Lecture #7 | Genetic Drift
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Evolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over time
Genetic Drift
Change in allele frequencies cause by random sampling in populations
random process
always acting at some level in real populations
represents the constant “background noise” of evolution
How can we observe drift over time?
Tracking the frequency (proportion) of one allele
What causes random sampling in real populations?
Any process that has the effect of randomly adding or subtracting fitness irrespective of genotype
Meiosis lottery
One large source of random sampling
ex: oogenesis
Which allele becomes the ovum
¼ alleles end up in the egg and ¾ do not
Other causes for random sampling
Random environmental events
Resources and mates can be randomly encountered or lost
Natural disasters can kill individuals randomly
What does it mean that drift is always happening?
Main driver of allele frequency change (evolution) at the genetic level
It is the “null hypothesis” when testing for other evolutionary processes
Buri drift experiment
began with a balanced 8 males and 8 females that are heterozygous
This was done 19 times
Most populations in Buri’s experiment fixed (100% frequency) of one of the two alleles
Conclusion: Drift caused genetic diversity to be lost
What populations are impacted most be genetic drift?
Smaller populations
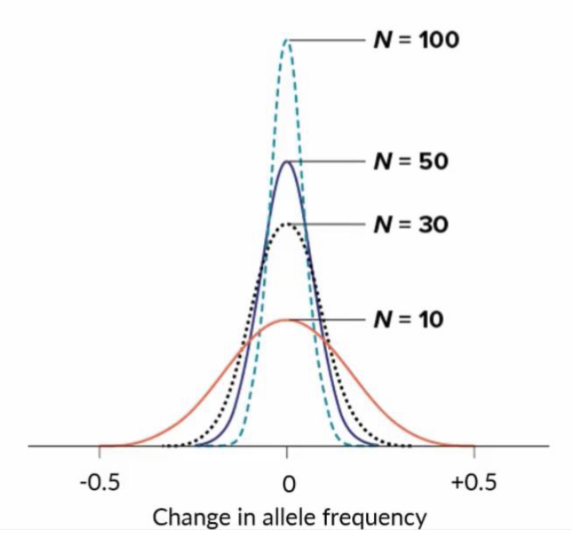
alleles are fixed more rapidly in small populations resulting in a loss of variation
Census size (Nc)
Count of all the individuals in the population
However, every individual may not contribute to the gene poll
Ex: animals where a single male monopolize multiple females results in some males not breeding
Population size may also be fluctuating through time
Effective population size: Ne
The number of breeding individuals in an idealized populations that would show the same amount of genetic drift as seen in the population being studied
dictated the strength of drift, not Nc
reductions in effective population size can cause drift to become stronger
Bottlenecking effect
Only a few individuals contribute to a gene pool before population grows
magnifies the effect of genetic drift
example: cheetahs have very low levels of genetic diversity due to multiple bottlenecks
Founder effects
Occurs when some individuals become isolated from a larger population
very common on islands
How can we detect the effects of genetic drift
Quantify heterozygosity
Drifts cause populations to lose genetic variation
We expect populations that have experienced more drift to have lower heterozygosity
Key points about genetic drift
its unbiased
Its stringer in smaller populations
It causes genetic variability to be lost
It causes populations to become different
Drift causes alleles to fix
How do large fitness effects impact drift
Large fitness effects can easily overcome drift
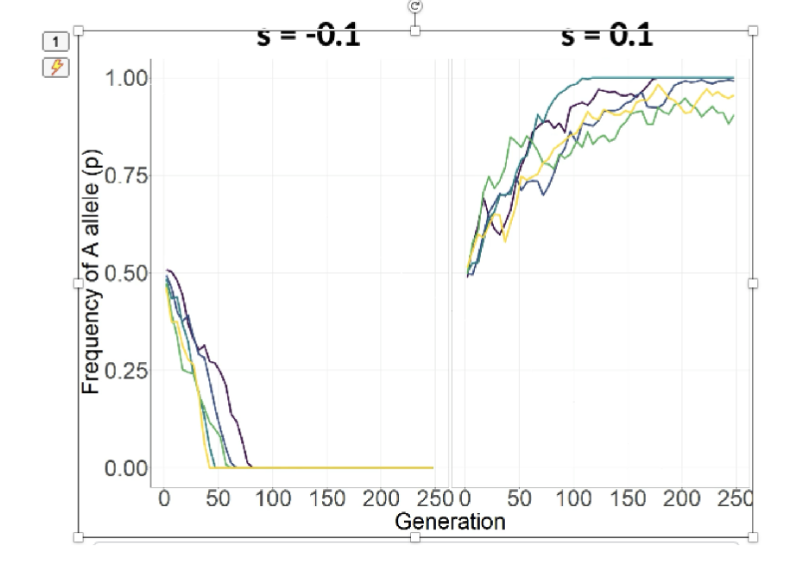
Small fitness effects (s) cant overcome drift
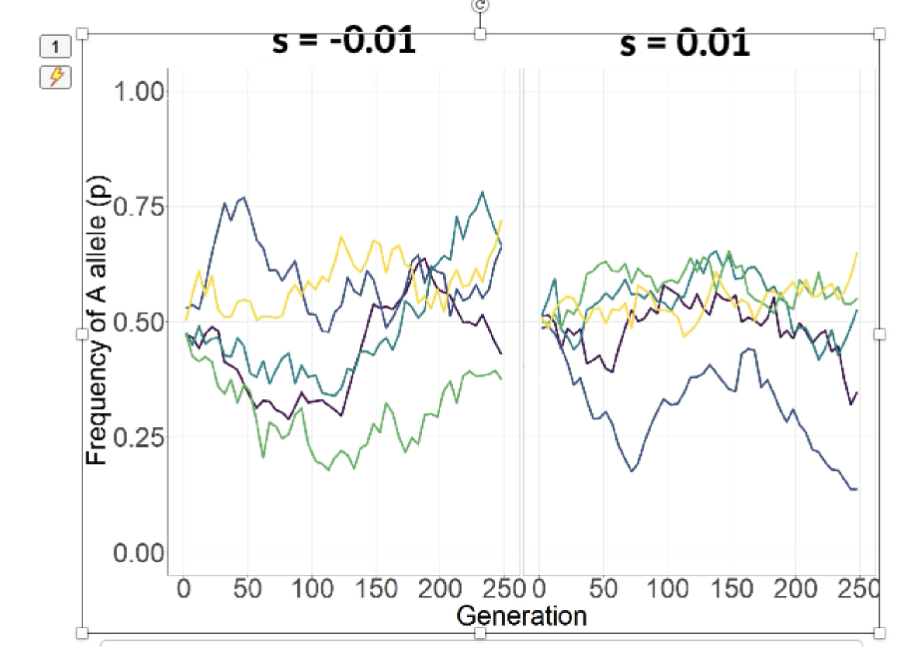
Relationship between drift in small populations and deleterious alleles
Drift can cause deleterious alleles to fix