T1: reproductive anatomy and physiology (female)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
abdomen anatomy
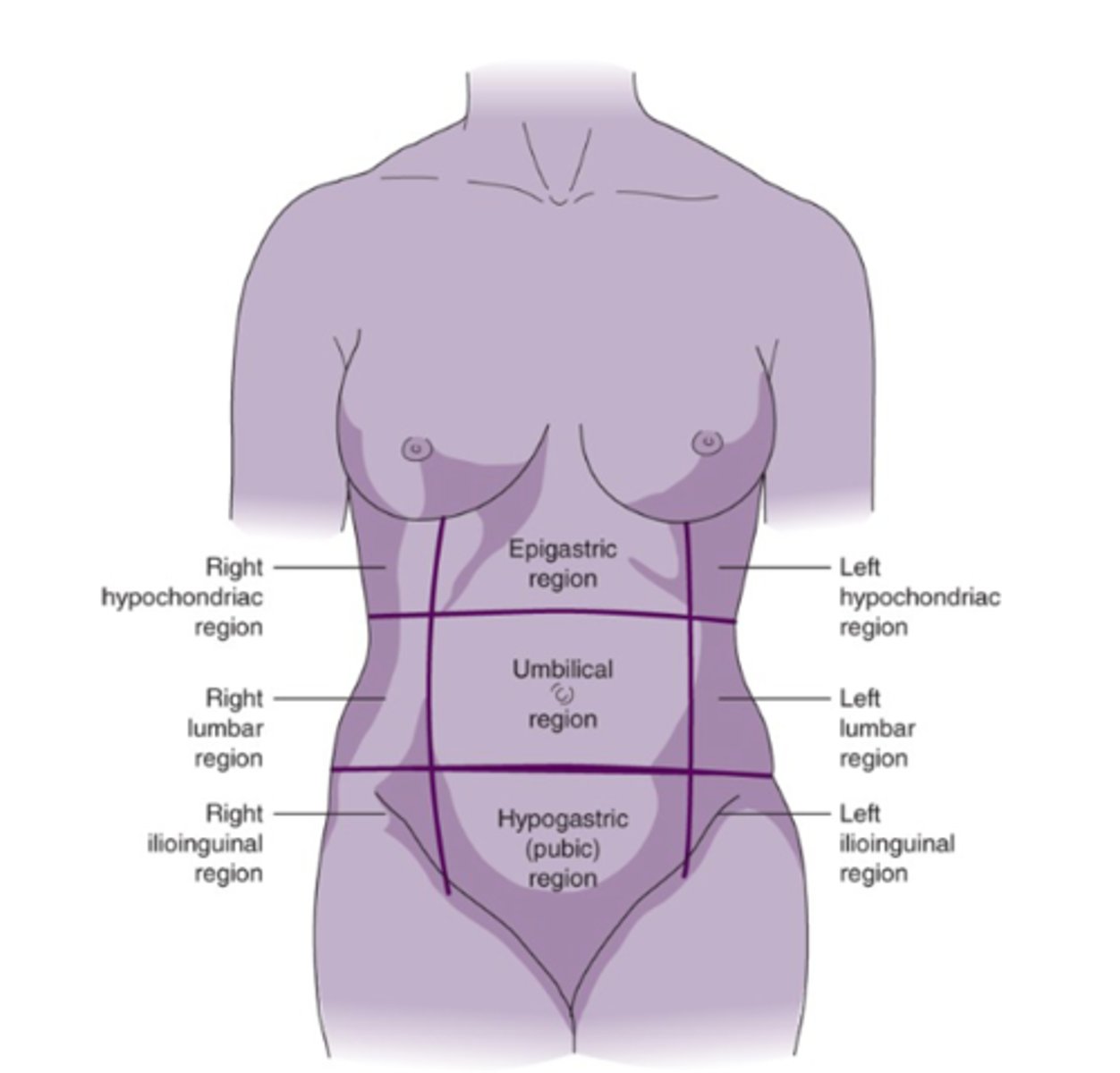
-contains and support the intestines, urinary bladder, ureters, urethra, uterus, uterine tubes, ovaries
-composed of: ilium, ischium, pubis
-pubic symphysis synarthrodial joint for child birth
pelvis purpose
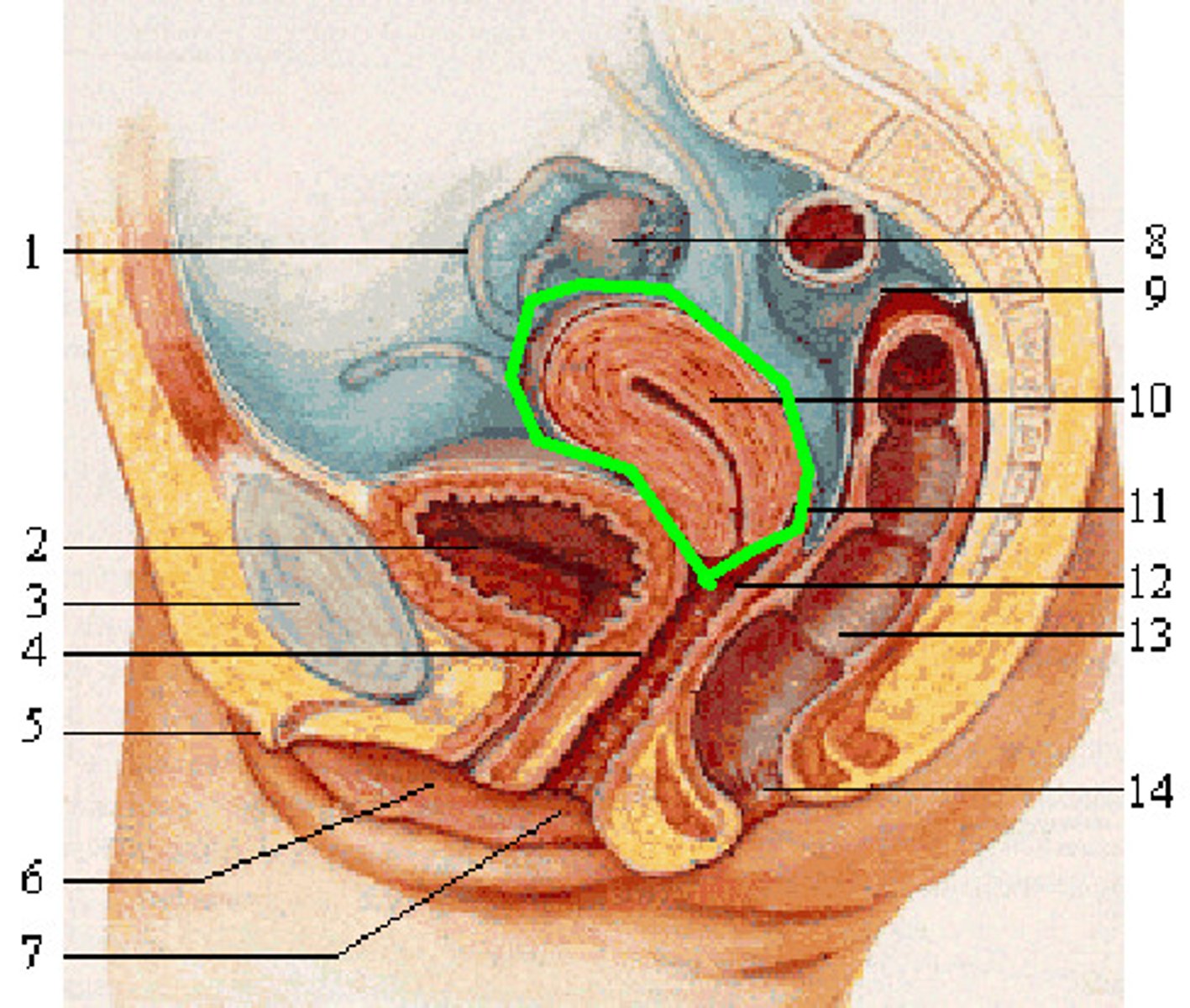
female reproductive anatomy (sagittal view)
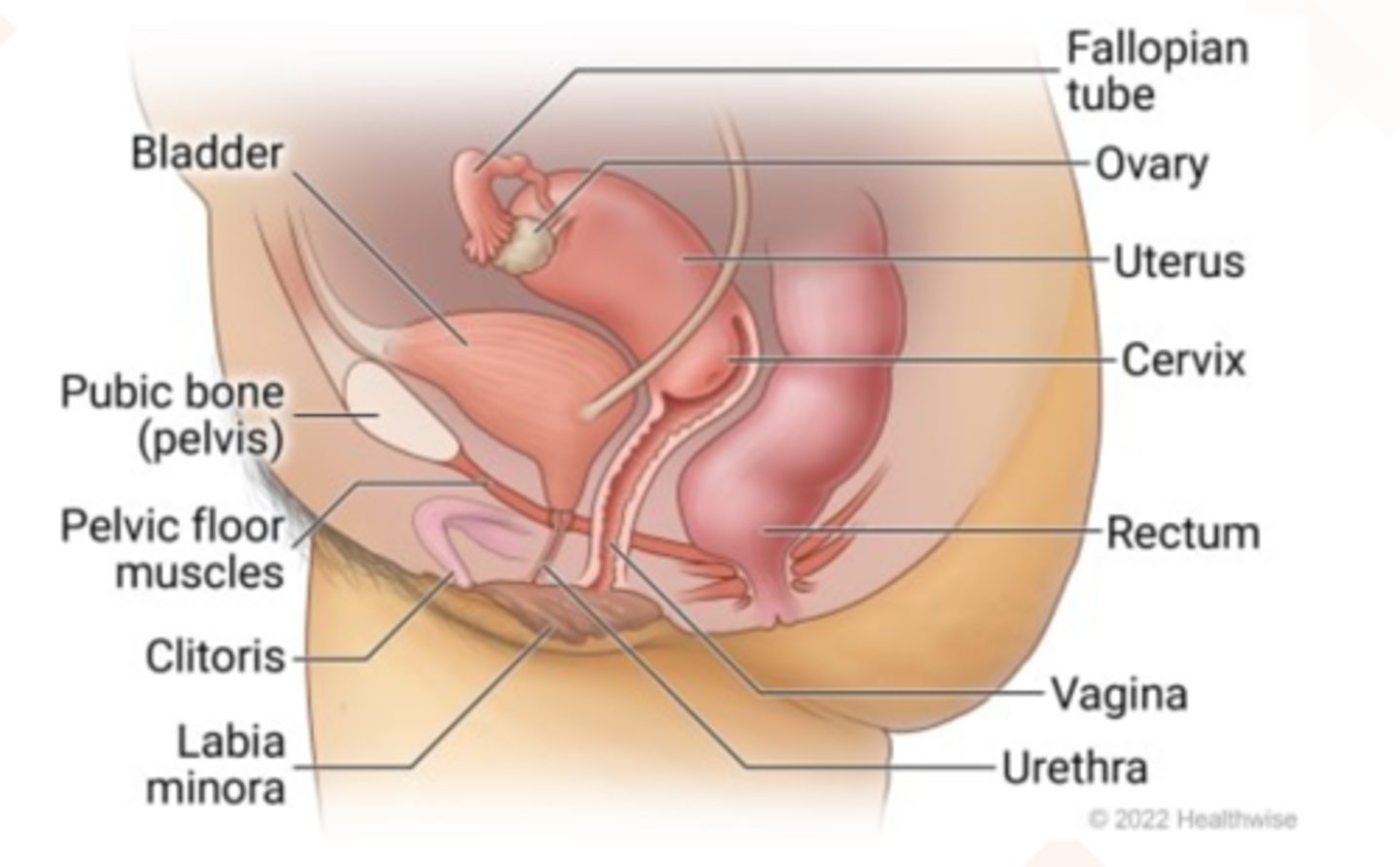
primary female sex organ because they produce eggs (ovum or oocytes) and sex hormones (estrogen)
-posterior region of broad ligament, near lateral pelvic cavity
-responsible for ovulation
-supplied by ovarian artery (aortic origin)
ovaries
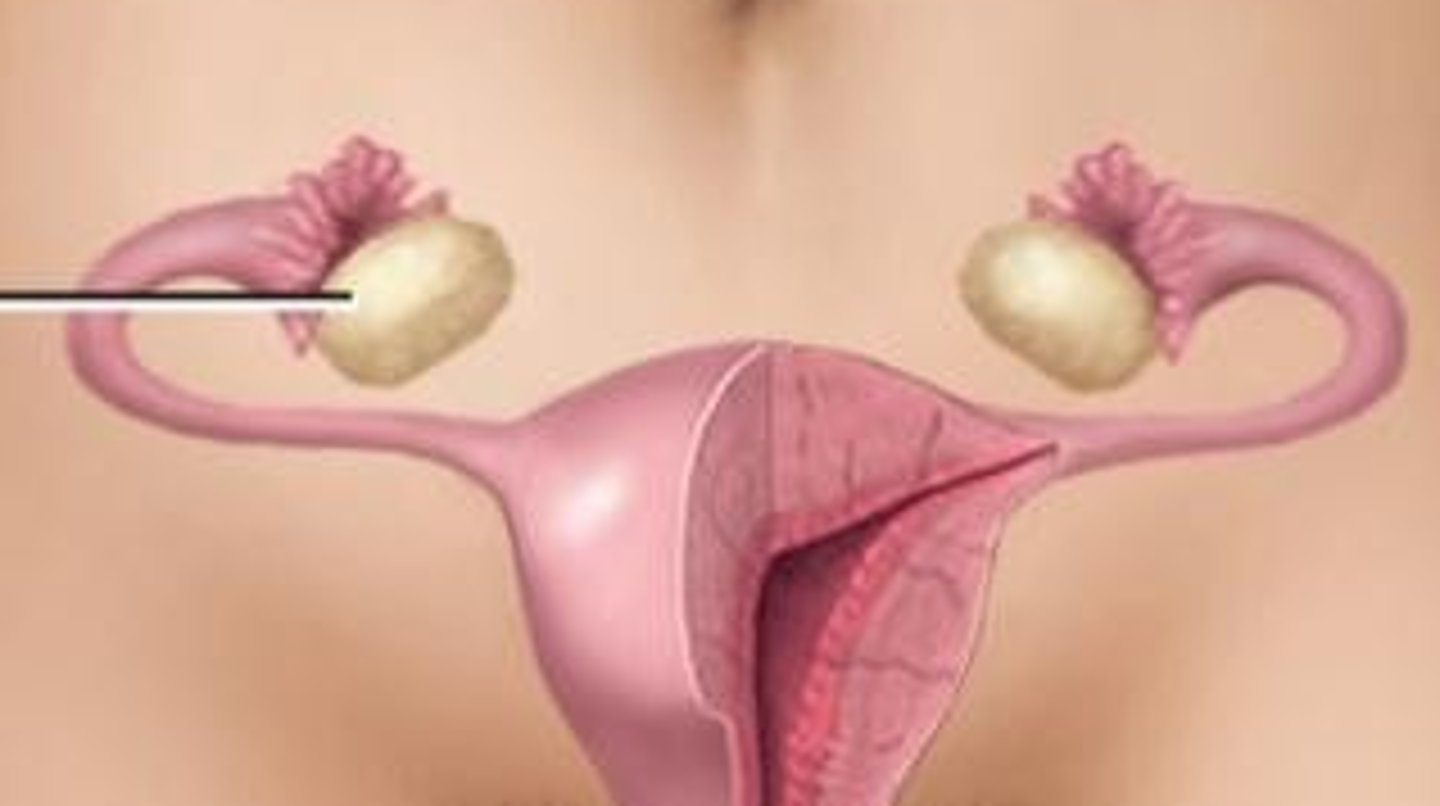
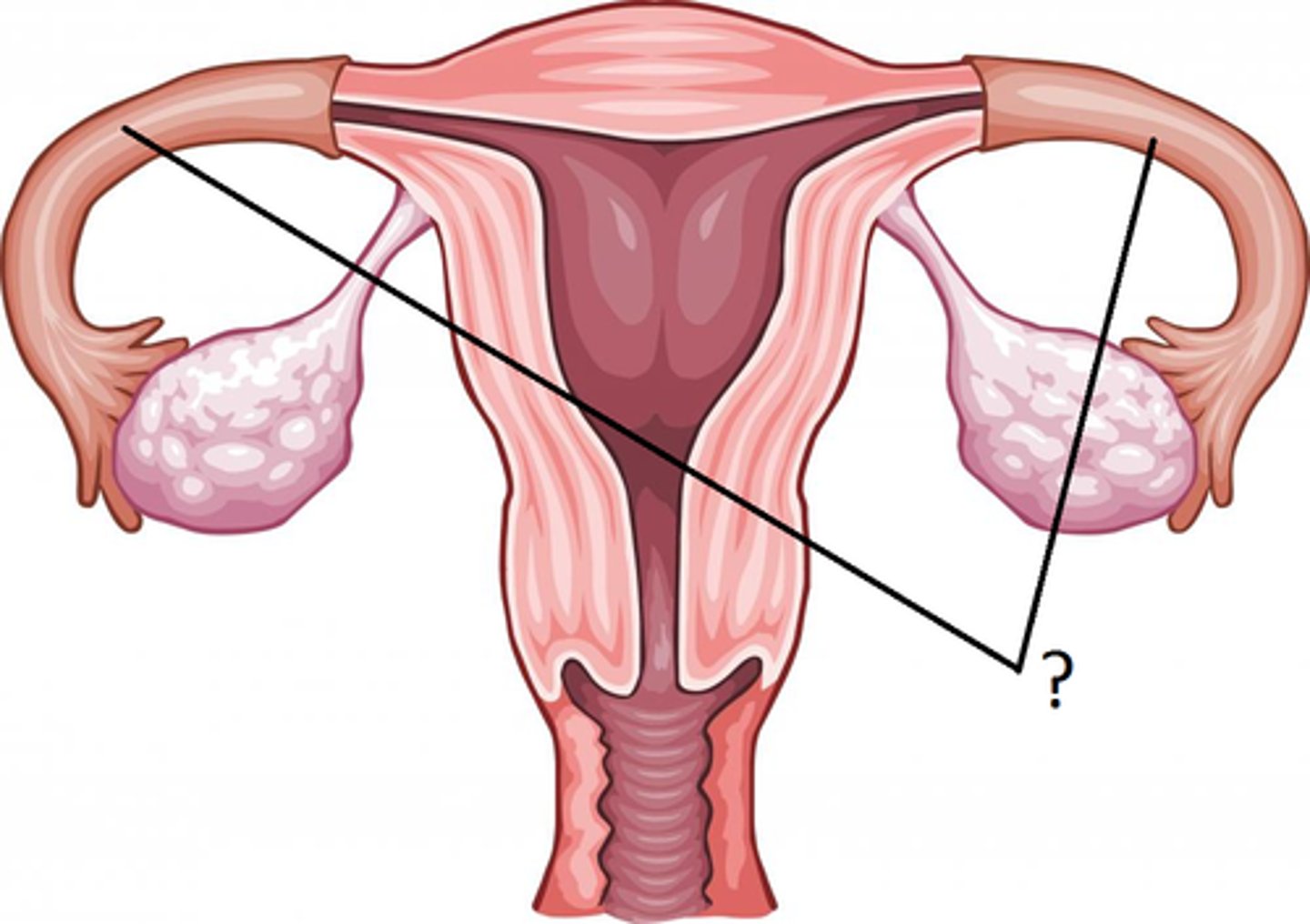
-as wide as human hair
-separate from the ovaries
-transport oocytes, transport spermatozoa, connects uterine cavity with peritoneal cavity
fallopian tubes
-hollow organ, inverted pear
-between rectum and urinary bladder
-receives and nourishes a fertilized oocyte until birth
-flexed anteriorly
-uterine artery and ovarian artery
uterus
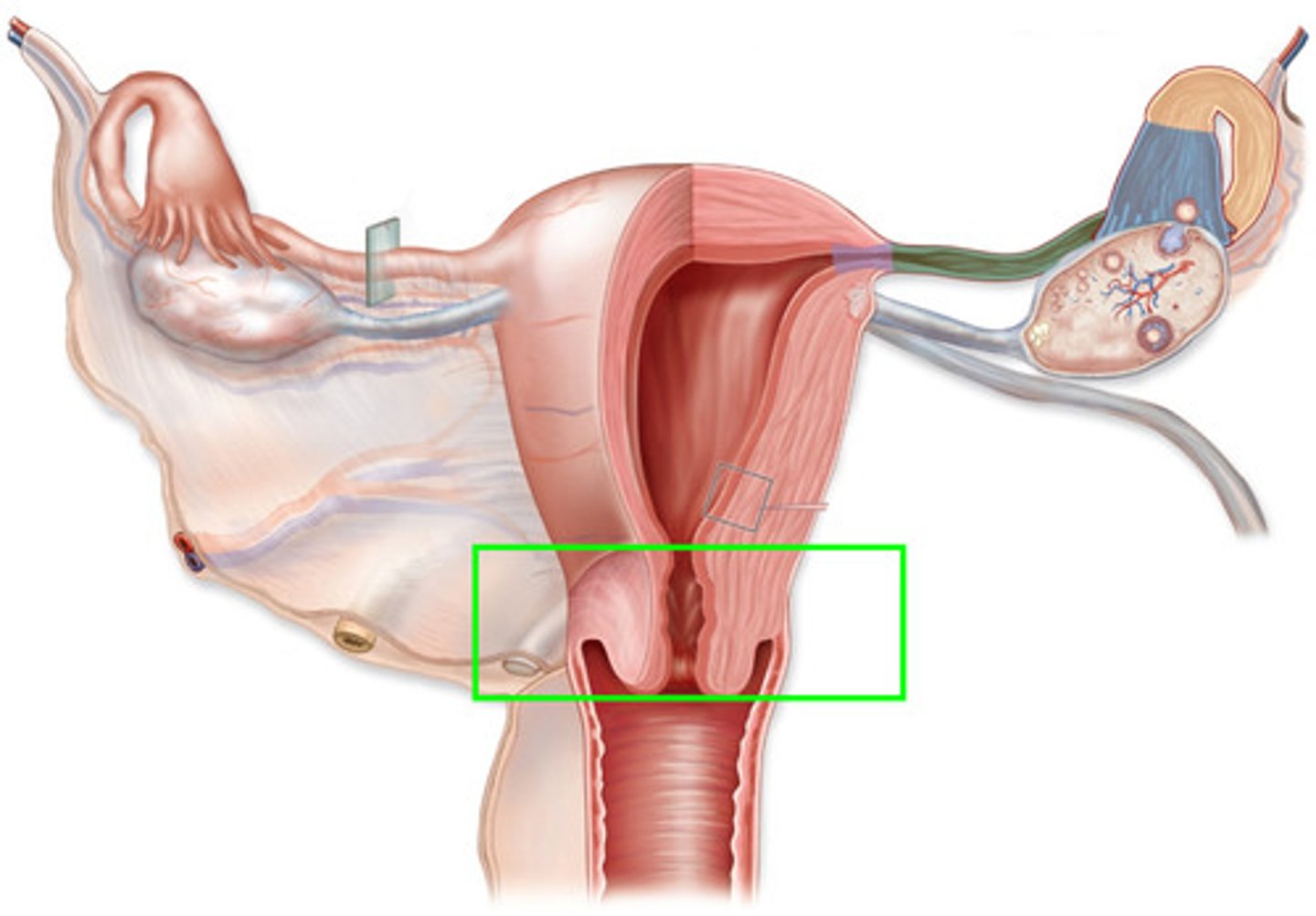
-internal os: junction of the cervical canal and uterine body
-external os: communicates with the vaginal canal
cervix
-double layer of peritoneum that cover the anterior, superior and posterior surface of the uterus, uterine tubes, ovaries
-mesosalpinx, mesovarium, mesometrium
broad ligament
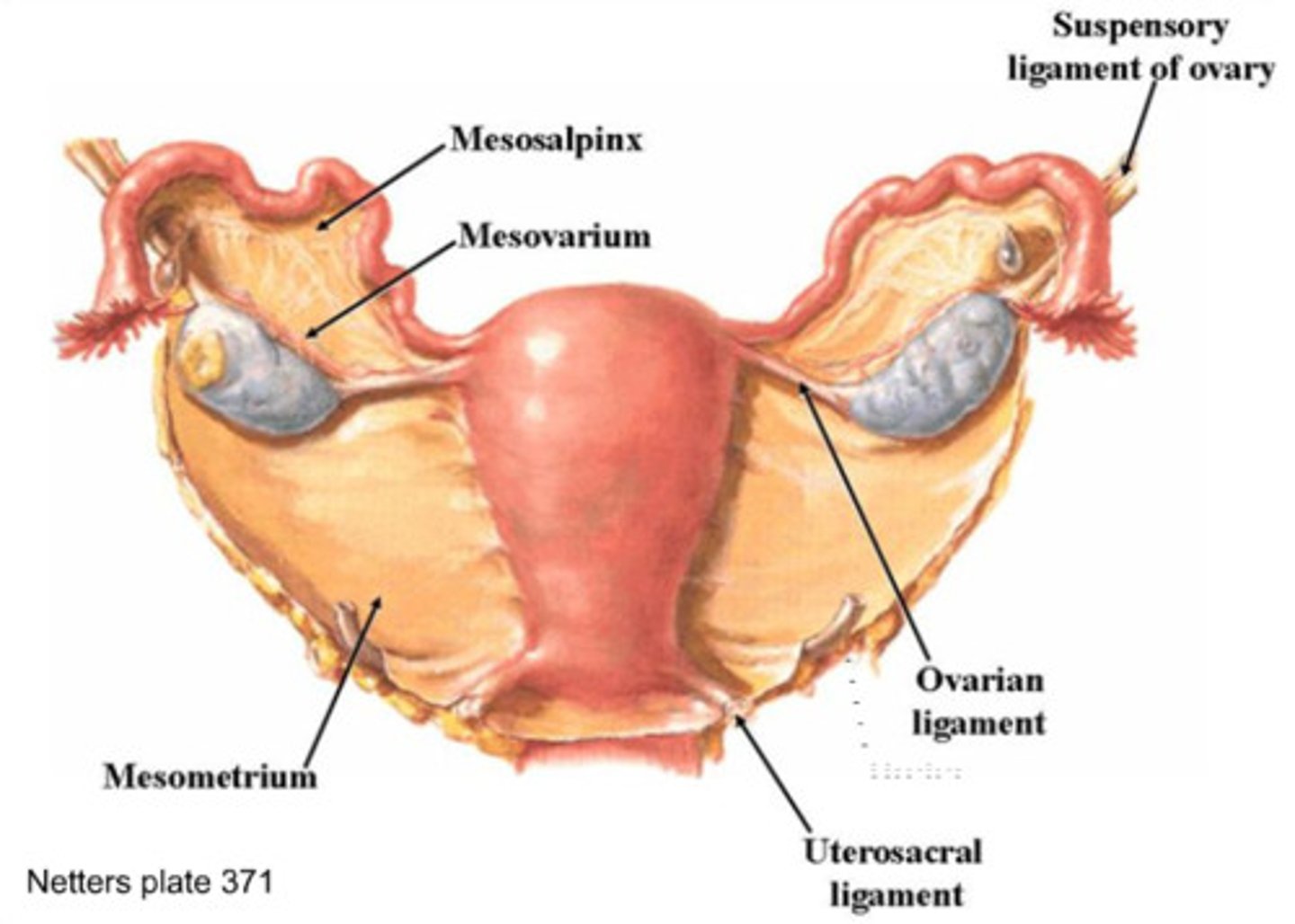
-region of broad ligamnet surrounding the ovarian ateries and veins
suspensory ligament of the ovary
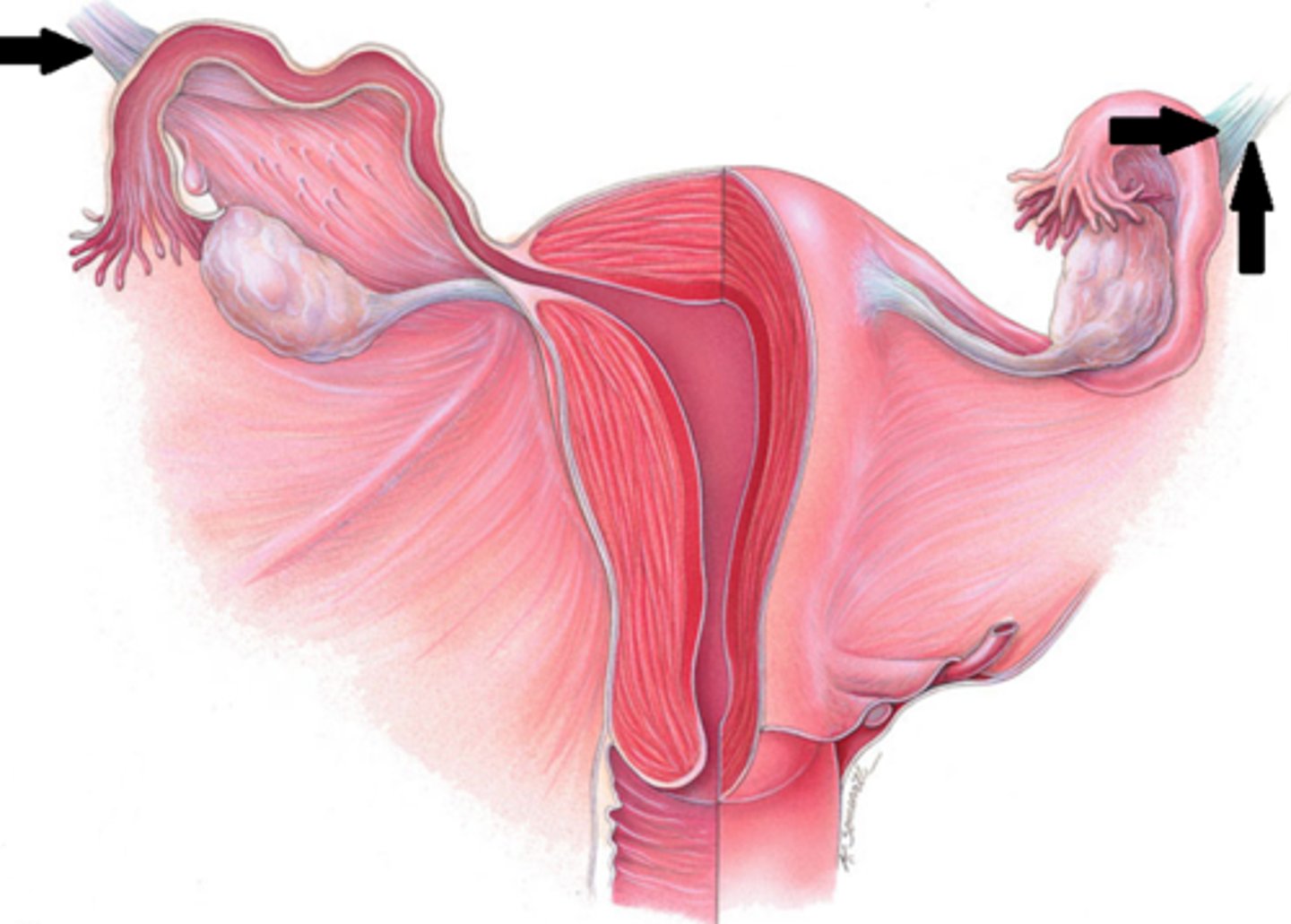
-fibourus cord that courses from the uterus through the deep ingual ring and inguinal canal
round ligament
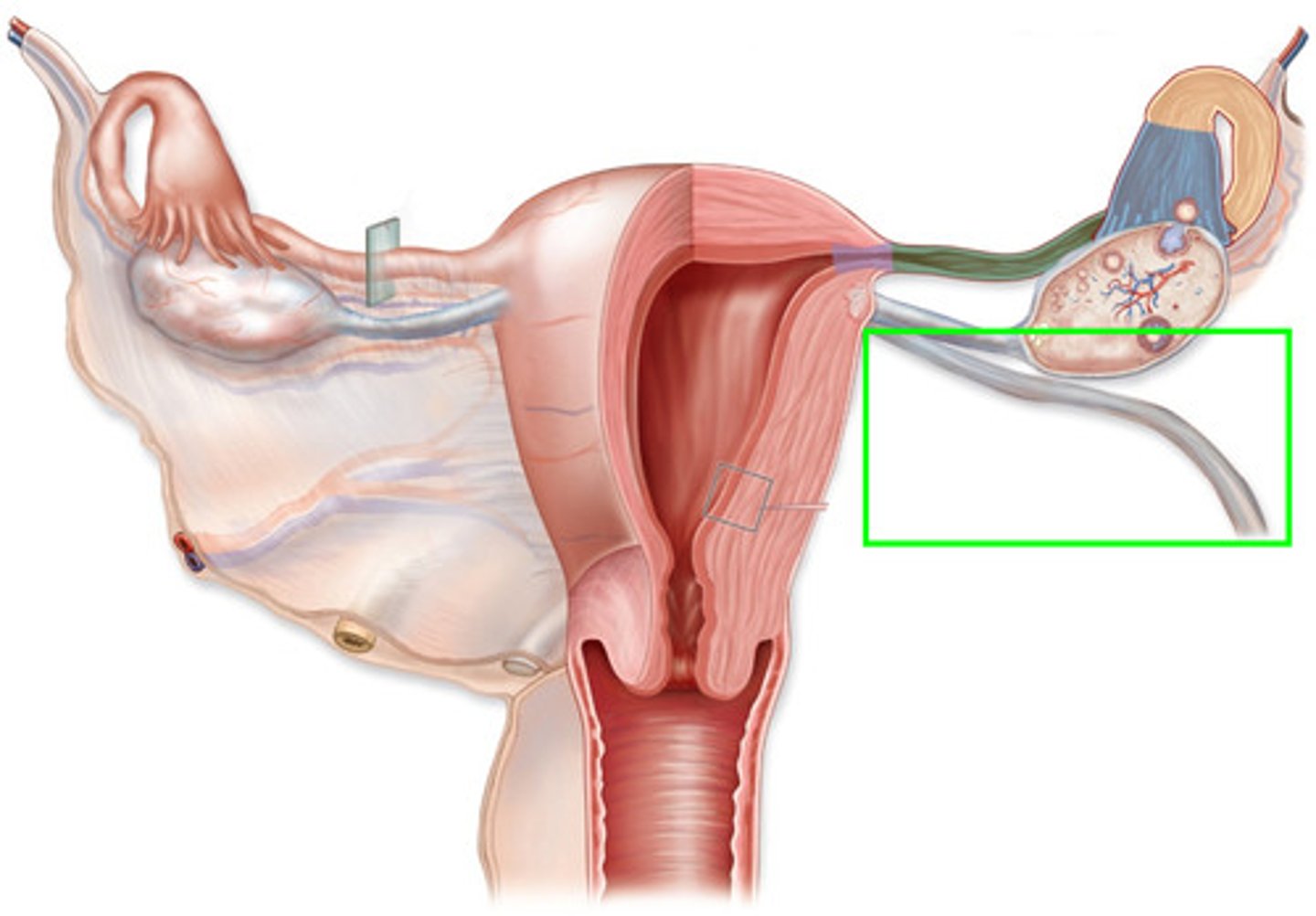
-fiborus cord that connects the ovary to the uterine body
ovarian ligament
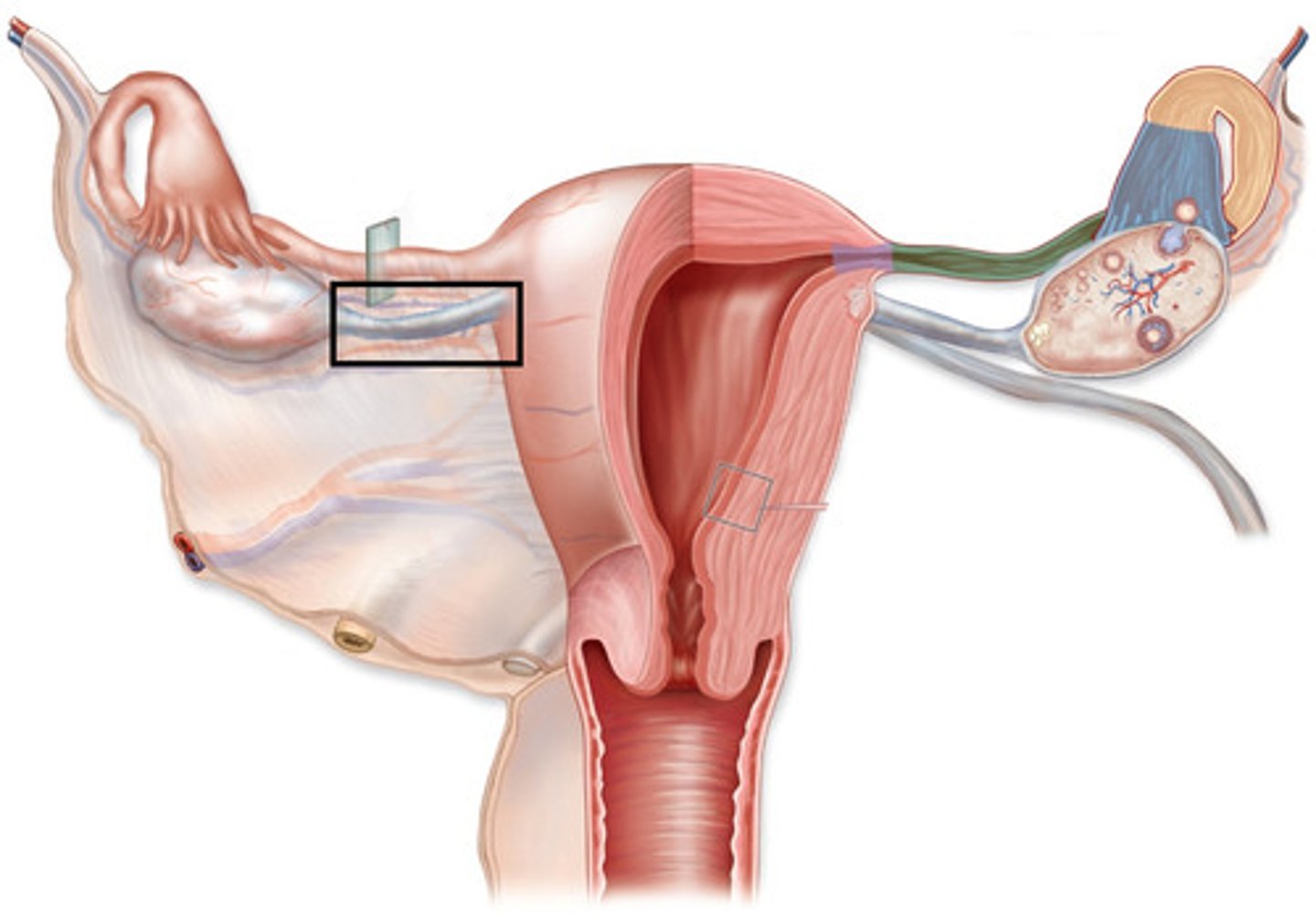
-condensation of extraperitoneal fascia around the cervix to support the uterus
transverse cervical ligament
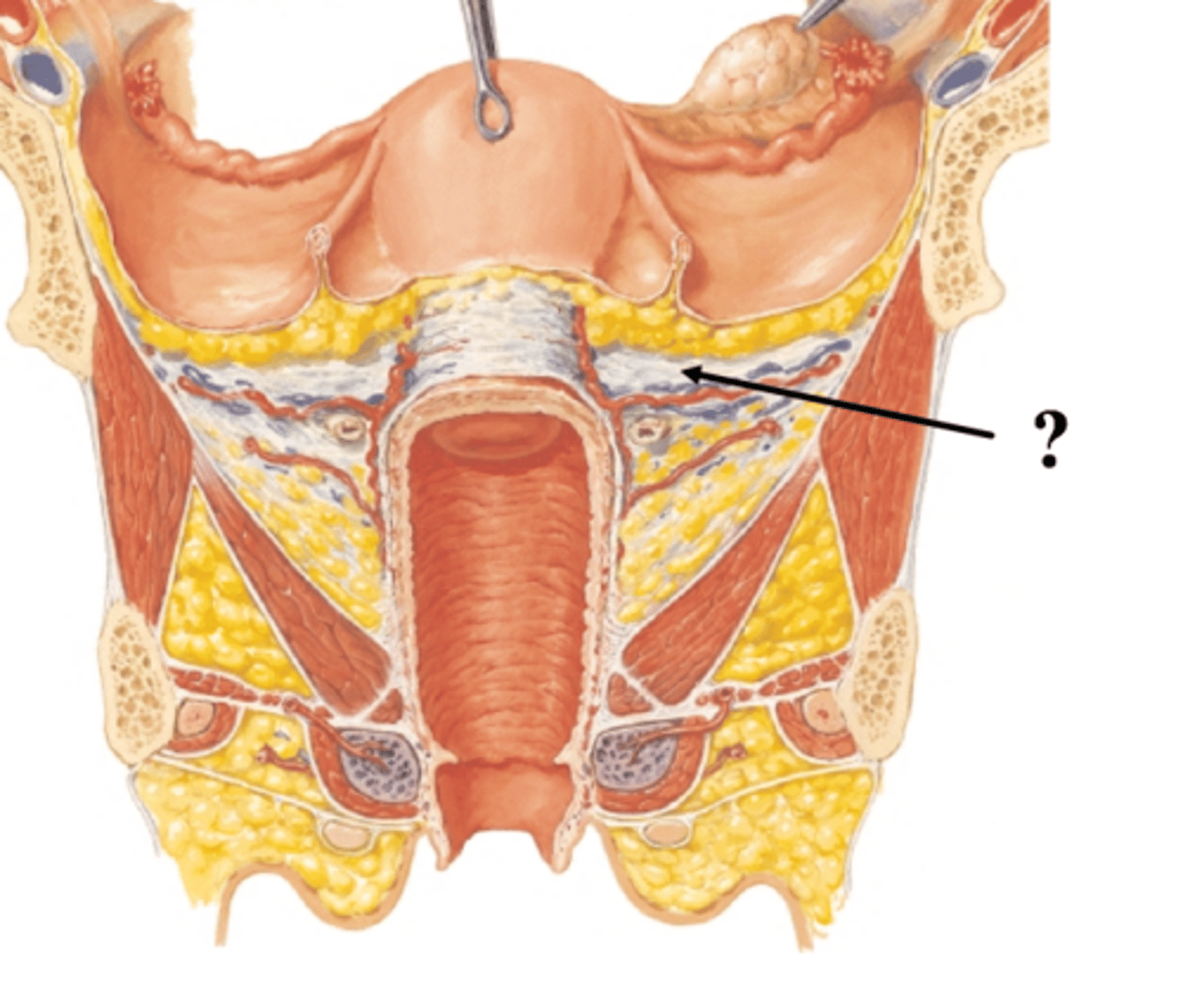
-birth canal
-menstruation
-receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse
-vaginal branches of the uterine artery and internal iliac artery
-lymph drains upper region to internal iliac nodes, lower region from superficial inguinal nodes
vagina
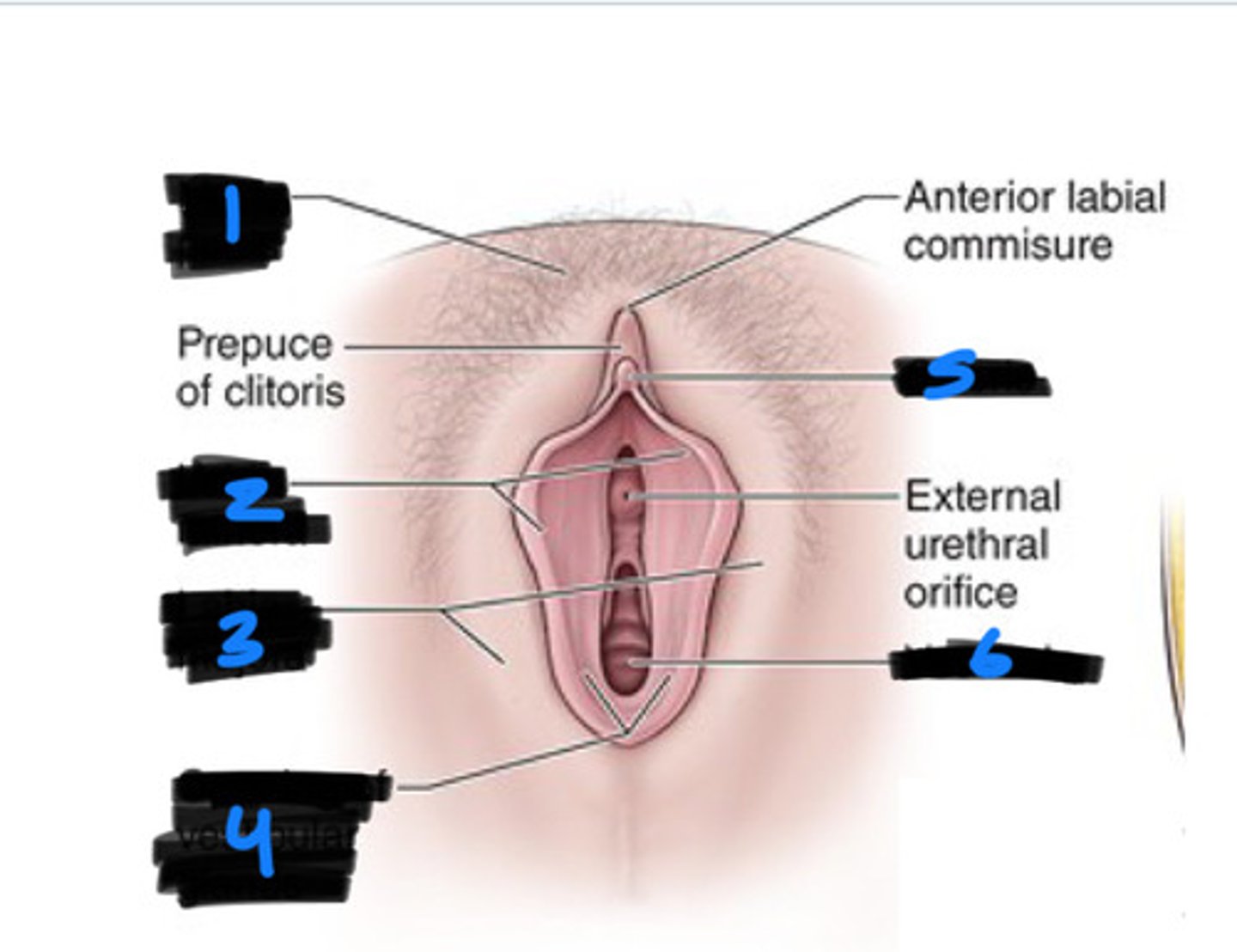
mons pubis
1
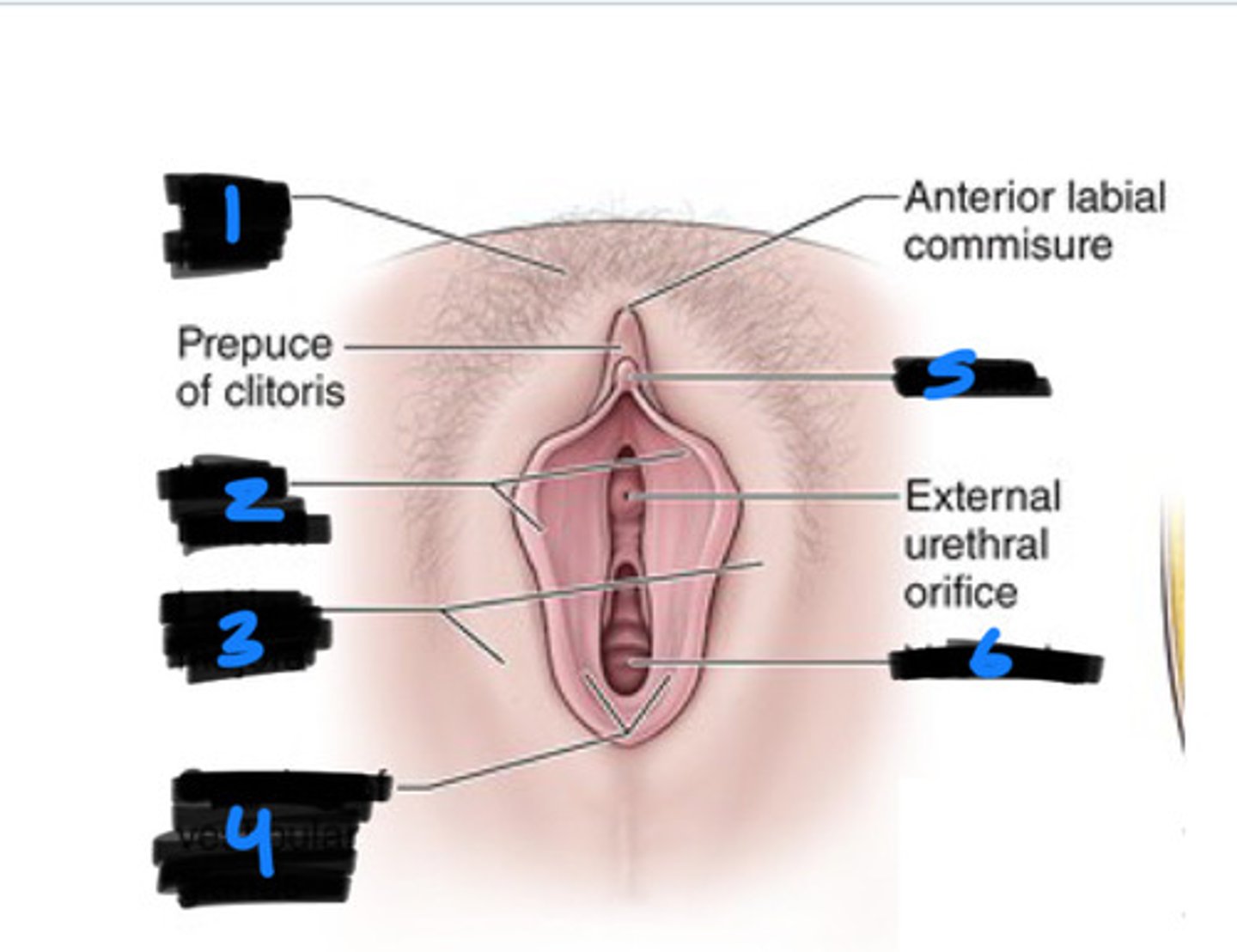
labia majora
2
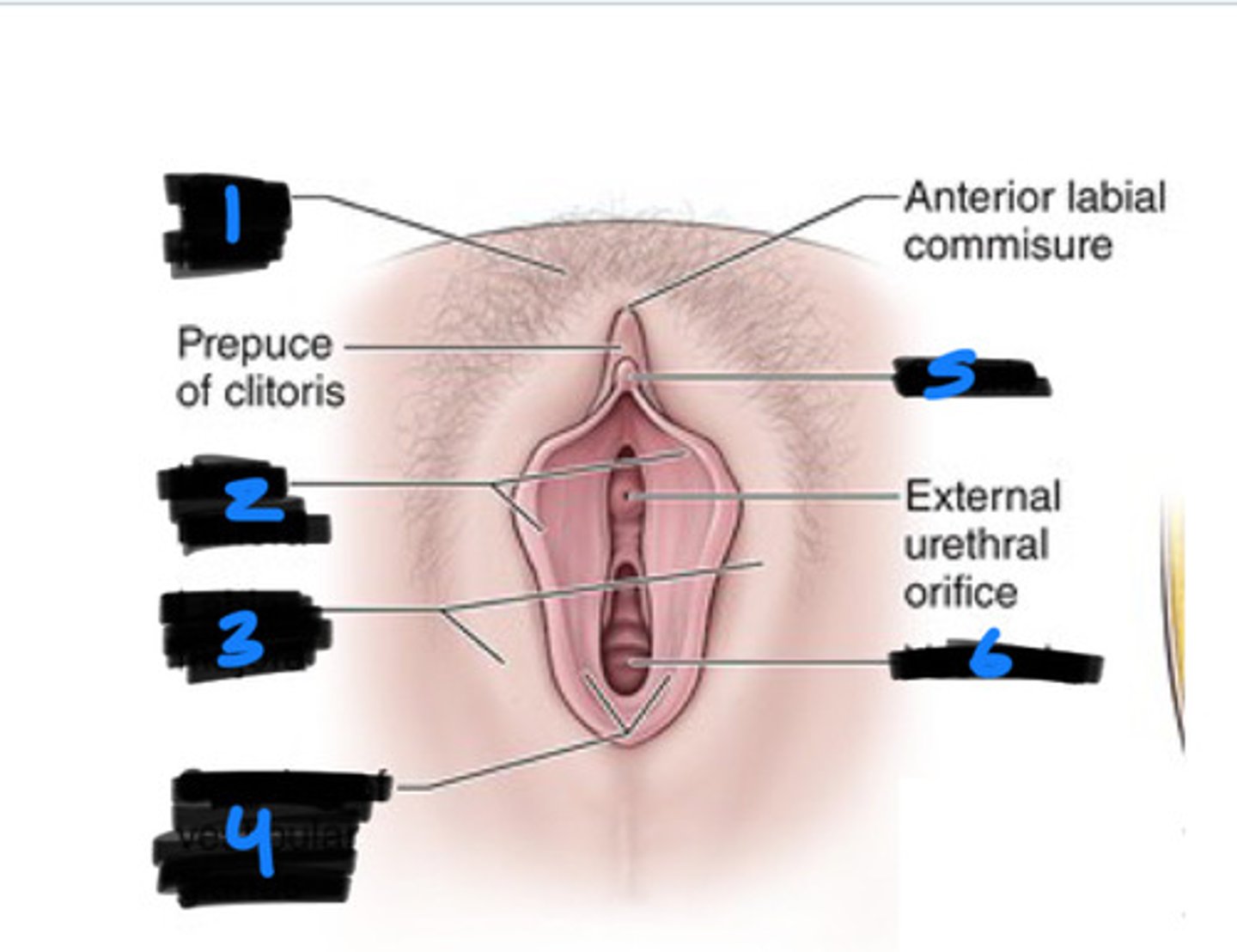
labia minora
3
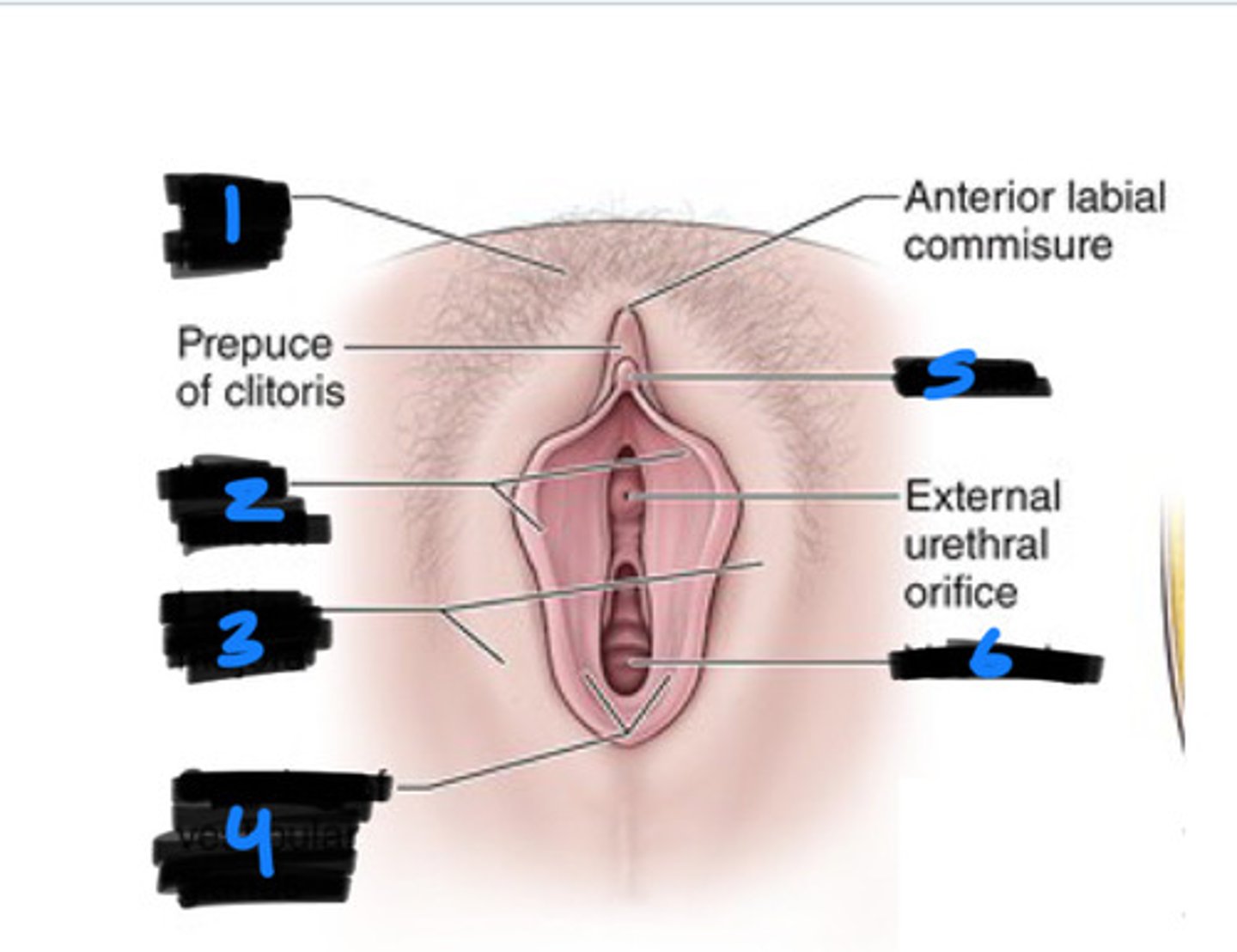
vestibule
6
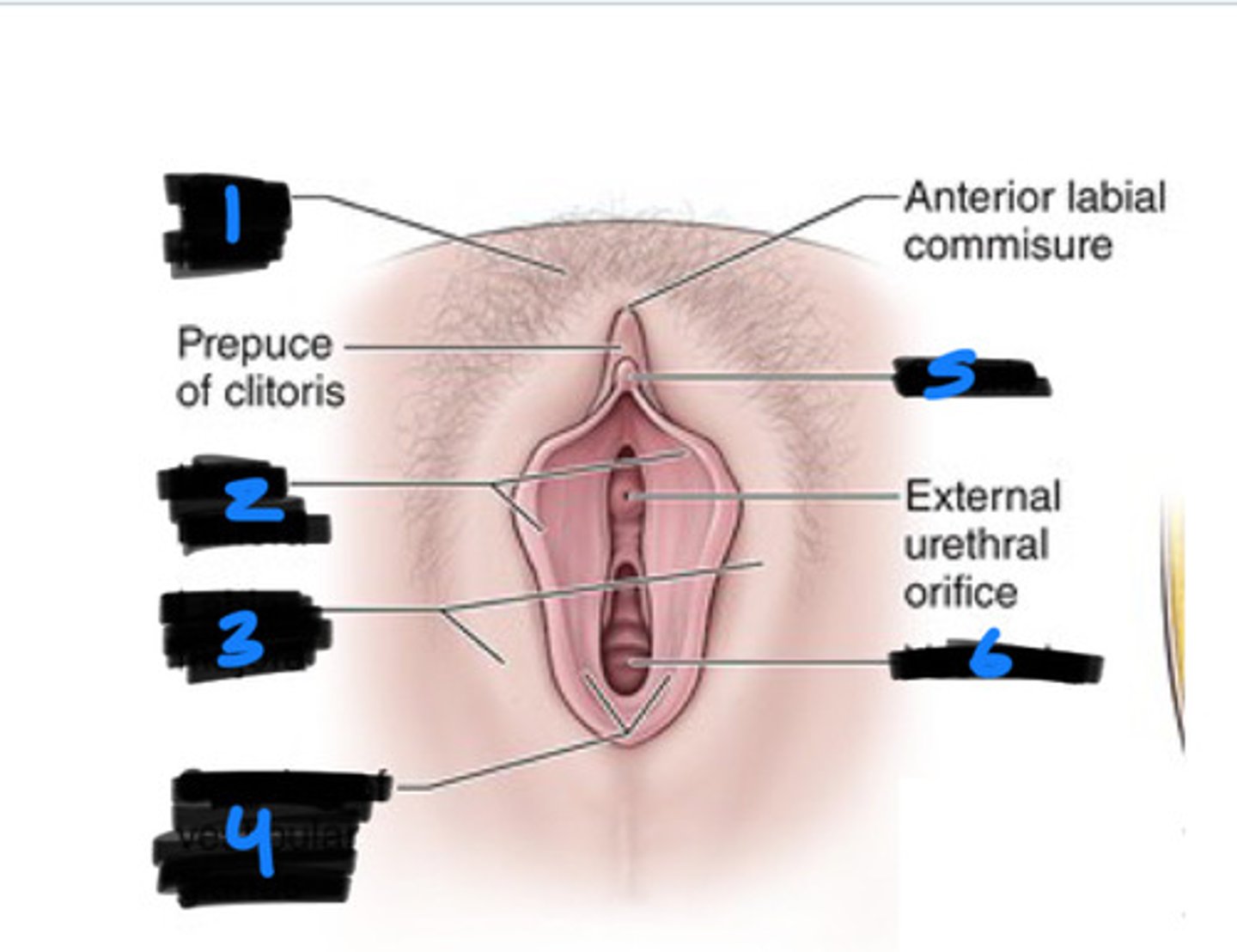
clitoris
5
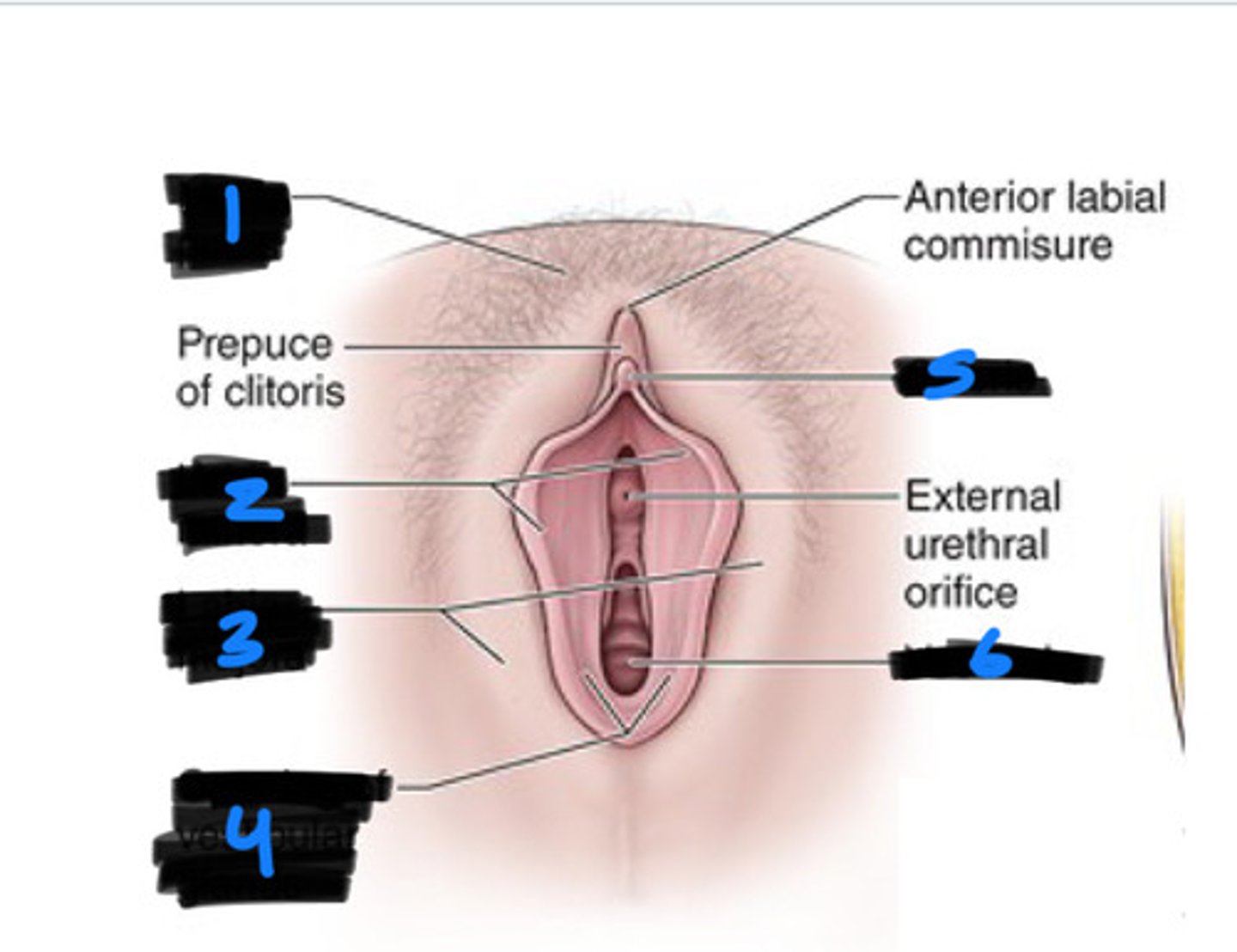
bulb of vestibule
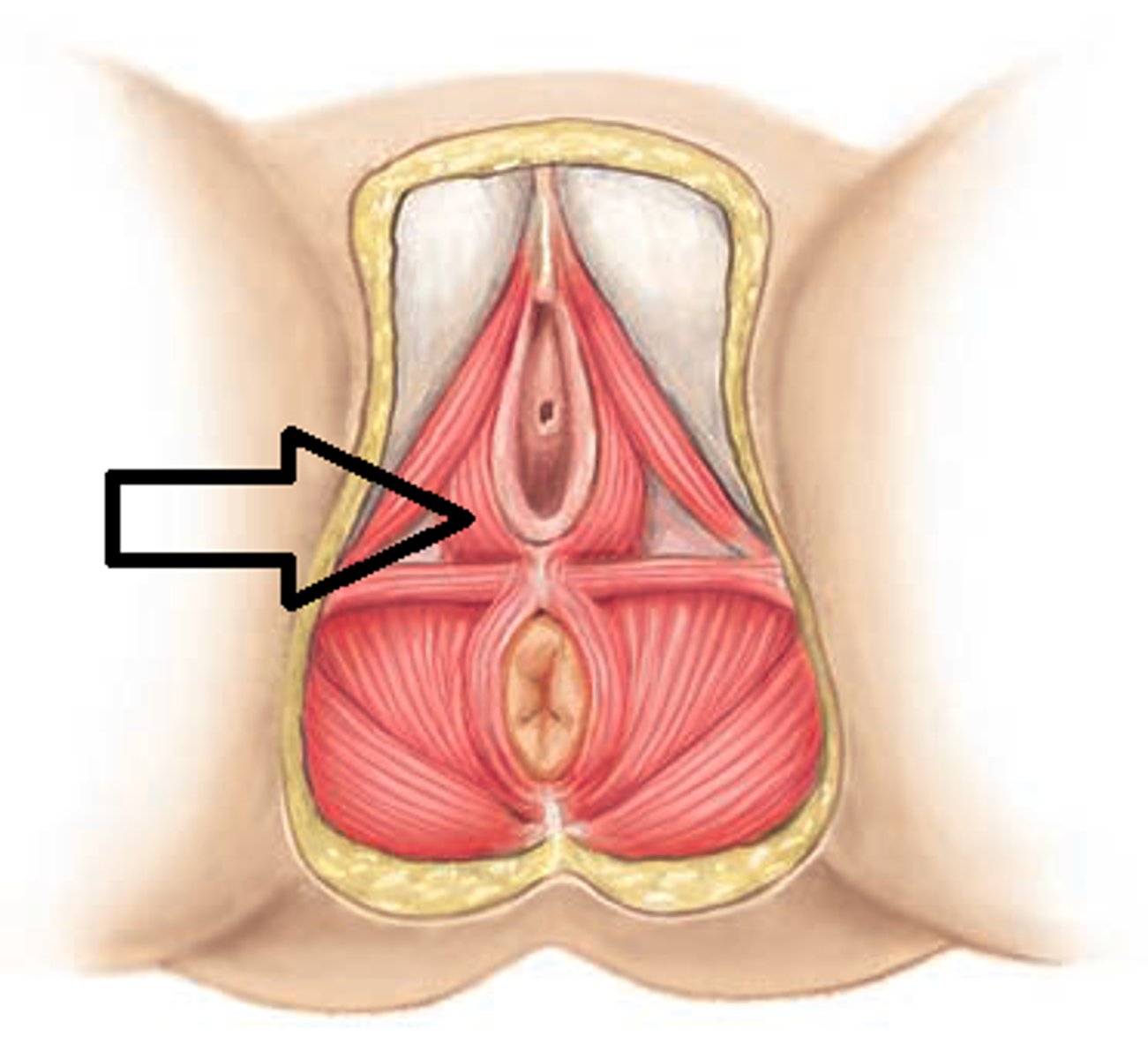
greater vestibular glands
4
- Internal pudendal artery
-external pudendal artery
vascular supply of perineum
Pudendal nerve (S2-S4)
innervation of perineum
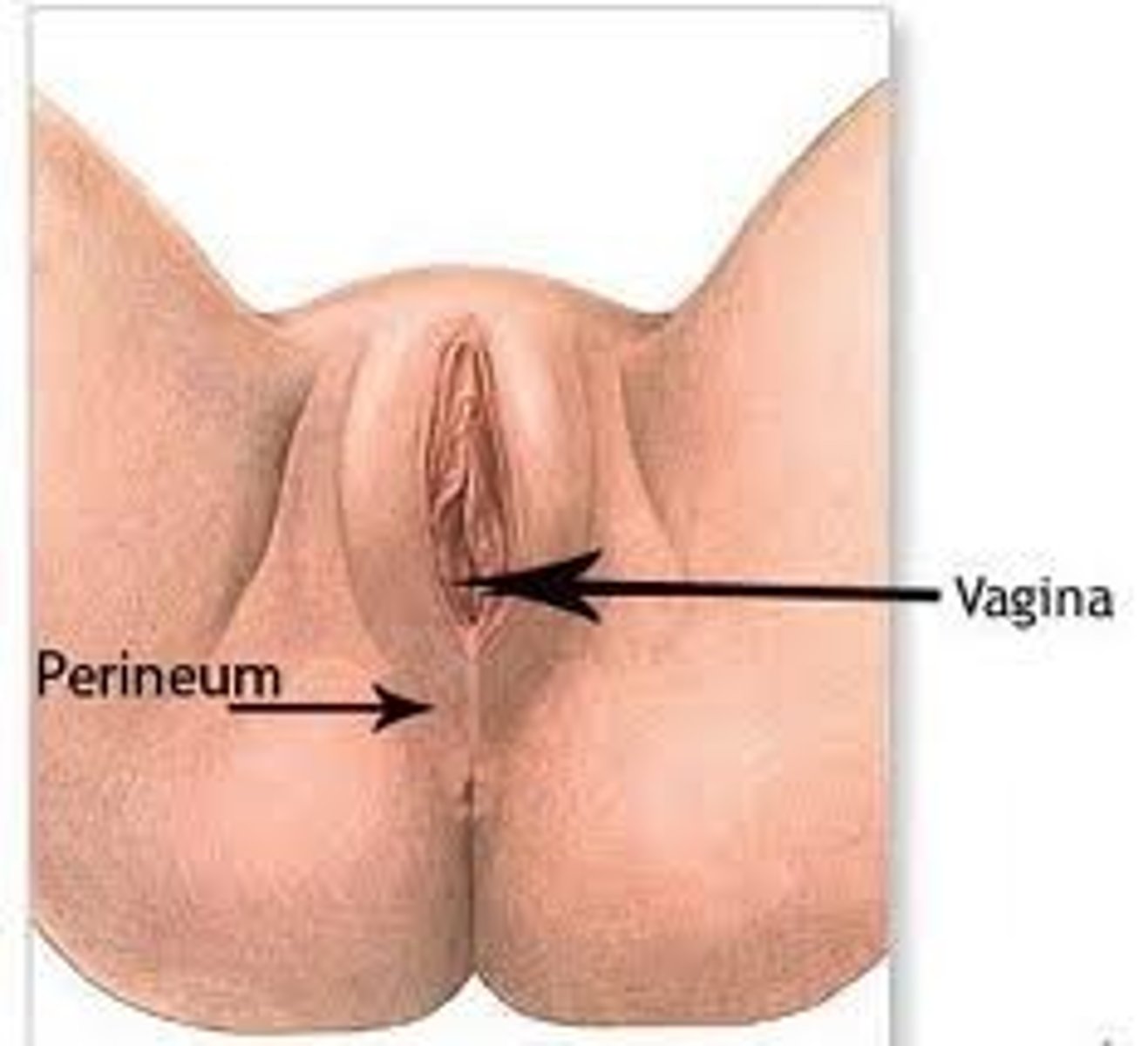
in females, the area between the anus and the vagina
perineum
fibromuscular mass located at the center of the
perineum, between the anus and vagina. Serves as an attachment site for
the superficial perineal, deep perineal, levator ani, and external anal
sphincter muscle
perineal body
-motor: Superficial perineal muscles (ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus,
superficial transverse perineal) and deep perineal muscles (external urethral sphincter)
-sensory: sensation of perineum
somatic innervation
-L1-L2 and course through the lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves to the inferior hypogastric plexus, which innervates the smooth muscle of pelvic organ
sympathetic innervation
S2-S4 spinal cord levels and courses through the pelvic splanchnic nerves to the inferior hypogastric plexus, which innervates the smooth muscle of perineal arteries and the vestibular gland
parasympathetic innervation
-mammary glands produce milk for infant nutrition
-respond to hormonal changes throughout menstrual cycle and pregnancy
breasts
-release GnRH
-regulate pituitary hormone release
hypothalamus hormones
-FSH: stimulate follicle growth
-LH: trigger ovulation
anterior pituitary hormones
-estrogen: endometrial growth, egg maturation
-progesterone: prepares endometrium for implantation
-inhibin: suppresses FSH production
ovaries hormones
-respond to estrogen and progesterone
-endometrium and sheds during menstrual cycle
uterus hormones
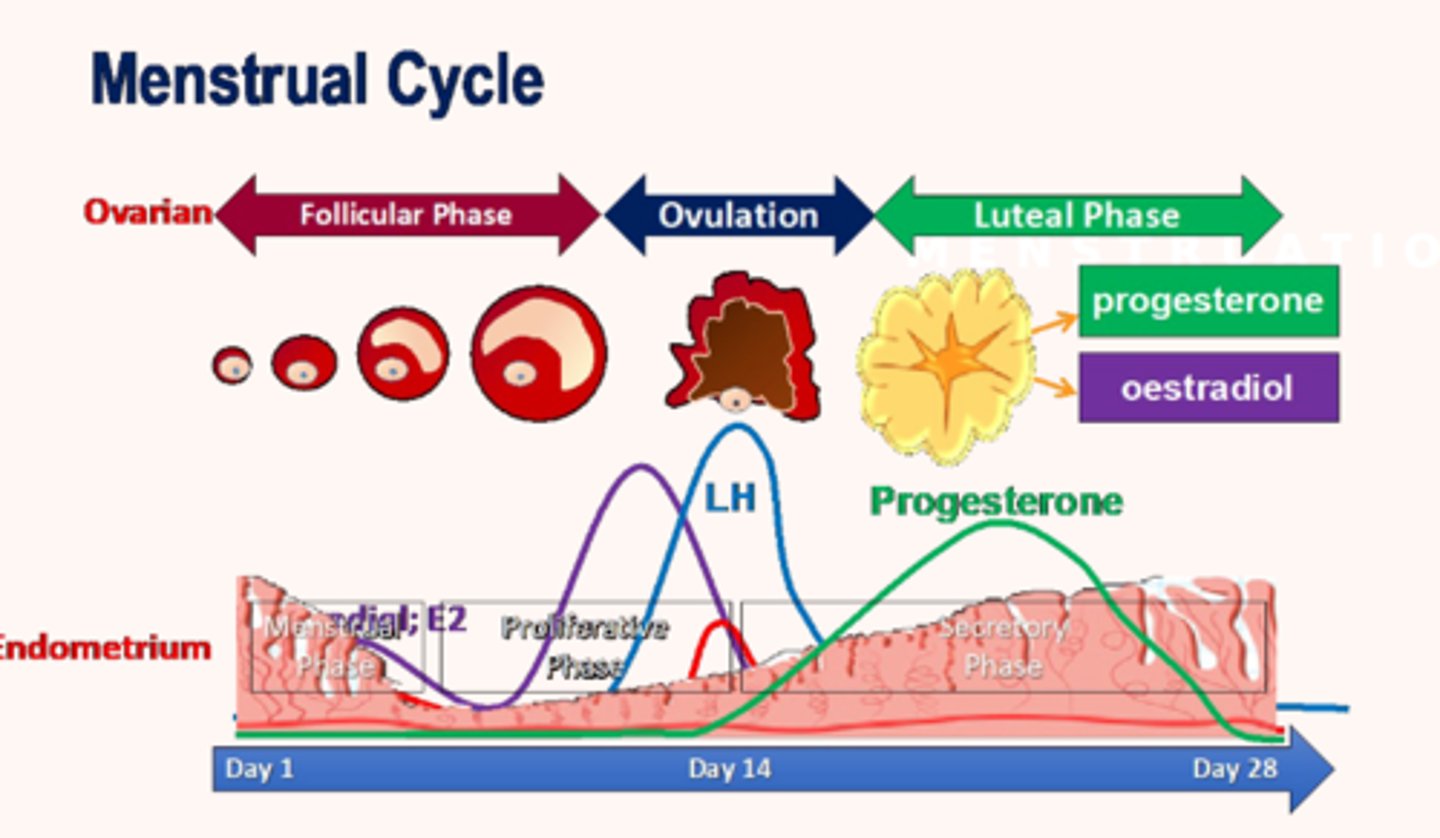
physiology reproductive hormones (female)
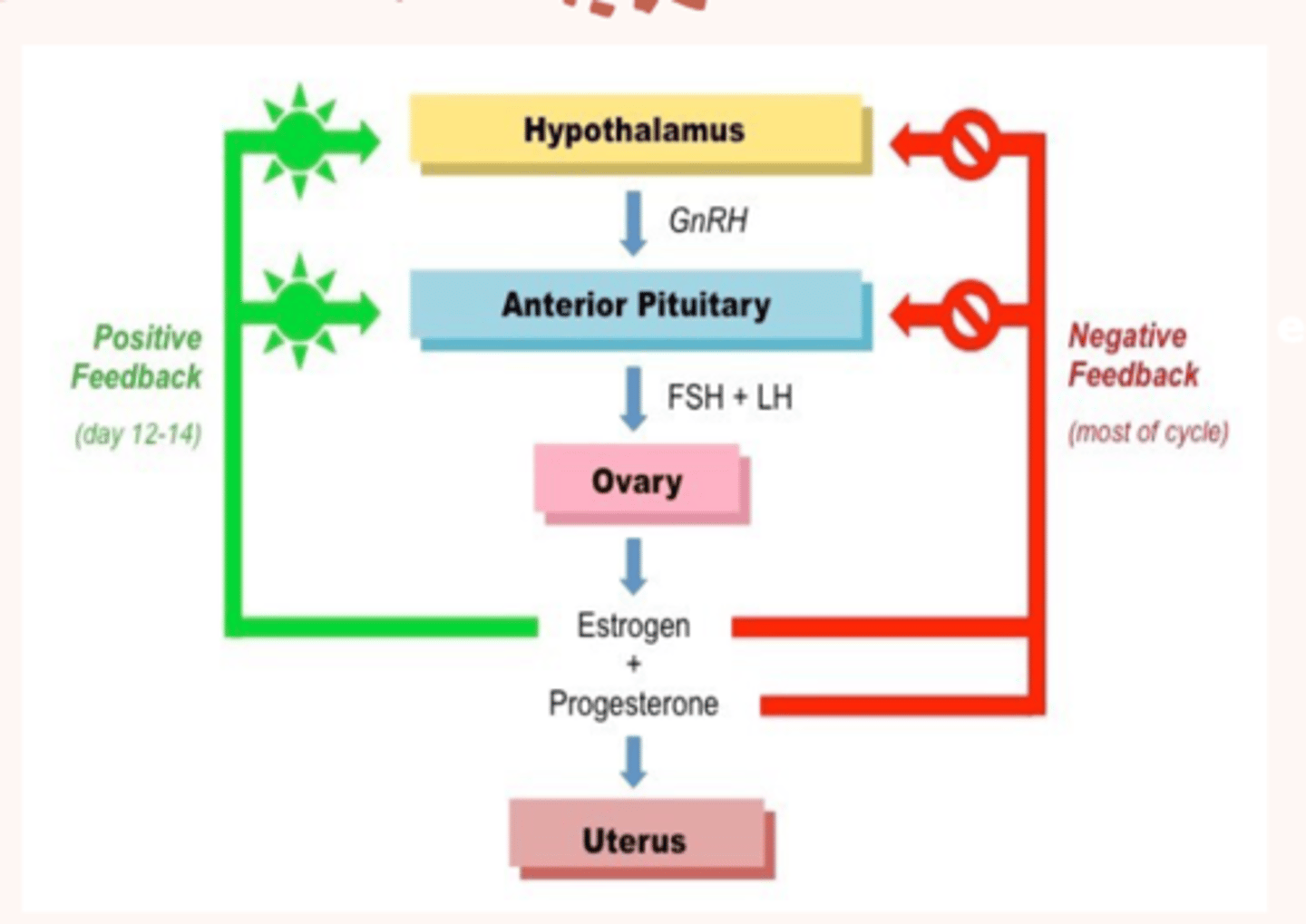
-follicular phase: rising estrogen
-ovulation: LH surge
-luteal phase: progesterone dominance
-menstruation: hormone levels drop
key hormone fluctuation
menstrual cycle
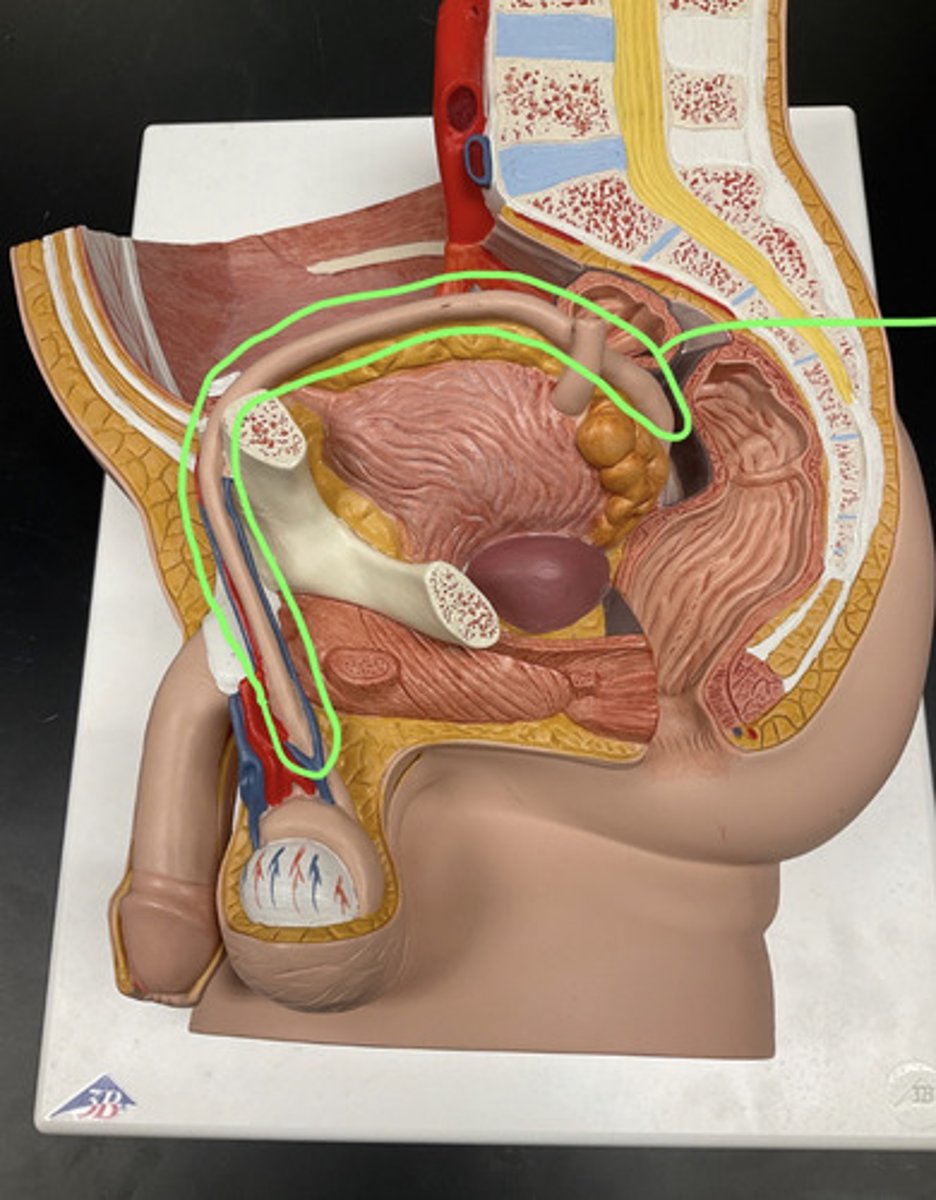
-highly coiled tube attached to the testis
-stores and matures sperm
-approximately 6 meters long if uncoiled
epididymis (male)
-musclular tube connecting epididymis to urethra
-transport sperm during ejaculation
-part of spermatic cord
vas deferens (male)
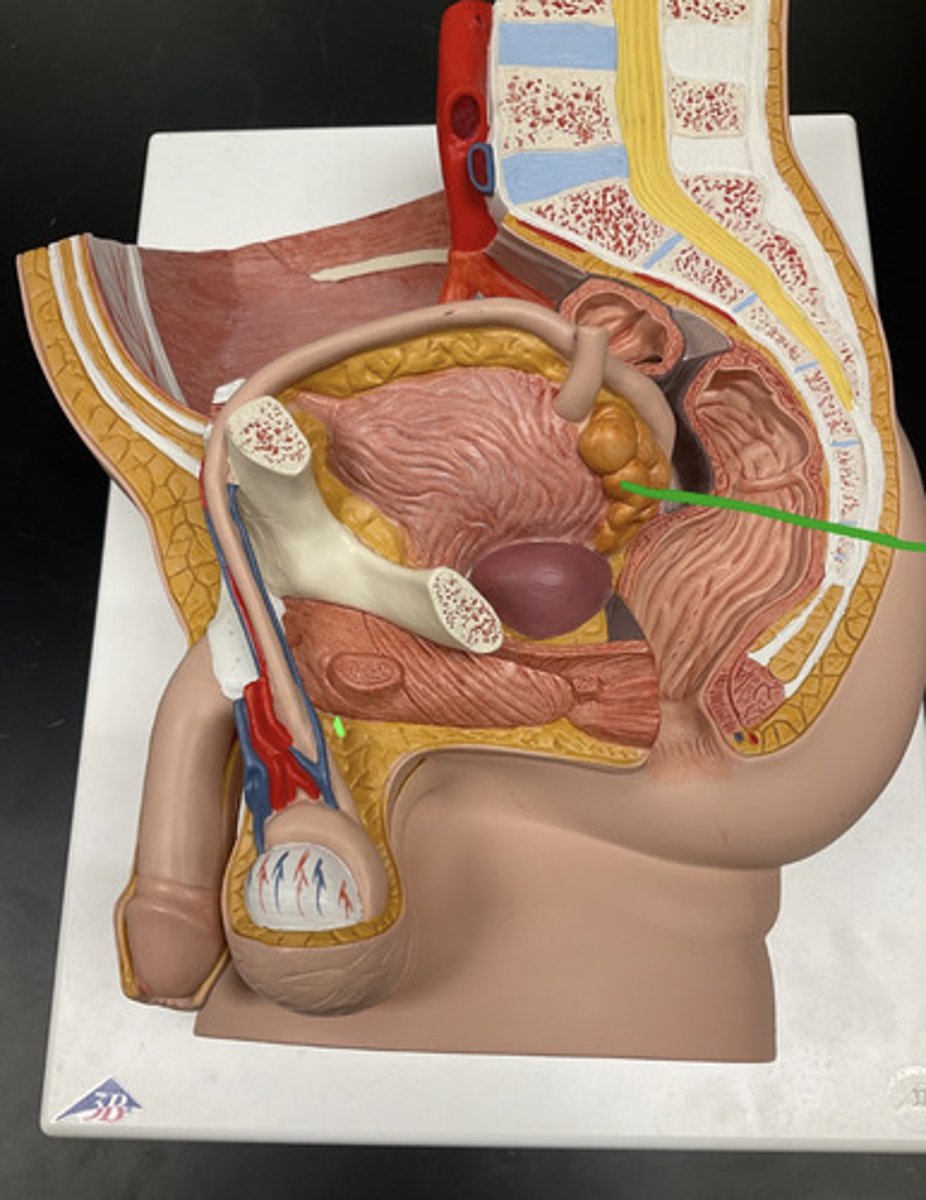
-paired glands behind the bladder
-produced fructose rich fluid
-secretion nourish and activate sperm
seminal vesicles (male)
- Walnut-sized gland below bladder
- Produces alkaline fluid (30% of semen volume)
- Secretions protect sperm in acidic vaginal environment
prostate gland (male)
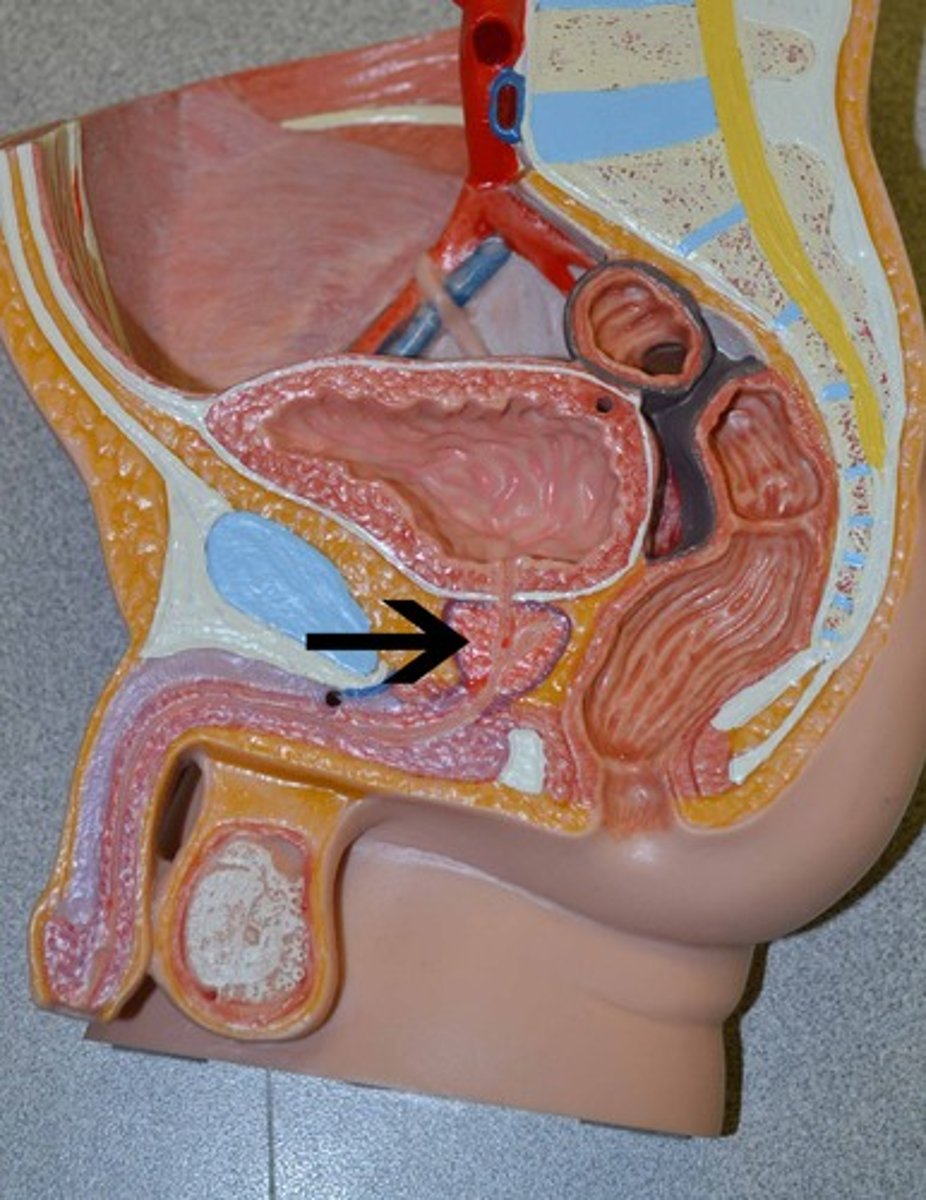
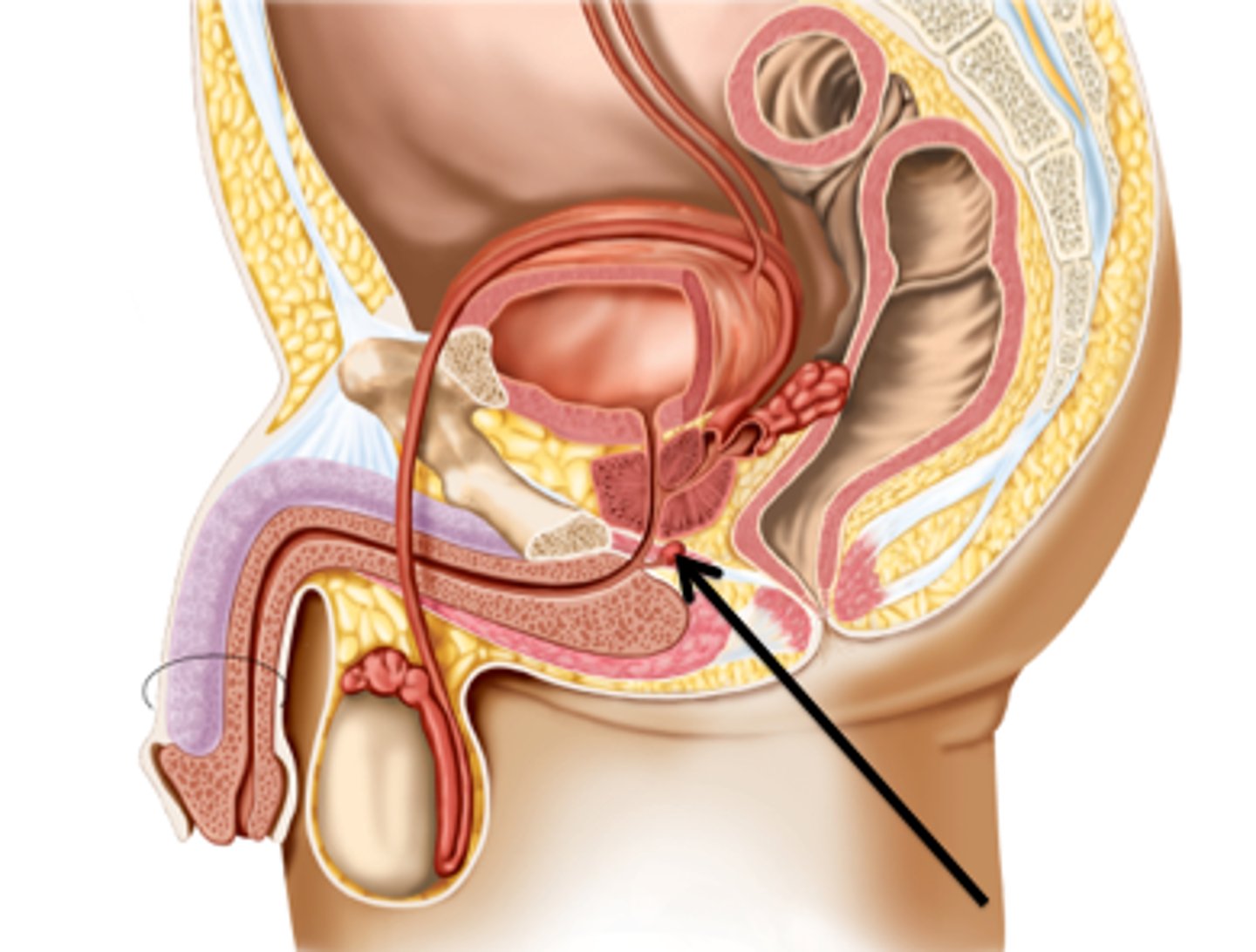
- Pea-sized glands near prostate
- Produce clear, lubricating fluid
- Neutralize urine traces in urethra before ejaculation
bulbourethral glands
- Process of sperm production in testes
- Takes about 74 days
- Continuous process from puberty onward
spermatogenesis
- GnRH from hypothalamus
- FSH and LH from anterior pituitary
- Testosterone from Leydig cells
- Inhibin for negative feedbac
hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis
- Produced by Leydig cells in testes
- Stimulates spermatogenesis
- Promotes development of male secondary sex characteristics
- Influences libido and muscle mass
testosterone production and effects