Physio Lect 14 - Smooth Muscle Excitation Contraction Coupling
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
T/F - Skeletal muscle is innervated by the somatic nervous system, smooth and cardiac is innervated by the autonomic nervous system
T
T/F: Smooth muscle is the only muscle that we focus on that lacks striations
T
What is unique about smooth muscles that allows them to contract and constrict blood vessels in the manner they do?
They are almost in the shape of being wrapped around something like twine, thus when they contract they constrict the tube that they make up
What is unique about the way the smooth muscle constructs the bladder?
it looks like a woven basket, the structure is related to the function.
What is unique about the smooth muscle in the intestines?
they have two beds of smooth muscle, there is a circular muscle and a longitudinal muscles where they contract and move the waste down the intestine while also compressing it
What components do all smooth muscle cells have?
dense bodies - cytoplasmic/in membrane
dense plaques - usually at junctions where two smooth muscles come together
intermediate filaments - links dense bodies and membrane associated dense bodies
gap junctions - between smooth muscle cells - pts of communication
extracellular matrix - surrounds smooth muscle (collagen and elastin fibers) provides anchor points
What do sphincters do?
they close something off, normally contracted
What spaces of the body have smooth muscle that defaults to relaxation?
esophagus, bladder
How can we describe the contraction activity of the stomach and the intestines?
phasically active
How can we describe the contraction activity of blood vessel and airways?
Normally partially contracted
How does the autonomic nervous system regulate smooth muscle?
the sympathetic side usually regulates smooth muscle contraction, using the postganglionic transmitter, NE, and NE receptors like alpha-1 receptors in blood vessels
T/F: Smooth muscles are distinctly different from skeletal muscle
T
T/F: Smooth muscle cells aren’t necessarily anchored to each other.
T
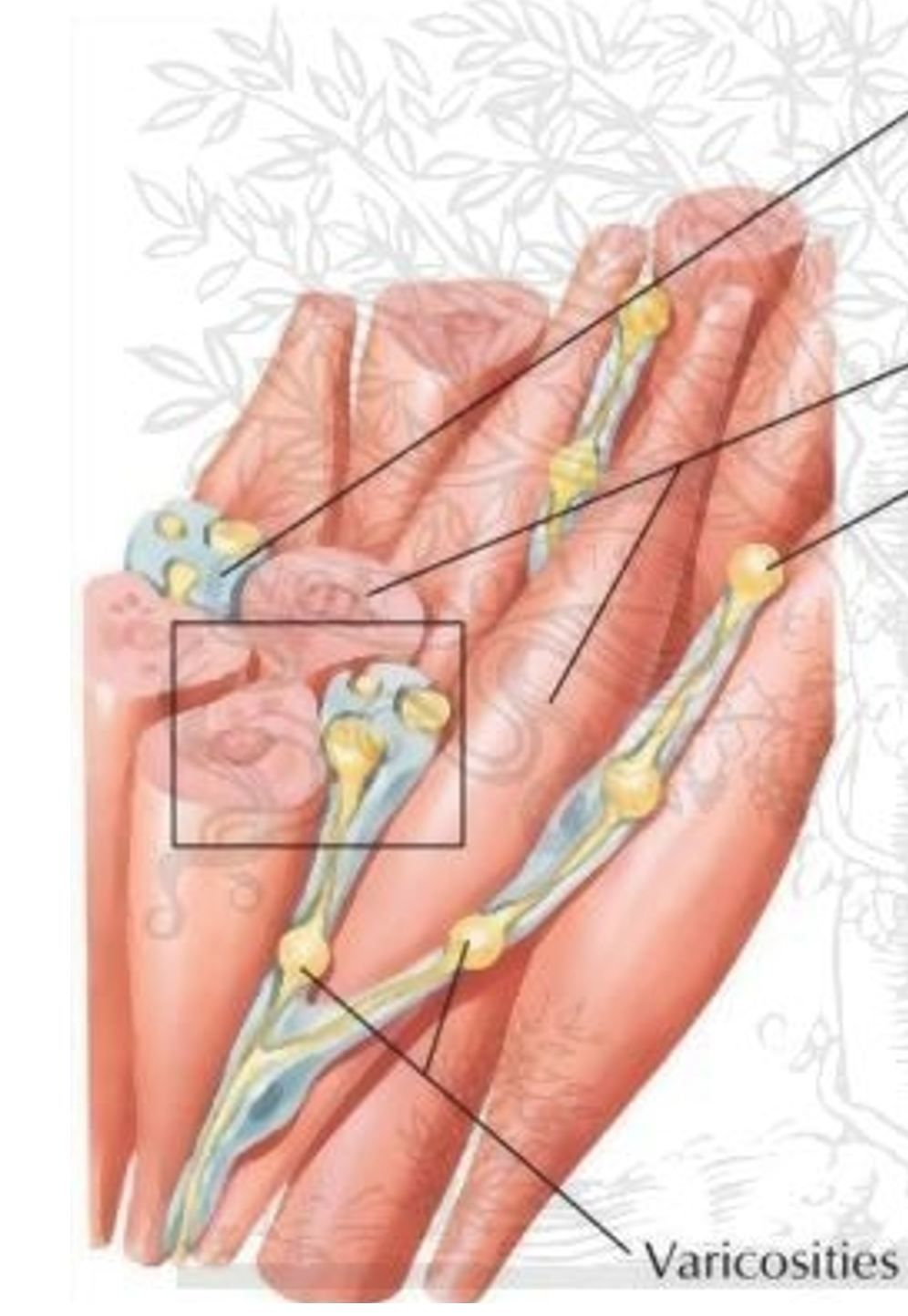
How do the smooth muscle cells communicate?
Interwoven with the cells is the autonomic nervous system, the periodic swellings are called varicosities which contain NTs like NE
What are some of the extrinsic factors that regulate contraction?
Nerves, circulating factors, hormones
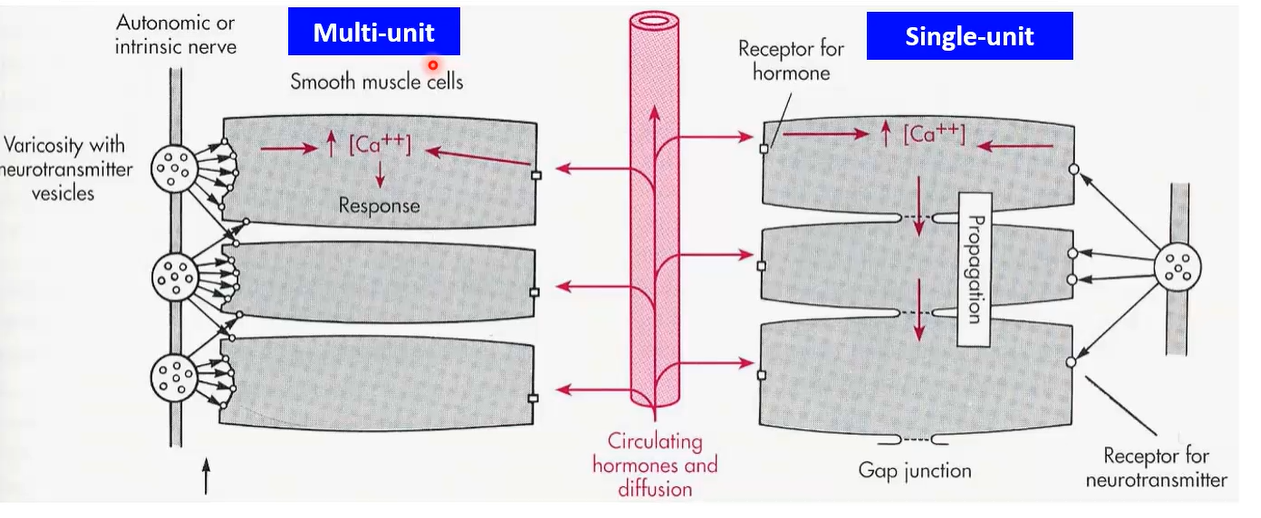
What are the two types of extrinsic regulation for contractions in smooth muscle?
Multi-unit - cells are not connected in any way, and multiple varicosities interact with each cell
Single unit - cells are connected via gap junctions, one varicosity is enough to interact with all nearby cells
What is myogenic tone?
The spontaneous contraction of the smooth muscle cell. Intrinsic force development is often sensitive to changes in the physical and chemical environment such as stretch of the cell or changes in tissue pH or O2 tension.
What is a myogenic contraction?
when the smooth muscle senses a stretch it automatically contracts - happens intrinsically against something
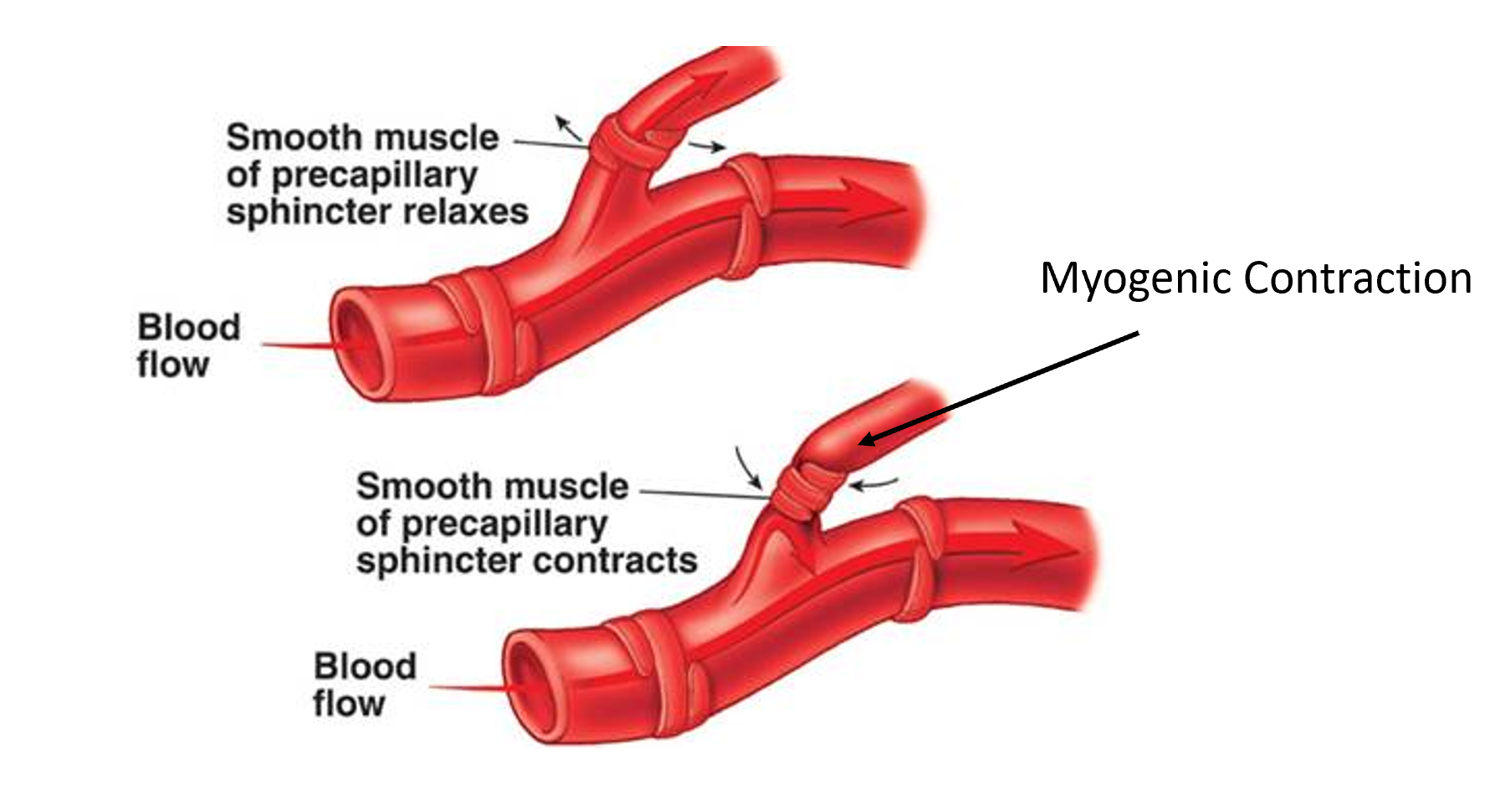
How do we regulate myogenic tone?
Calcium content (the ability to contract is dependent on it)
What are the two intrinsic factors for regulation of contraction?
Myogenic tone and endothelial tissue layers
In smooth muscle contraction, are the myosin heads phosphorylatable?
yes
What is thick filament regulation?
regulated by phosphorylation of myosin heads
What are some of the key items involved in thick filament regulated contractions?
Myosin light chain kinase
Myosin phosphatase
Calmodulin
Calcium
What four channels are involved in calcium entry into the cell from extracellular fluid?
Ligand gated - receptor operated, opens upon binding
Voltage gated - voltage dependent, opens when depolarized enough (high K+ closes)
Stretch - opens during mechanical deformation
Store - opens when internal Ca stores are reduced
When do we release Calcium from the intracellular stores?
agonist stims formation of IP3, opens channel in SR
Ca induced release - high calcium causes release through ryanodine receptor
What are the two main processes for calcium removal from the cell?
Calcium ATPase pumps (on extracellular membrane or in SR) - use energy to move against gradient and out of cell
Ca/Na exchanger, every calcium out brings every sodium in, uses Na/K ATPase to maintain sodium gradient and allow passive transport of sodium into cell
Increase in calcium ____ the contraction of smooth muscle.
favors
Increase in phosphatase activity favors ____ of smooth muscle.
relaxation
Is phosphatase calcium dependent?
no
T/F: Phosphatase activity can change independent of calcium concentration.
T
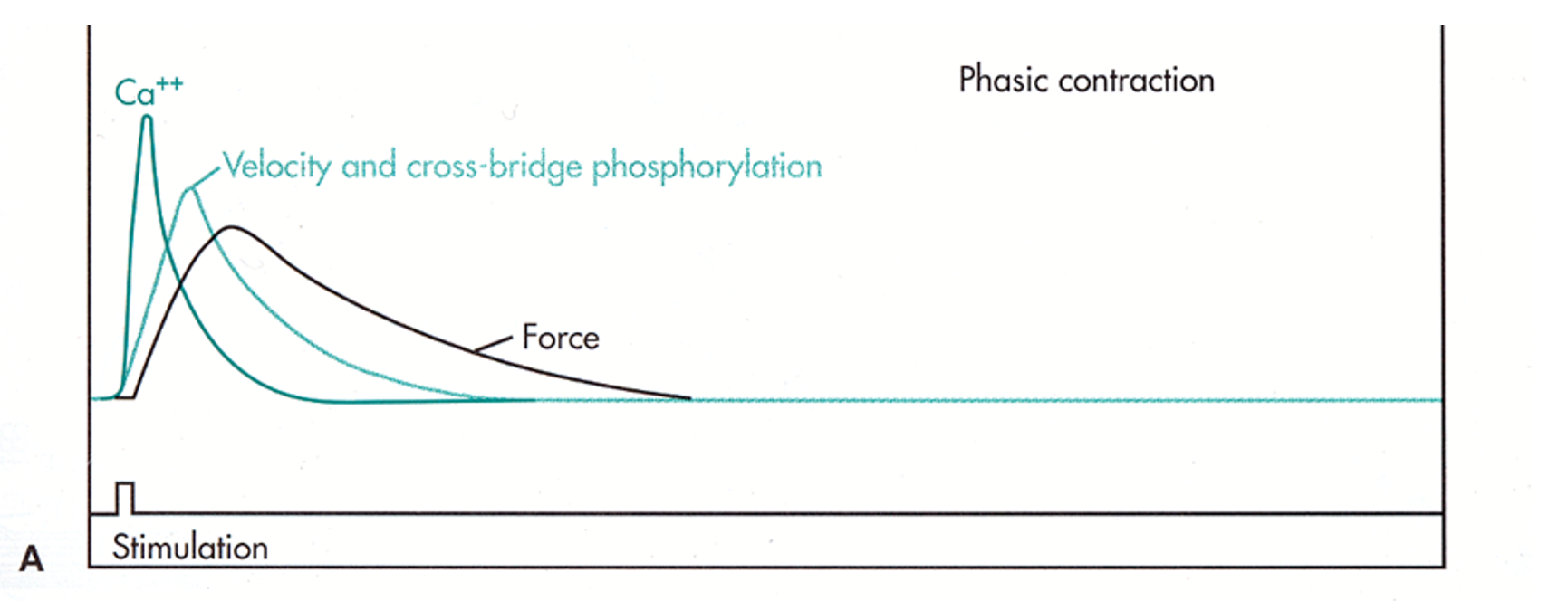
T/F: Phasic contraction can arise from repeated transient stimulations.
T
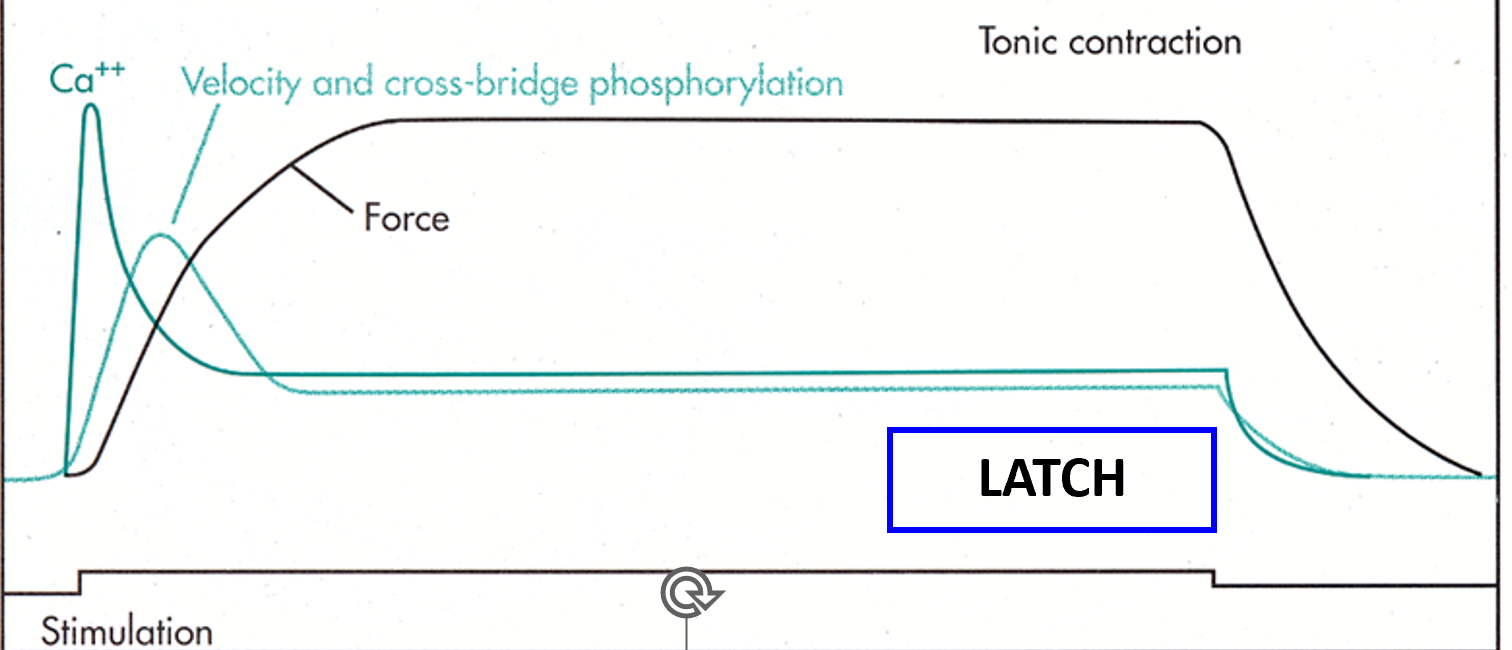
T/F: Tonic contraction involves continuous stimulation in which Ca++ and MLC phosphorylation fall to suprabasal levels, but high levels of force are maintained (latch).
T
T/F: Latch is a very efficient process that consumes little ATP
T