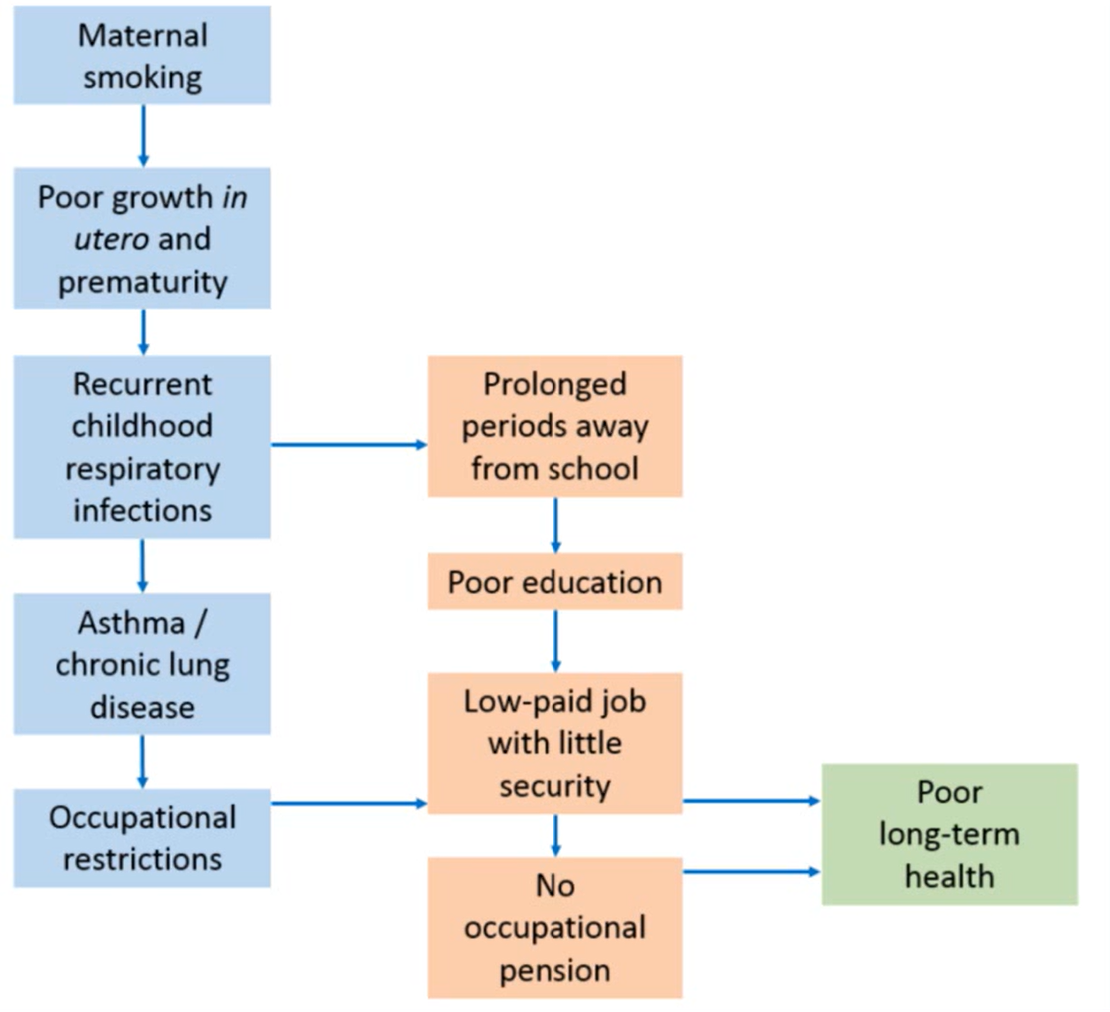
patterns of health inequalities in UK
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
block 2 week 2 socpop
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
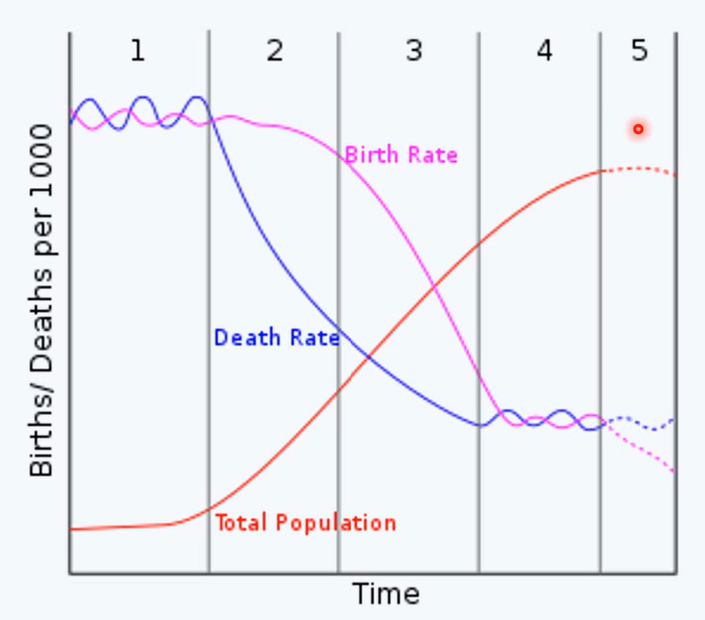
epidemiological transition
phase 1: pestilence and famine
high mortality
infectious disease
malnutrition
phase 2: receding pandemics
reduction in rate of infectious disease mortality
phase 3: degenerative and man-made disease
more non-communicable disease
phase 4: declining CVD mortality, ageing and emerging disease
phase 5: aspired quality of life with persisting health inequalities
indicators of population health
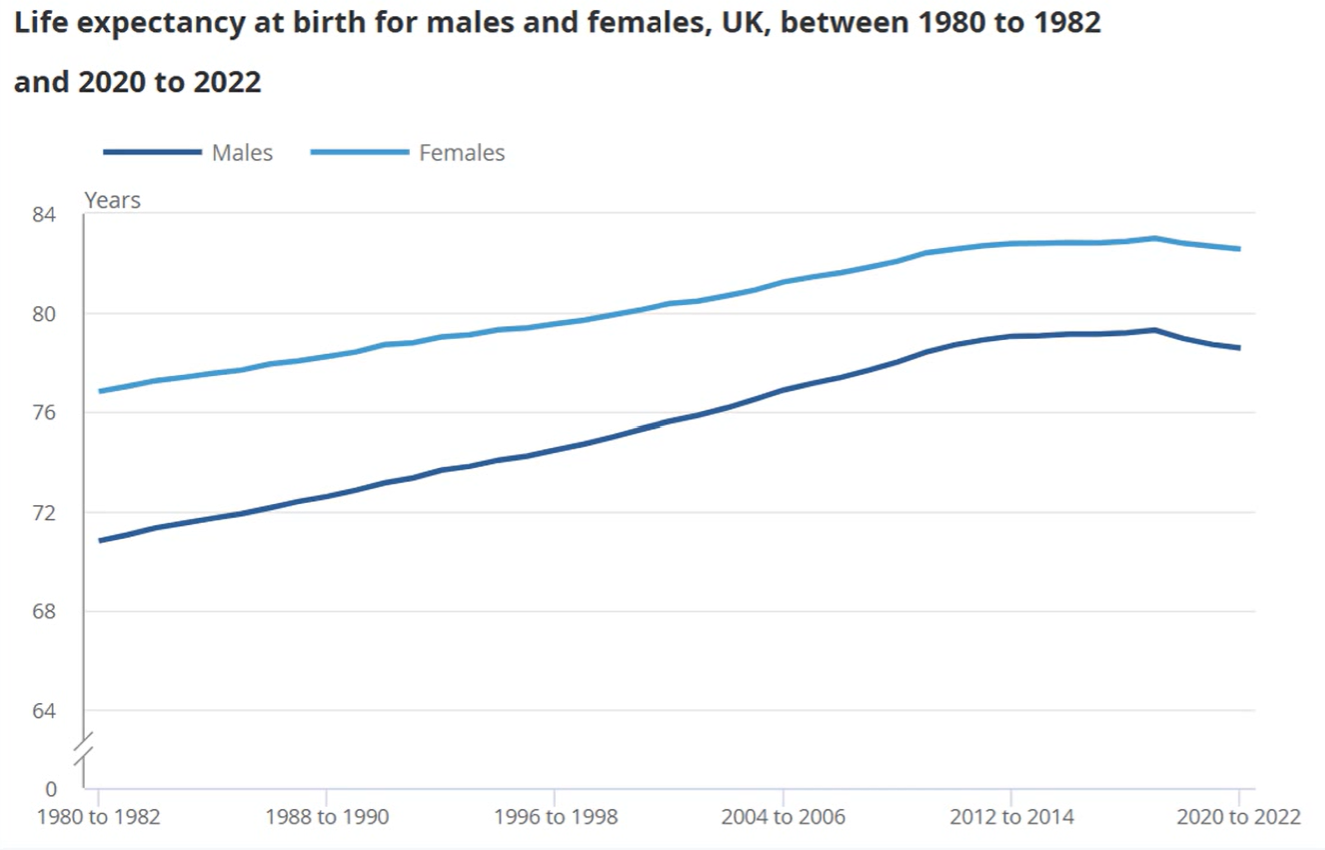
life expectancy
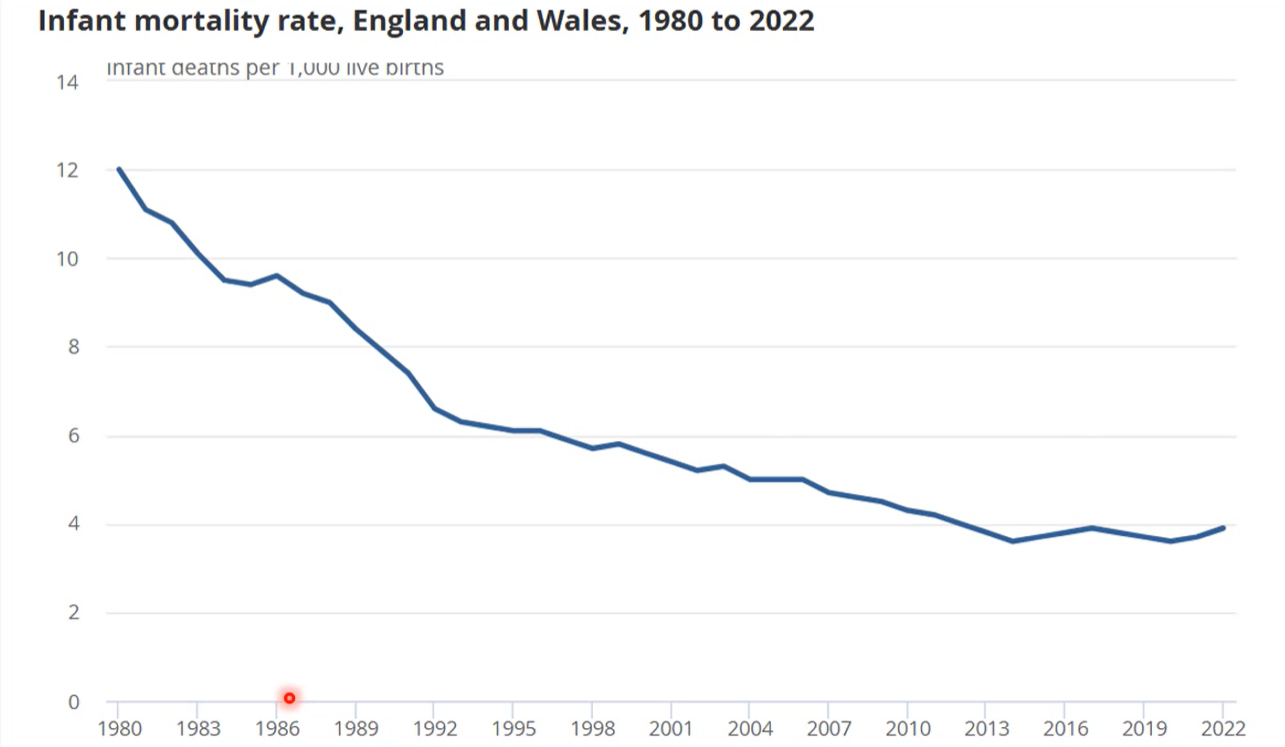
infant mortality
correlates well with other measures but simple to measure
sensitive to social determinants of health
healthcare use (hospital or emergency admission)
public health or disease specific indicators
trend of life expectancy
trend of infant mortality
leading cause of death in England and Wales (2022)
dementia (11.5%)
ischaemic heart disease (10.3%)
chronic respiratory disease (5.2%)
cerebrovascular disease (5.1%)
lung cancer (5%)
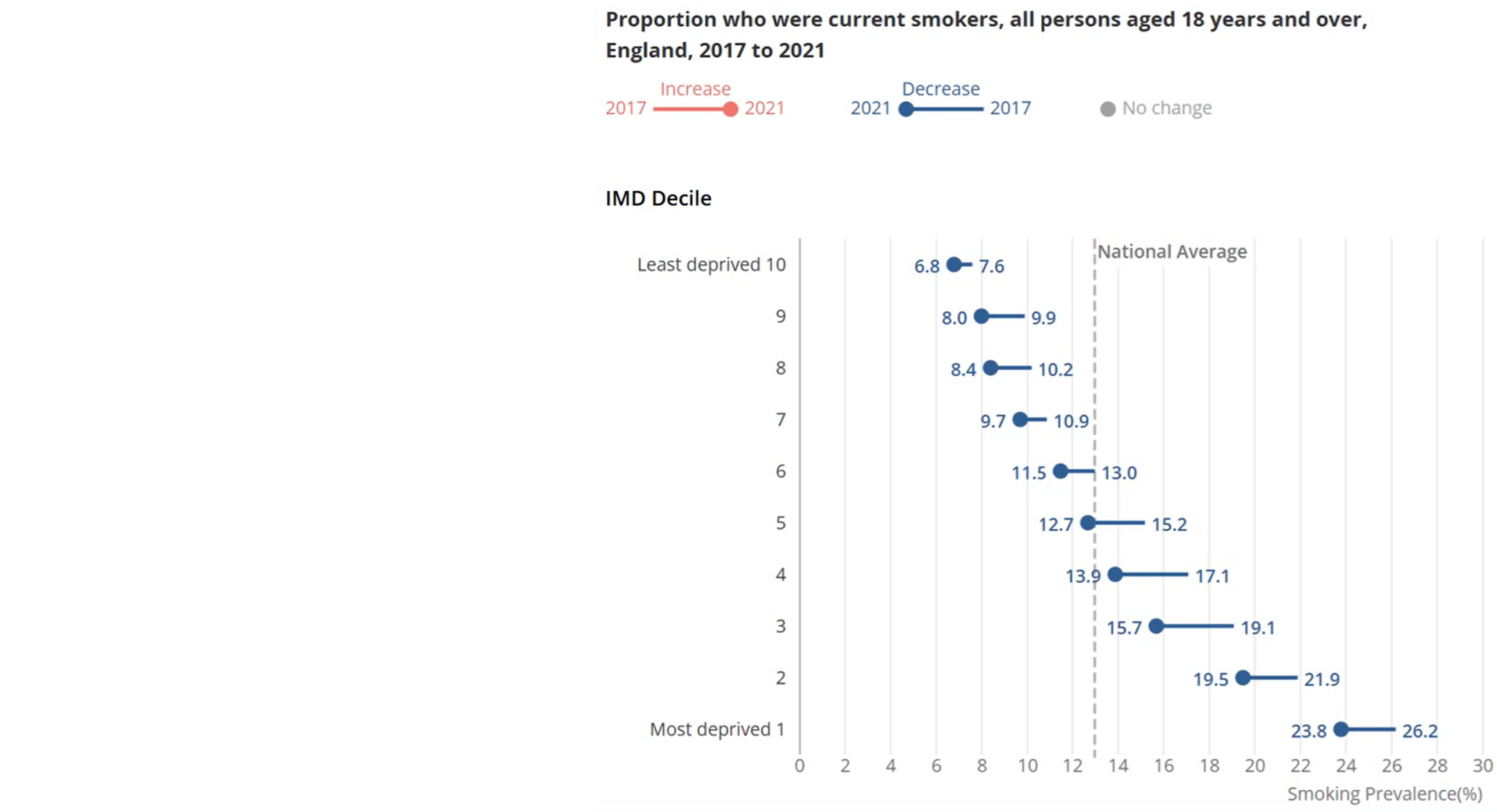
social gradient
index of multiple deprivation (IMD): composite measure
includes income, education, health, crime, living environment

health pattern by assigned sex
females live longer than males
but spend more of their life in poorer health
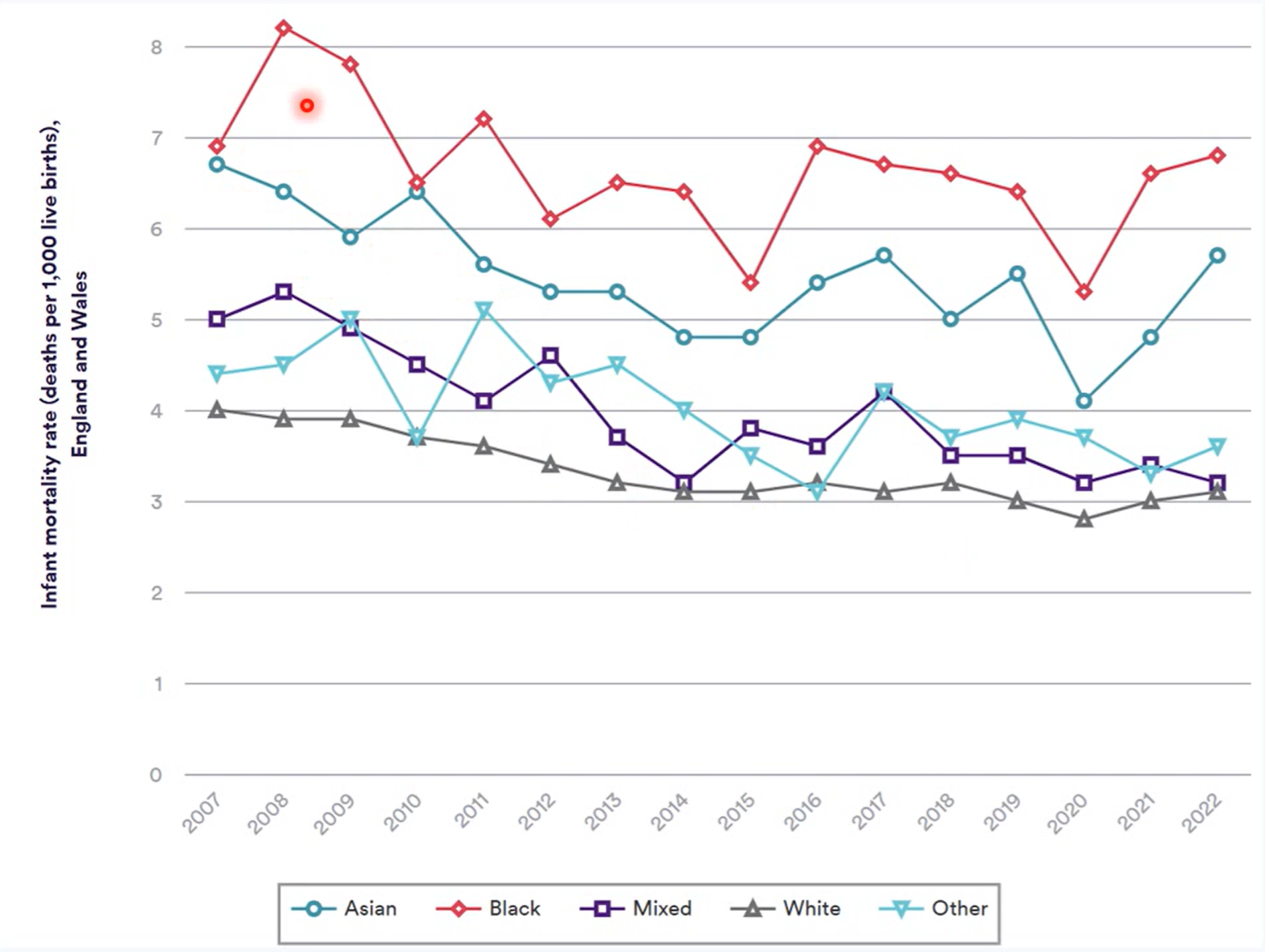
health pattern by ethnicity: infant mortality
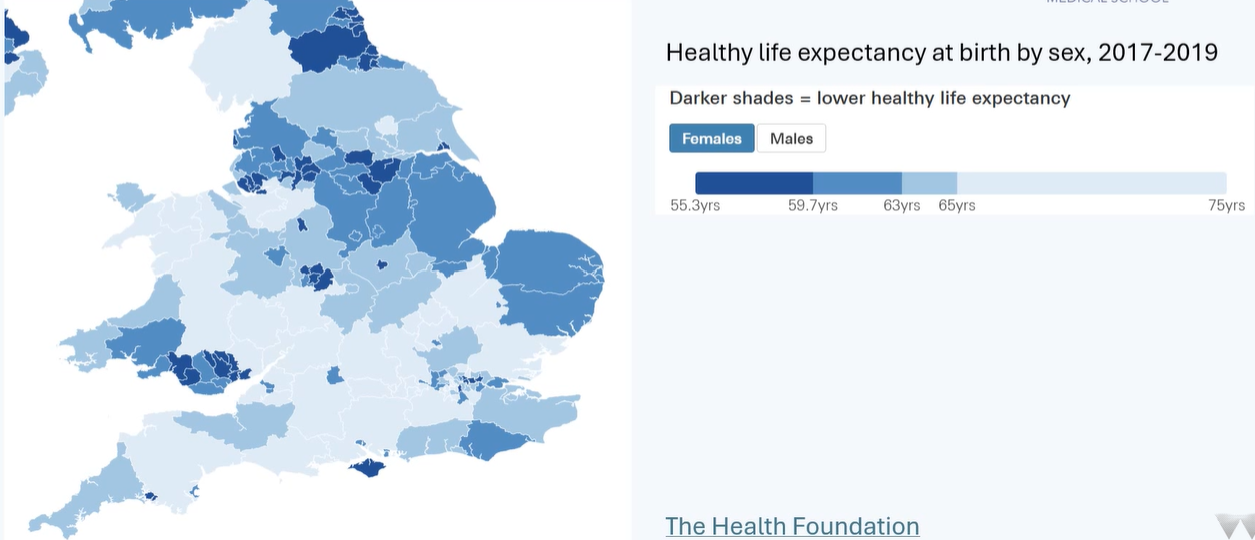
health pattern by geography
equality
equal rights, treatment or opportunities that are of the same form, value, benefit
equity
fair and impartial rights, treatments or opportunities so everyone has the same overall benefit
vaccination example of equality vs. equity
equality → available to all if you attend a central vaccination clinic
equity → mobile vaccination clinic sent to remote, underserves areas
healthcare facilities example of equality vs. equity
equality → all hospitals have same level of workforce, beds, equipment
equity → areas with older, sicker people have more staff and better access to specialised services
inequality vs. inequity
inequality → measurable differences in health between different groups
may be avoidable or unavoidable
inequity → avoidable differences in health between different groups
may be due to systemic barriers or discrimination
subset of inequalities
examples of inequalities
older people have more health needs than younger people (ageing is inevitable)
life expectancy is different in those born male and female
examples of inequities
geographical access → rural residents have more difficult access to facilities
prevention → wealthier people have better opportunities for health and fitness
chronic disease management→ lower availability of community support programmes in areas of deprivation
horizontal vs. vertical inequity in access to healthcare
horizontal inequity → those with the same need to not have the same access
vertical inequity → those with different needs are not provided with the level of resource appropriate for those needs
explanations for social gradient
behavioural model
materialist and neo-materialist model
psychosocial model
life course model
behavioural model
inequitites result frm variations in lifestyle behaviours
materialist/neo materalist
materialist
inequities from differences in direct access to material resources (housing quality, income, working conditions)
neo-materialist
additional importance of access at a community level
access to good education, healthcare, nutritious food
psychosocial model
stress leads to inequities in health
due to low income and poor material circumstances
due to relative lower position in social hierarchy
due to poor social capital
can affect health
directly: neuroendocrine response to stress
indirectly: adoption of unhealthy behaviours
life course model
describes interlinking of factors through life and accumulation of adverse factors to health