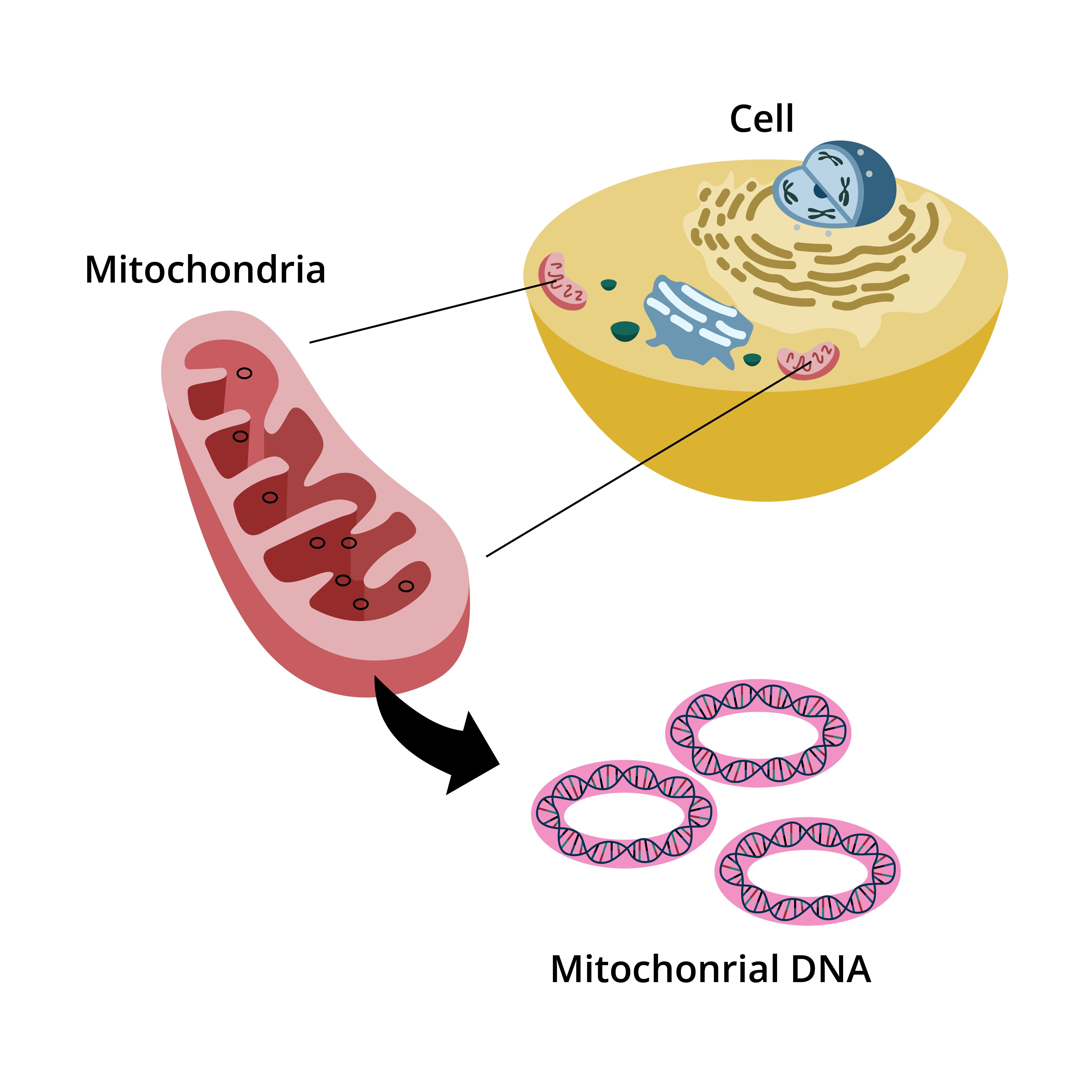
mitochondrial DNA
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)?
A type of genetic material found in the mitochondria
Where is mtDNA found?
In the mitochondria, the organelles responsible for cellular respiration
How is mtDNA inherited?
Only from the mother (maternally inherited)
What shape is mtDNA?
Circular strands of DNA
What does mtDNA code for?
Proteins and RNA molecules involved in cellular respiration
Why is mtDNA useful in forensic science?
It can identify individuals when other types of DNA are degraded or missing
How can mtDNA be used to trace ancestry?
It helps trace maternal lineages and evolutionary history
Why is mtDNA analysis useful for ancient populations?
It helps trace migration patterns when records are missing
What is a limitation of mtDNA analysis?
It only provides information about the maternal lineage
Does mtDNA give information about your father's ancestry?
No, it does not trace paternal lineage
Can mtDNA analysis give definitive proof of ancestry?
No, it only provides evidence—not definitive proof
Why can mtDNA still be analyzed when nuclear DNA is degraded?
Because mtDNA is more abundant and protected in the mitochondria
Why is mtDNA analysis helpful in studying ancient humans?
It reveals maternal migration patterns and genetic links between populations
How is mtDNA different from nuclear DNA?
MtDNA is maternally inherited and circular, while nuclear DNA is inherited from both parents and linear
Figure 1: Mitochondrial DNA.