Chapter 14- Lymphatic system
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Provide a physical barrier to the entrance of pathogens
Which of the following is NOT a direct function of the lymphatic system?
Cardiovascular system
Which organ system transports antibodies to where they are needed?
Helps propel lymph through the lymphatic vessels
Which of the following is one way the muscular system aids the lymphatic system?
SCID
A child born with the inability to develop either cell- or antibody-mediated immunity is diagnosed with
T cells becoming less responsive to antigens.
Changes in the immune system that accompany aging include
lymphocytes
Which are the primary cells of the lymphatic system?
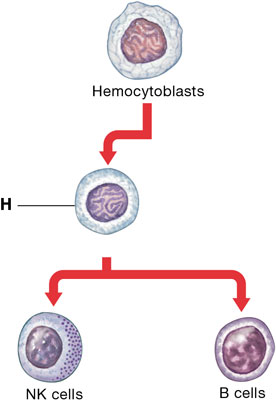
lymphoid stem cell
Which type of cell (labeled "H") gives rise to B cells and NK cells from the bone marrow?
right lymphatic duct
Lymph from the right axillary region would empty into the ___________.
T cells, B cells, and NK cells
The three main classes of lymphocytes found in the blood are __________.
lymph nodes
Which of the following is separated from surrounding tissues by a fibrous connective tissue capsule?
inguinal
A bacterial infection in the foot would most likely affect lymph nodes in which of the following regions?
antibodies
What binds to specific chemical targets called antigens?
protect against particular threats.
Adaptive defenses
inflammation
Swelling, redness, heat, and pain are classical characteristics of which of the following defense mechanisms?
redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
Major events produced by inflammation include
phagocytes
Which of the following is the "first line of cellular defense" against foreign compounds or pathogens?
diapedesis
The ability of certain phagocytes to move through the wall of a capillary is called ________.
Kupffer cells
________ are macrophages found in and around blood channels in the liver.
Interferons impart resistance to viral infections.
Choose the correct statement about interferons.
makes capillaries more permeable and speeds up blood flow through the area of damaged tissue
Which is the action of histamine?
NK cells recognize abnormal or cancer cells by a specific antigen on their cell membrane.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Natural Killer (NK) cells?
interferons
Which of the following innate internal defenses work by interfering with viral replication?
The phagocytes recognize molecules on pathogens not normally found on body cells.
How do phagocytes recognize foreign cells or bacteria?
complement proteins
Which of the innate defense mechanisms can lyse bacteria and mark cells for phagocytosis?
antibodies and complement proteins
Which of the following can act as opsonins on bacteria, thus enhancing phagocytosis?
developing immunity after getting infected by a pathogen
Which of the following is an example of naturally acquired active immunity?
T cells
Which cells have a primary role in cell-mediated
immunity?
T cells
When an antigen triggers an immune response, it usually activates ________ first.
antibodies
During a typical immune response, activated B cells mature into cells that produce ________, which bind(s) to and attack(s) foreign invaders.
Memory cells
________ enable the immune system to launch a faster, stronger response to a previously encountered
antigen.
naturally acquired passive immunity
Immunity that results from antibodies ingested from breast milk is which type of immunity?
naturally acquired active immunity
A child develops symptoms of chicken pox, produces antibodies against its specific antigens, and recovers from the illness. Later as an adult, he is immune to another exposure to the chicken pox virus. This is an example of which type of immunity?
artificially induced passive immunity.
A virus is injected into a rabbit and the rabbit is allowed to make antibodies against the viral antigen. These antibodies are then removed from the rabbit plasma and injected into a human to combat an infection by the same virus. This would be an example of
naturally acquired active immunity.
Allowing small children to be exposed to some dirt is one way of imparting
plasma cells
Which of the following secretes antibodies that have the same target as the antibodies on the surface of sensitized B cells?
IgE/accelerates inflammation
Identify the correct match between the immunoglobulins and their characteristics.
IgE
Immunoglobulins that can bind to antigens, stimulating basophils and mast cells, are called ________ antibodies.
IgM
After receiving a blood transfusion, a patient develops signs indicating a cross reaction between incompatible blood types. Which class of immunoglobulins is responsible for these signs?
They are responsible for defense against many viruses, bacteria, and bacterial toxins.
What is the function of IgG antibodies?
agglutination
The clumping of red blood cells, which occurs when incompatible blood types are mixed, is an example of
________.
Plasma cells
__________ synthesize and secrete large quantities of antibodies.
it transports cells and dissolved materials, including nutrients, wastes, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Recall that the lymphatic system defends against infection and disease and returns tissue fluids to the bloodstream (as you saw in Chapter 1: An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology). The tissue (interstitial) fluid that is transported by lymphatic vessels is called lymph. Recall also that lymph is a fluid connective tissue. Along the way to the cardiovascular system, lymph is monitored for signs of injury and infection. This recirculation of fluid is essential for homeostasis. What is the function of the cardiovascular system?
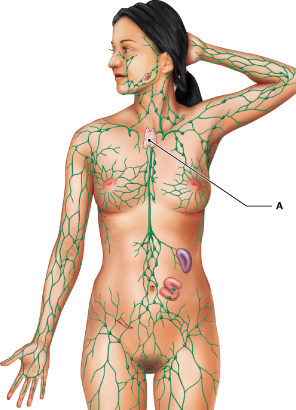
thymus
Identify the lymphoid organ labeled "A."
purify lymph before it reaches the veins.
Lymph nodes
filters blood.
The role of the spleen is slightly different from other lymph organs because it
interferons
Cells infected with viruses will release __________.
complement proteins
Which of the following are activated by antibodies and actually cause destruction of the pathogen?
breast milk
Which of the following is an example of naturally acquired passive immunity?
an immediate rise in IgG concentrations occurs.
During the secondary response to antigens following a previous initial exposure,
immunodeficiency; allergy
Failure of the immune system to respond to the presence of antigens is known as _________________; overreaction of the immune system to the presence of antigens is known as
__________________.
helper T cells
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that causes the disease known as AIDS selectively infects ________, which leads to clinical problems.
multiple sclerosis
Which of the following is an example of autoimmune
disease?
Immune surveillance is depressed.
Why does the risk of cancer increase in AIDS
patients?
IgE antibodies
Sensitization to an allergen during the initial exposure leads to the production of large quantities of
________.
Immunological competence
________ is the ability to produce a normal immune response upon exposure to an antigen.
allergies
Inappropriate or excessive immune responses to antigens are defined as
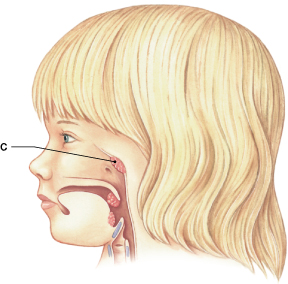
pharyngeal
Identify the tonsil labeled "C."
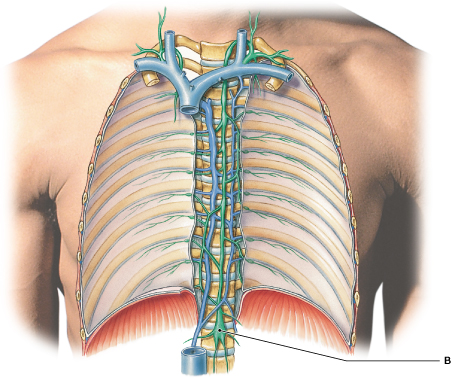
cisterna chyli
Identify the structure labeled "B."
transport of dissolved gases
Which of the following is NOT a function of the lymphatic system?
thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct.
The two collecting ducts that ultimately drain the lymphatic vessels are the
spleen
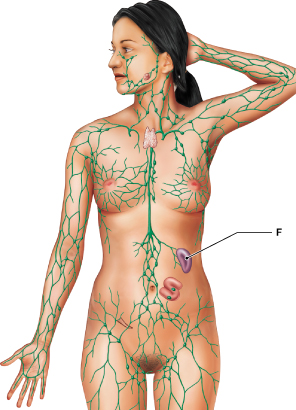
Identify the lymphoid organ identified as "F."
medulla
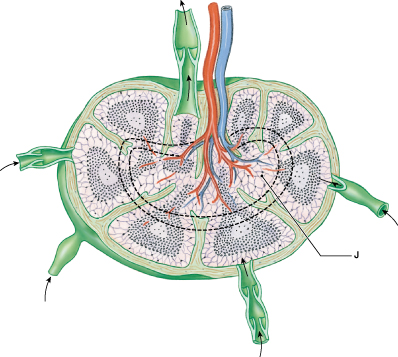
Identify the region of the lymph node labeled "J."
T cells
The group of lymphoid stem cells that migrates to the thymus and divides repeatedly produces which type(s) of lymphocytes?
Tonsils
________ are large lymphoid nodules that are located in the walls of the pharynx.
posterior to the sternum.
The thymus gland is positioned
Peyer patches
________ are clusters of lymphoid nodules located beneath the epithelial lining of the intestines.
production, maintenance, and distribution of lymphocytes
Which of the following is a primary function of the lymphatic system?
efferent lymphatic vessels.
Lymphatic vessels, which exit the lymph node and carry the lymph toward the venous system, are called
hilum
Splenic blood vessels and lymphatic vessels connect with the spleen at the
veins
The wall structure of lymphatics and the flow of lymph through them are comparable to those of
80
Within lymph nodes, fixed macrophages and dendritic cells remove at least ________ percent of antigens arriving in lymph.
subclavian veins.
Lymph returns to the venous circulation by way of emptying into the
lymphadenopathy
Chronic or excessive enlargement of lymph nodes, a sign called ________, may occur in response to bacterial or viral infections, endocrine disorders, or cancer.
They differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies.
Choose the most accurate characteristic of B
cells.
macrophages
Which of the following is NOT a type of circulating
lymphocyte?
mast cells
Which cell population plays a pivotal role in the process of inflammation?
antibodies
All EXCEPT which of the following are examples of innate or nonspecific immunity?
Tolerance
________ exists when the immune system does not respond to normal tissues and their antigens.
can also cross the placenta and provide passive immunity to the fetus.
IgG antibodies
IgC
All EXCEPT which of the following are immunoglobulins?
chemotaxis
The ability of certain cells to respond to chemicals in their environment is called ________.