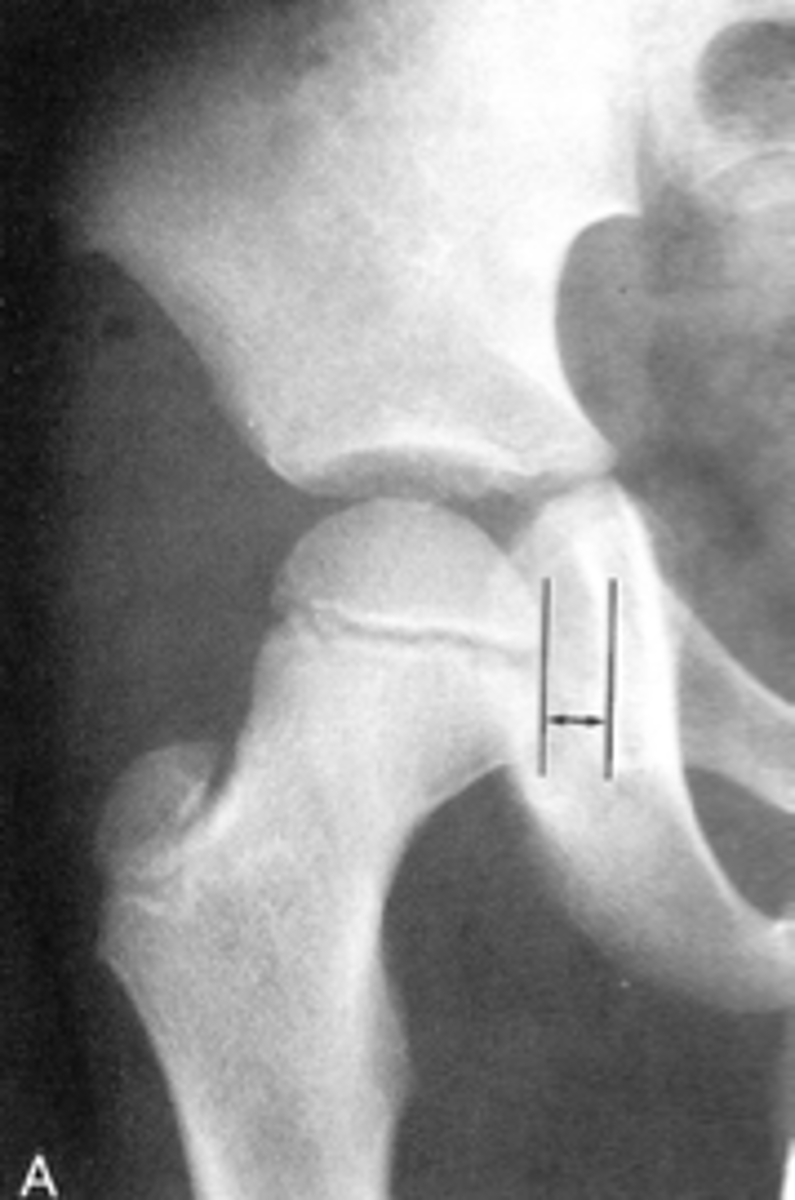
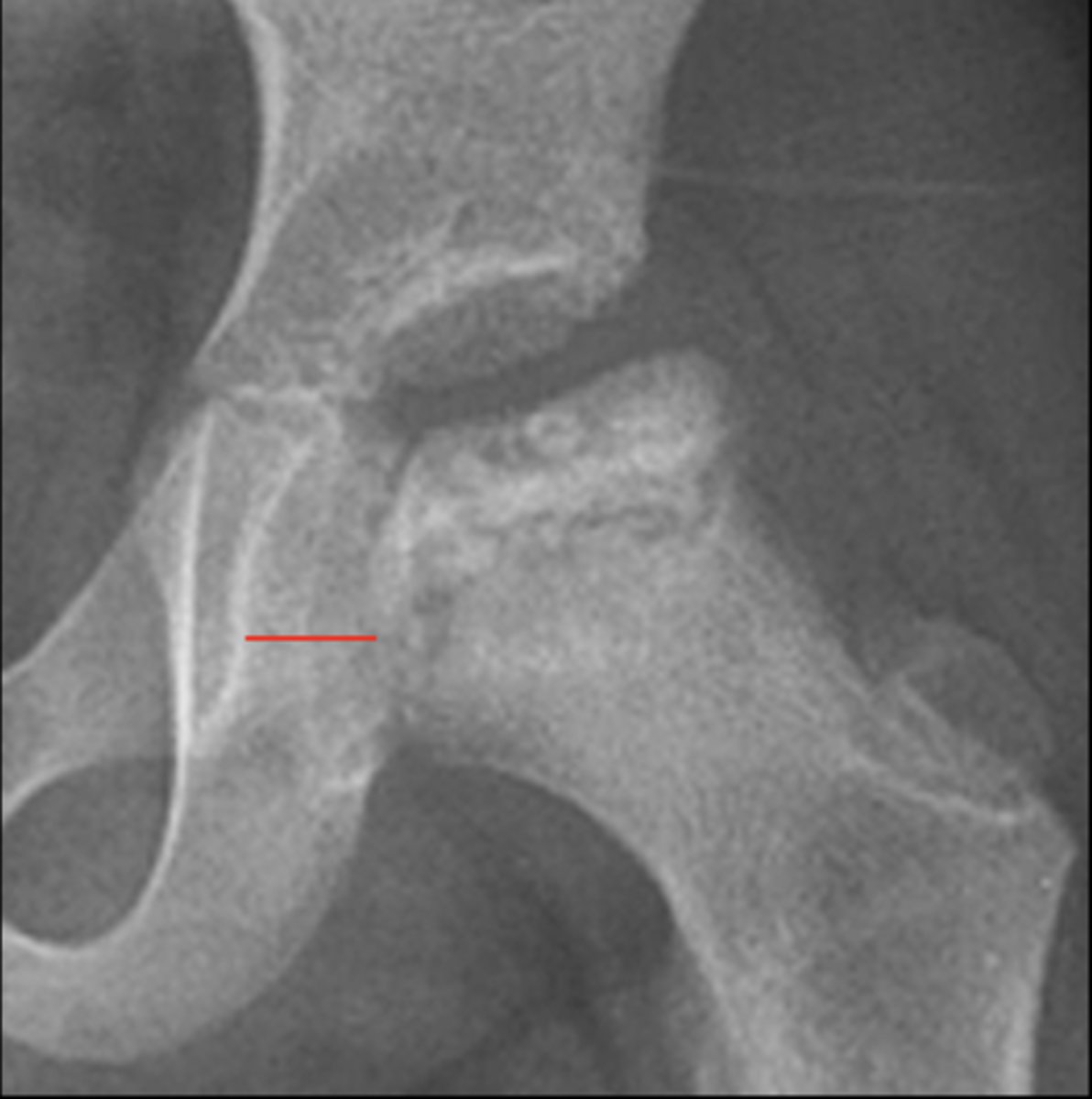
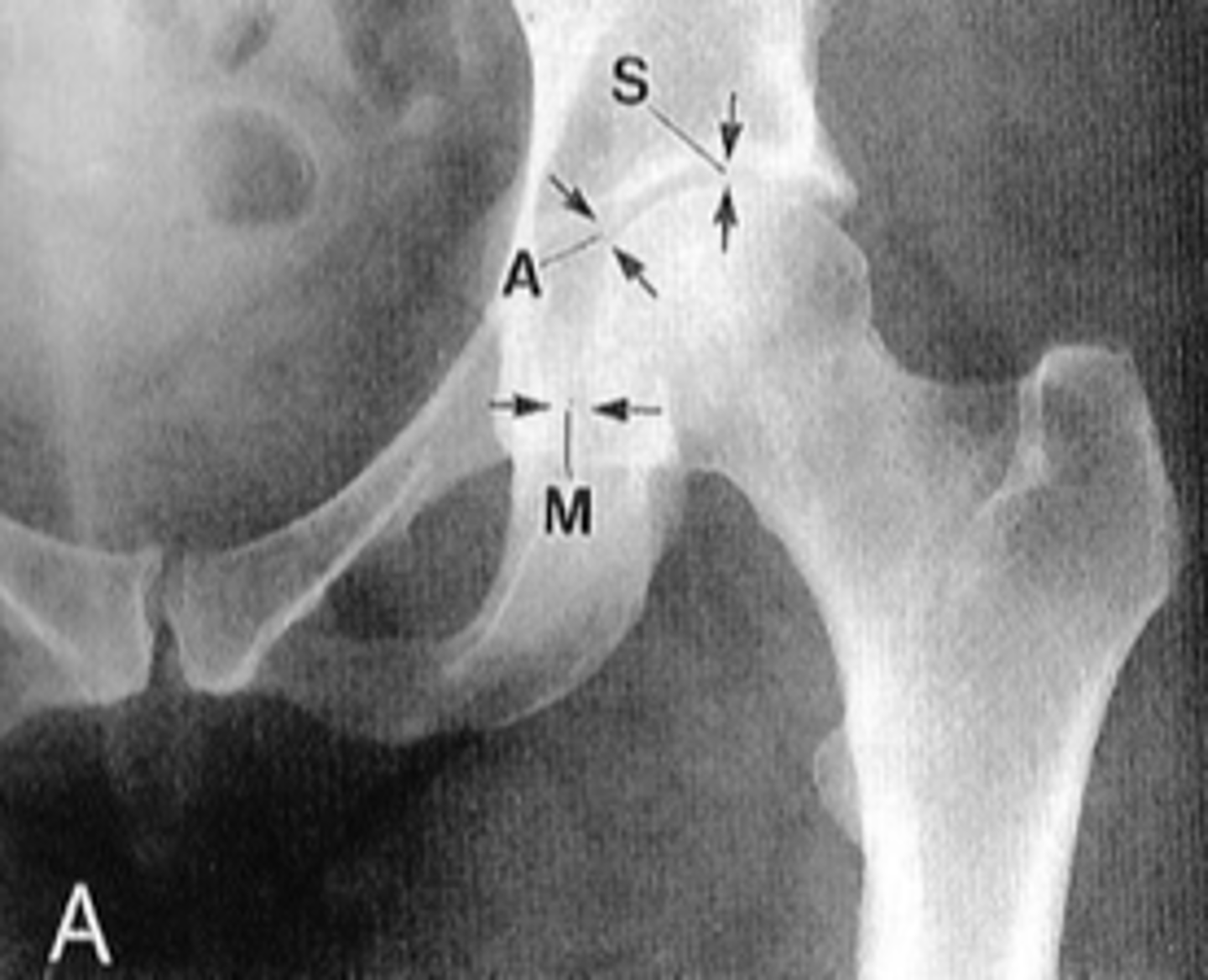
Hip joint space width
ID measurement
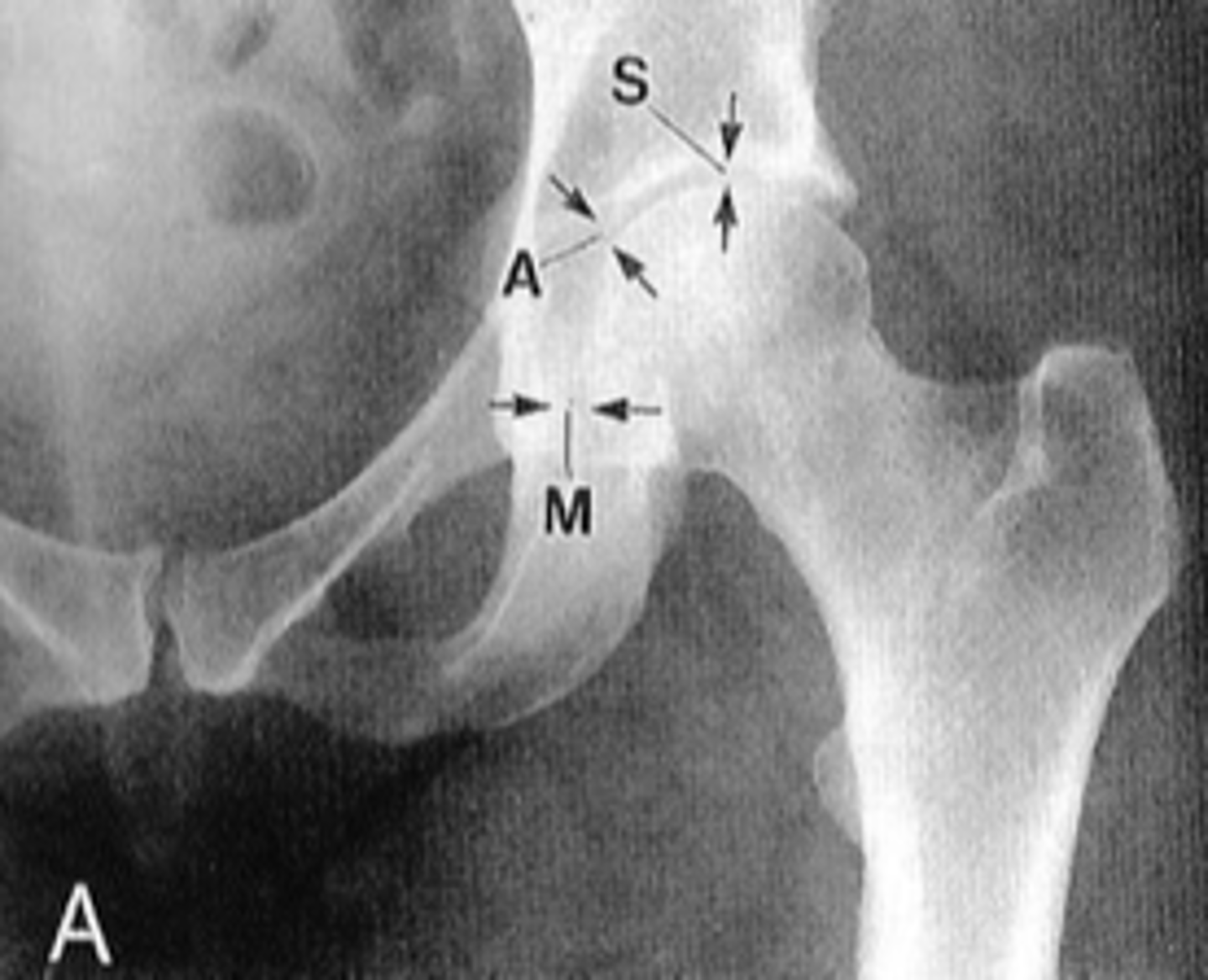
Superior, axial, medial joint spaces (SAM)
Hip joint space width landmarks
3-6 mm
Normal superior hip joint space width
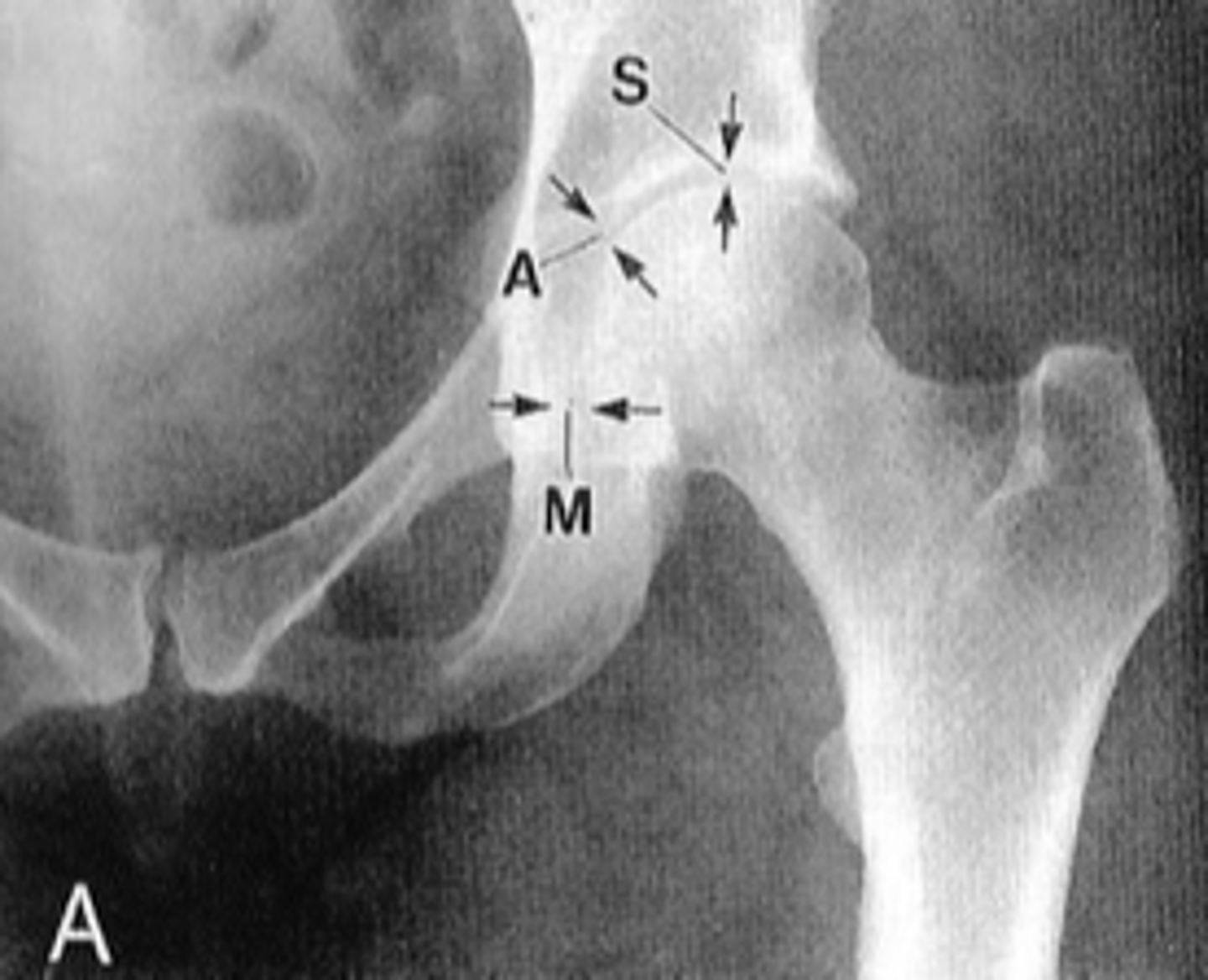
3-7 mm
Normal axial hip joint space width
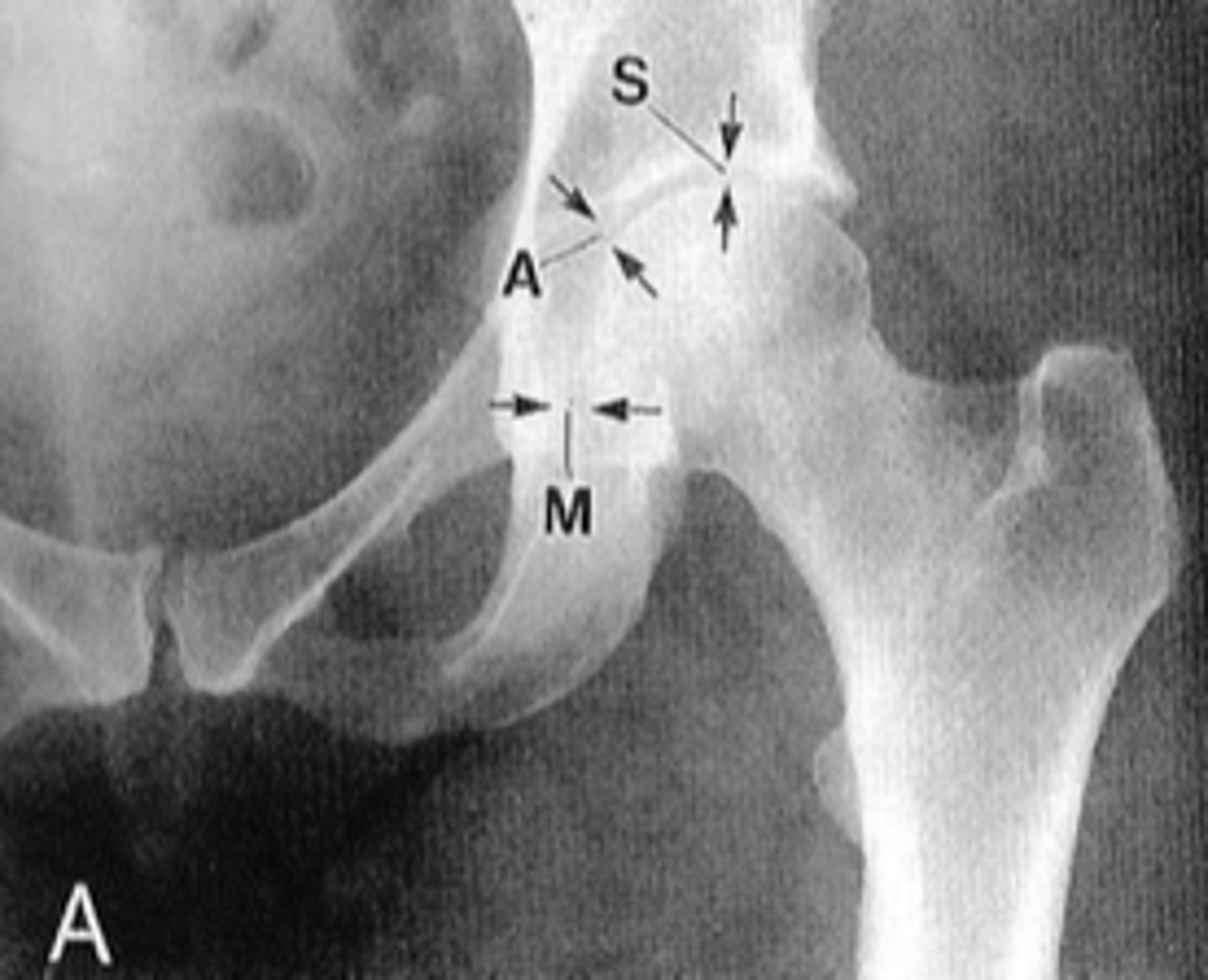
4-13 mm
Normal medial hip joint space width
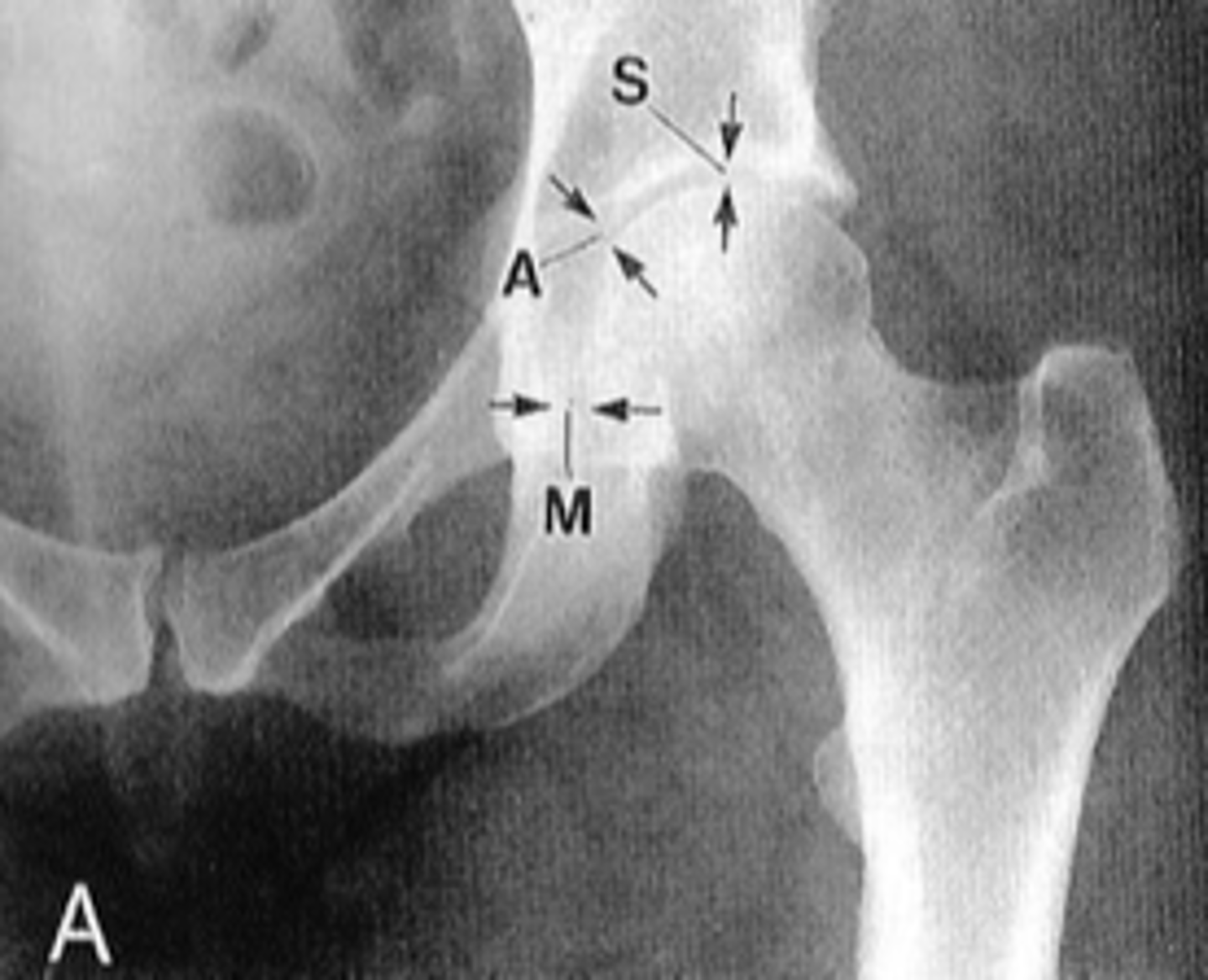
Joint effusion
Clinical significance of a wide hip joint space
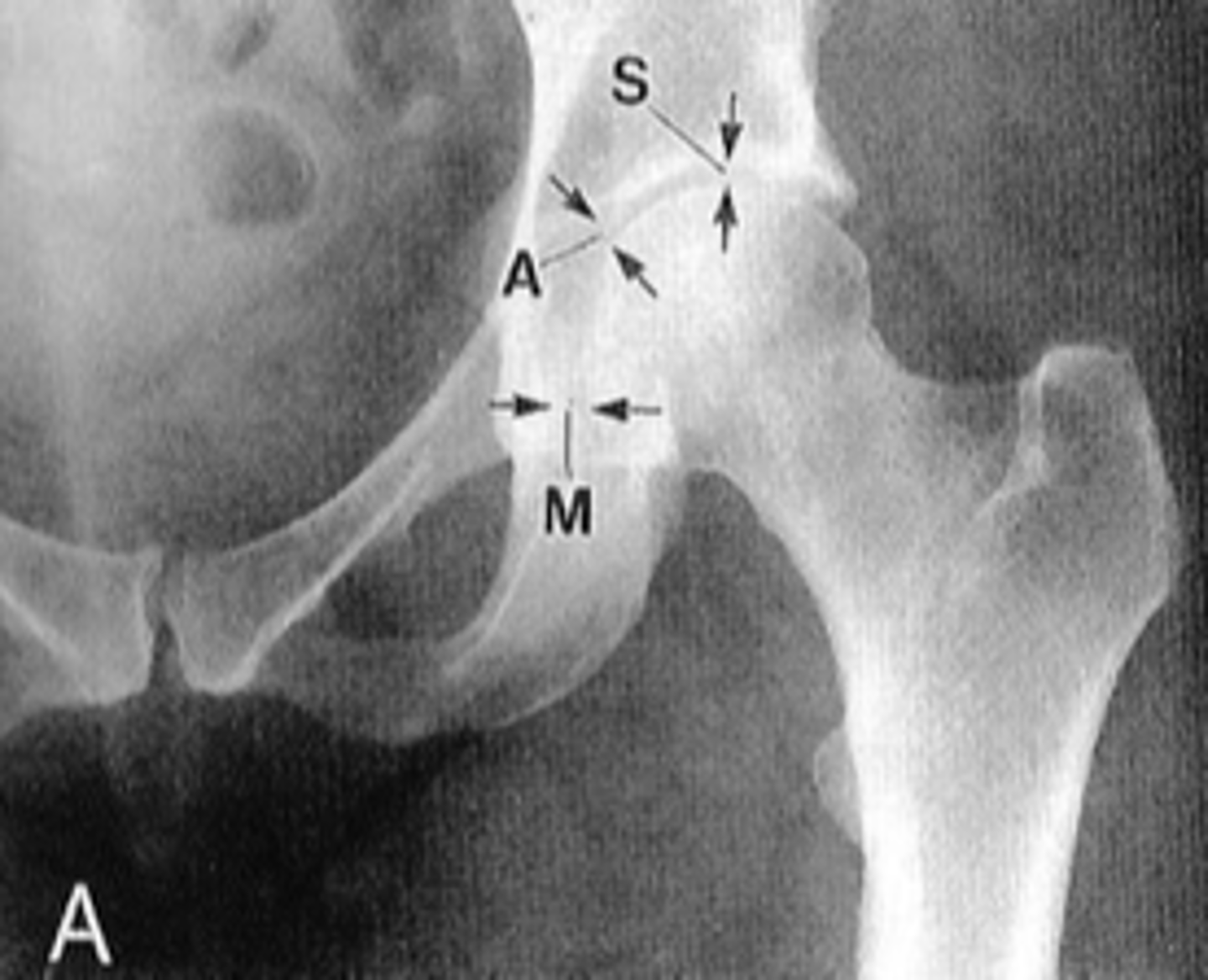
Arthritis
Clinical significance of a narrow hip joint space
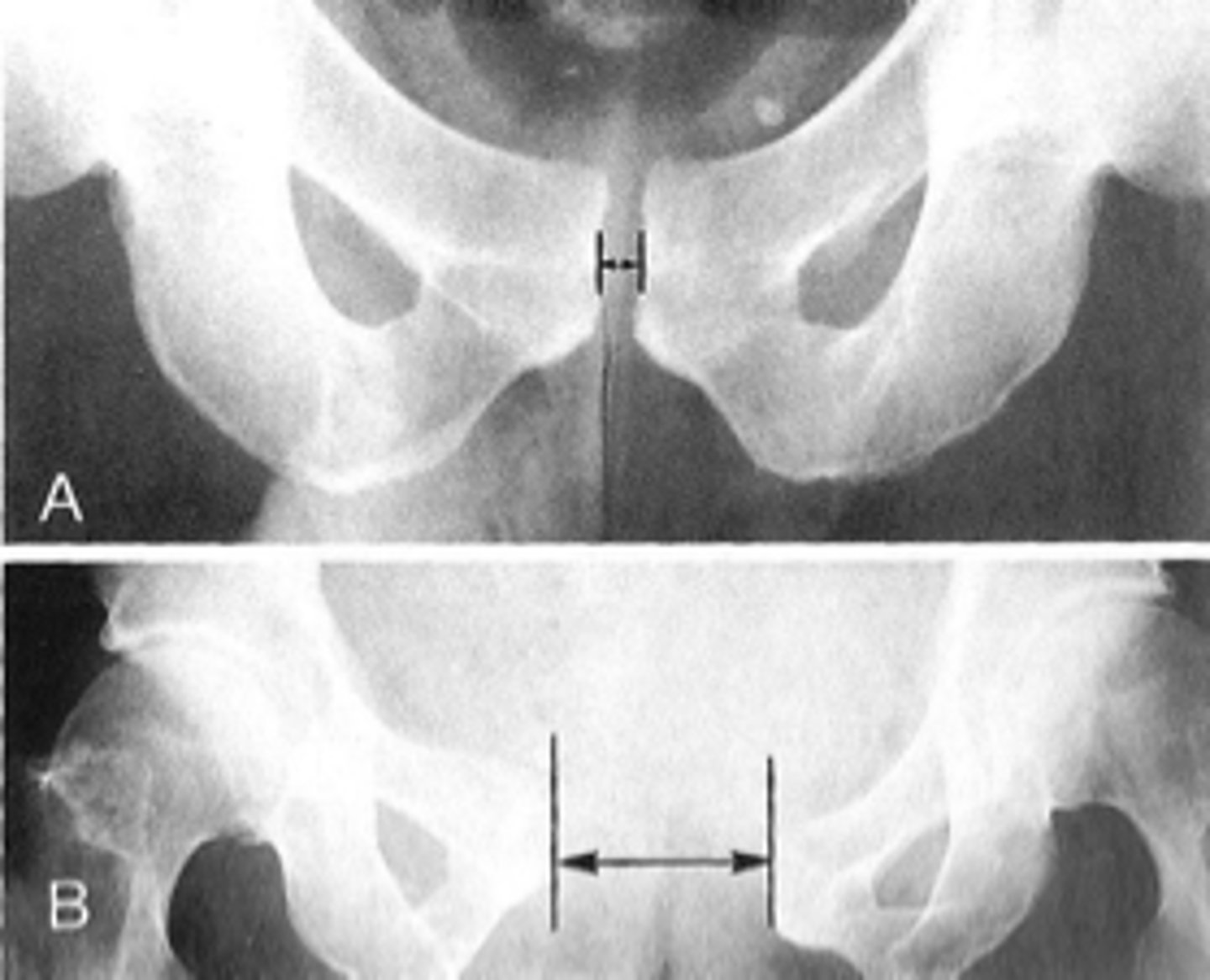
Symphysis pubis width
ID measurement
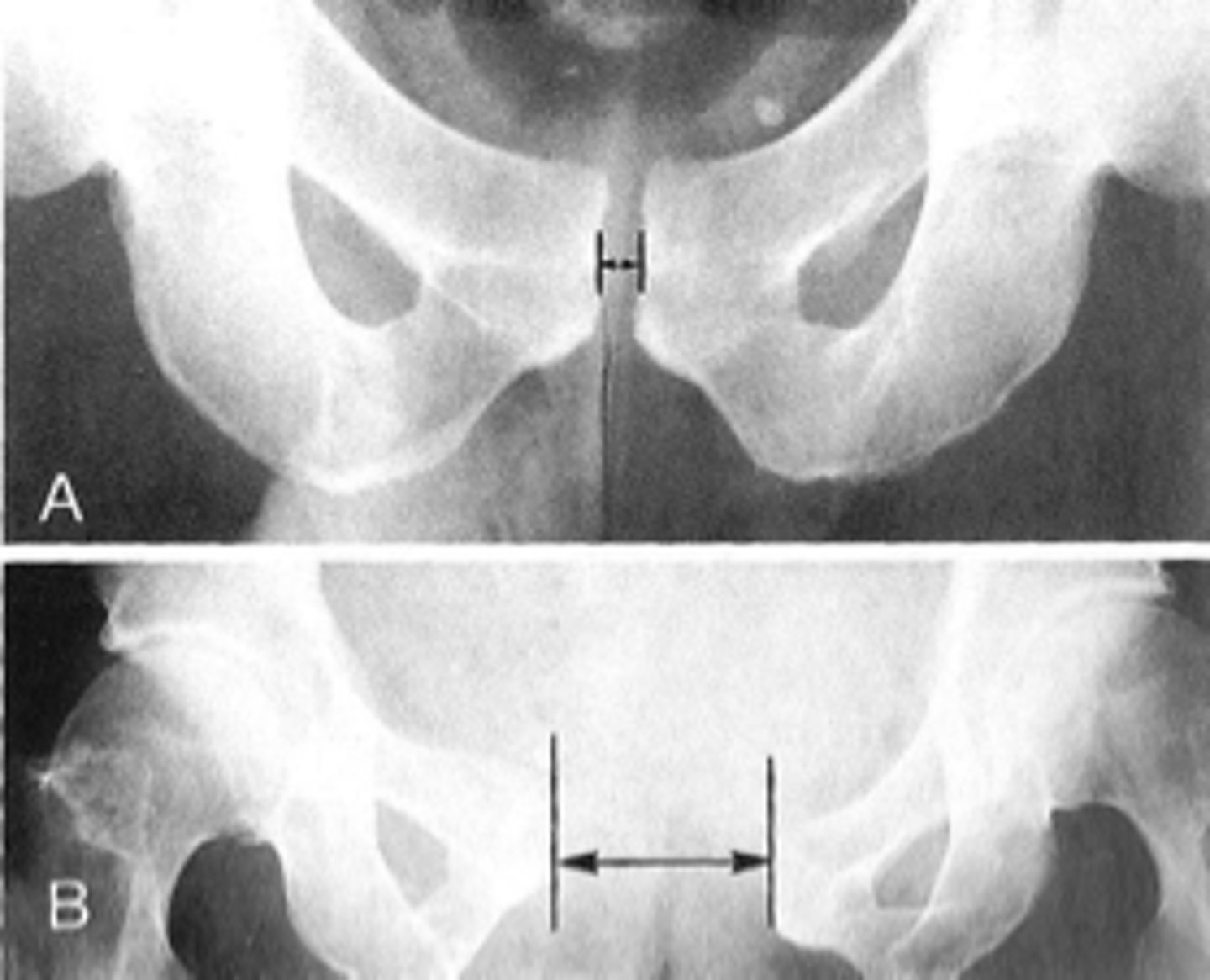
AP pelvis
What view is used to see the symphysis pubis width?
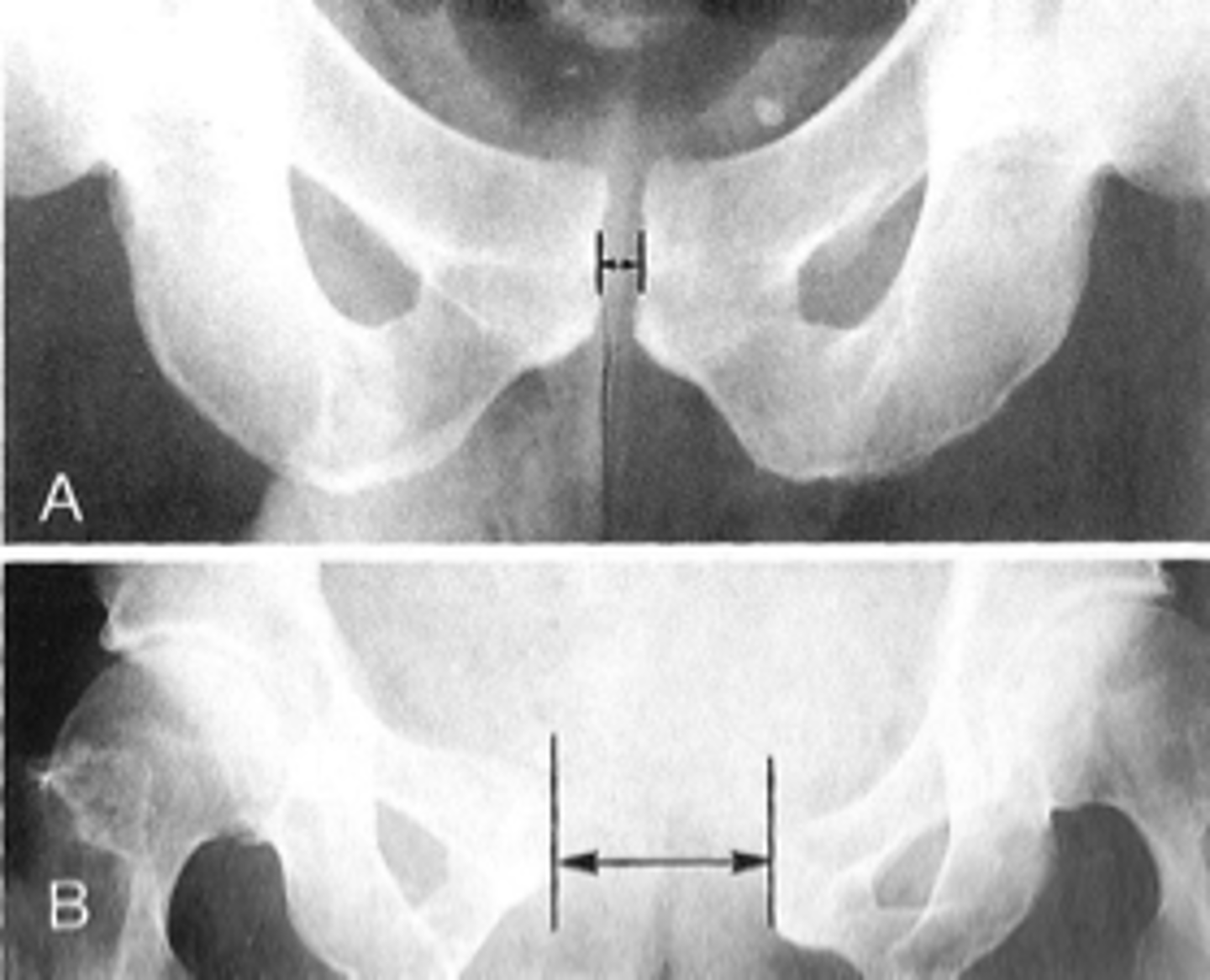
Distance between opposing articular surfaces
Symphysis pubis width landmarks
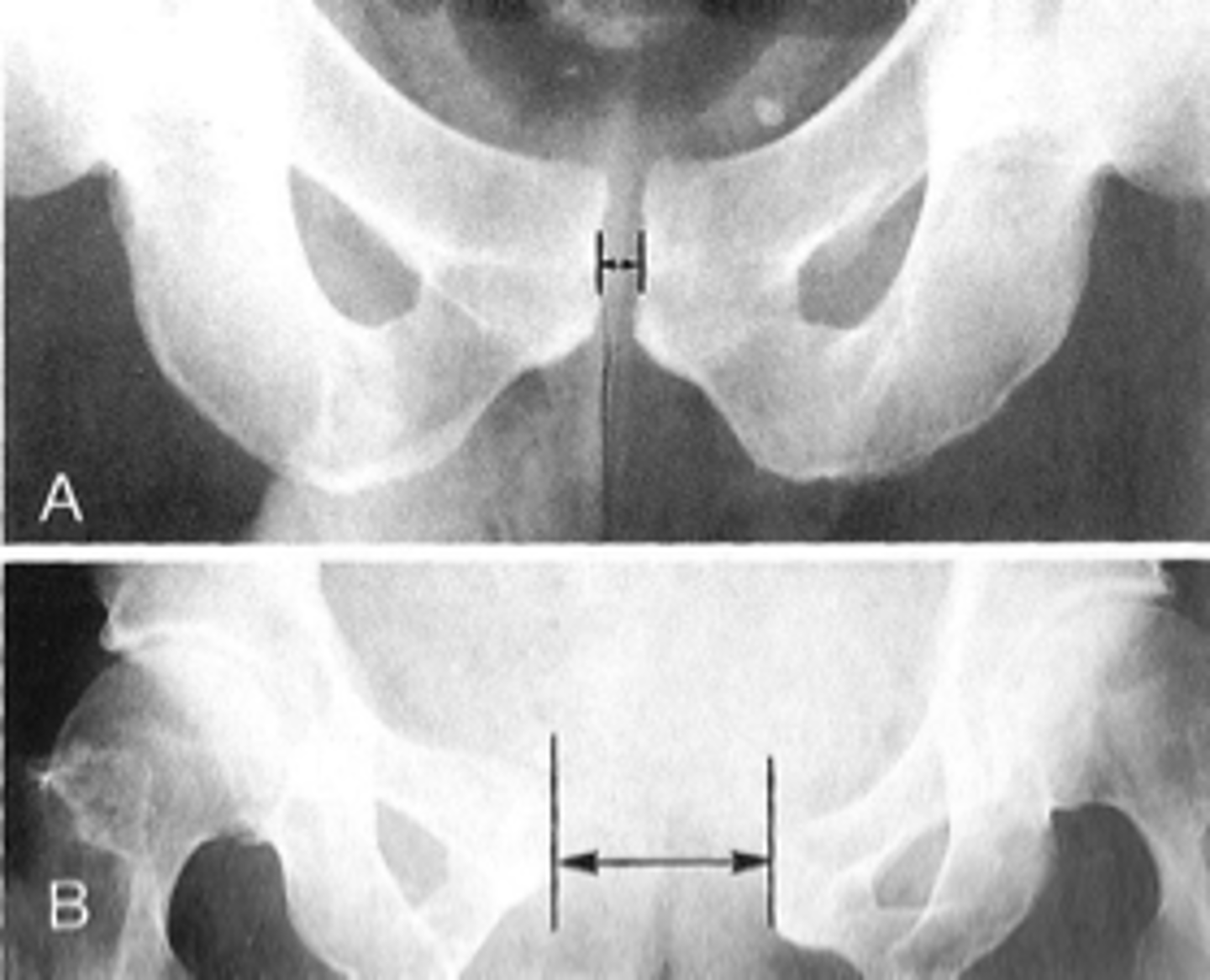
8 mm
Maximum symphysis pubis width measurement in adults
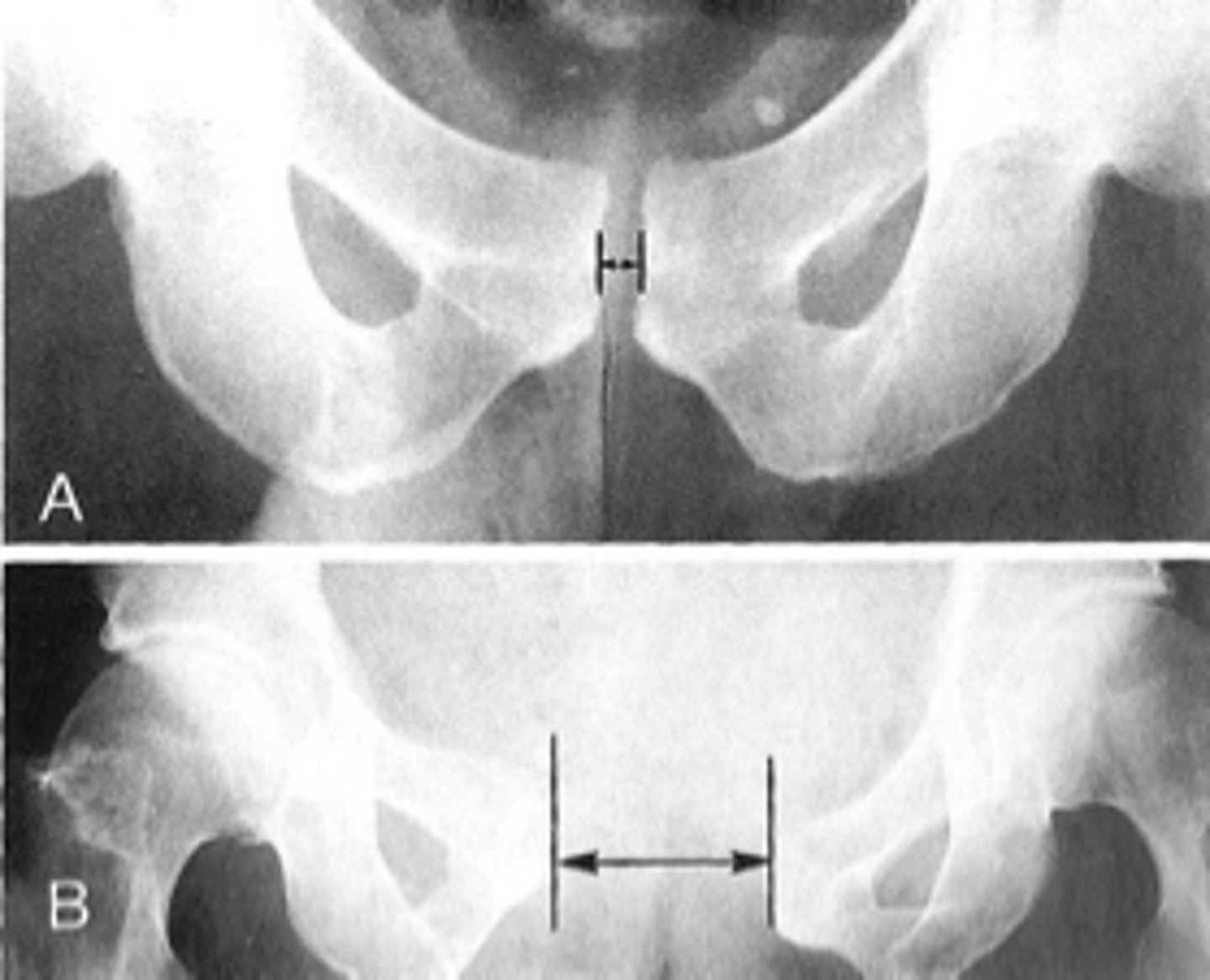
10 mm
Maximum symphysis pubis width measurement in children
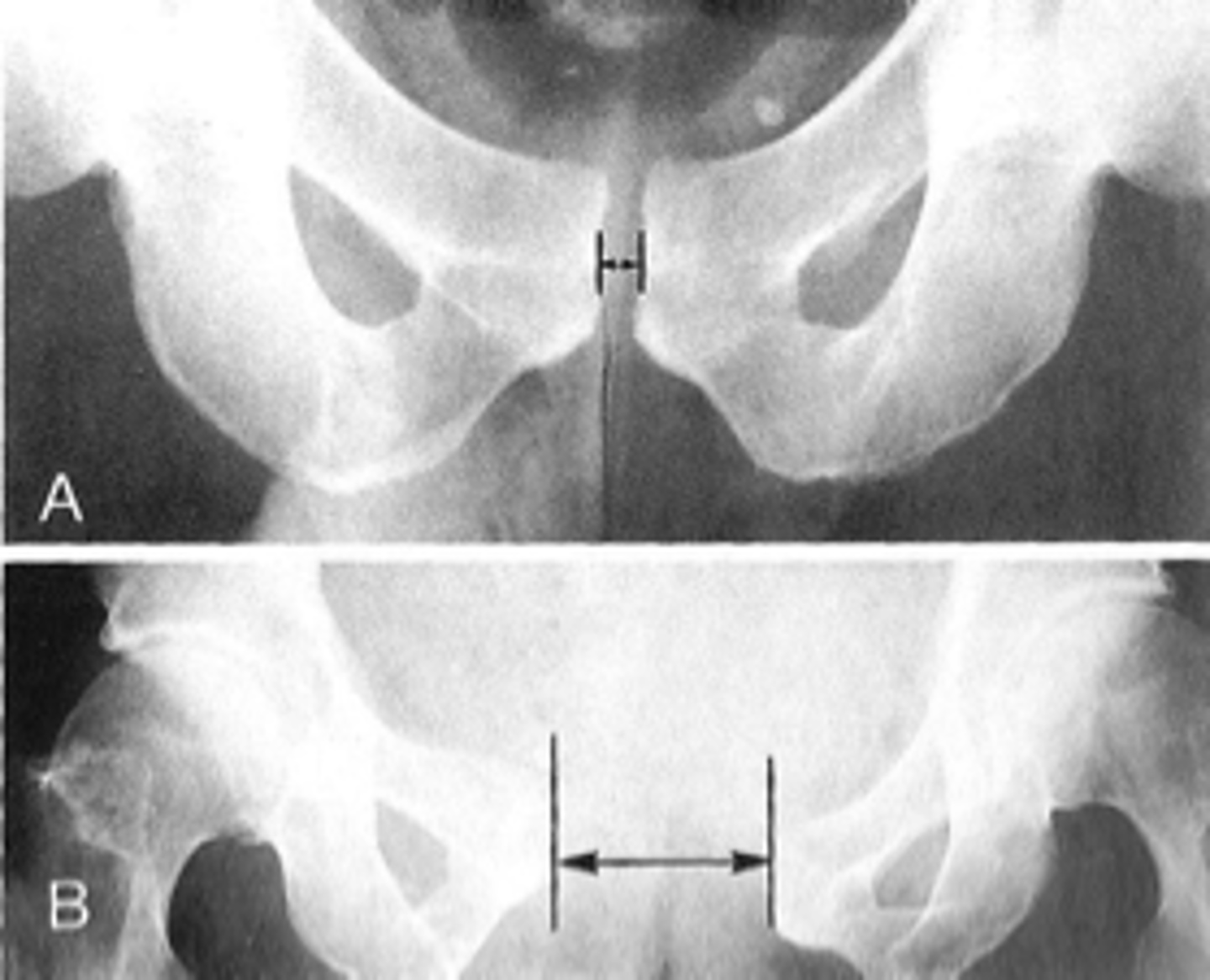
Pregnancy/postpartum
The symphysis pubis width may be larger in _____
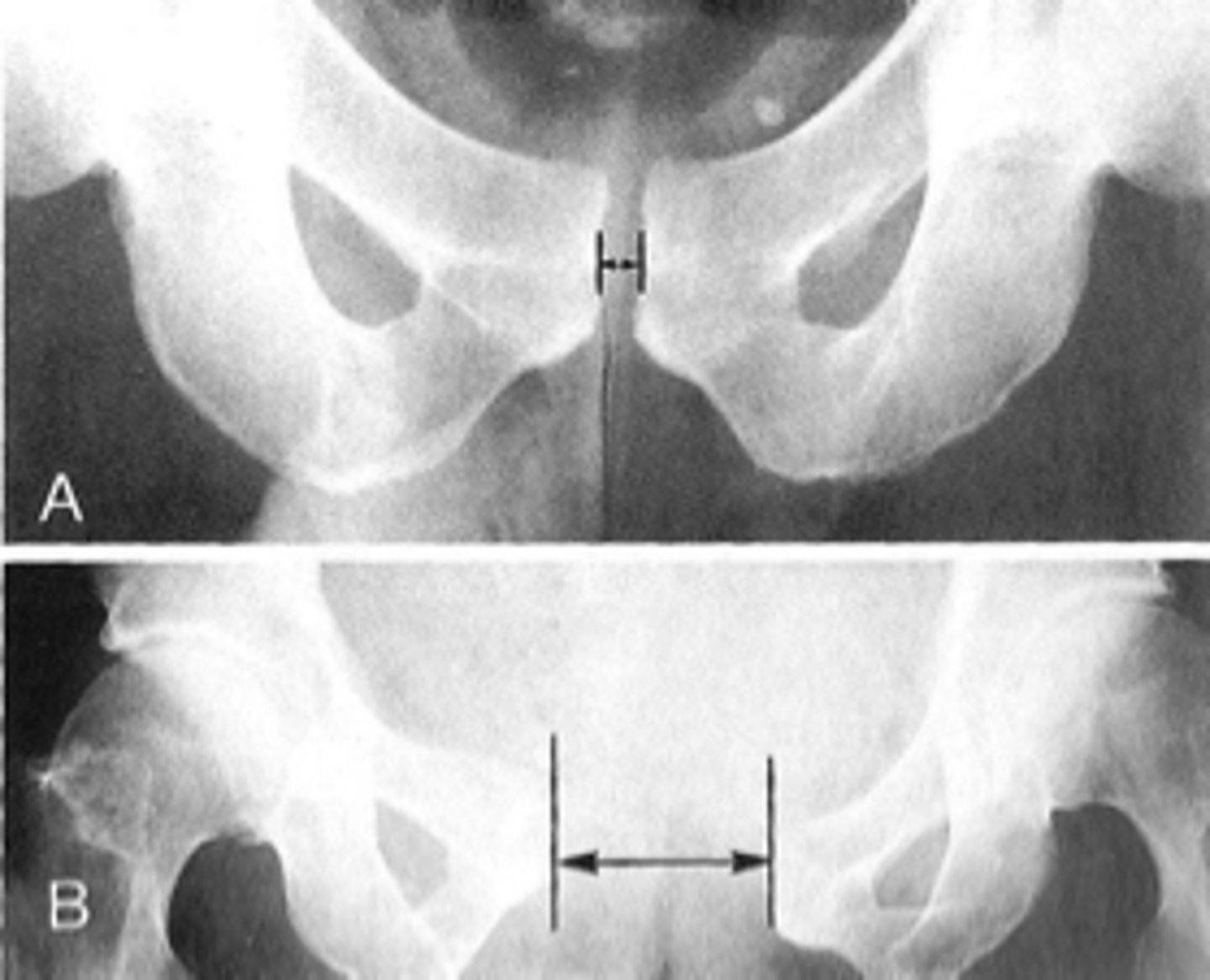
Diastasis
Clinical significance of a widened symphysis pubis
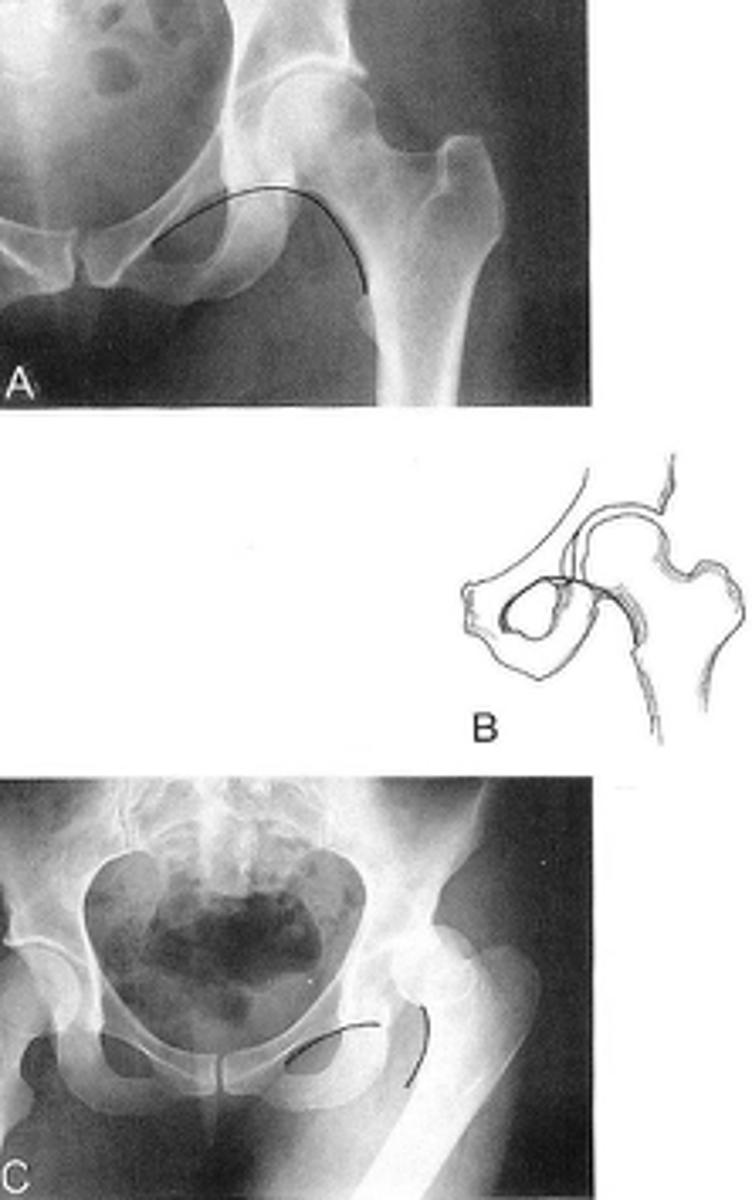
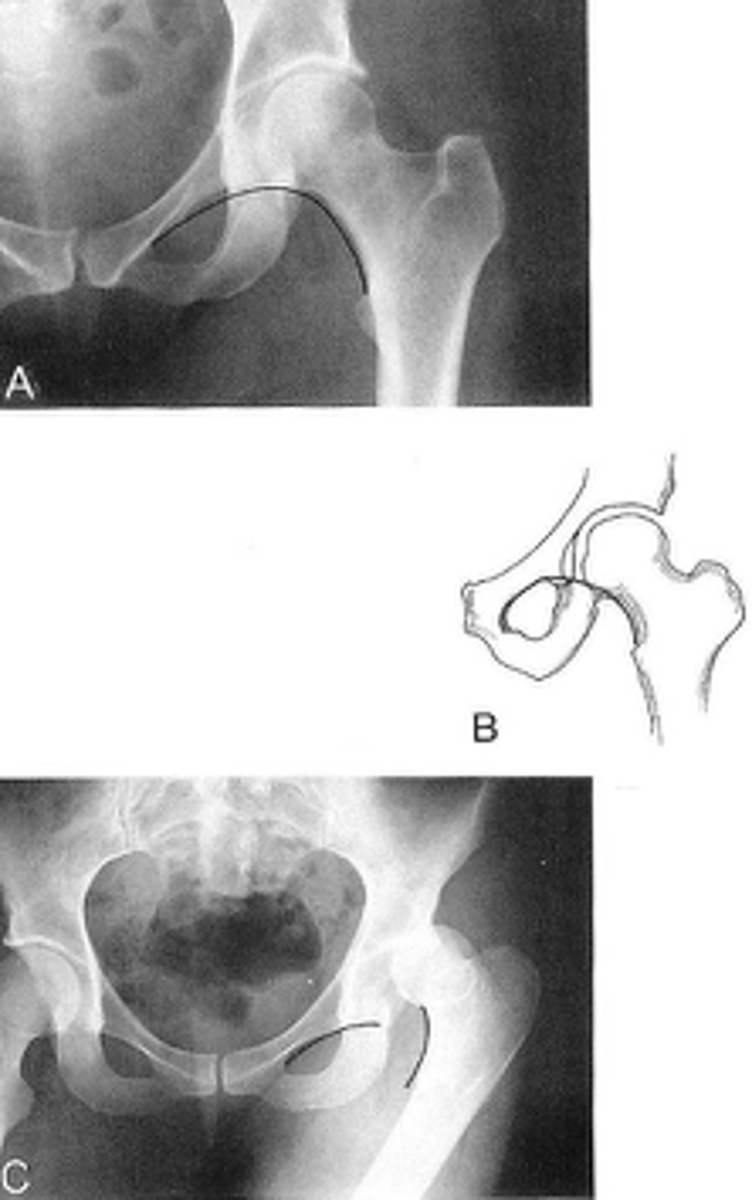
Shenton's line
ID measurement
- AP hip
- AP pelvis
What views are used to see Shenton's line?
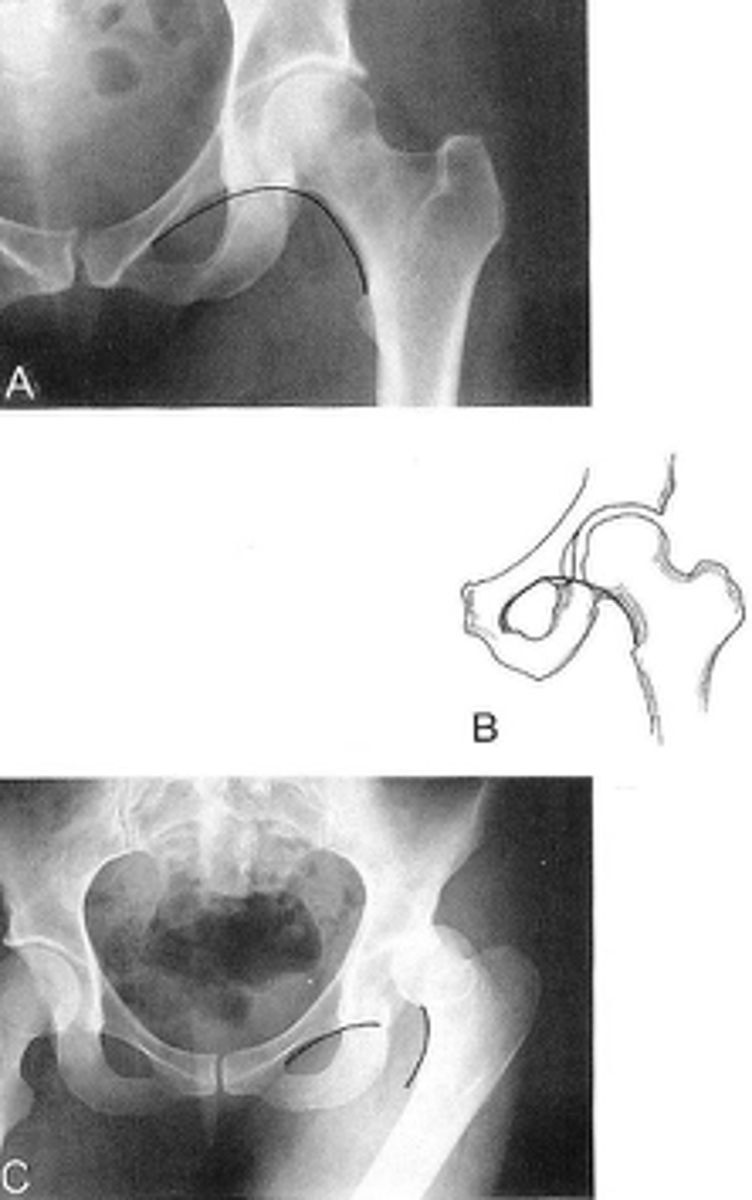
- Smooth arc along femoral neck
- Obturator foramen
Shenton's line landmarks
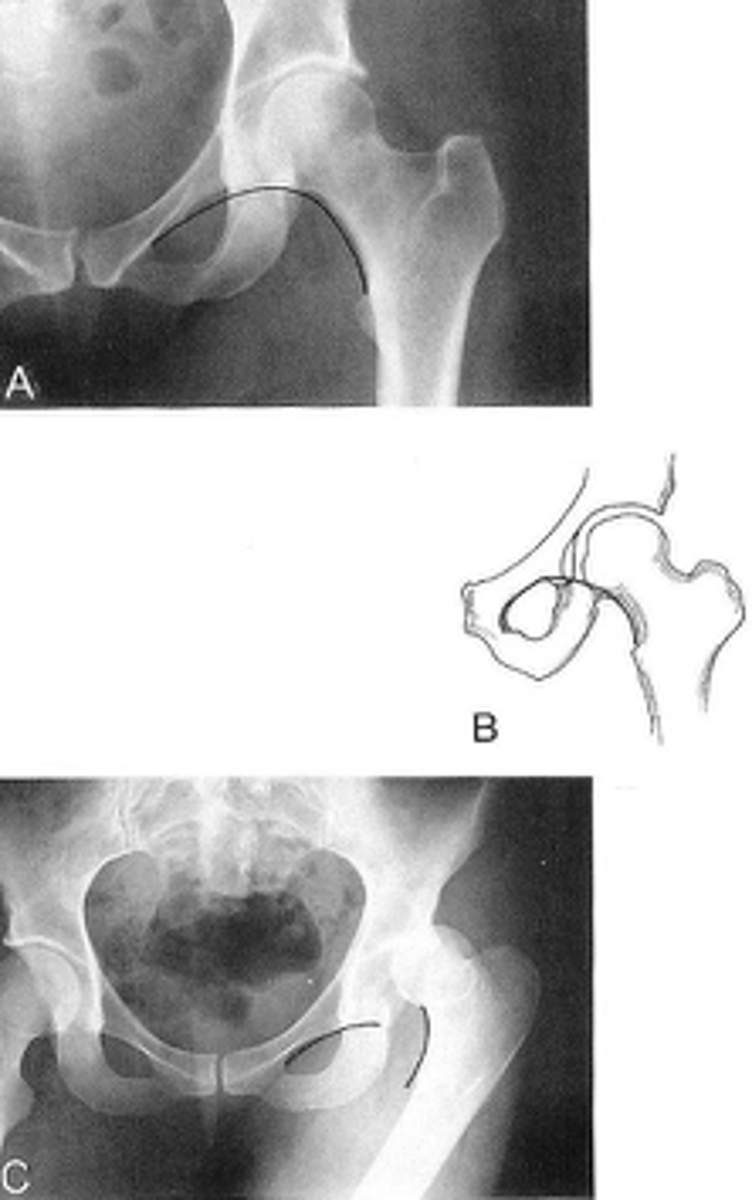
Continuous and smooth
Shenton's line normal measurements
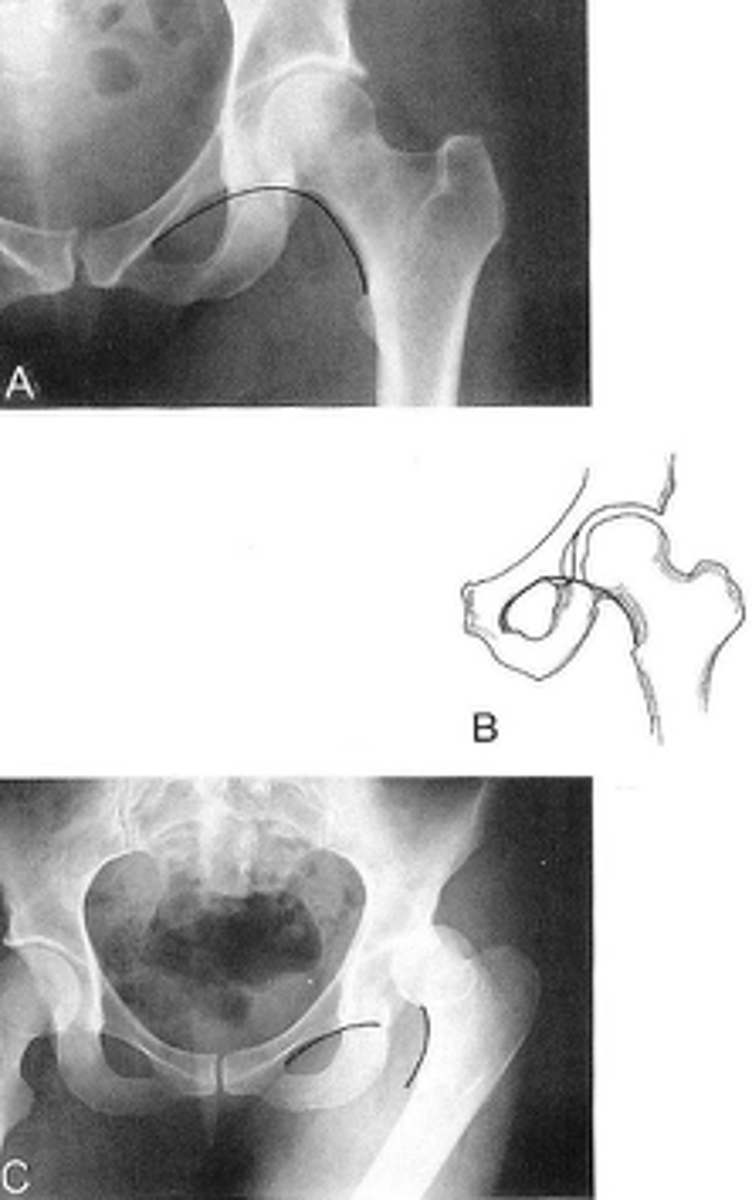
- Hip dislocation
- Femoral neck fracture
- Slipped epiphysis
Clinical significance of Shenton's line
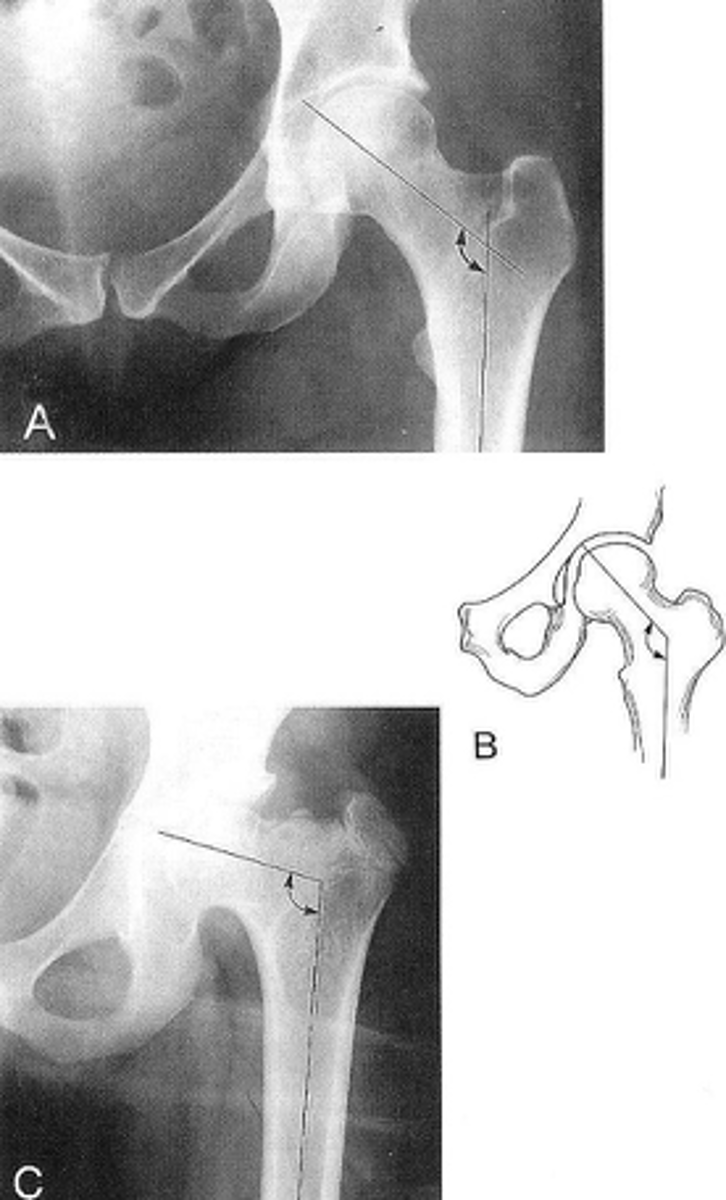
Femoral angle
ID measurement
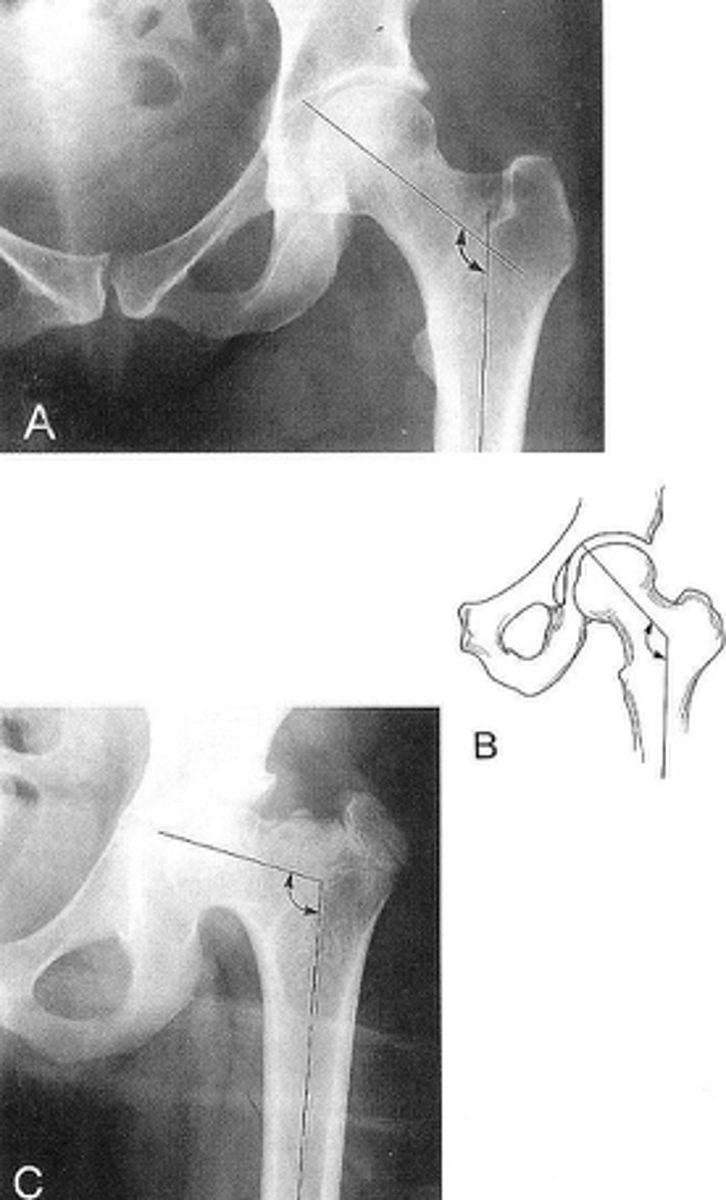
- AP pelvis
- AP hip
What views are used to measure the femoral angle?
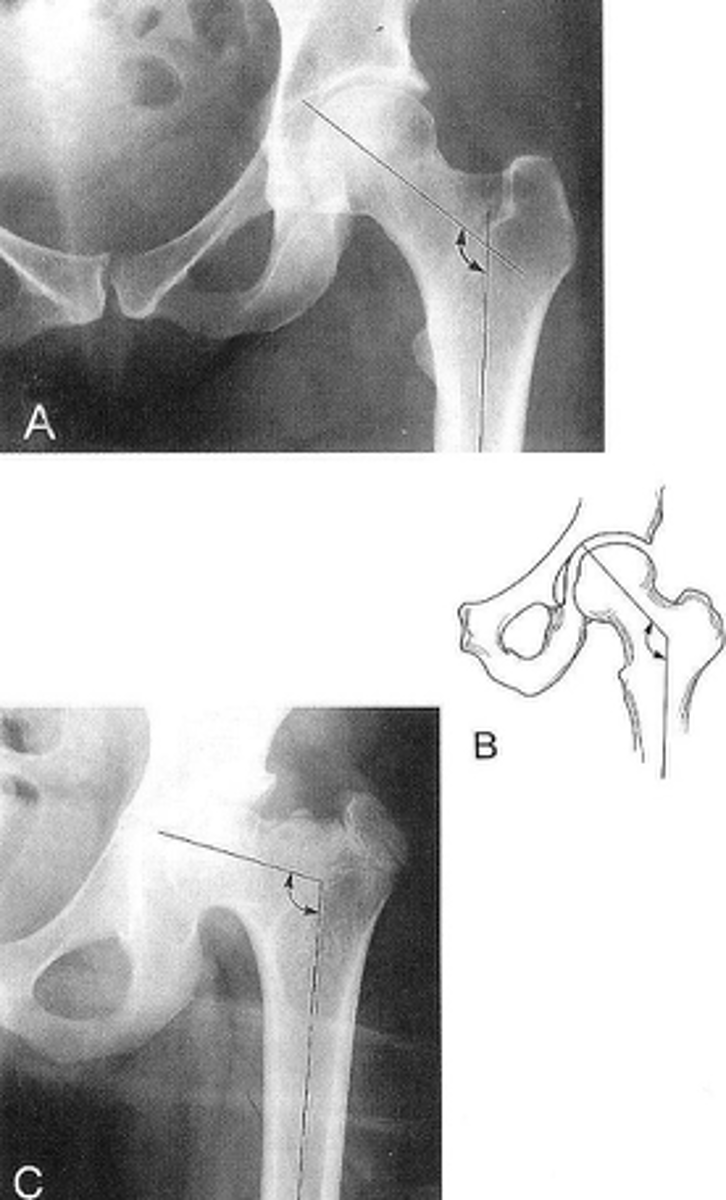
- Mid-axis of femoral shaft
- Mid-axis of femoral neck
- Intervening angle
Femoral angle landmarks
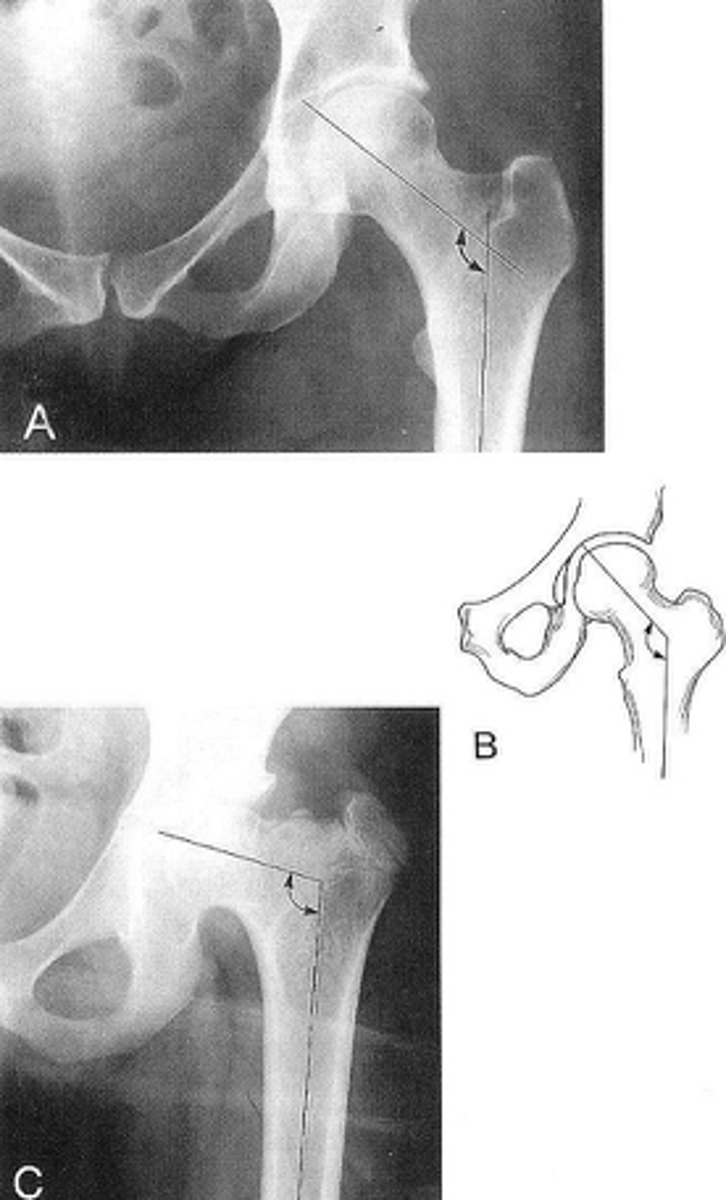
120-130˚
Normal femoral angle measurement
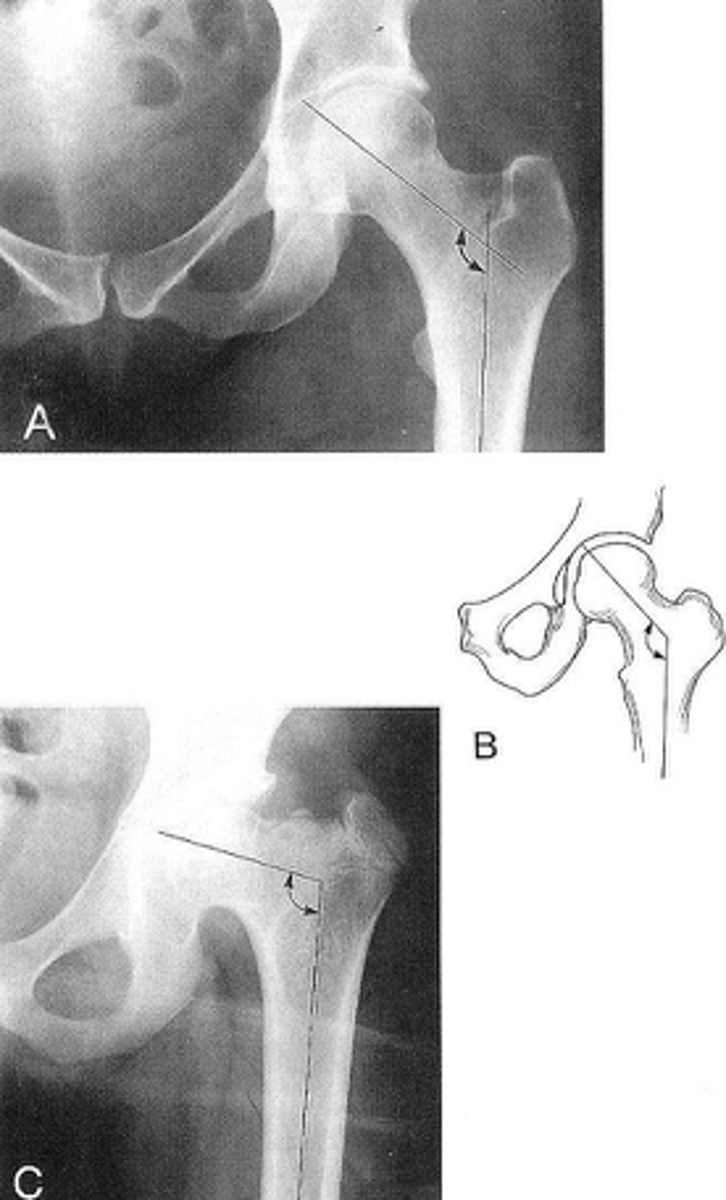
Coxa vara
Femoral angle <120˚
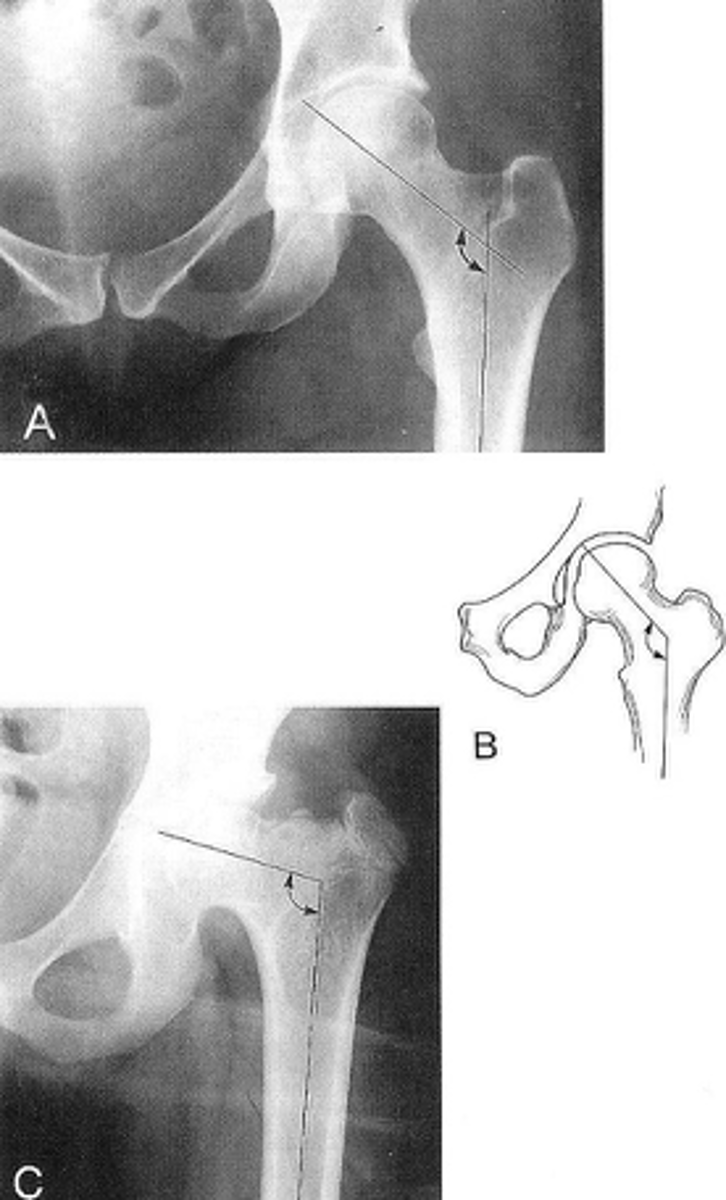
Coxa valga
Femoral angle >130˚
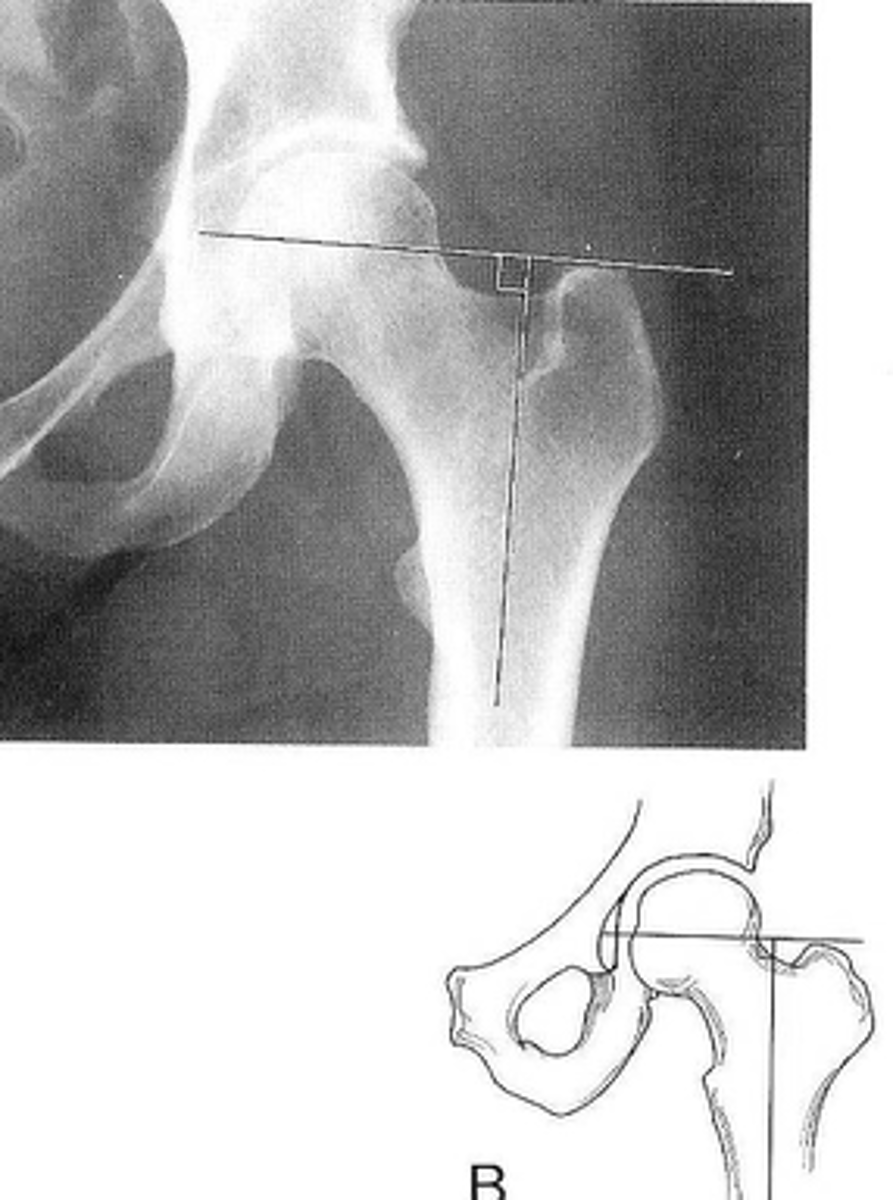
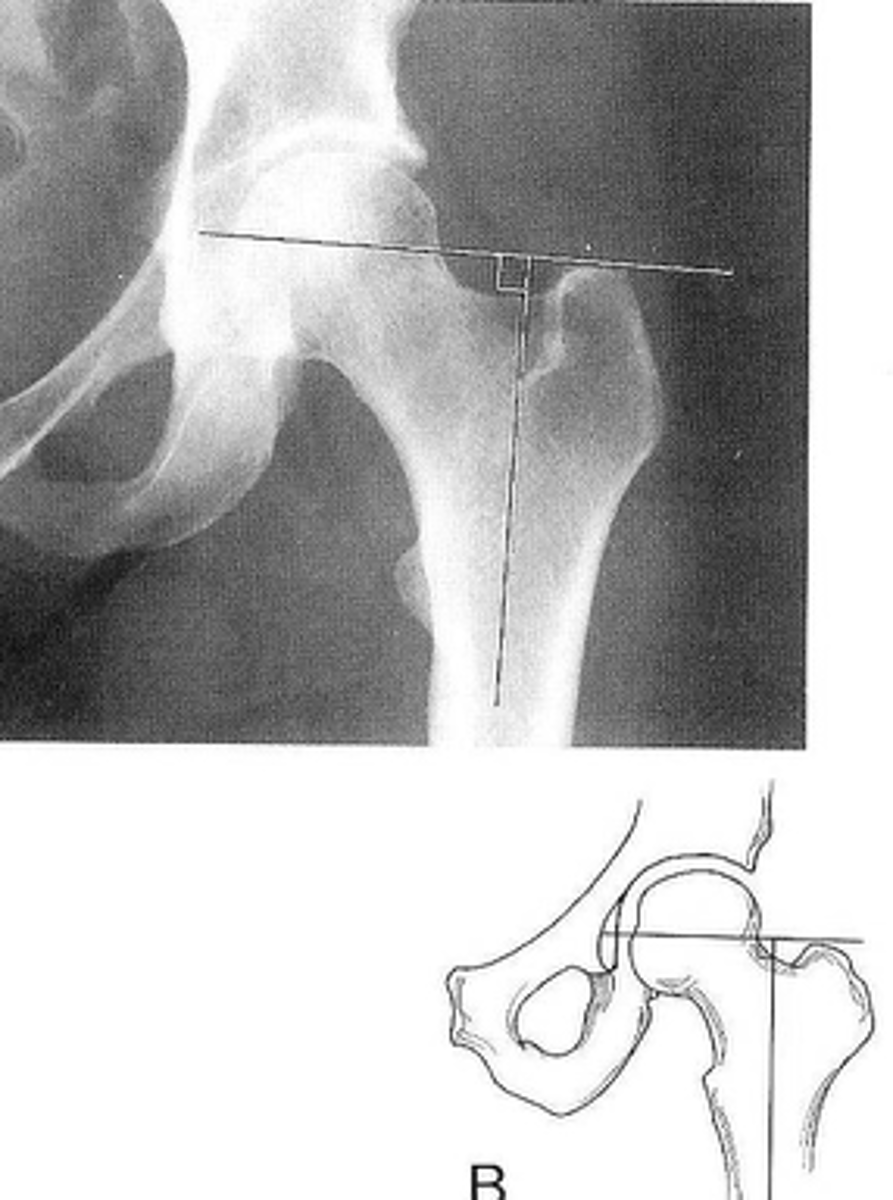
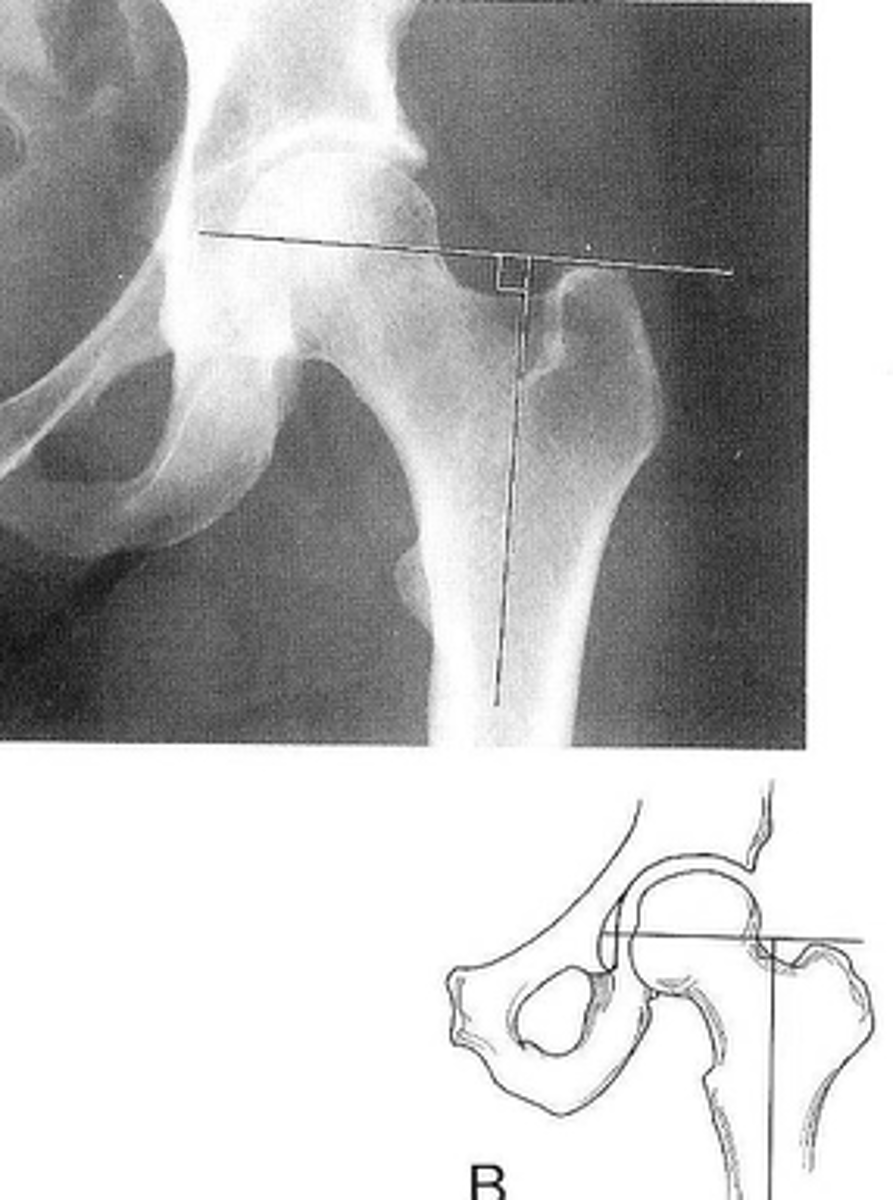
Skinner's line
ID measurement
- AP hip
- AP pelvis
What views are used to see Skinner's line?
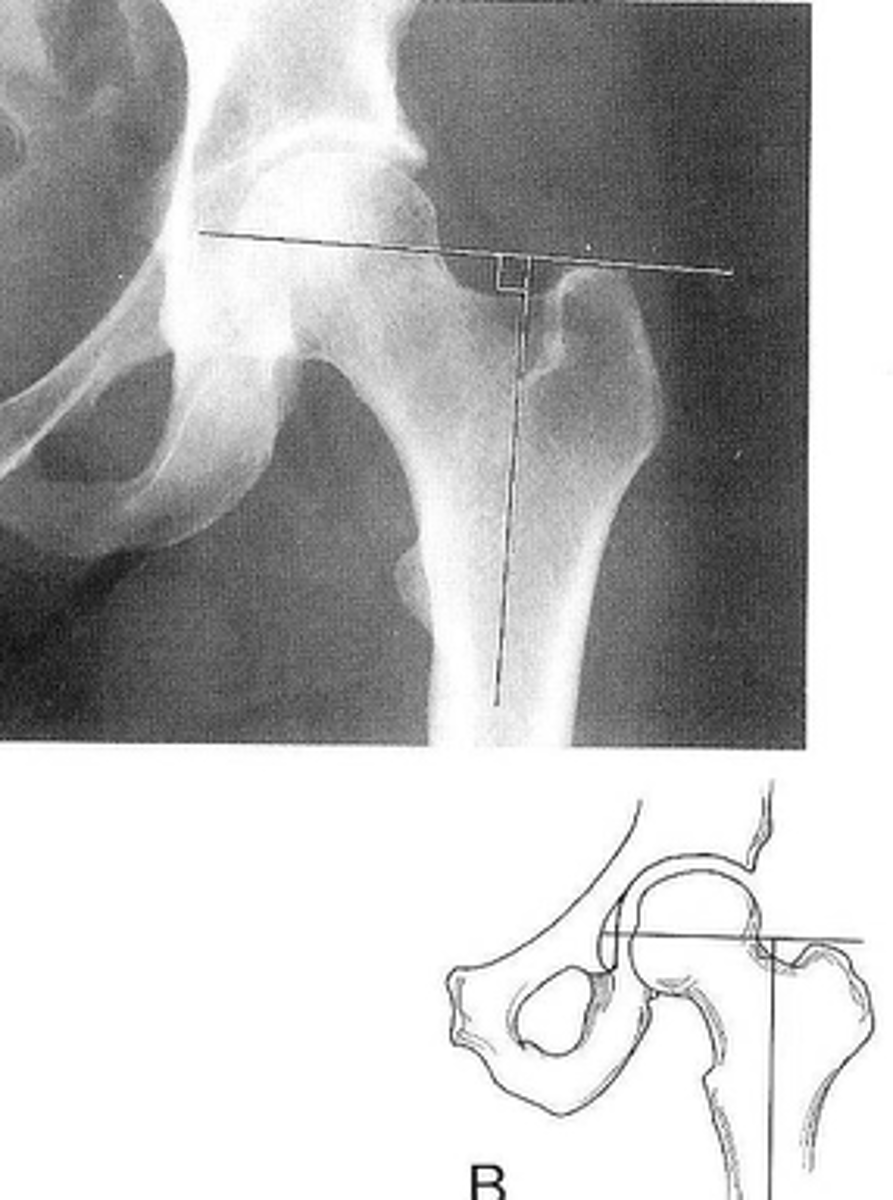
- Mid-axis of femoral shaft
- Right angle tangent to tip of greater trochanter
Skinner's line landmarks
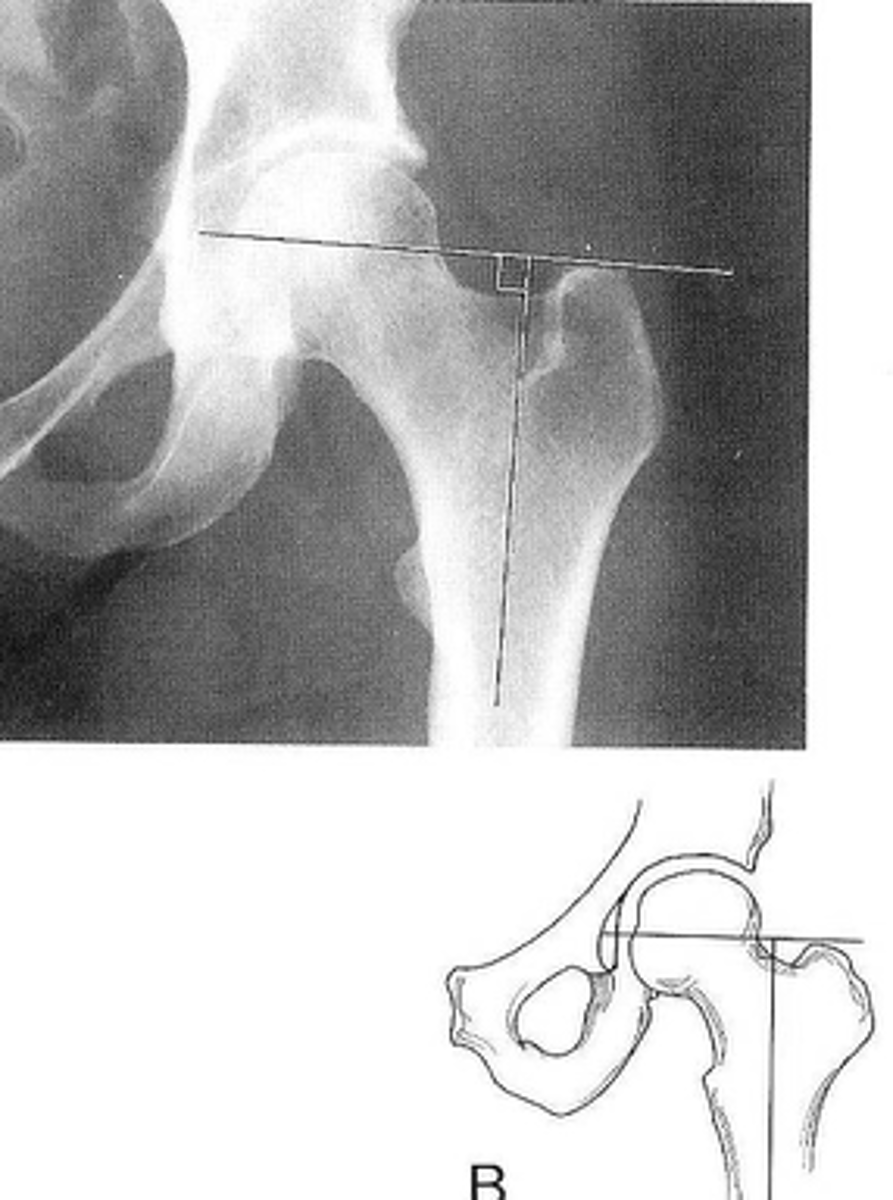
Fovea capitis should lie above or at level of trochanteric line
Skinner's line normal measurement
Fracture or other causes of coxa vara
Clinical significance of Skinner's line
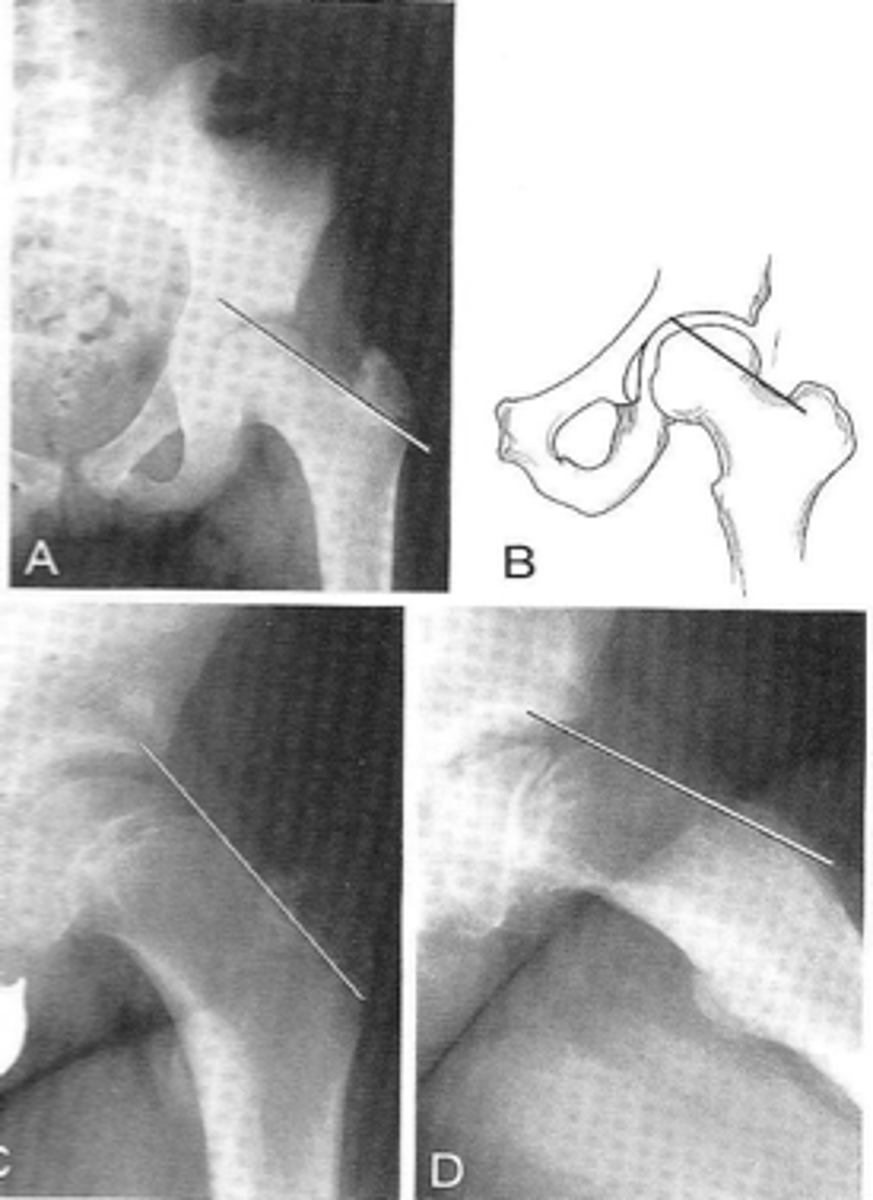
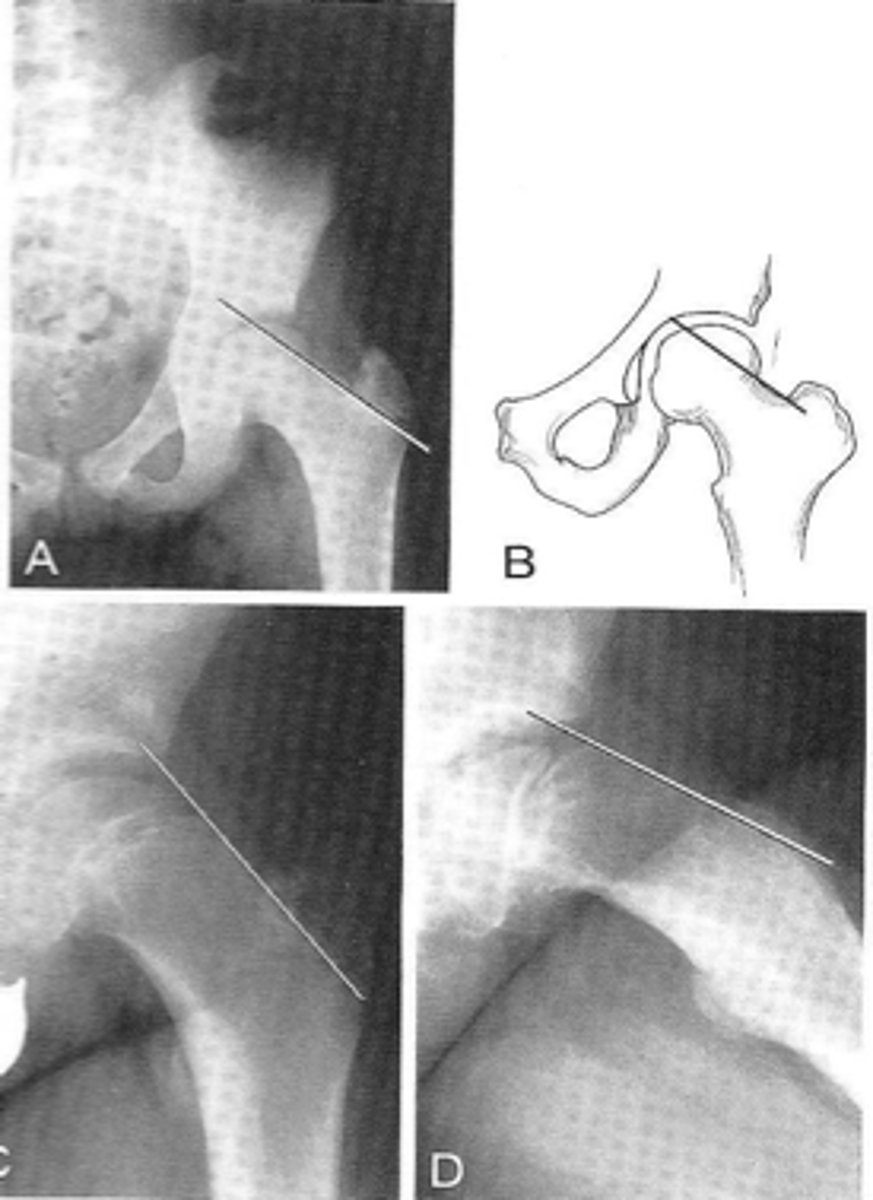
Klein's line
ID measurement
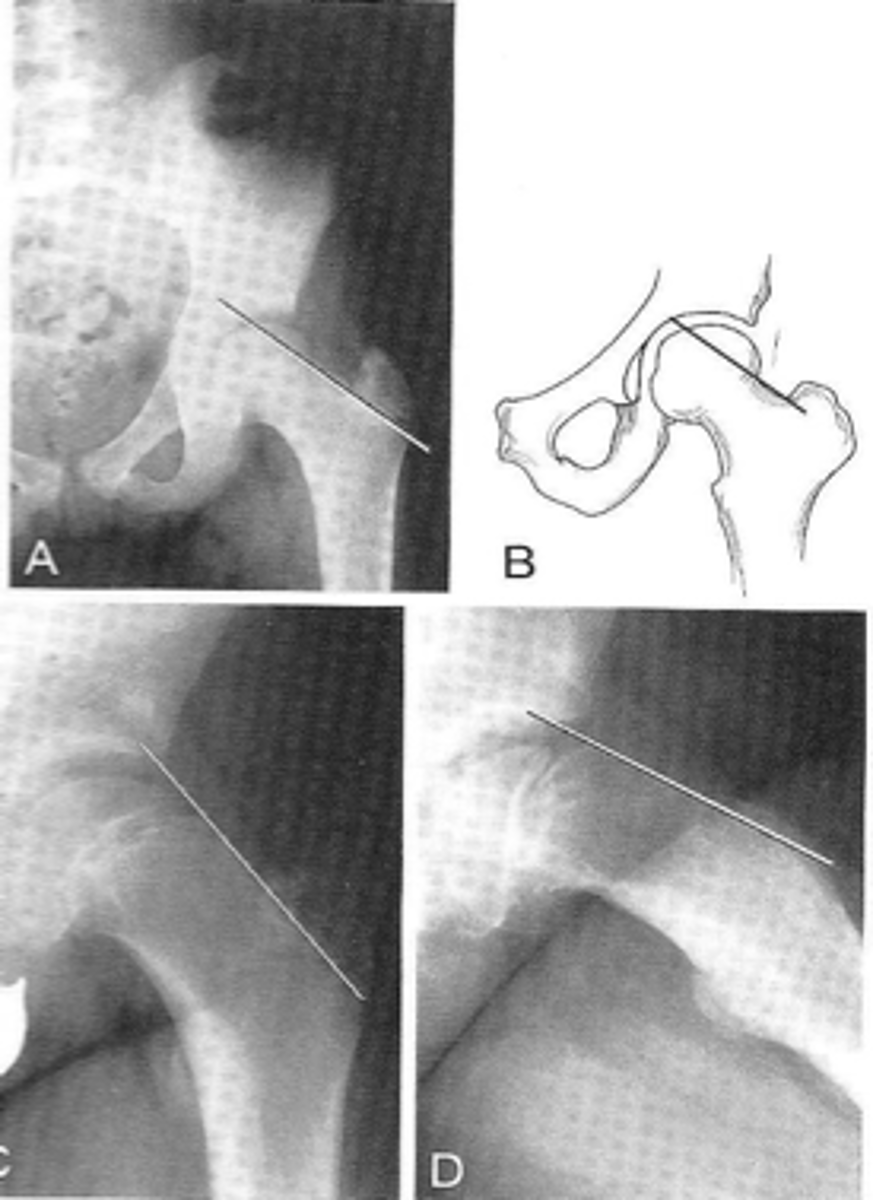
- AP pelvis
- AP hip
What views are used to see Klein's line?
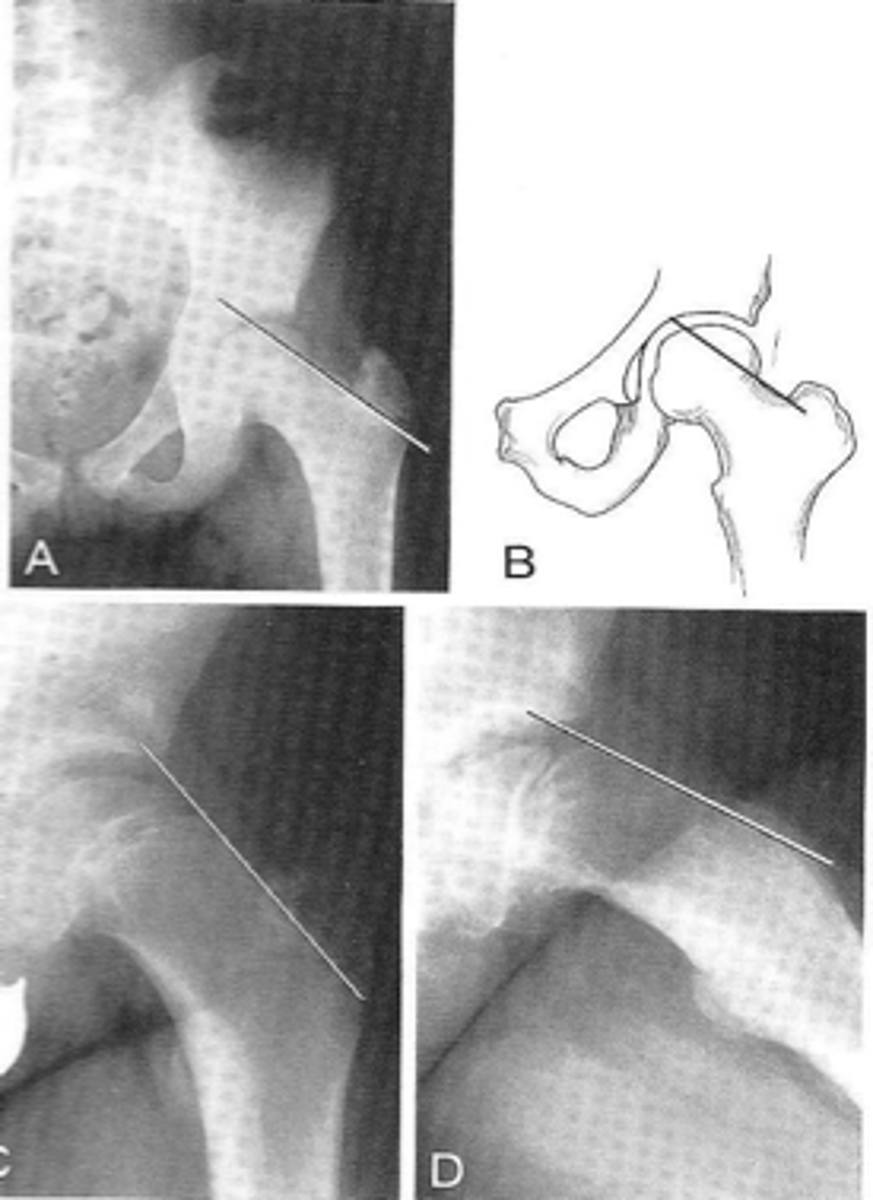
Line along femoral neck
Klein's line landmarks
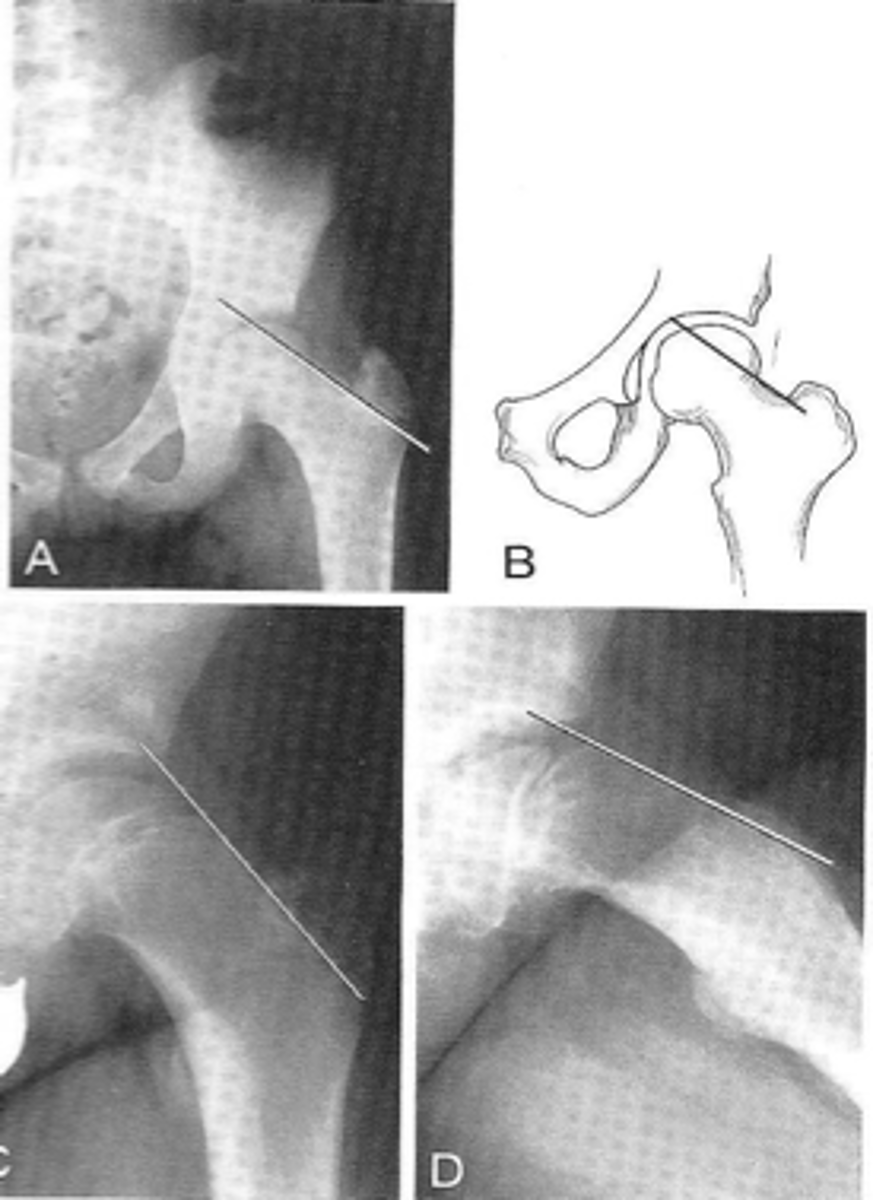
Line should intersect portion of femoral head
Klein's line normal measurement
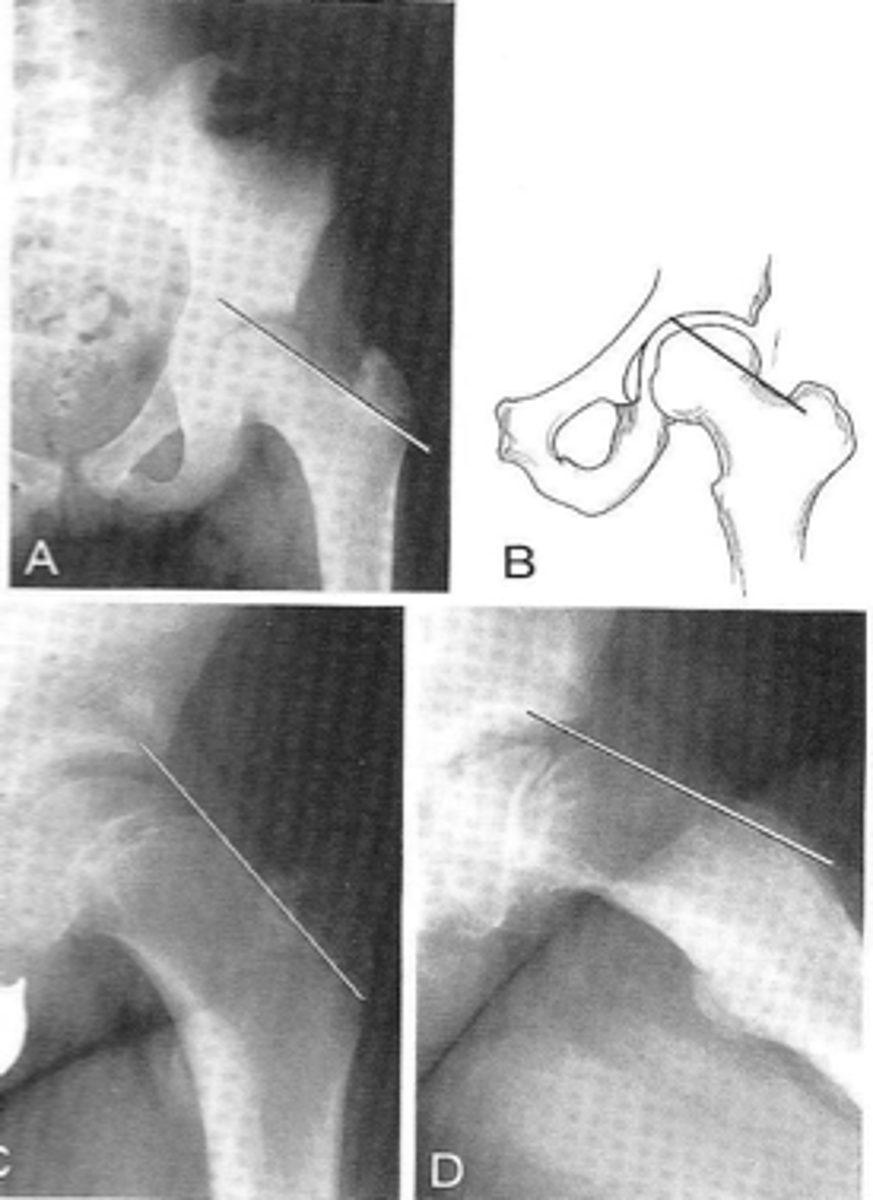
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Clinical significance of Klein's line
Growth plate
A slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a _____ fracture
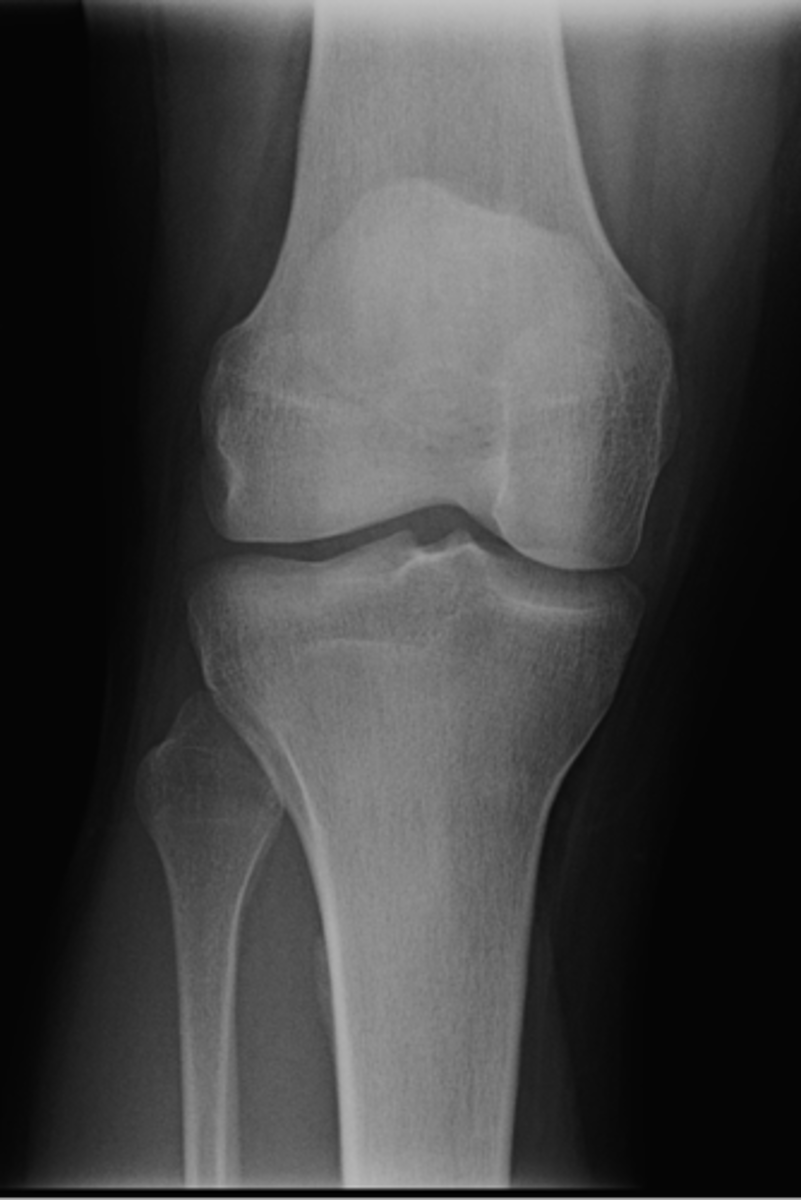
- AP knee
- Lateral knee
- Tunnel (intercondylar) knee
State the standard knee projections
AP knee
ID standard knee projection
Lateral knee
ID standard knee projection
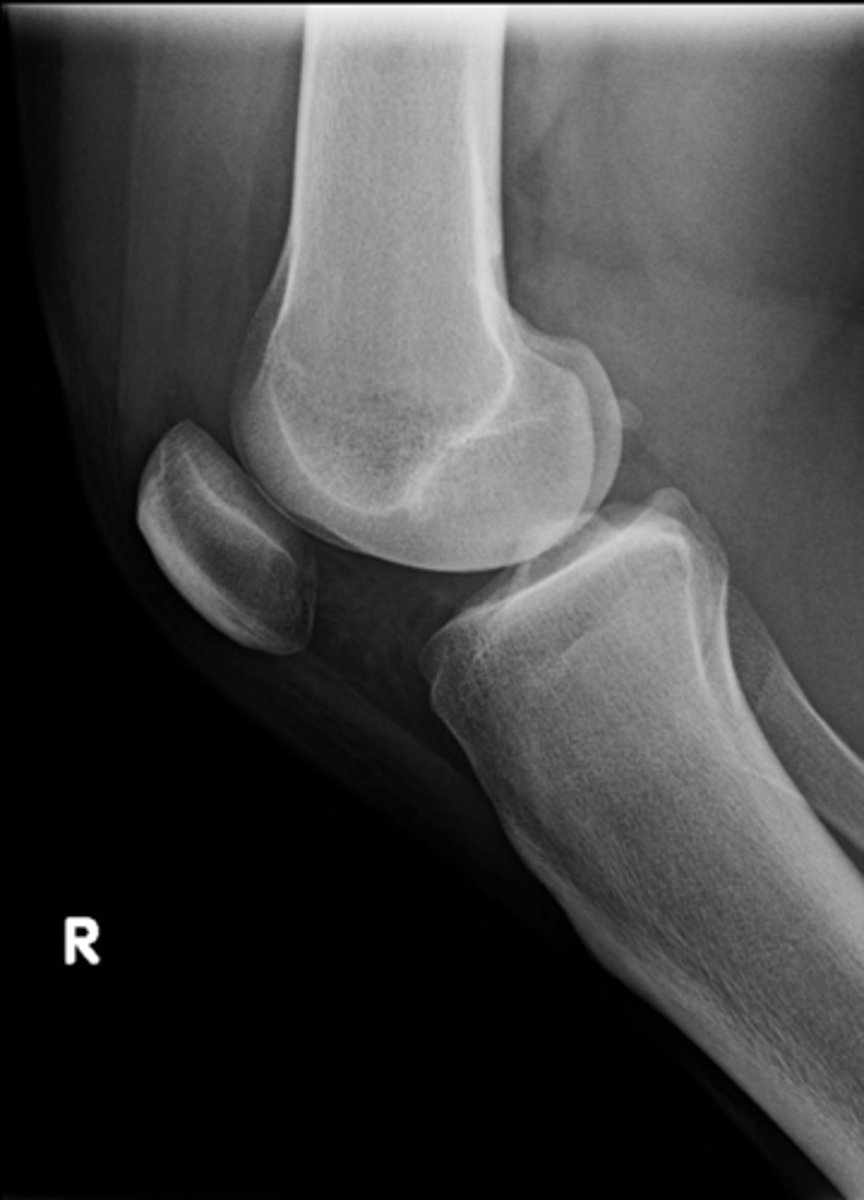
Flexion
Lateral knee projections are generally taken with _____
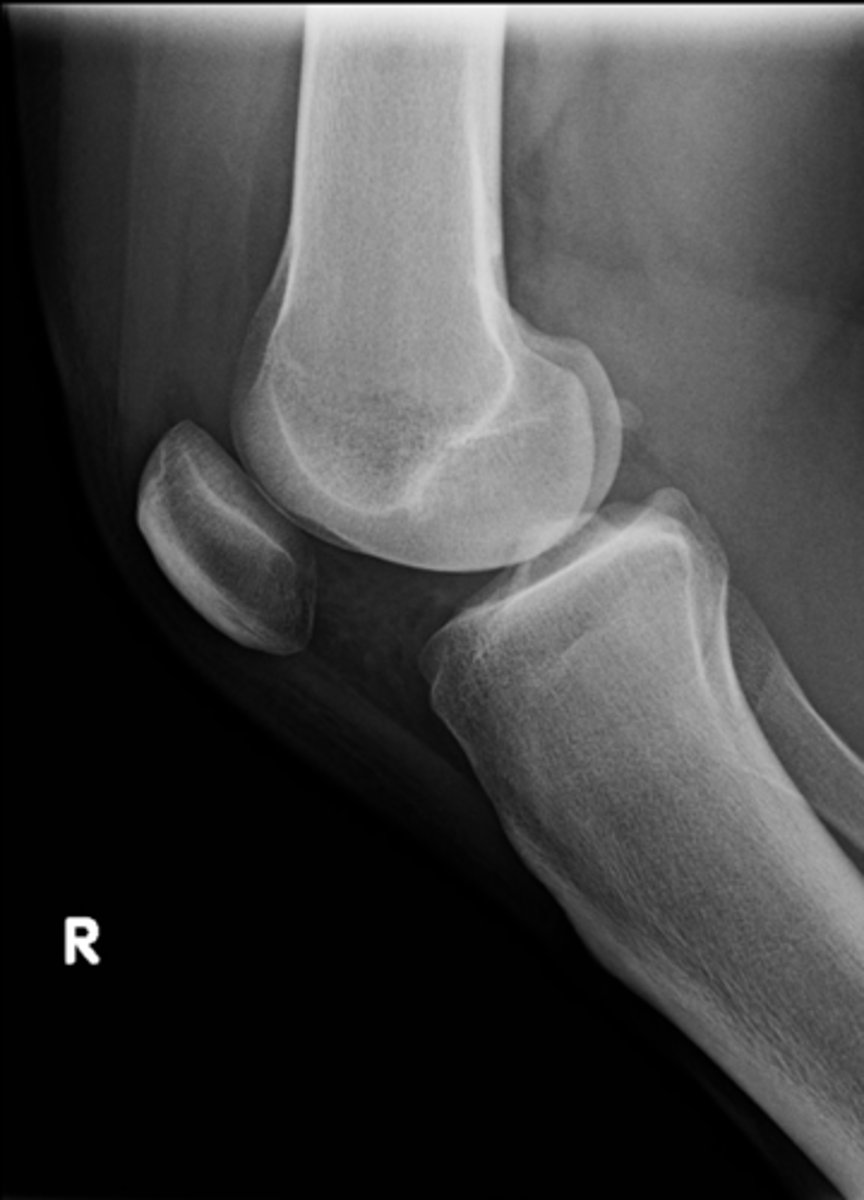
Tunnel (intercondylar) knee
ID standard knee projection
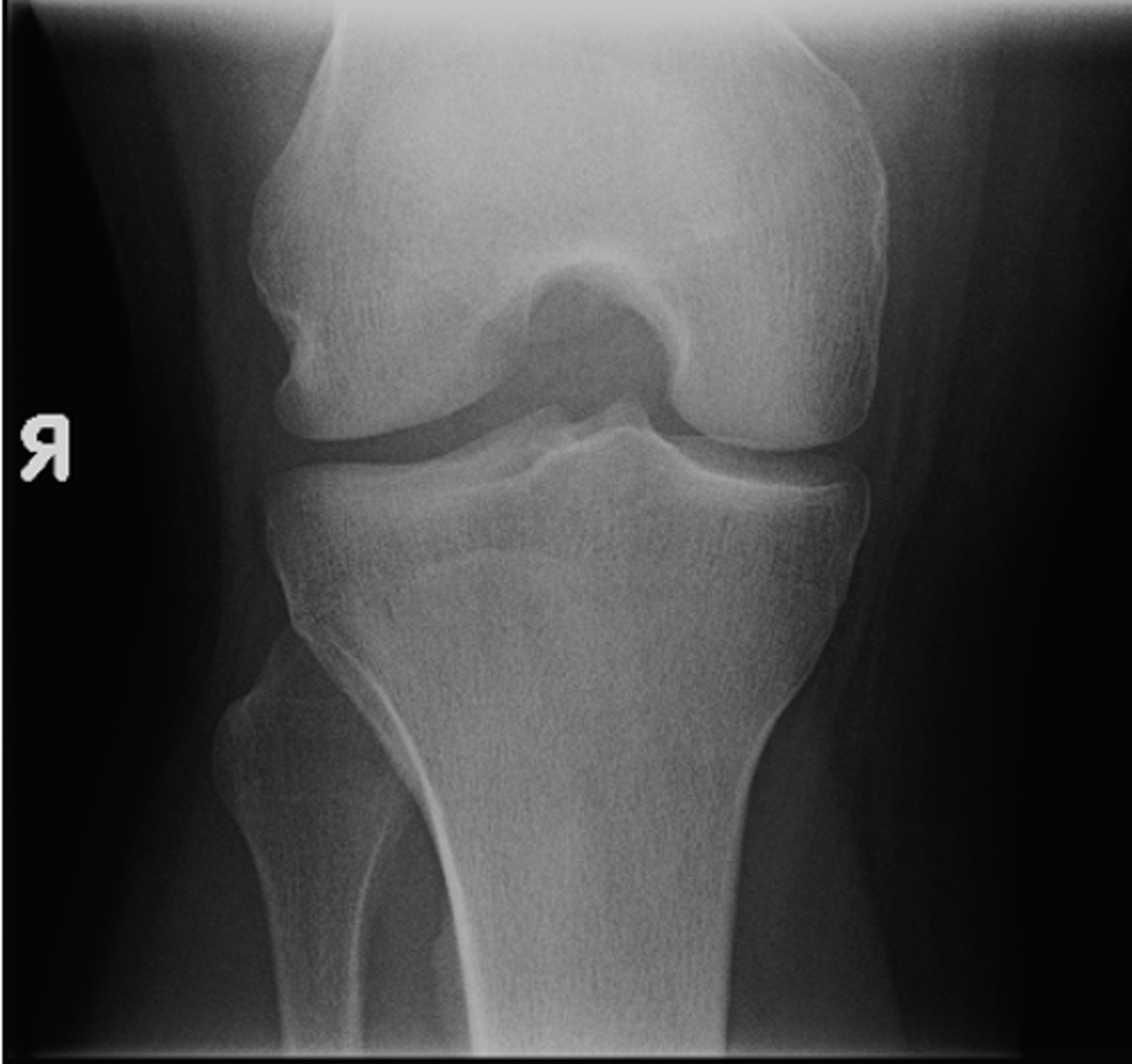
- Sunrise (tangential) knee
- Internal oblique knee
- External oblique knee
State the supplementary knee projections
Sunrise (tangential) knee
ID supplementary knee projection
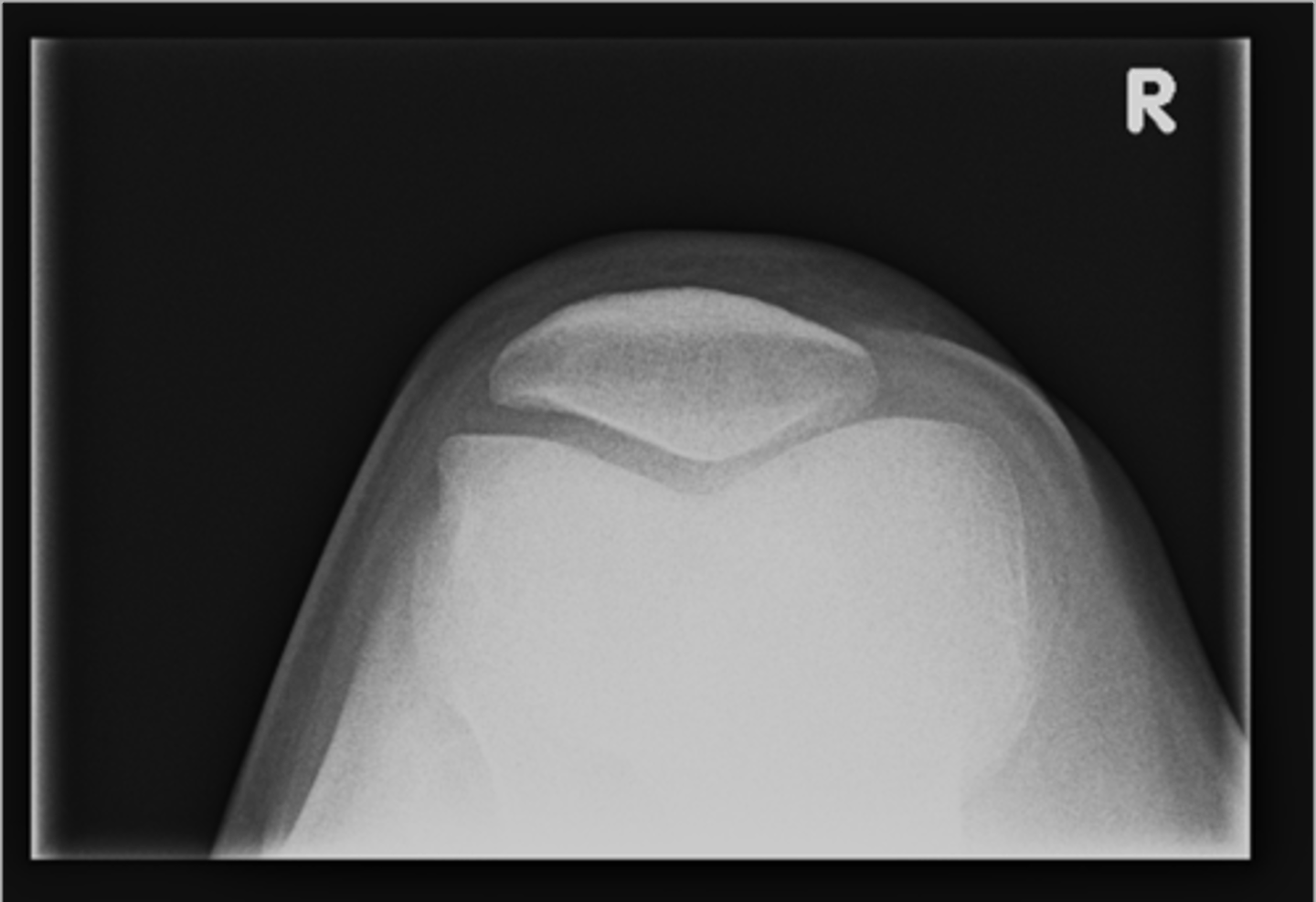
Patellofemoral joints
Sunrise knee projections help see the _____
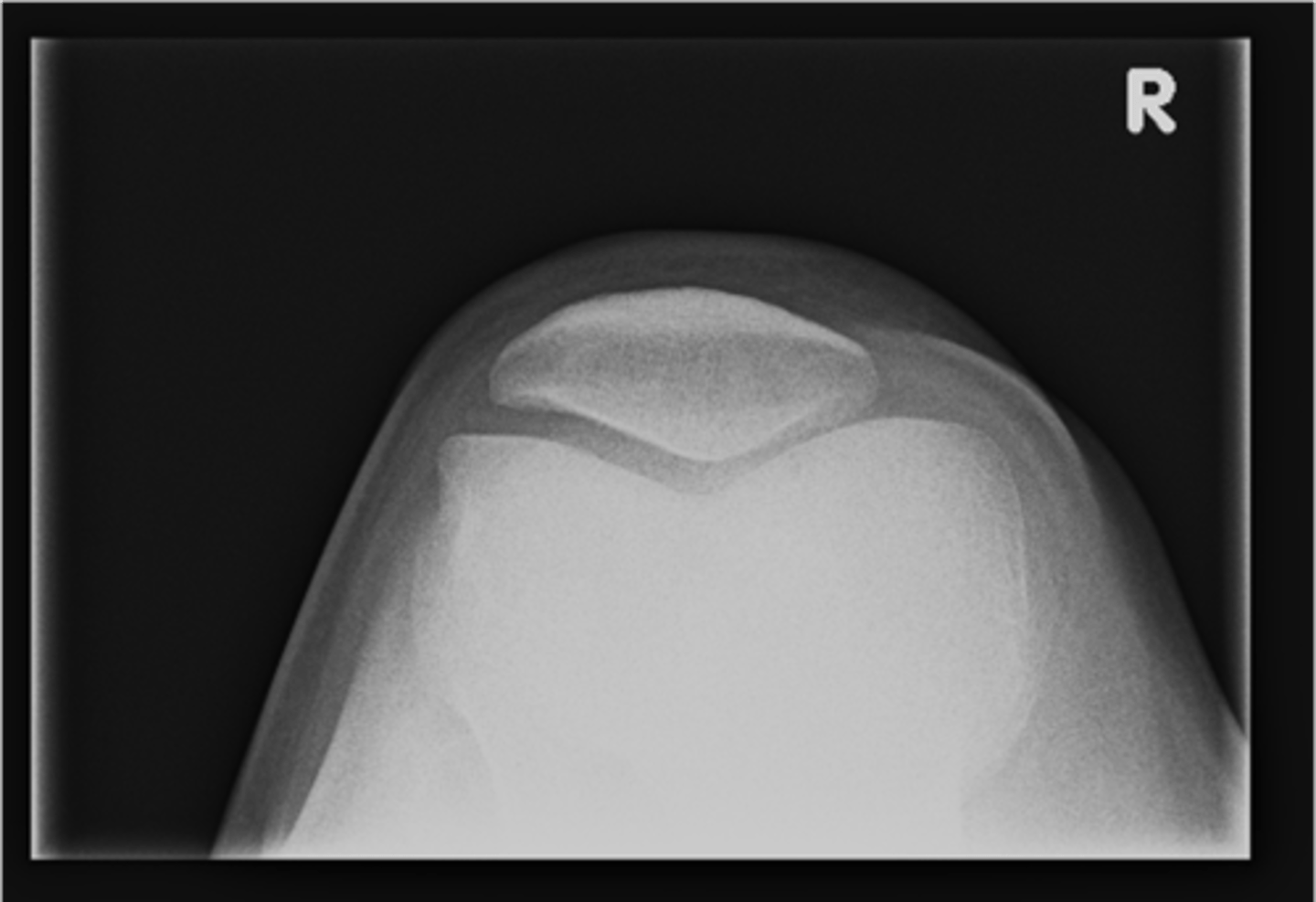
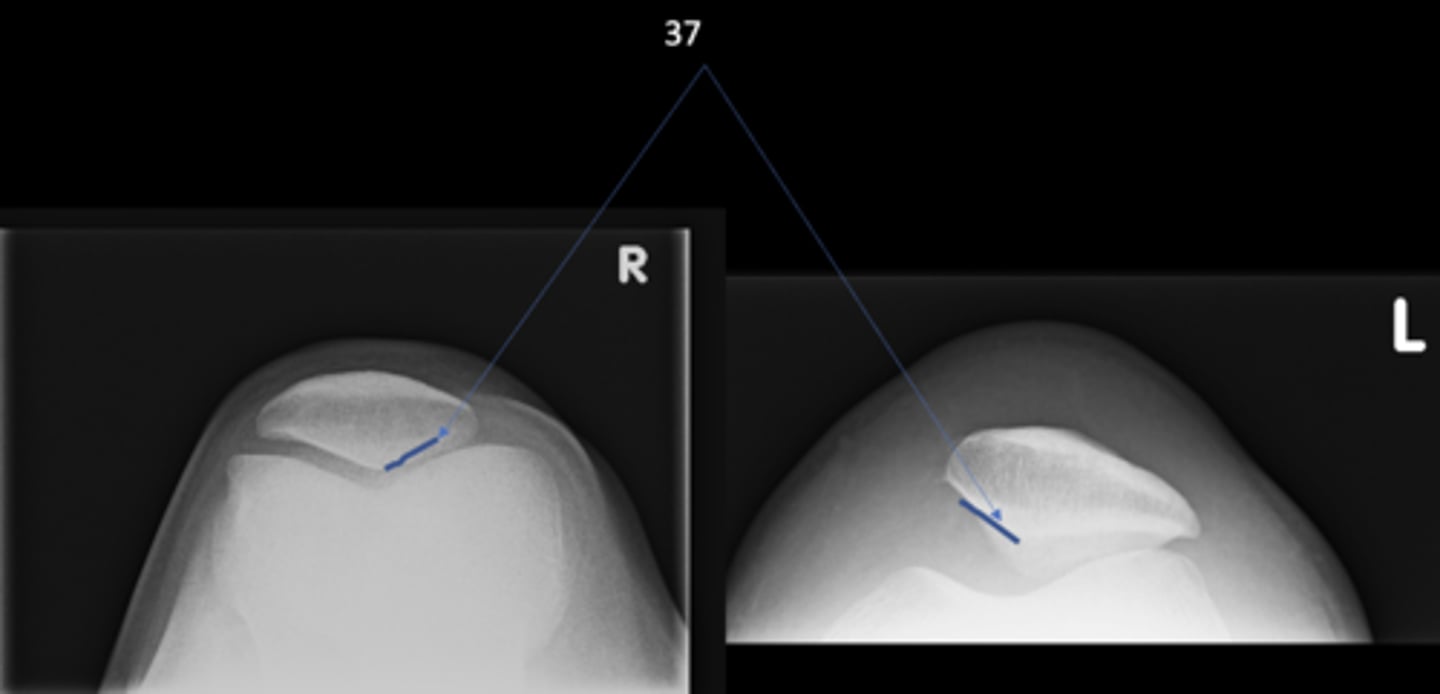
Medial patellofemoral joint
ID 37 (joint)
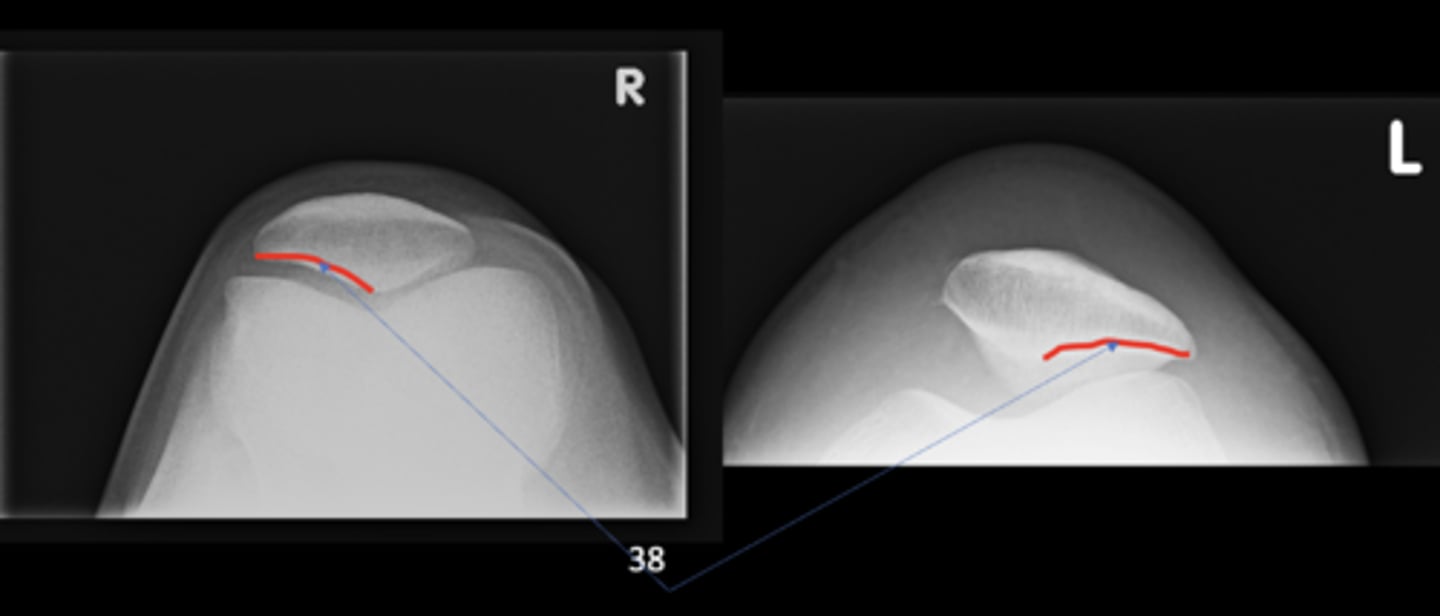
Lateral patellofemoral joint
ID 38 (joint)
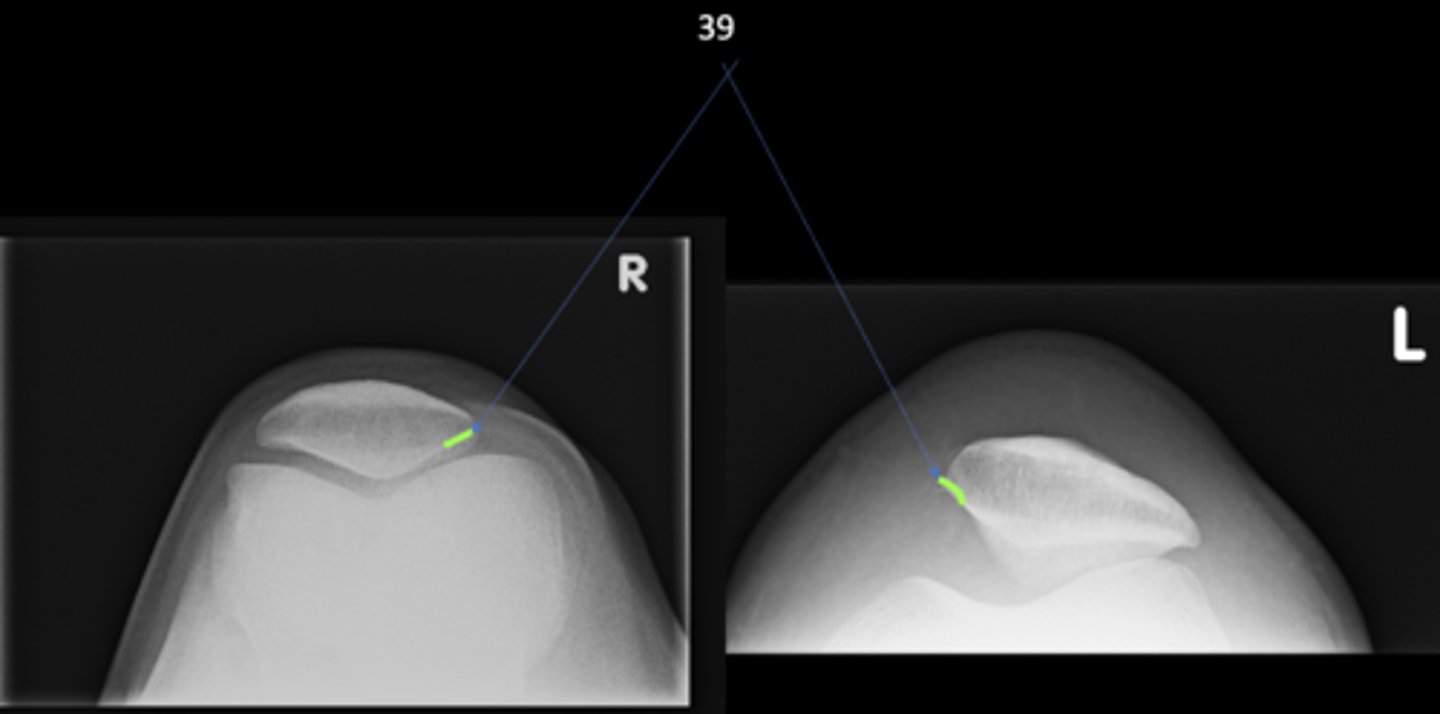
Odd facet
ID 39
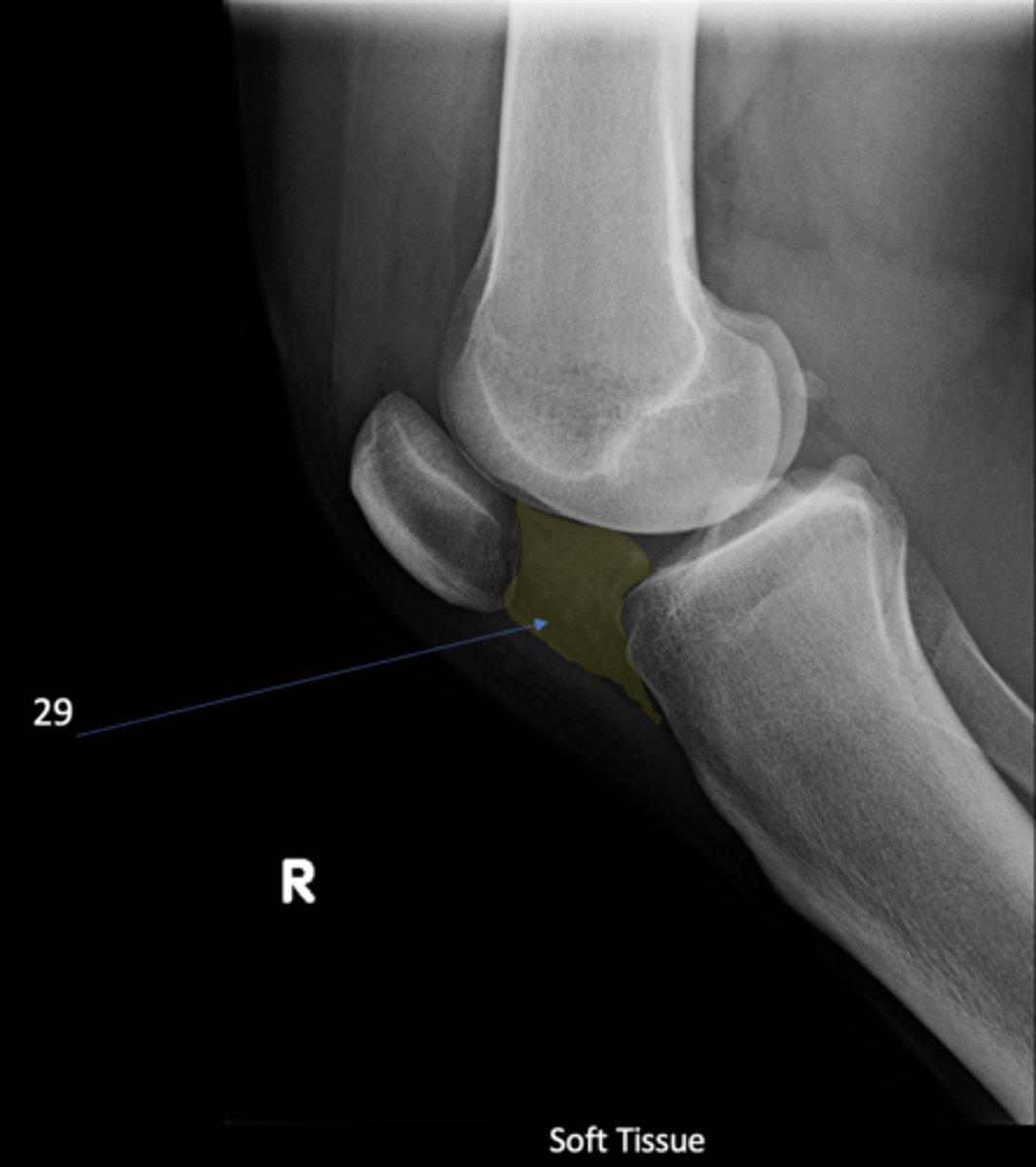
Infrapatellar pouch
ID 29
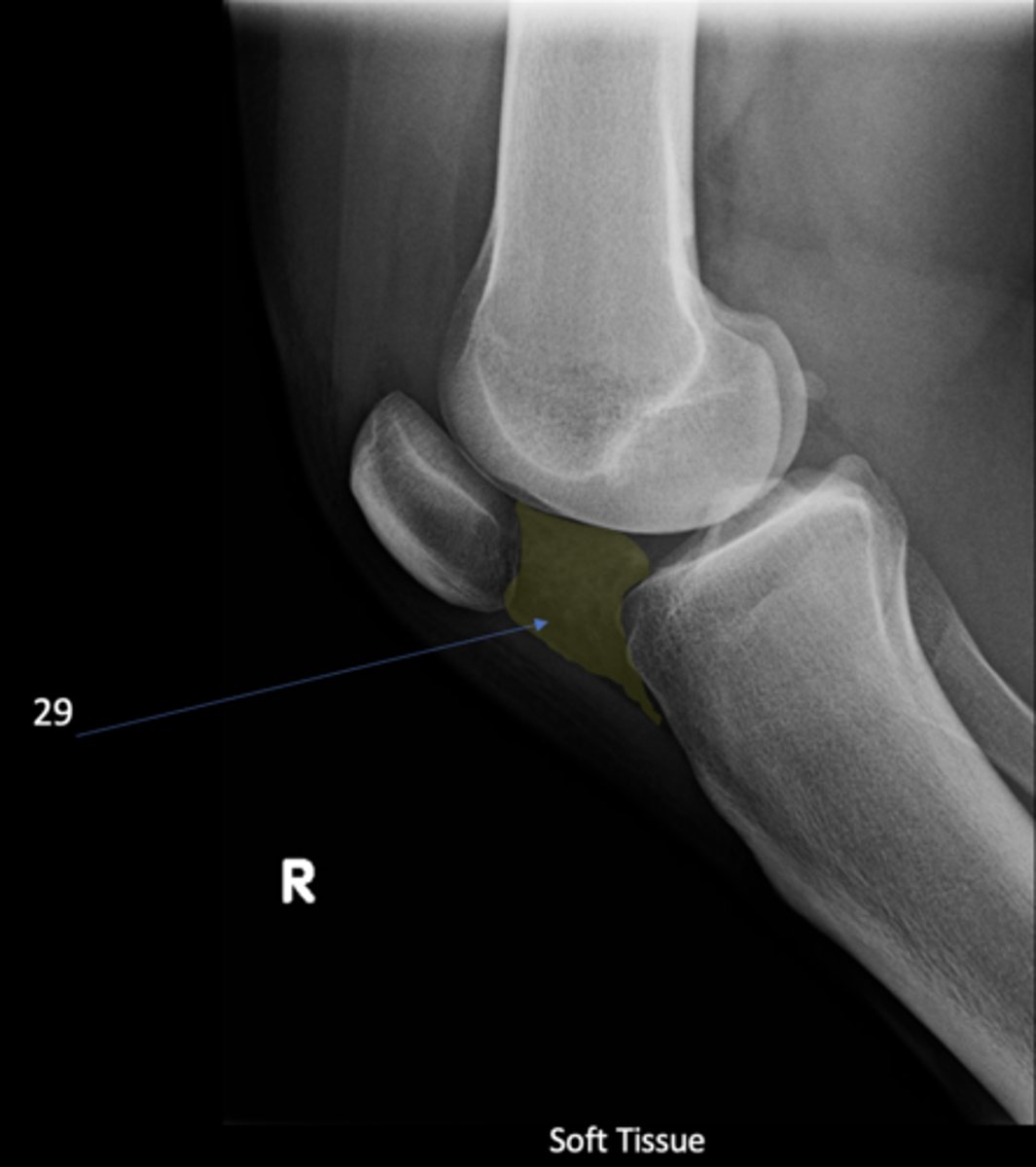
Hoffa's fat pad
Another term for infrapatellar pouch
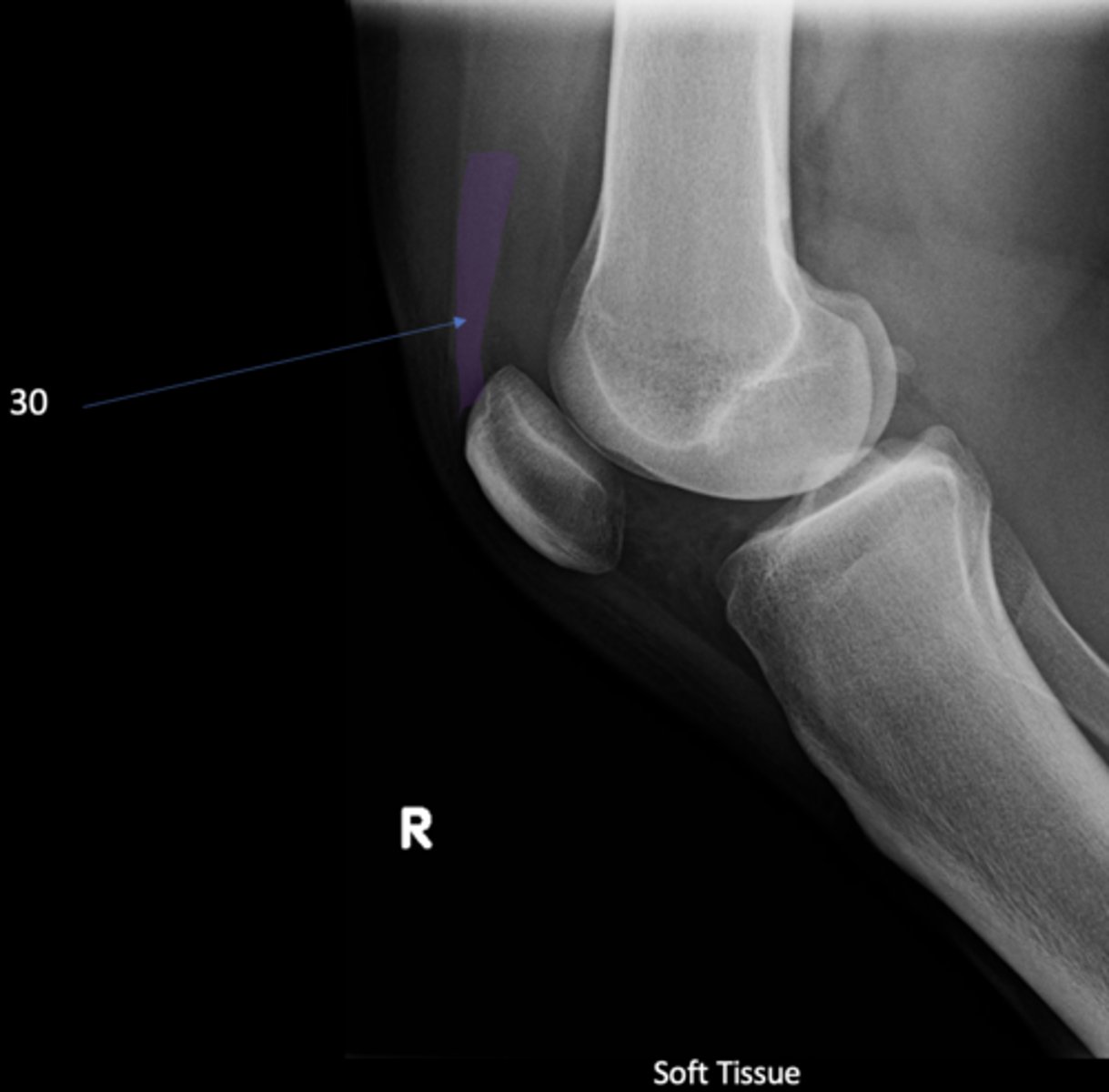
Quadriceps tendon
ID 30
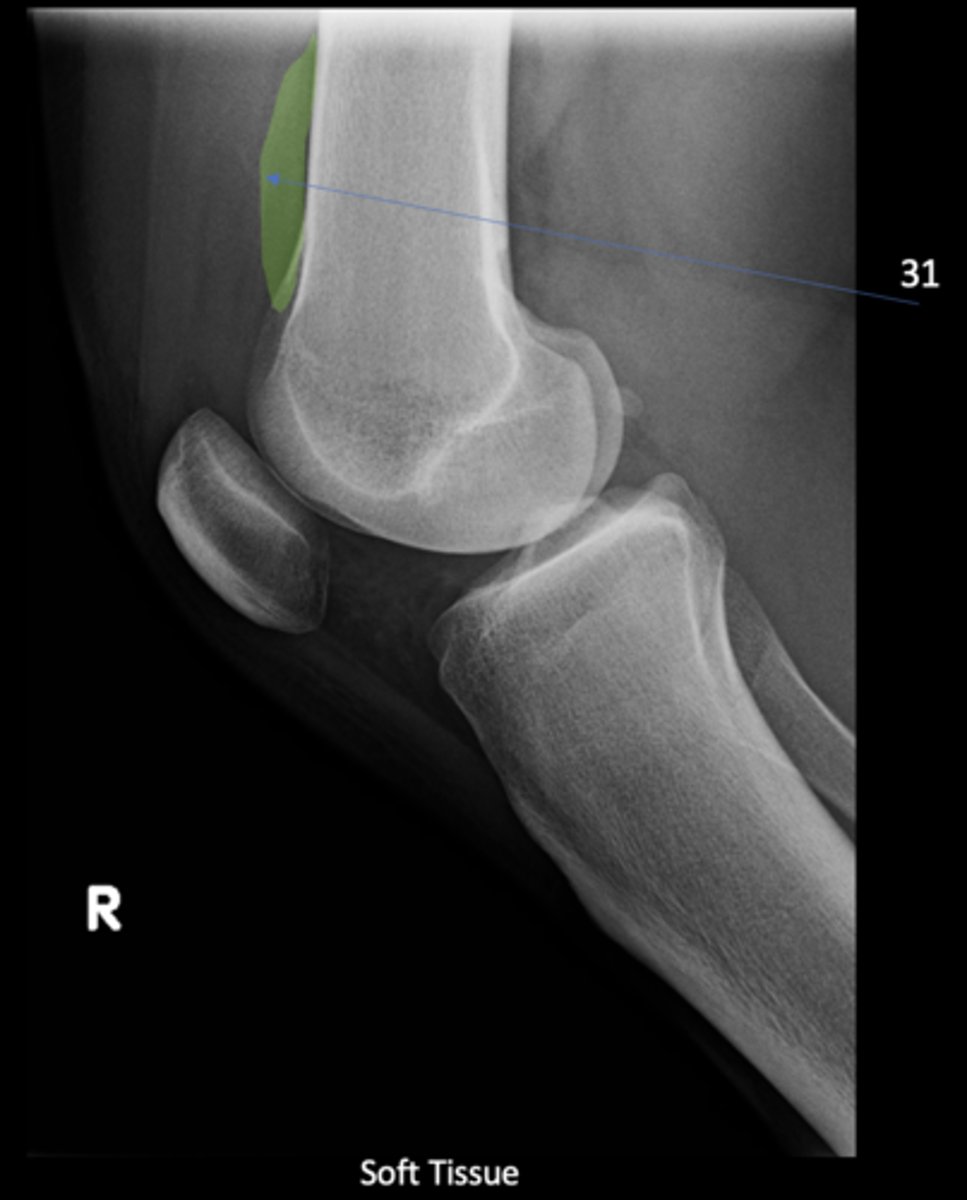
Prefemoral fat pad
ID 31
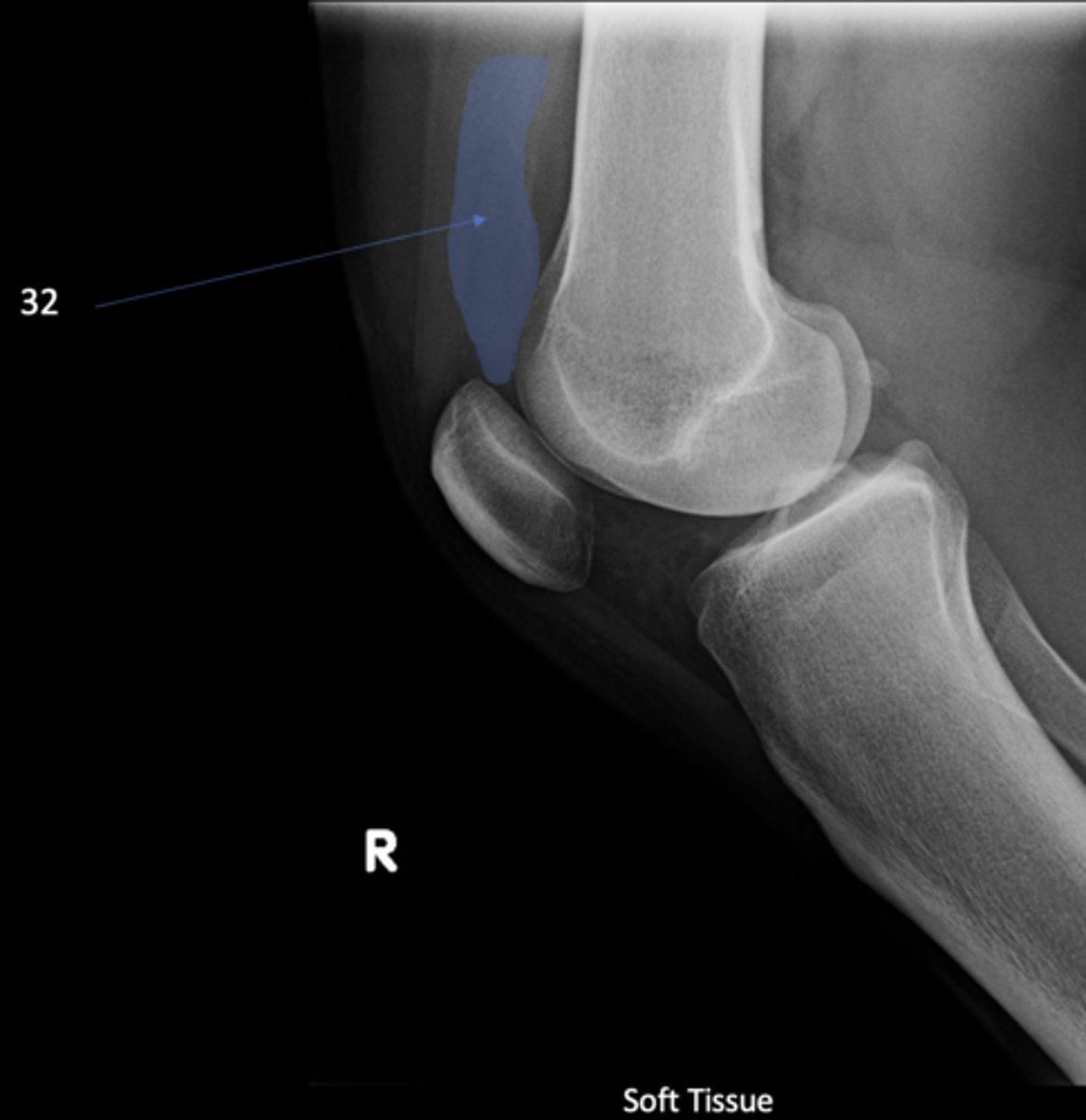
Suprapatellar pouch
ID 32
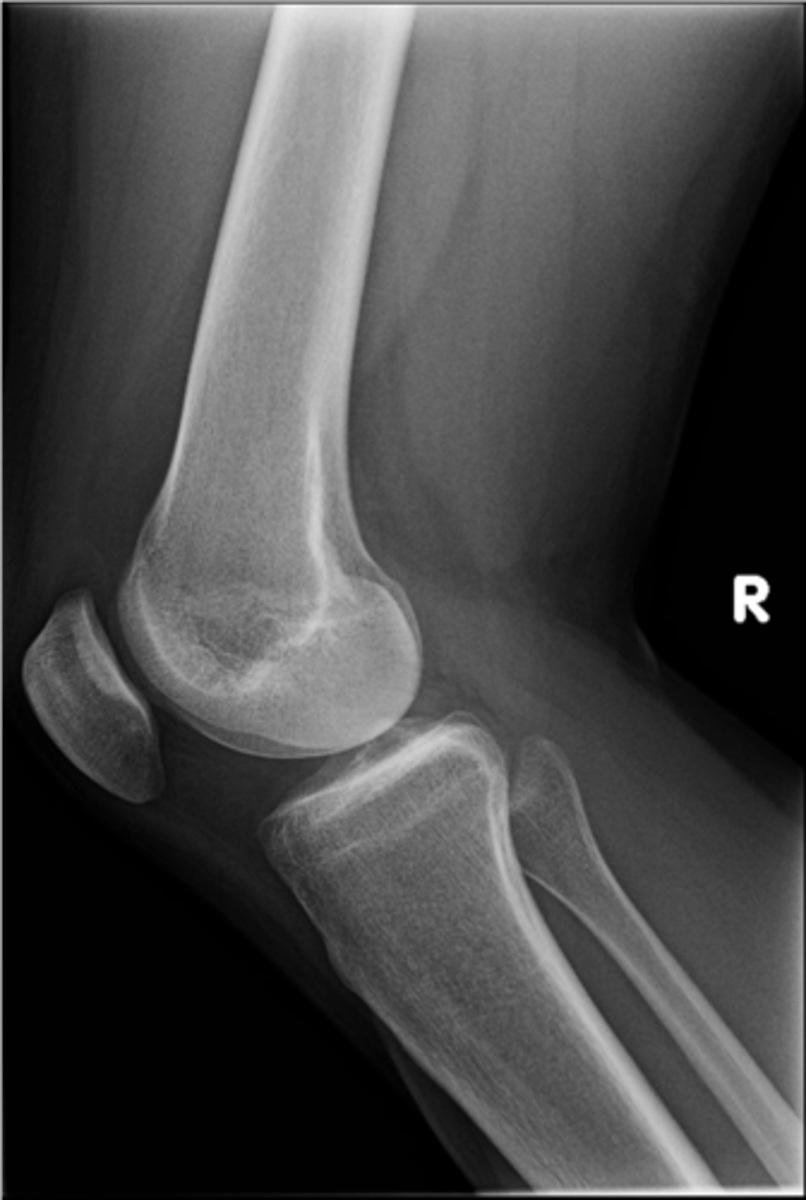
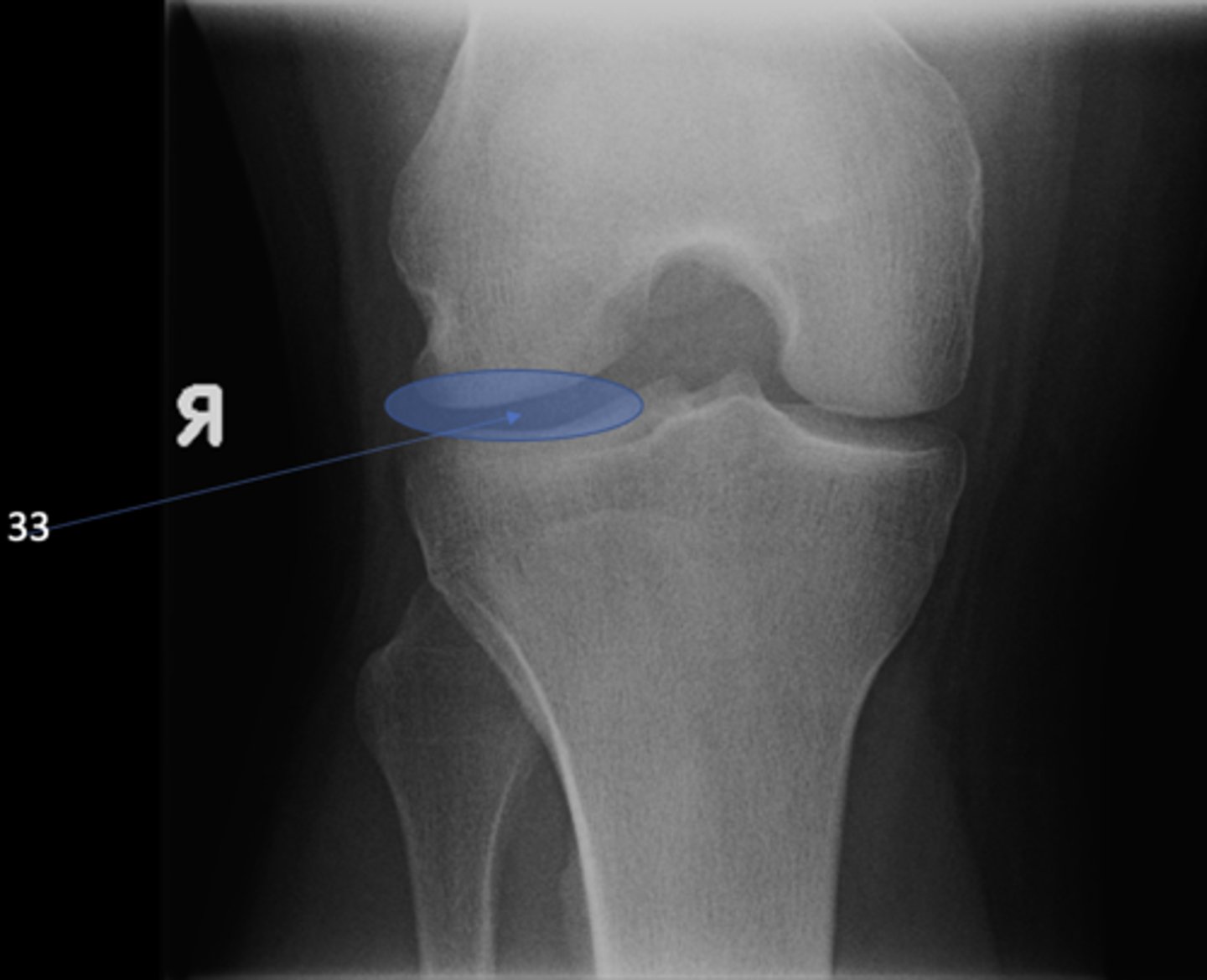
Lateral tibiofemoral joint
ID 33 (joint)
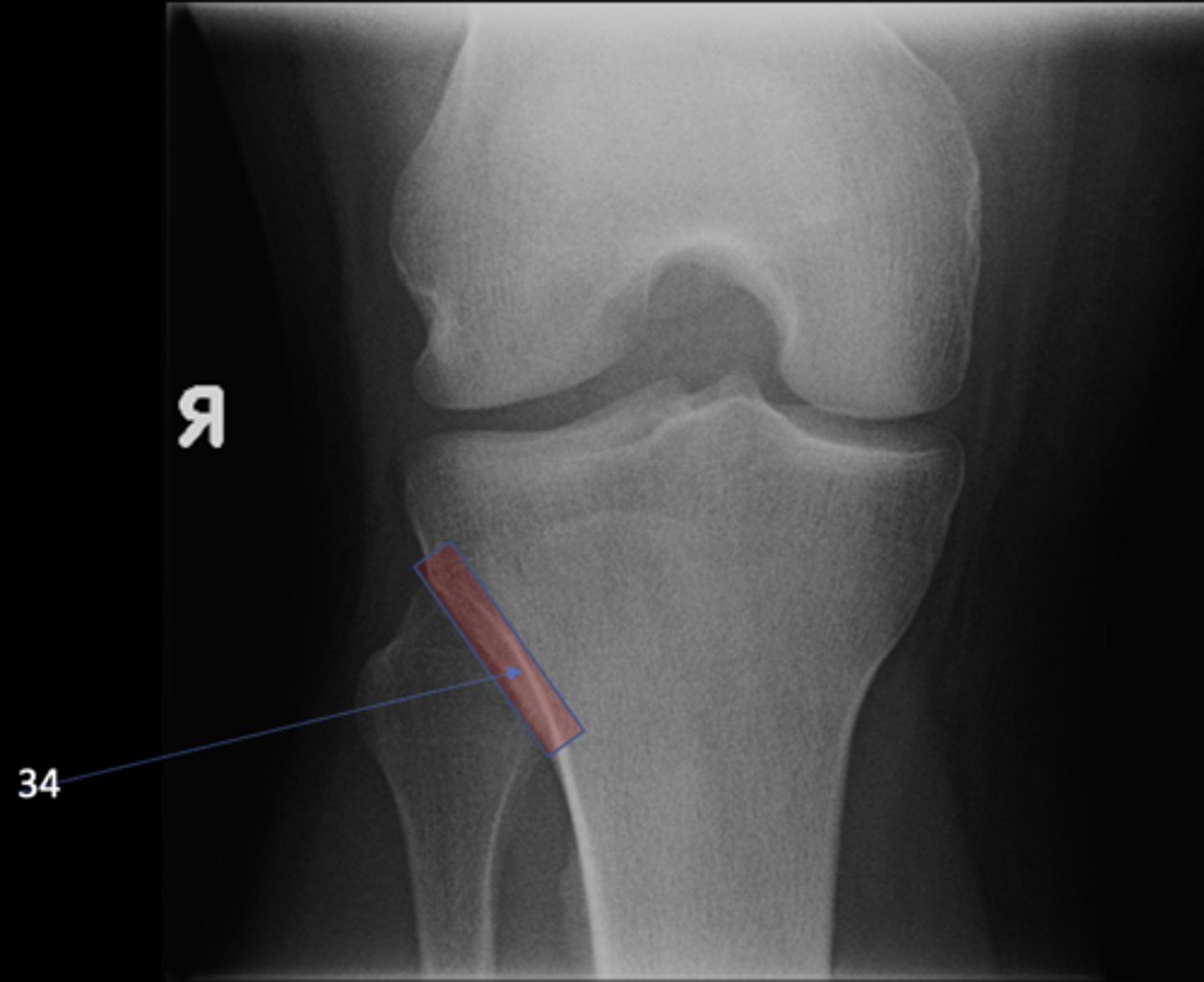
Proximal tibiofibular joint
ID 34 (joint)
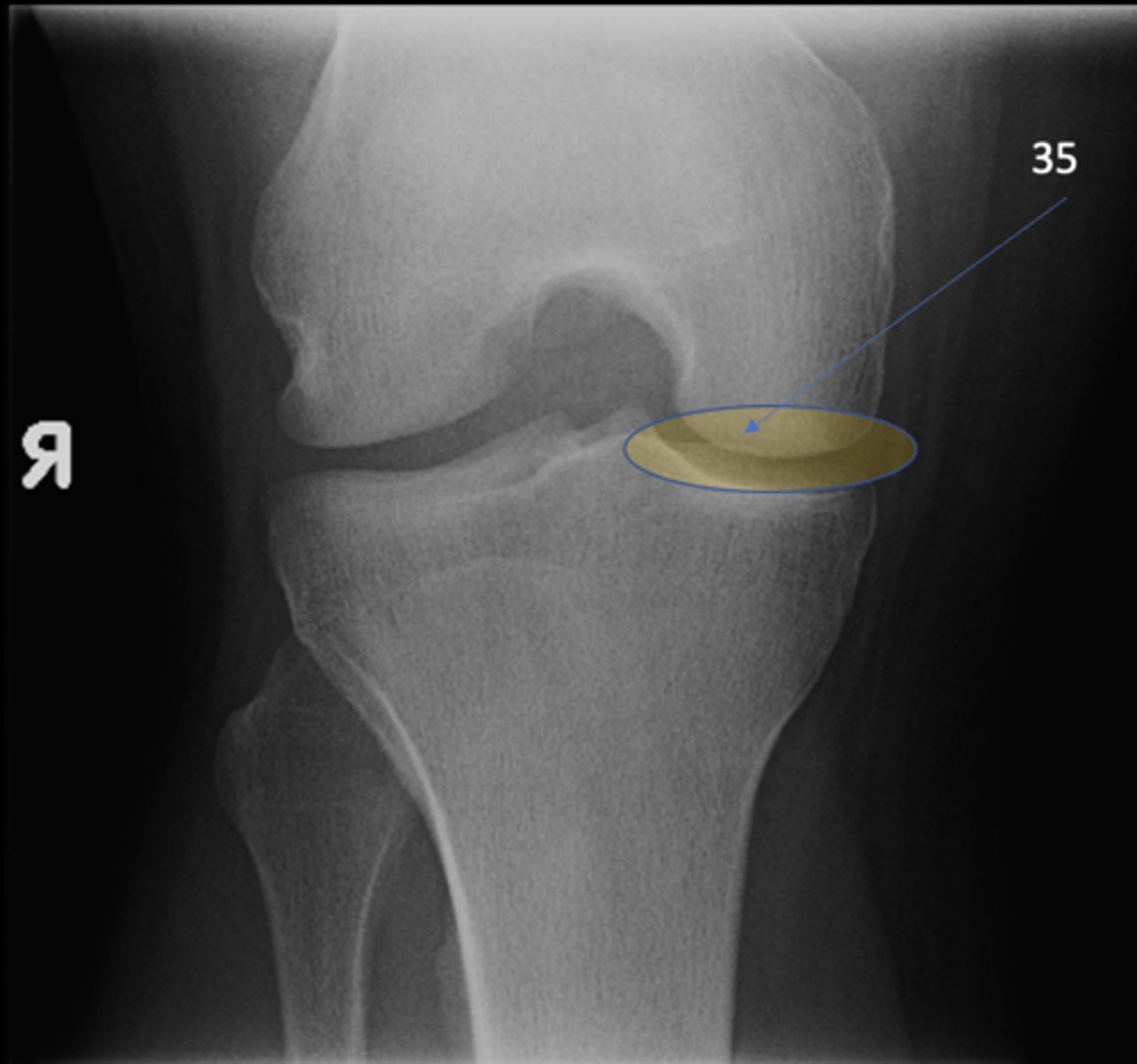
Medial tibiofemoral joint
ID 35 (joint)
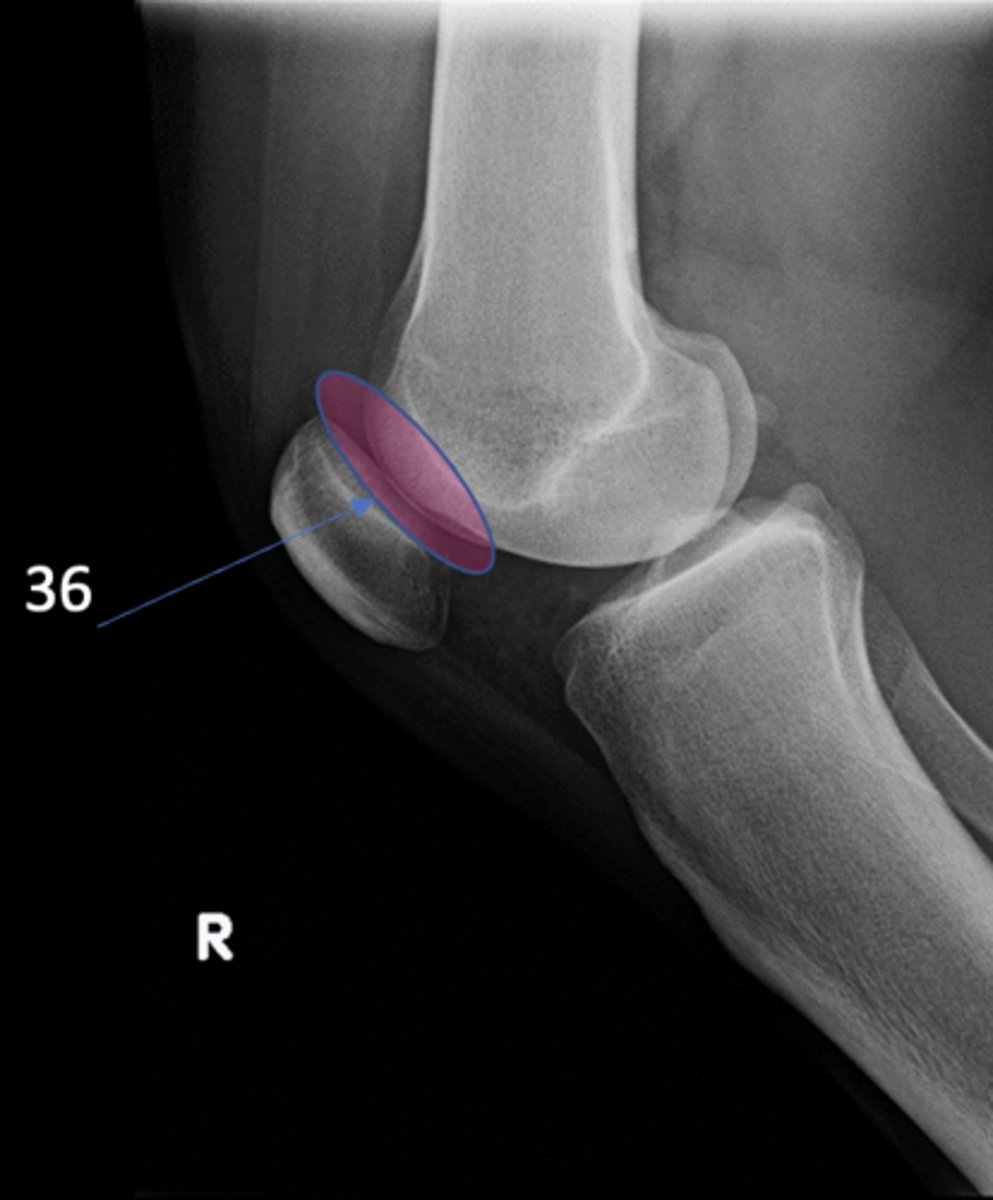
Patellofemoral joint
ID 36 (joint)
Ludloff's patch/spot
- Not a true anatomical structure
- Appears due to less bone being traversed anteriorly than posteriorly