APUSH exam review
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
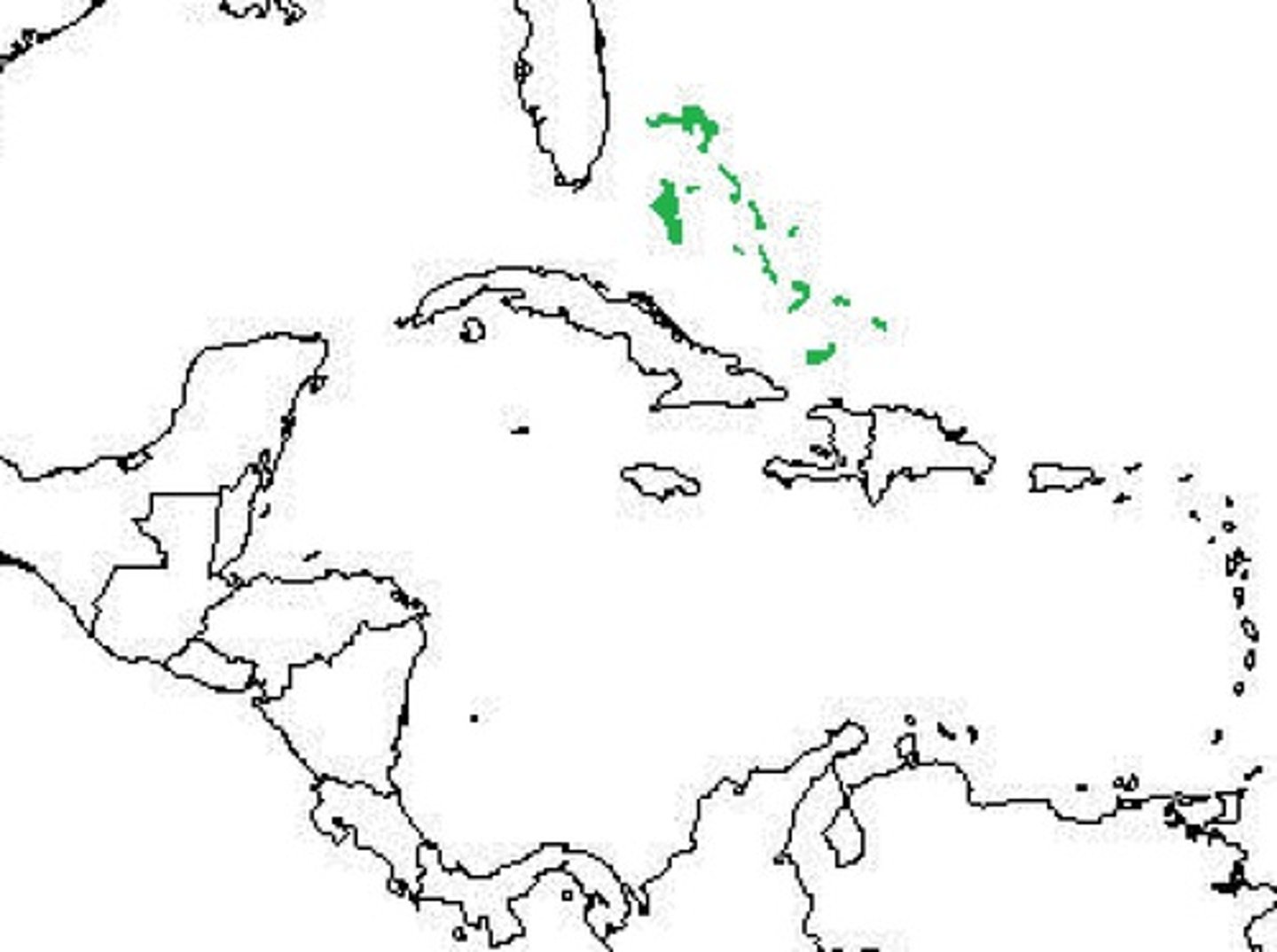
British West Indies
British dominate Barbados economy with sugar production. Slave based plantation societies. Provides raw sugar for refineries.
Indentured Servants
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years

Puritans
A religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England. They came to America for religious freedom and settled Massachusetts Bay.

Metacom/King Philip's War
Ended the native presence in the colonies (1676); Armed rebellion between Natives and colonists
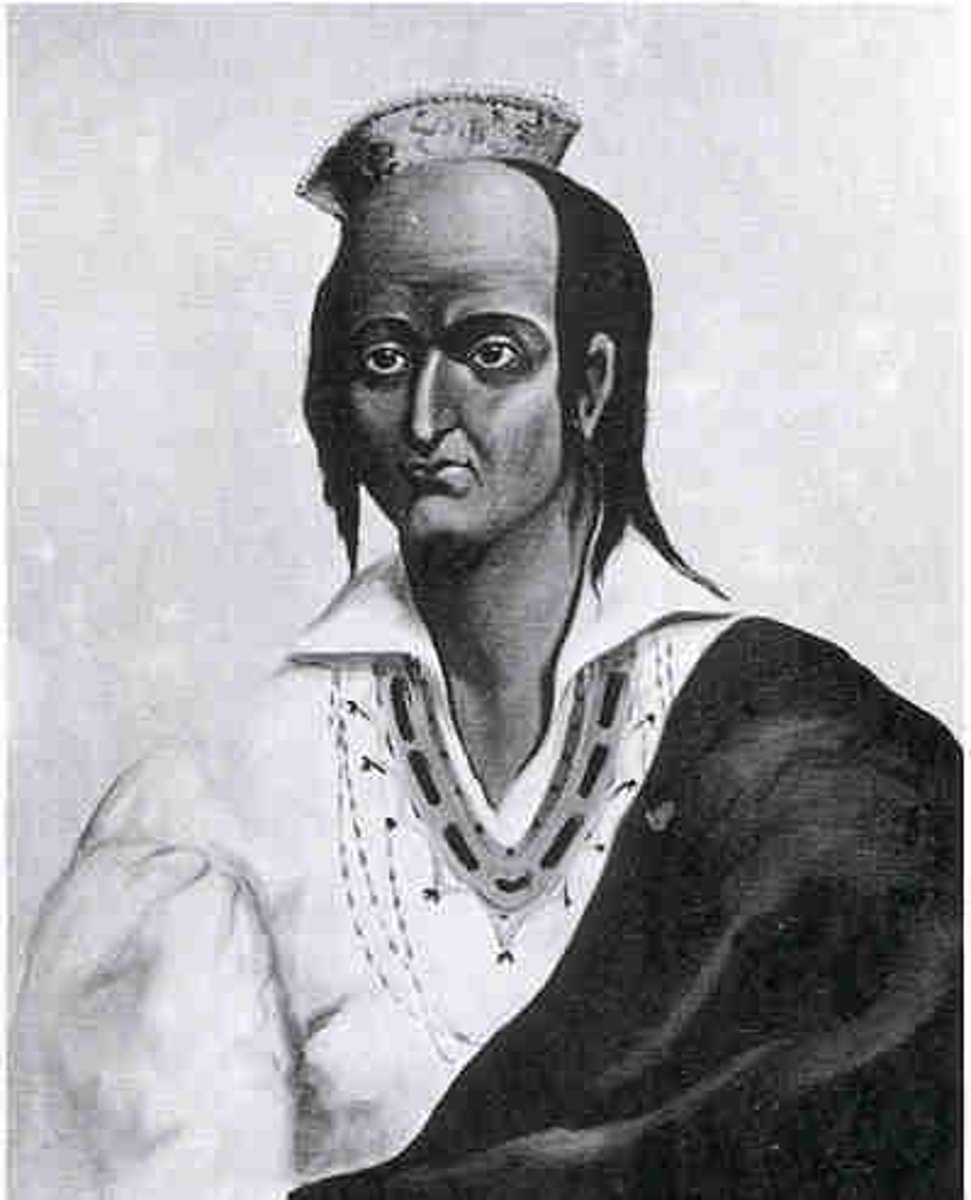

Pueblo Revolt
Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt

Great Awakening
Religious revival in the American colonies of the eighteenth century during which a number of new Protestant churches were established.

Enlightenment
A movement in the 18th century that advocated the use of reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions.
Anglicization
the colonial american desire to emulate English society, including English taste in foods, customs, and architecture
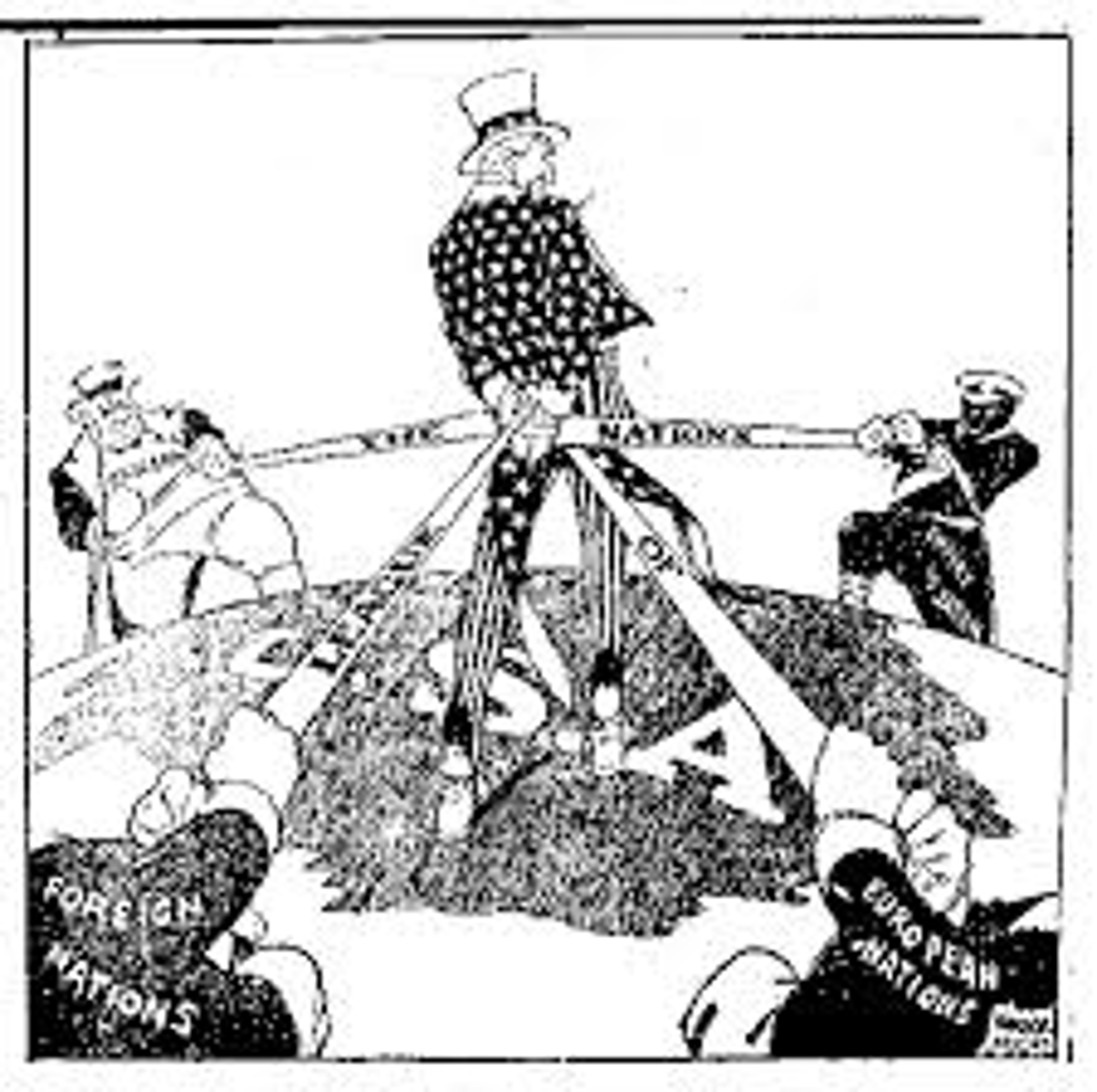
League of Nations
An international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations.

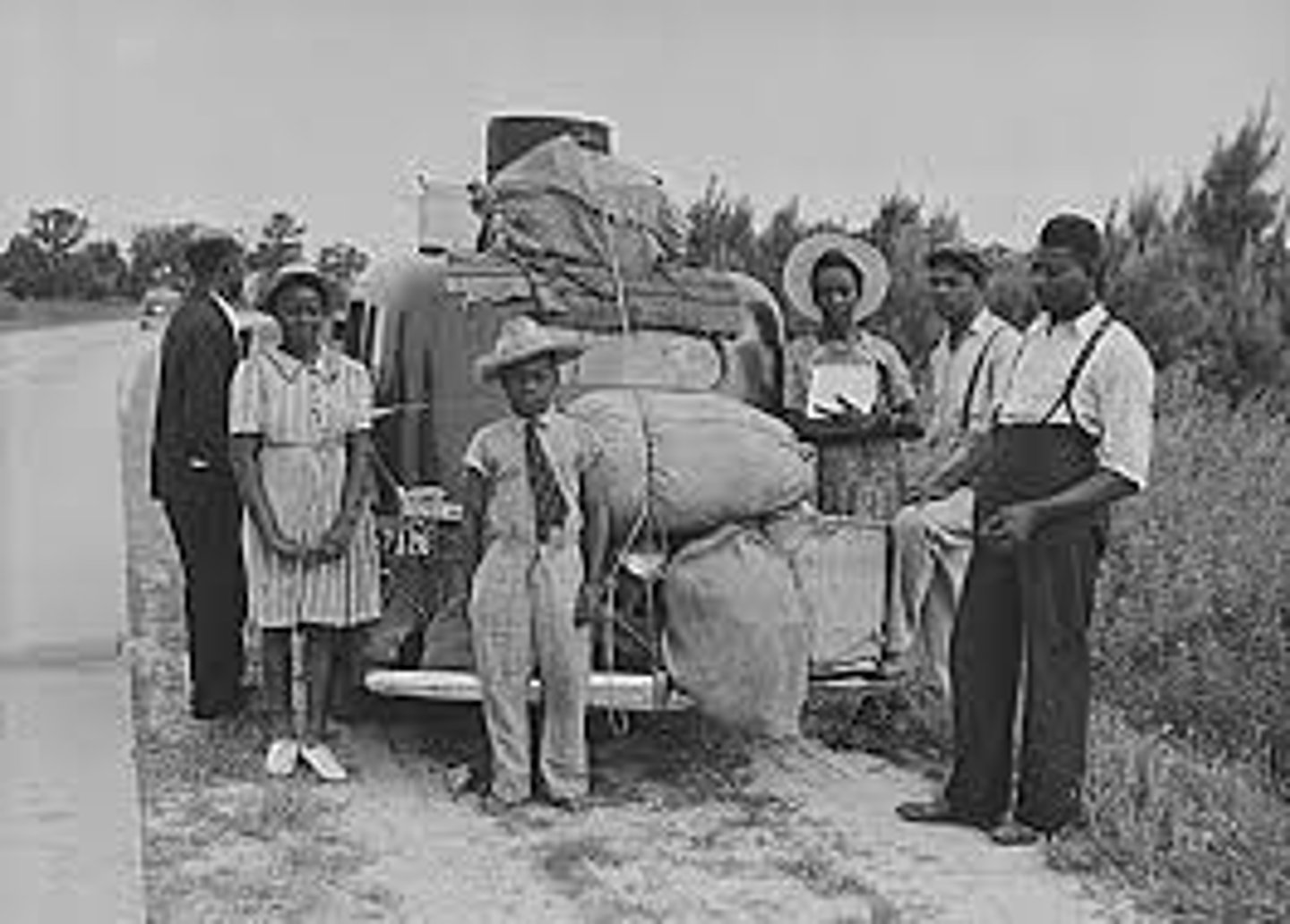
Great Migration
Movement of over 300,000 African American from the rural south into Northern cities between 1914 and 1920.

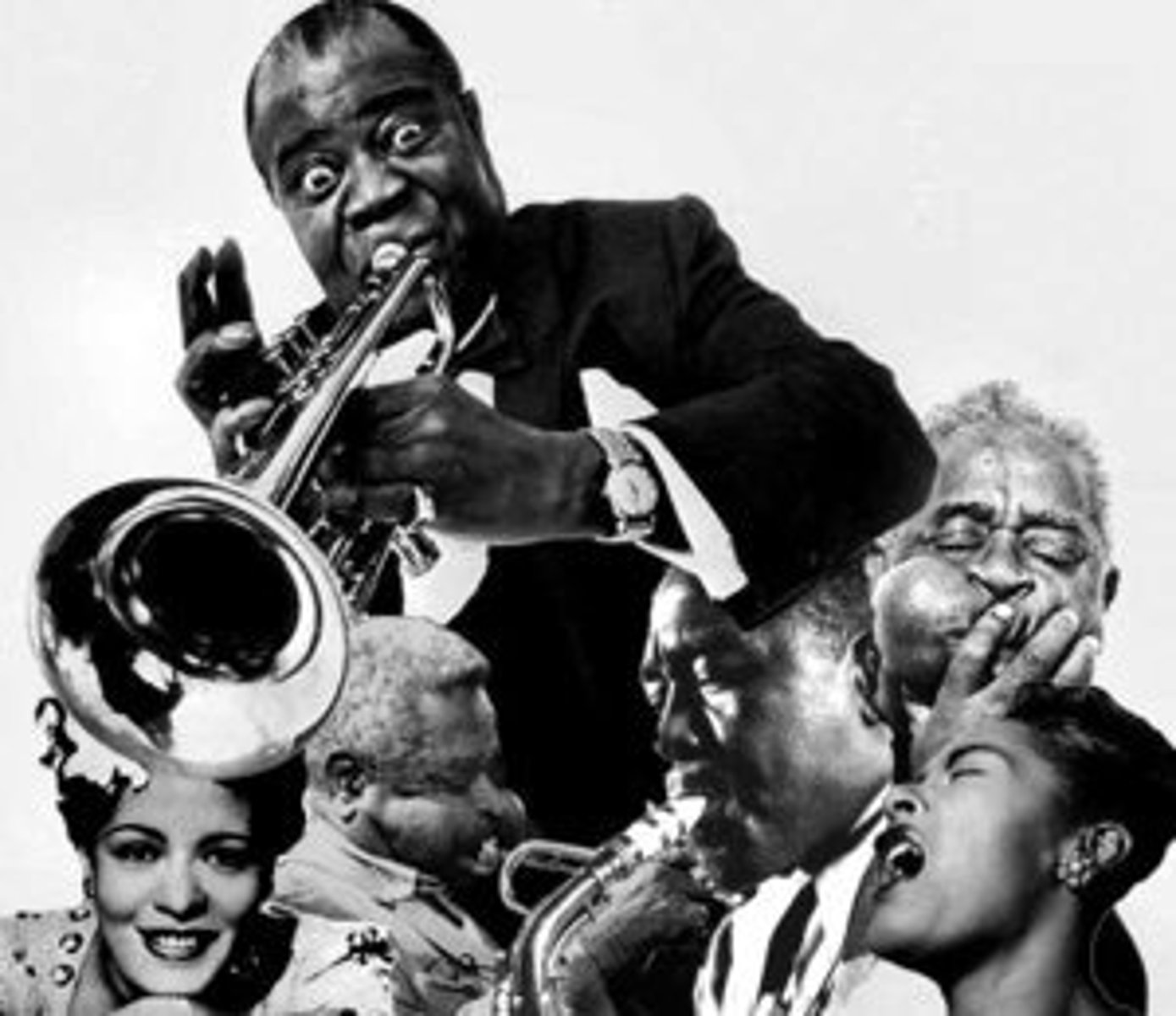
Harlem Renaissance
A period in the 1920s when African-American achievements in art and music and literature flourished.

Red Scare
Fear that communists were working to destroy the American way of life.

Immigration Quotas/Restrictions
Limitations on immigration that were passed by the U.S. government that established preferred immigration of those who were thought to be more "capable" and capable of success in the United States, while limited the immigration of those who were deemed "unnecessary."
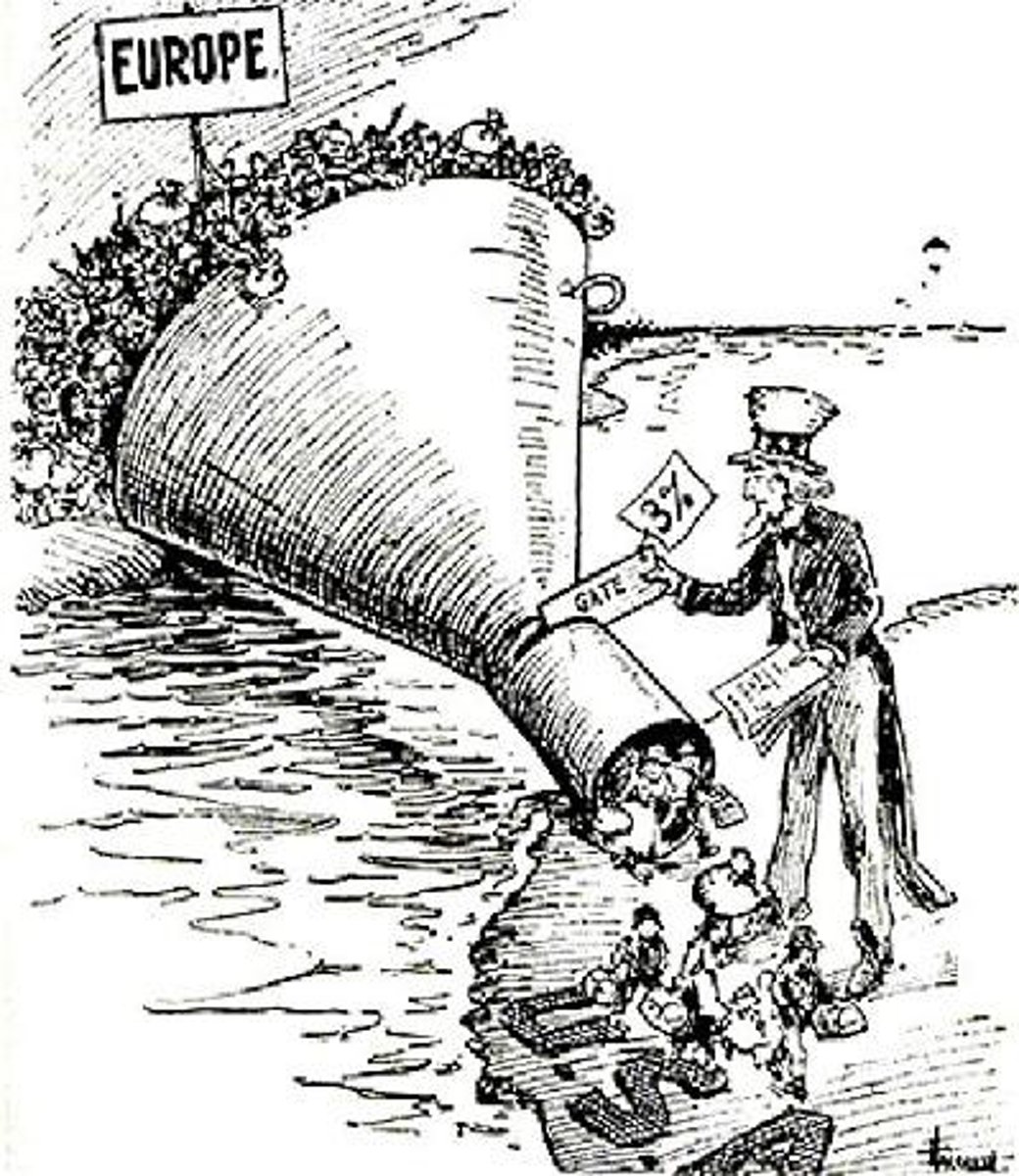

Great Depression
The economic crisis beginning with the stock market crash in 1929 and continuing through the 1930s.
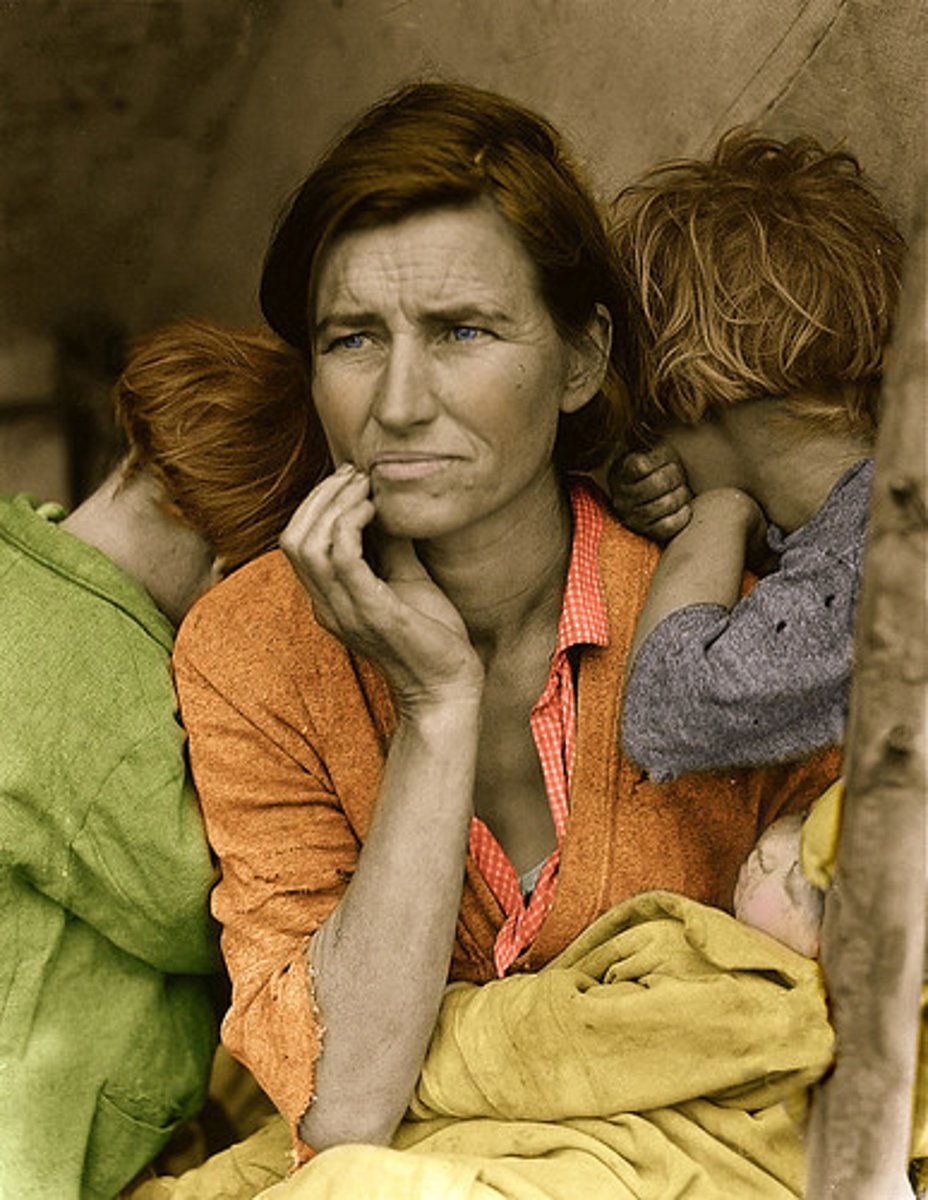

New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.

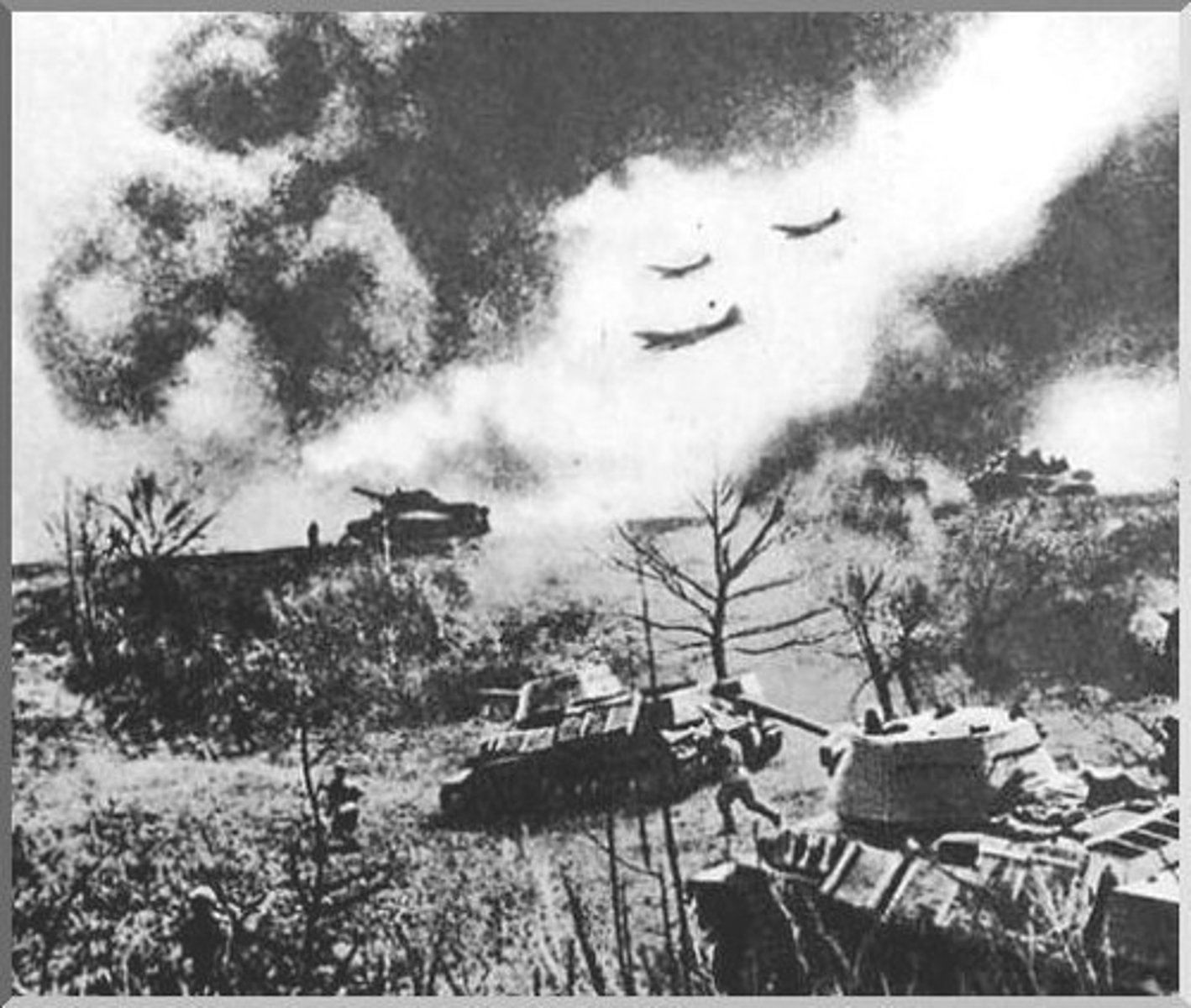
World War II (1939-1945)
Germany, Italy, Japan (Axis) against Great Britain, France, Russia, and the U.S. (Allied)

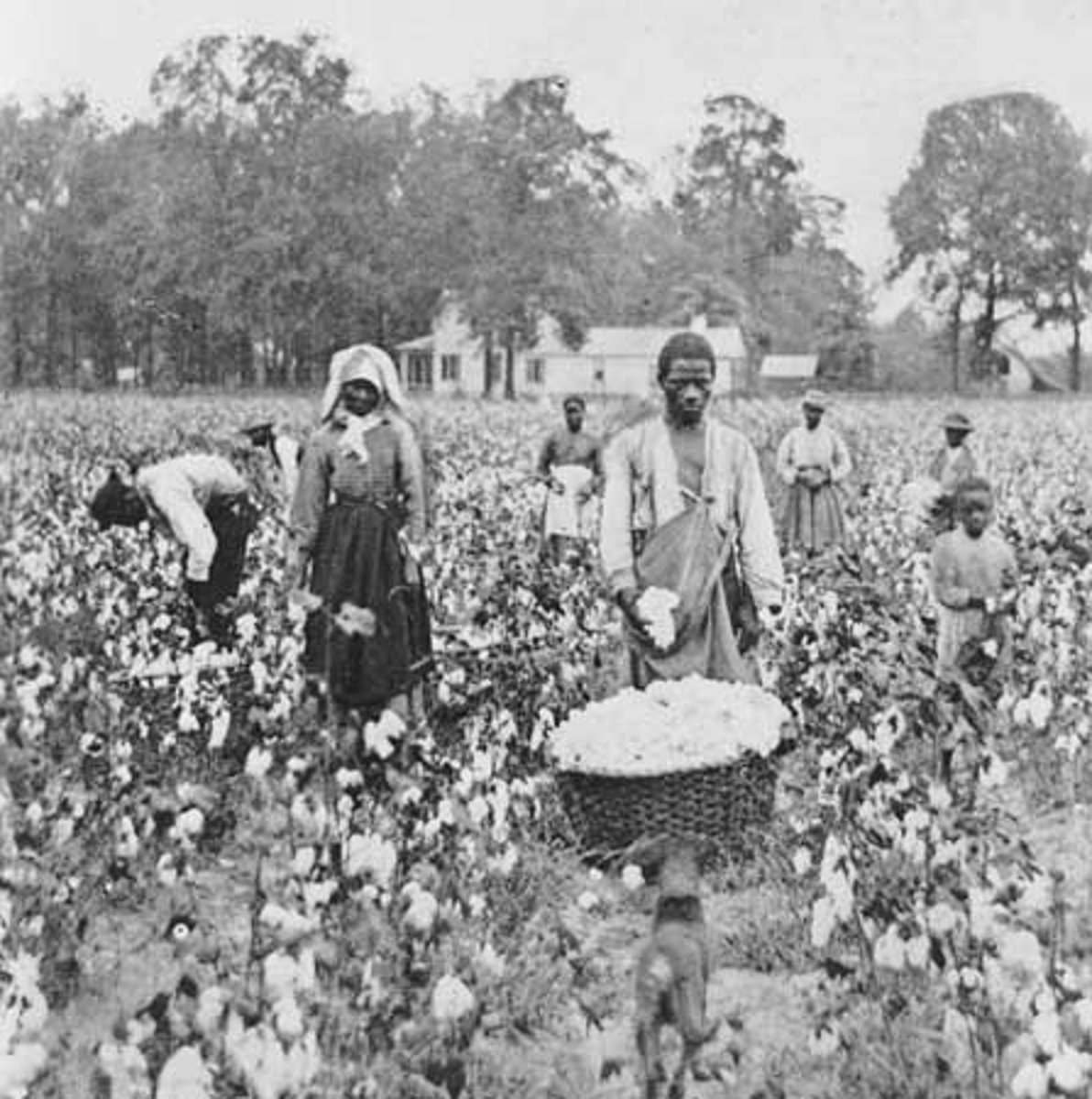
Reconstruction
the period after the Civil War when the southern states were reorganized and rejoined the Union

Radical Republicans
Post Civil War, a group that believed the South should be harshly punished and thought that Lincoln was too compassionate towards the South.

13th, 14th, 15 Amendments
The Reconstruction Amendments that led to the changes to our Constitution following the Civil war. The 13th made slavery illegal which was passed in 1865. The 14th allowed blacks to be considered citizens which were passed in 1868. The 15th prohibits the government from denying a citizen the right to vote based on color, race, or previous servitude which was ratified in 1870.

Sharecropping
A system in which farmers worked land owned by someone else in return for a small portion of the crops. A system that took place post civil war.

Supreme Court Decisions
legal determinations made by the highest court in the United States, sometimes determining the constitutionality of laws

industrial capitalism
an economic system based on industrial production or manufacturing
Trusts
Firms or corporations that join for the purpose of reducing competition and controlling prices known today as a monopoly. There are now anti-trust laws to help prevent this.

Laissez-faire
The idea that the government should pay minimal role in economic affairs.
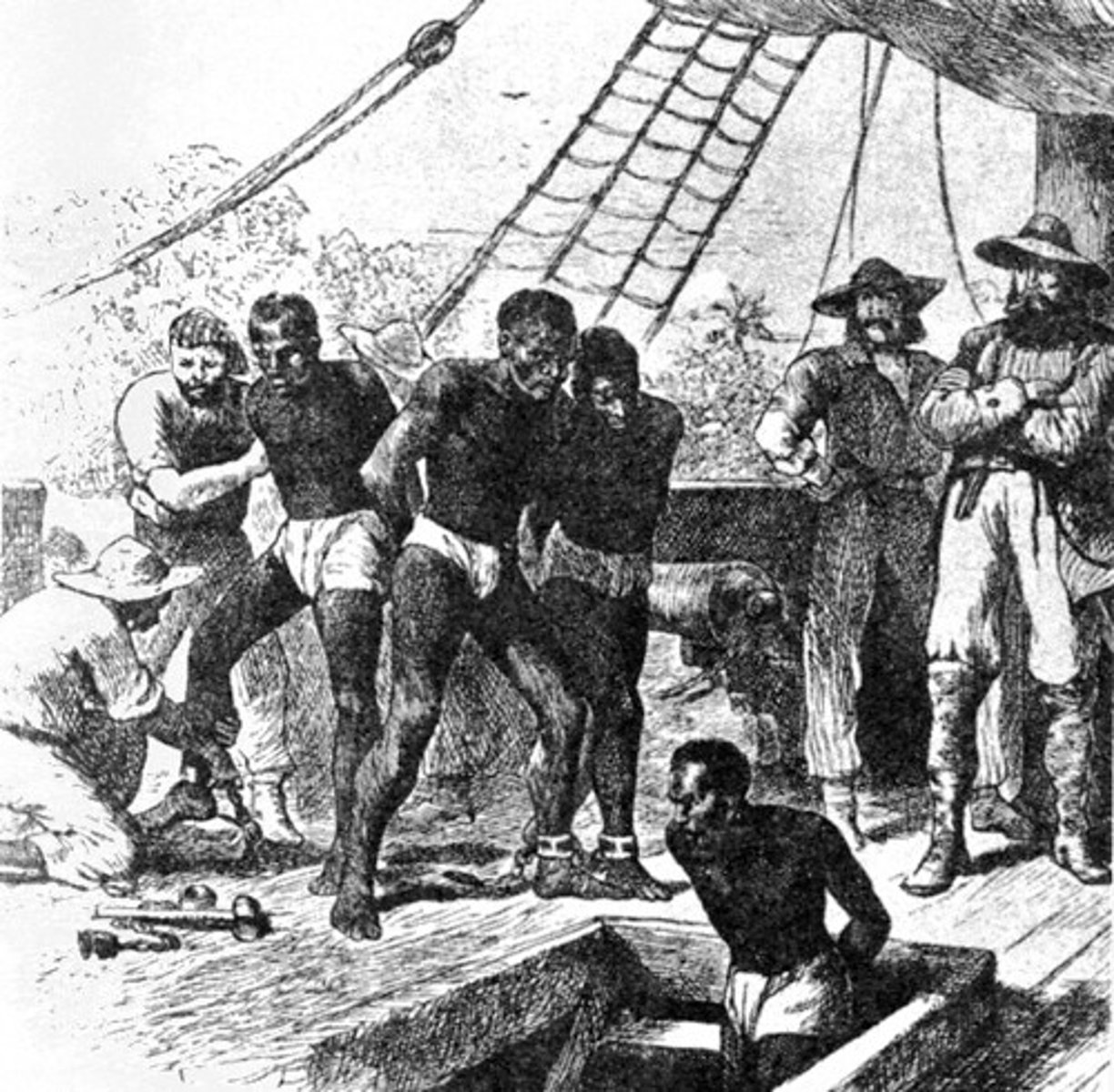
African Slavery
(Period 1)10-15 million people taken from Africa between 1500 and 1870, Several million more people killed in slave raids and forced marches to the coast. Most bought from African slave traders, at least 15% died in horrible conditions aboard slave ships.

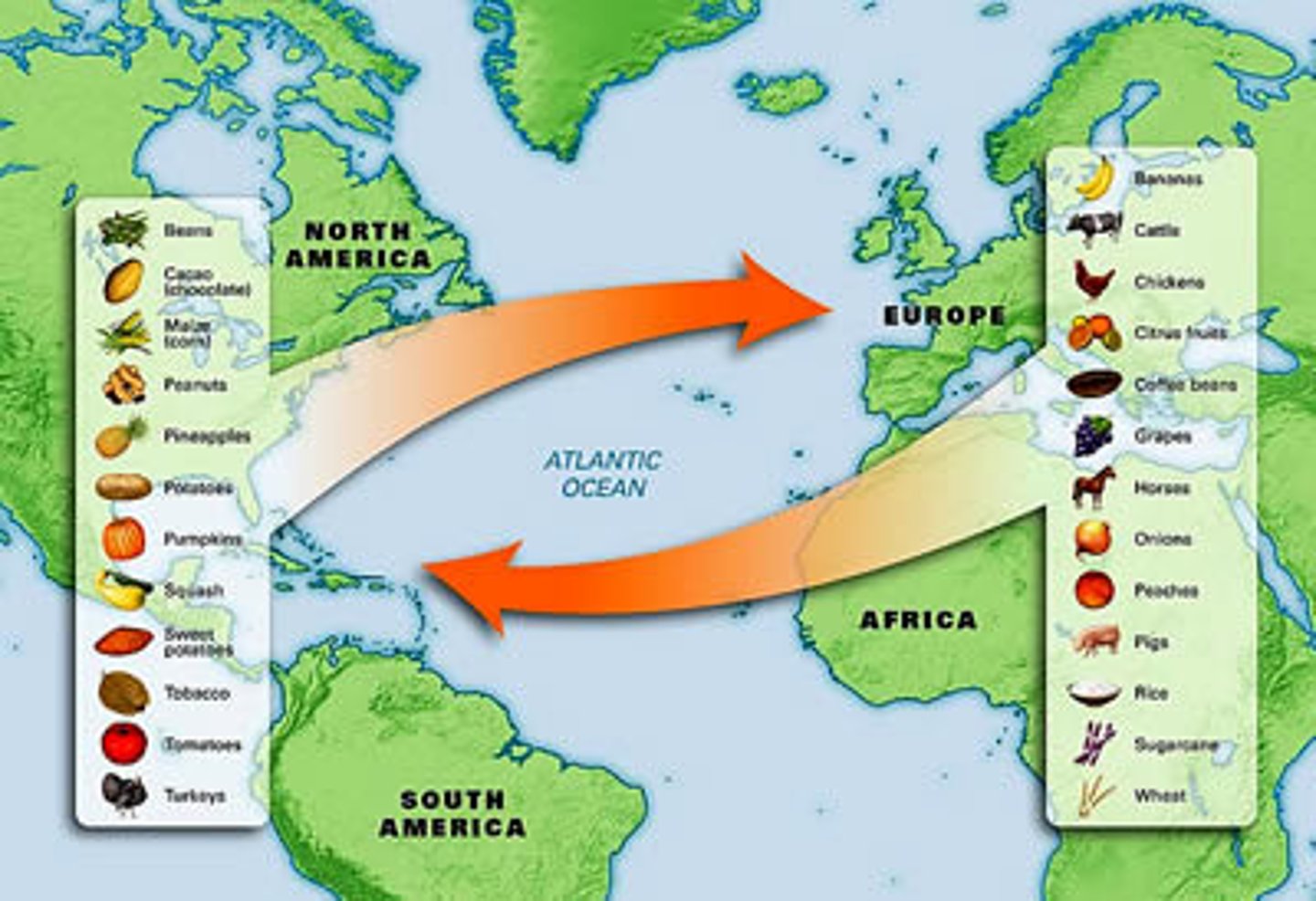
Colombian Exchange
(Period 1)the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, Asia, and Africa
Joint Stock Companies
(Period 1) businesses formed by groups of people who jointly make an investment and share in the profits and losses

Spanish colonizers
(Period 2)First to arrive, conquests all through S. America and the lower part of N. America (California, Florida), Encomienda system, 3 G's, convert natives, mine resources
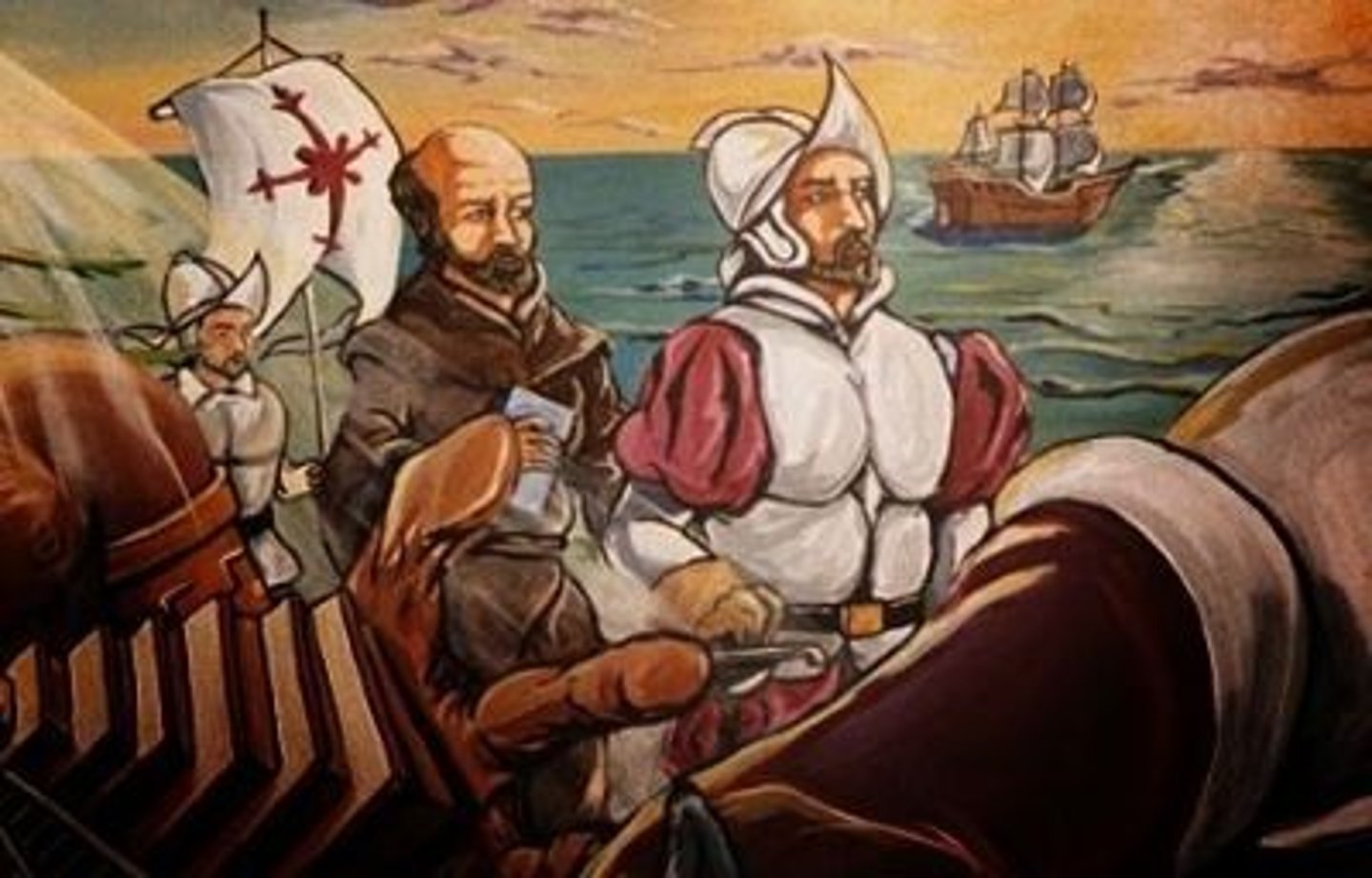

French Colonizers
(Period 2)The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued on into the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America.
Dutch Colonizers
(Period 2)The Dutch colonization of the Americas began with the establishment of Dutch trading posts and plantations in the Americas, which preceded the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. ... Actual colonization, with the Dutch settling in the new lands, was not as common as with other European nations.

British Colonizers
(Period 2)Formed the 13 colonies on the East Coast of N. America, took control of land owned by natives (resulted in conflict), many settlers fled for a new life in the New World (was a struggle), farmed for resources then traded to England, religious freedom

New England Colonies
(Period 2)Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire
Middle Colonies
(Period 2)New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware
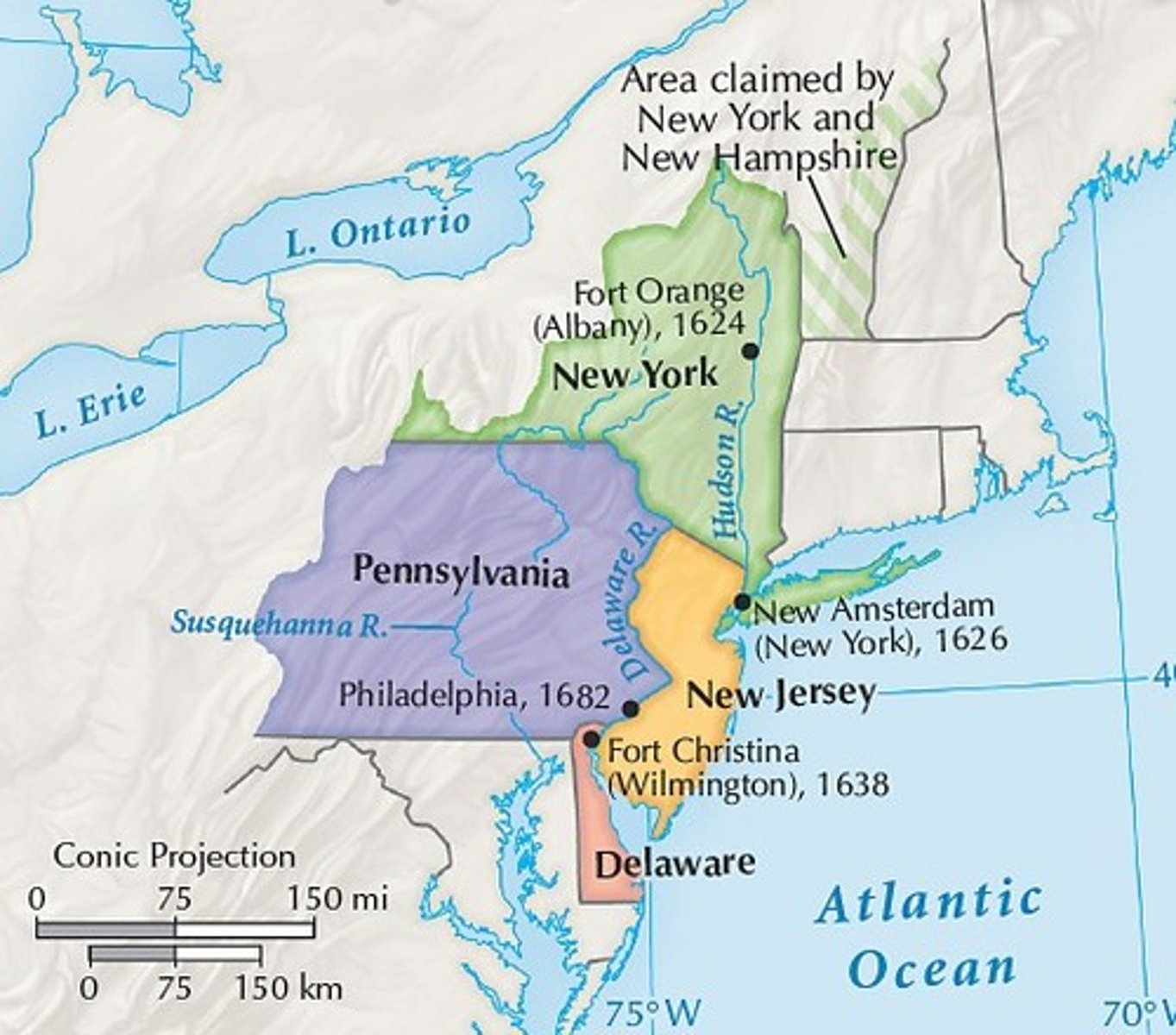
Chesapeake Colonies
(Period 2)Term for the colonies of Maryland and Virginia
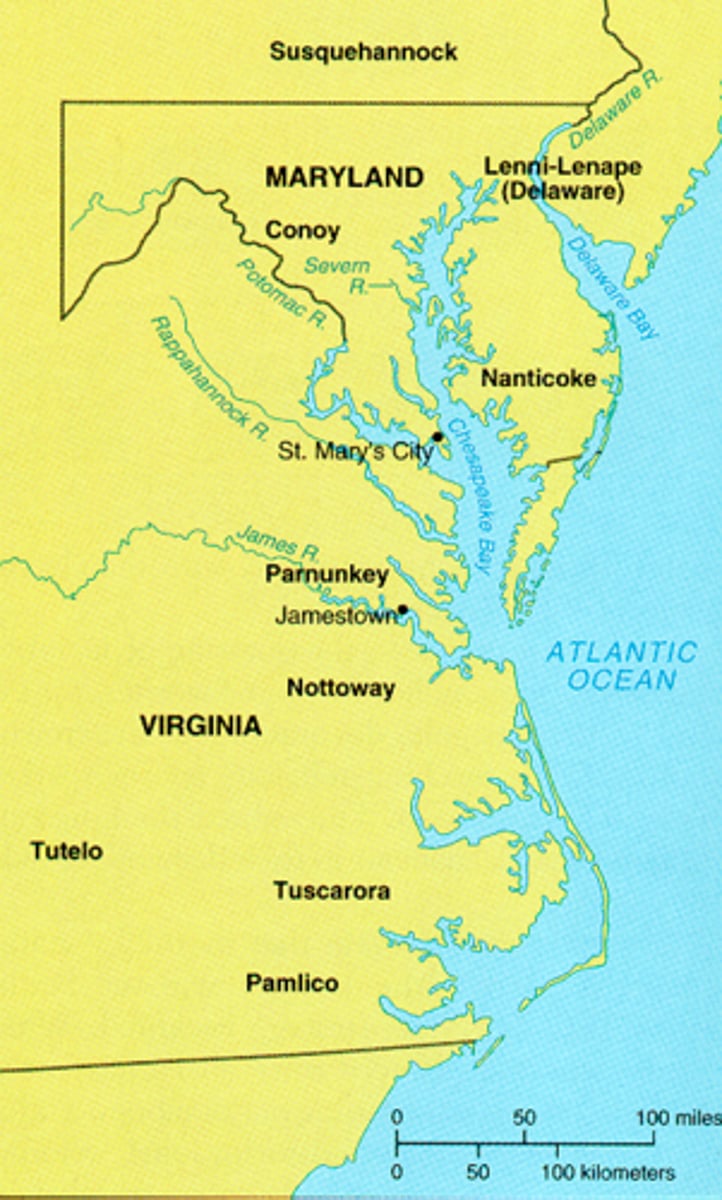
North Carolina Colonies
(Period 2)The North Carolina Colony was founded in 1653 by the Virginia colonists. - refer to Lords Proprietors and the Charter of Carolina. Carolina is derived from the Latin name Carolus, translated as "Charles." The state was named in honor Charles IX of France and then King Charles I and King Charles II of England.

Southern Colonies
(Period 2)Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia
Social Gospel
A movement in the late 1800s / early 1900s which emphasized charity and social responsibility as a means of salvation.

Jane Addams and Settlement Houses
A younger generation of poverty helping workers led by Jane Addams. Settlement houses were places run by women where poor immigrants could come and eat, attend classes, other things.

Plessy v. Ferguson
an 1896 Supreme Court decision which legalized state ordered segregation so long as the facilities for blacks and whites were equal

Progressive Era
time at the turn of the 20th century in which groups sought to reform America economically, socially, and politically

16th Amendment
Amendment to the United States Constitution (1913) gave Congress the power to tax income.

17th Amendment
Established the direct election of senators (instead of being chosen by state legislatures)
18th Amendment
Prohibited the manufacture, sale, and distribution of alcoholic beverages

19th Amendment (1920)
Ratified on August 18, 1920 (drafted by Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton), prohibits any United States citizen from being denied the right to vote on the basis of sex. The Constitution allows the states to determine the qualifications for voting, and until the 1910's most states disenfranchised women. The amendment was the culmination of the women's suffrage movement in the U.S.

21st Amendment
Amendment which ended the Prohibition of alcohol in the US, repealing the 18th amendment

Prohibition
the period from 1920 to 1933 when the sale of alcoholic beverages was prohibited in the United States by a constitutional amendment

Tenant farming
(1861-1865) system of farming in which a person rents land to farm from a planter

"New South"
(1880s-1890s) envisioned a post-Reconstruction southern economy modeled on the North's embrace of the Industrial Revolution

People's (Populist) Party
(1891) response to growth of corporate power; called for political reform and increased government involvement in the economy

Americanization
(1910s)Belief that assimilating immigrants into American society would make them more loyal citizens
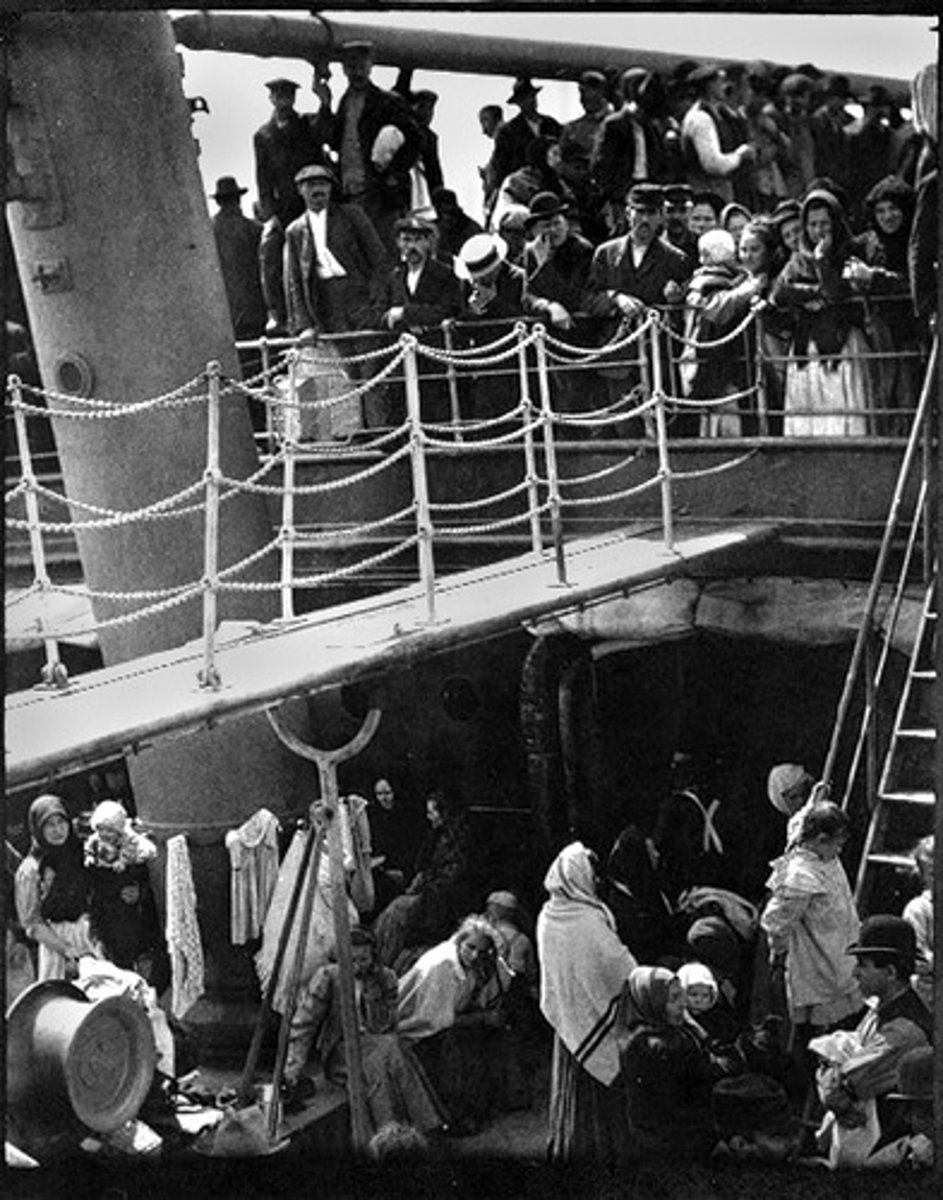

Political Machines
(1800s) Corrupt organized groups that controlled political parties in the cities, a boss leads the machine and attempts to grab more votes for his party.

Transcontinental railroad(s)
(1863-1869) a contiguous network of railroad trackage that crosses a continental land mass with terminals at different oceans or continental borders
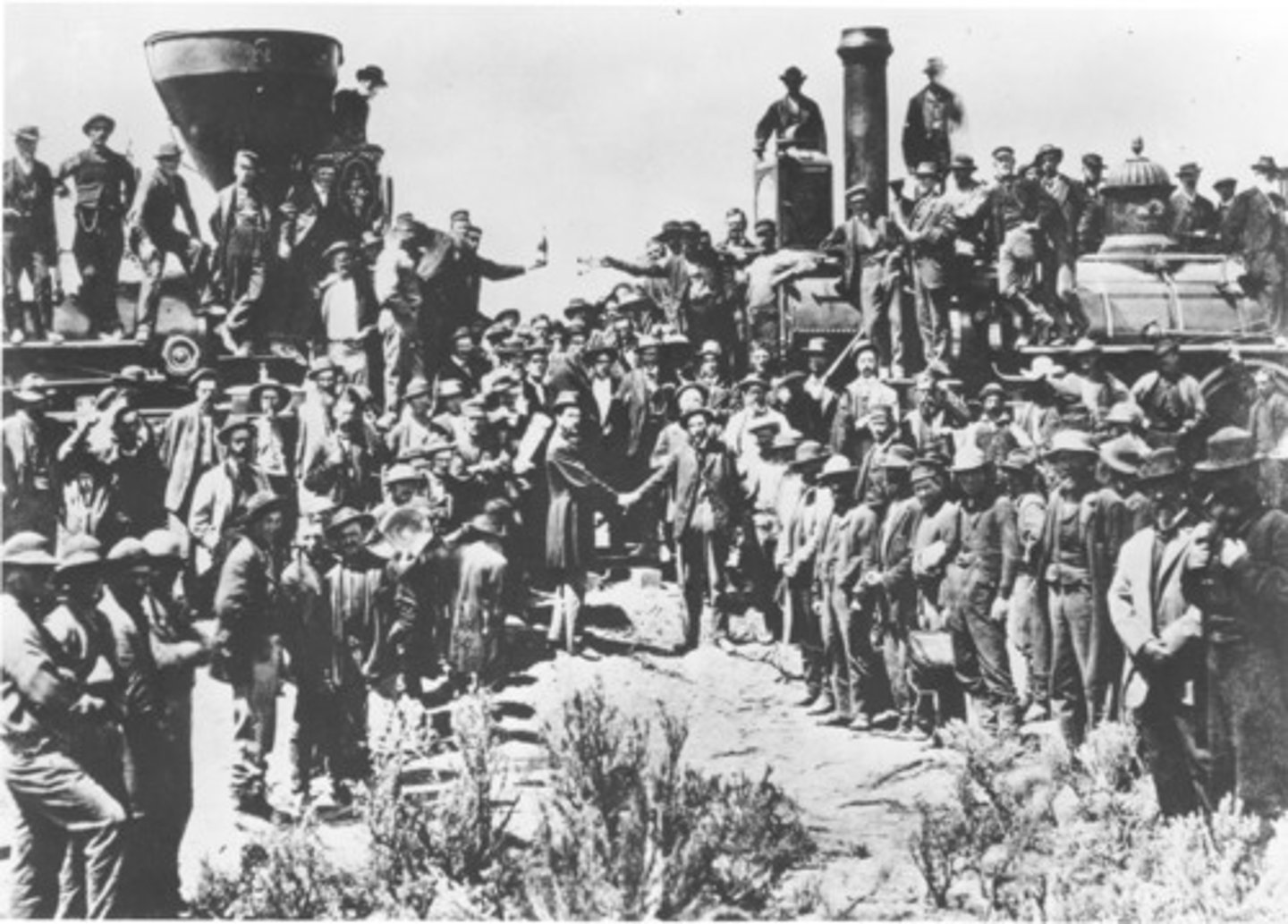

Indian Wars/reservations
(1622-1924) collective name for the various armed conflicts fought by European governments and colonists, and later the United States government and American settlers, against the native peoples of North America.

Gilded Age
1870s-1890s) time period of rapid economic growth, despite the corrupt politics & growing gap between the rich & poor

Social Darwinism
(1870s) Belief that only the fittest survive in political and economic struggle

Women's Suffrage
The right of women to vote and to stand for electoral office. (1848-1920)

Preservationist
Person concerned primarily with setting aside or protecting undisturbed natural areas from harmful human activities. (1865-1915)

conservationist
One who advocates the conservation of natural resources. (Progressive Era)
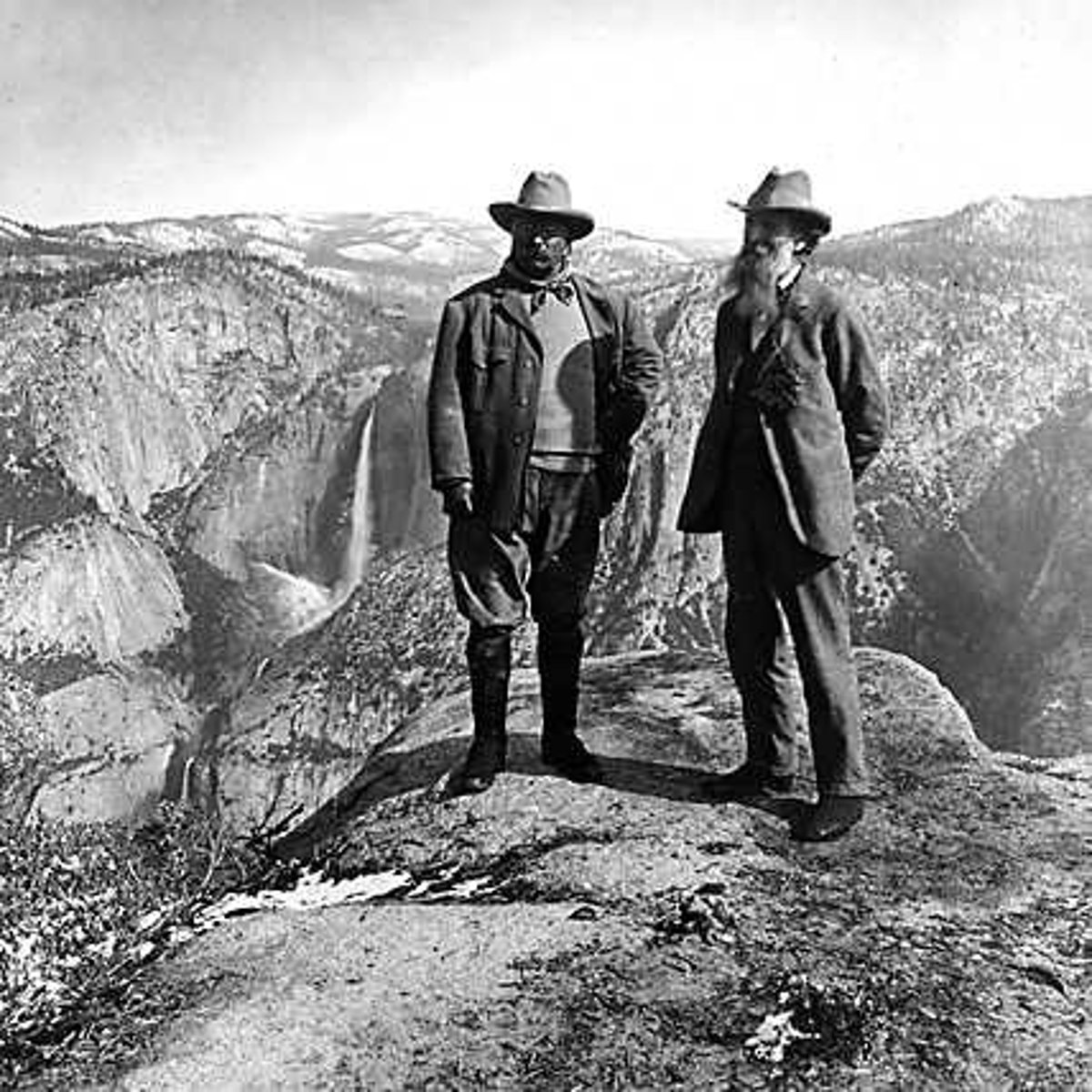

Imperialists
People who support imperialism, the policy of one nation acquiring, controlling, or dominating another. (late 19th- Early 20th century)
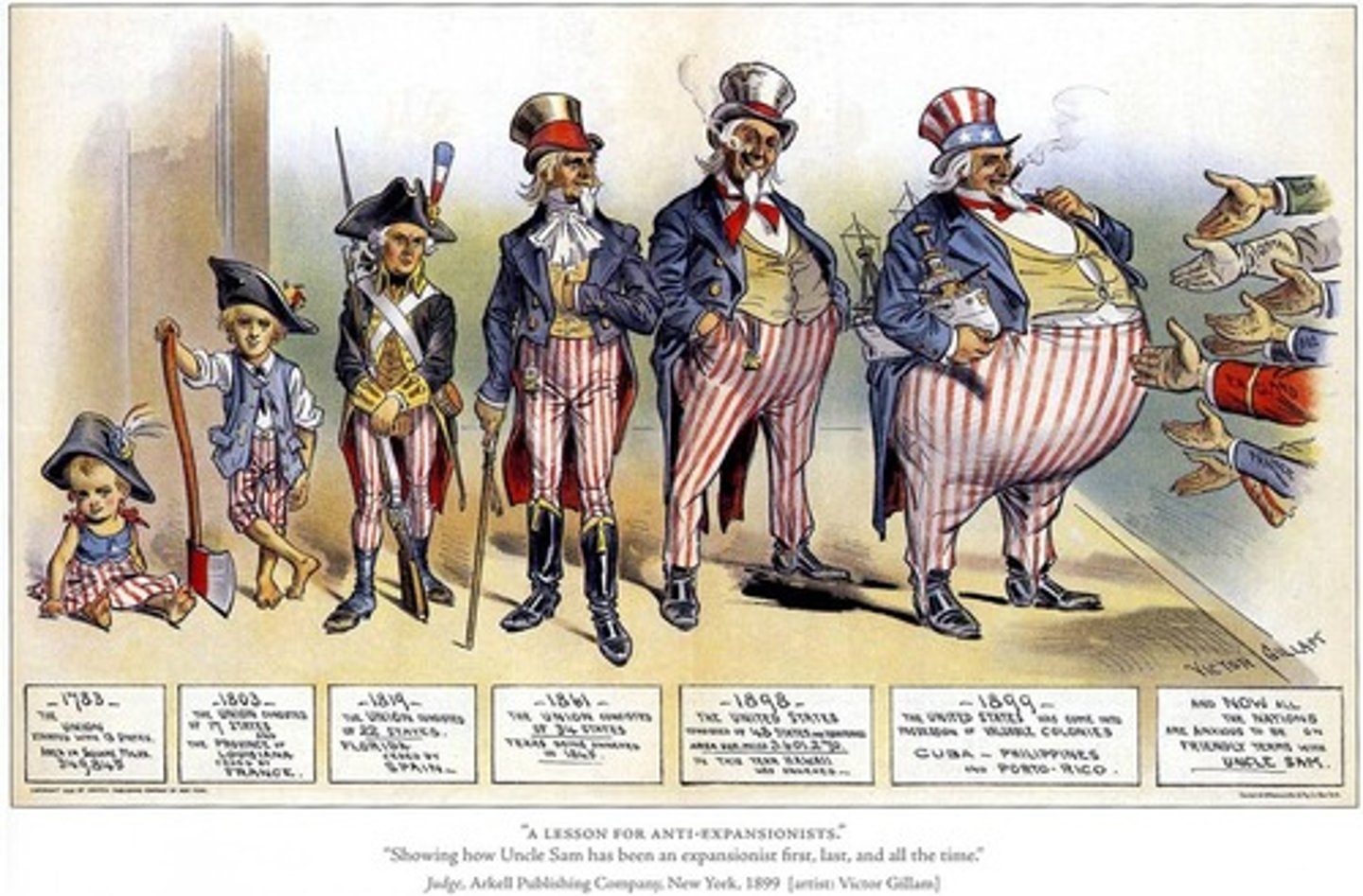

Anti-Imperialist
One who is against imperialism. (1898)
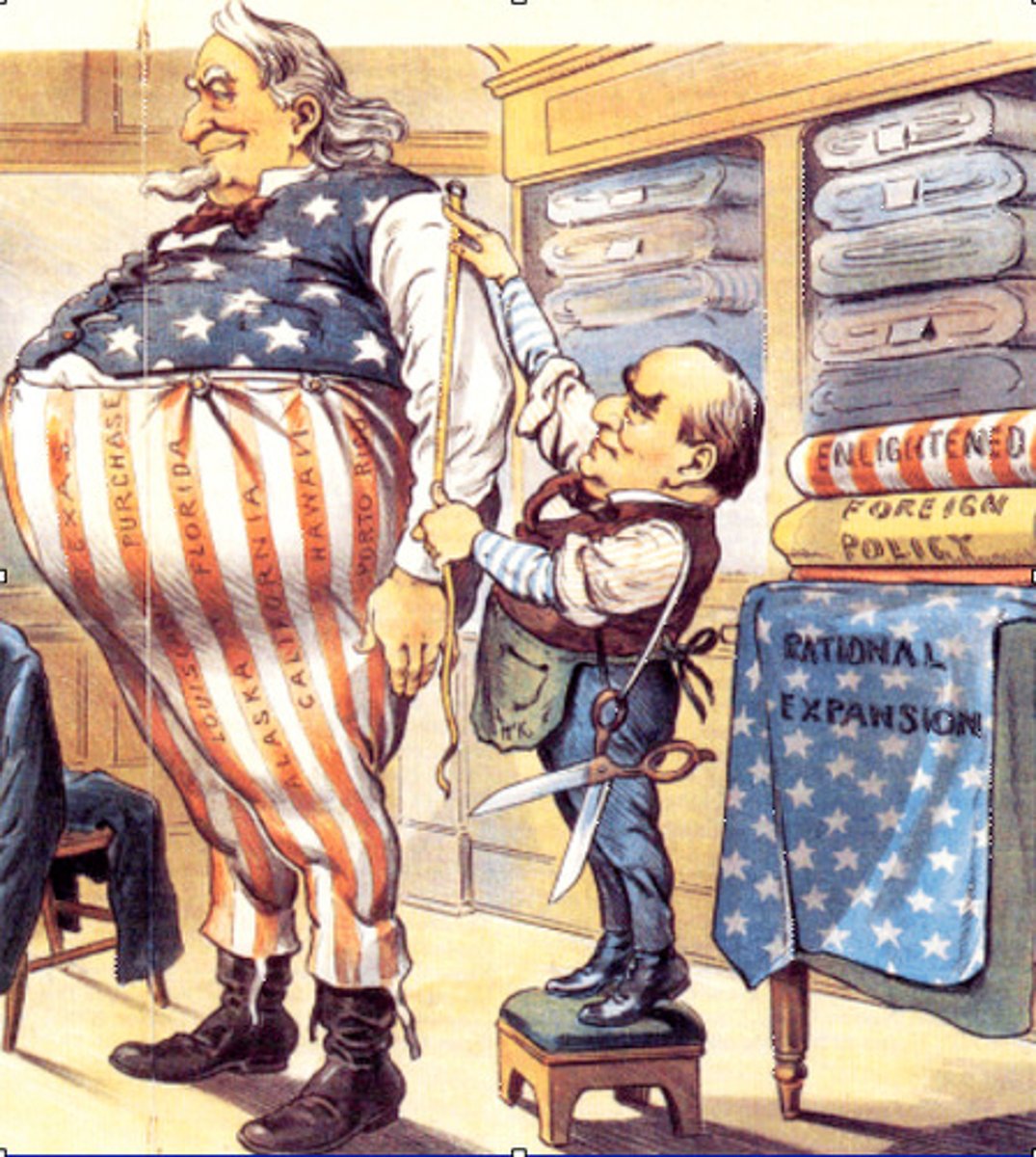
Isolationism
A policy of remaining apart from the affairs or interests of other groups, especially the political affairs of other countries.(1930's)

Spanish-American War
In 1898, a conflict between the United States and Spain, in which the U.S. supported the Cubans' fight for independence.

Woodrow Wilson
28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, created Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage (reluctantly), Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification), won Nobel Peace Prize(1913-1921)

World War I
A war between the allies (Russia, France, British Empire, Italy, United States, Japan, Rumania, Serbia, Belgium, Greece, Portugal, Montenegro) and the central powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey, Bulgaria) from 1914 to 1918.
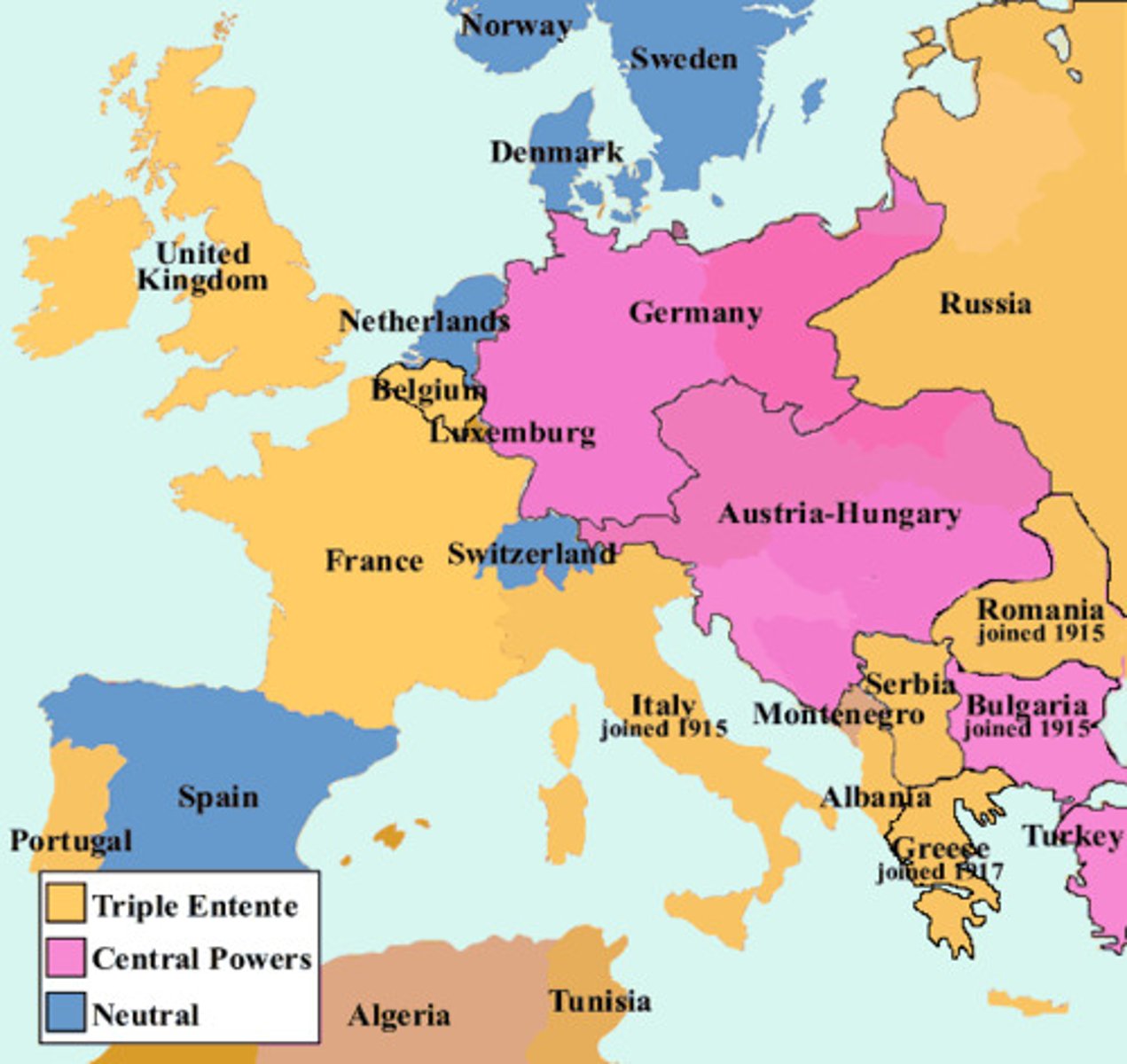
American Expeditionary Force
About 2 million Americans went to France as members of this under General John J. Pershing. Included the regular army, the National Guard, and the new larger force of volunteers and draftees and they served as individuals.(1917)

Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans.

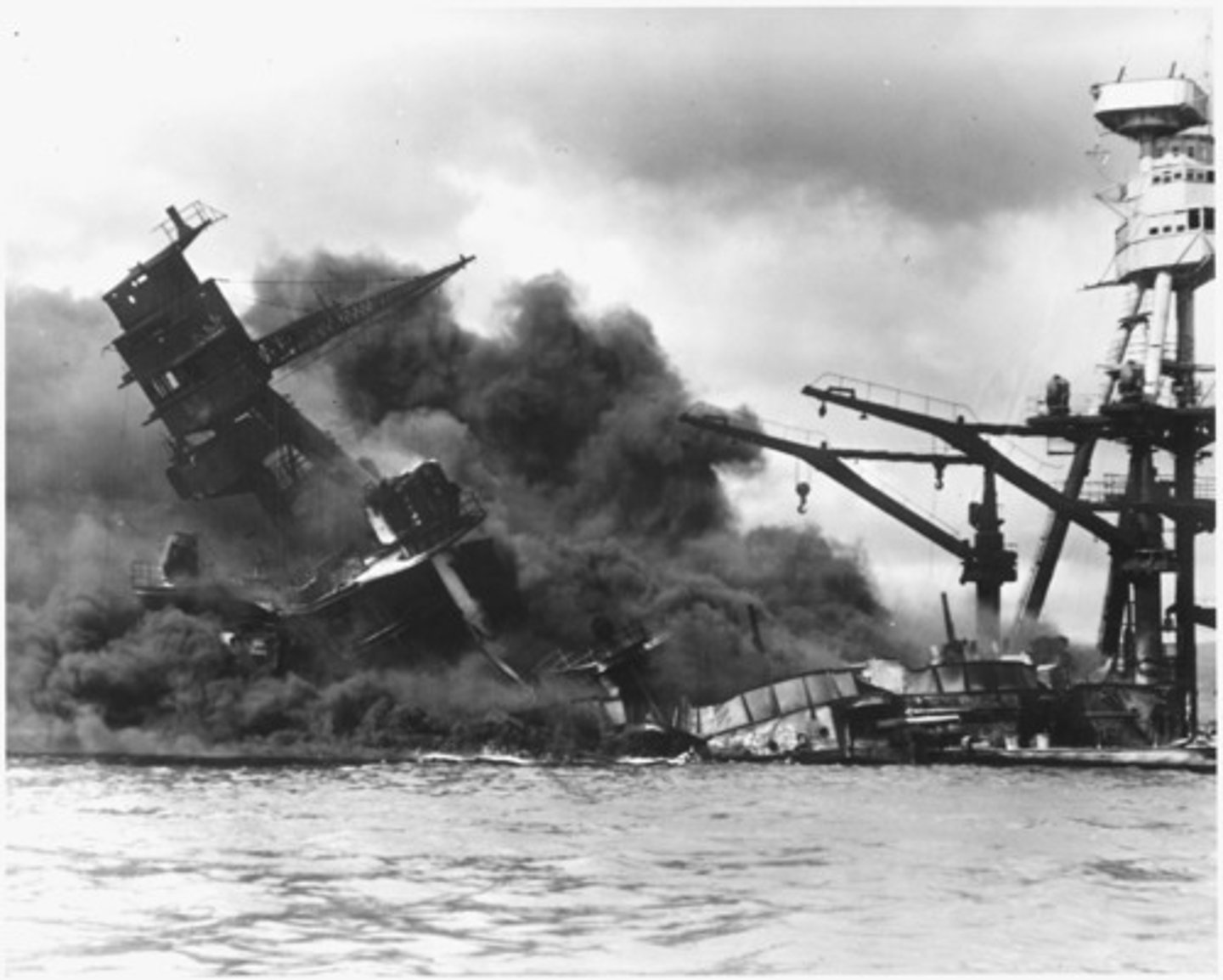
Pearl Harbor
7:50-10:00 AM, December 7, 1941 - Surprise attack by the Japanese on the main U.S. Pacific Fleet harbored in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii destroyed 18 U.S. ships and 200 aircraft. American losses were 3000, Japanese losses less than 100. In response, the U.S. declared war on Japan and Germany, entering World War II.

Fascism/Totalitarianism
A political system in which the state has total control over the lives of individual citizens. This was more common in Japan and Soviet Russia

Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.

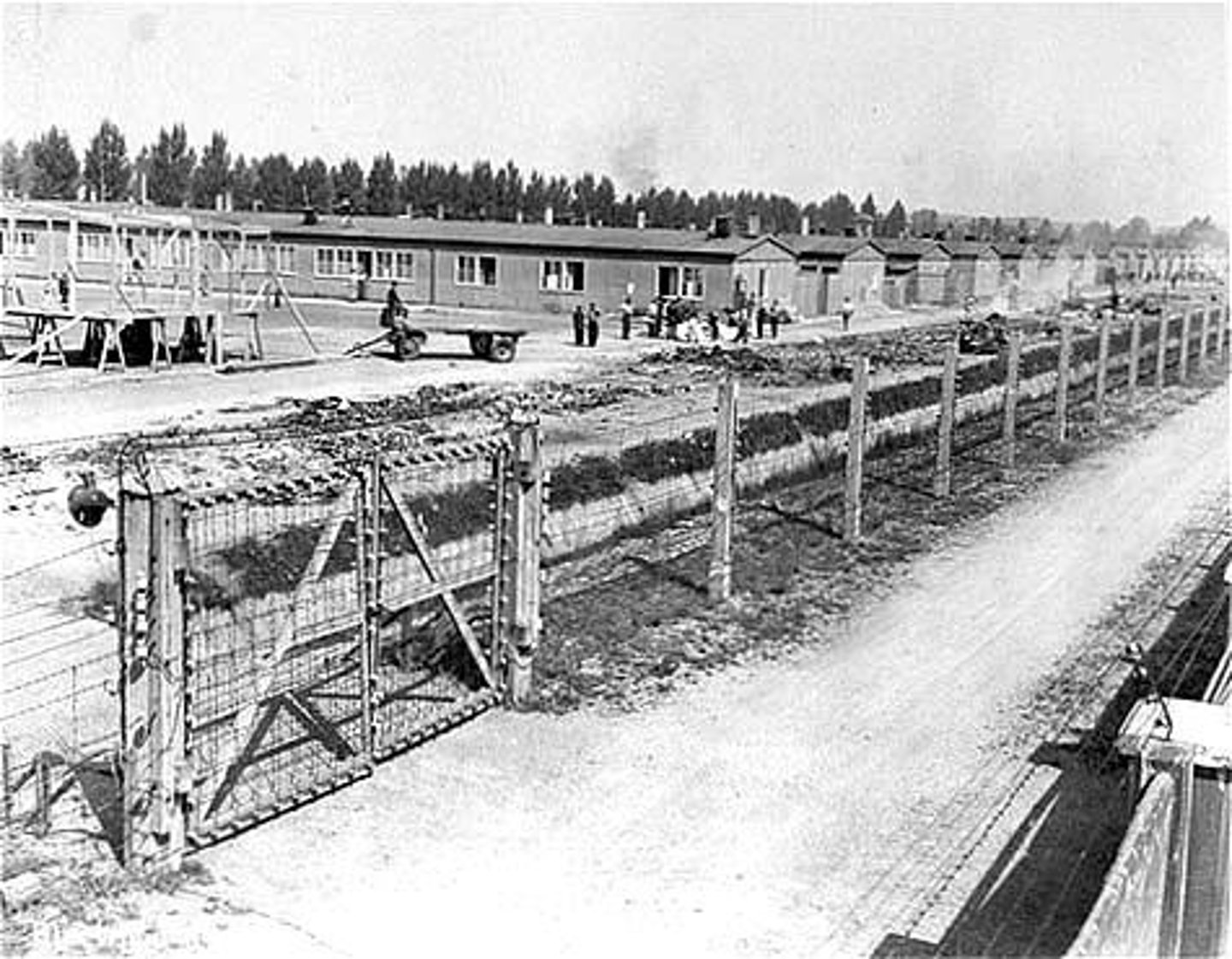
Nazi Concentration Camps
prison camps in Nazi Germany. Conditions were inhuman, and prisoners, were starved/worked to death, or killed. These camps inmates were communists, democrats, socialist, political criminals, homosexuals, and jews

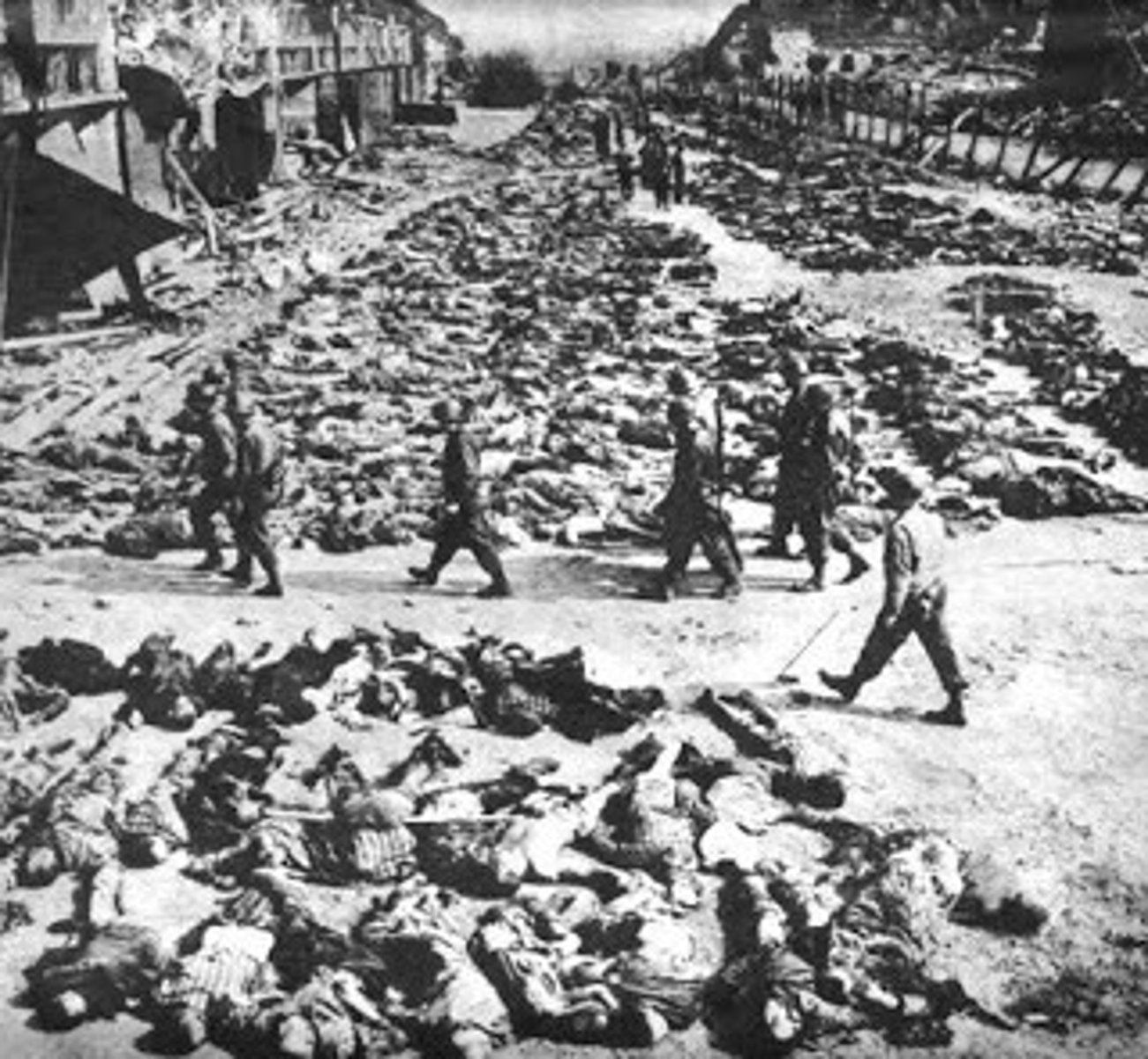
Japanese atrocities
In late 1937, over a period of six weeks, Imperial Japanese Army forces brutally murdered hundreds of thousands of people-including both soldiers and civilians-in the Chinese city of Nanking (or Nanjing)

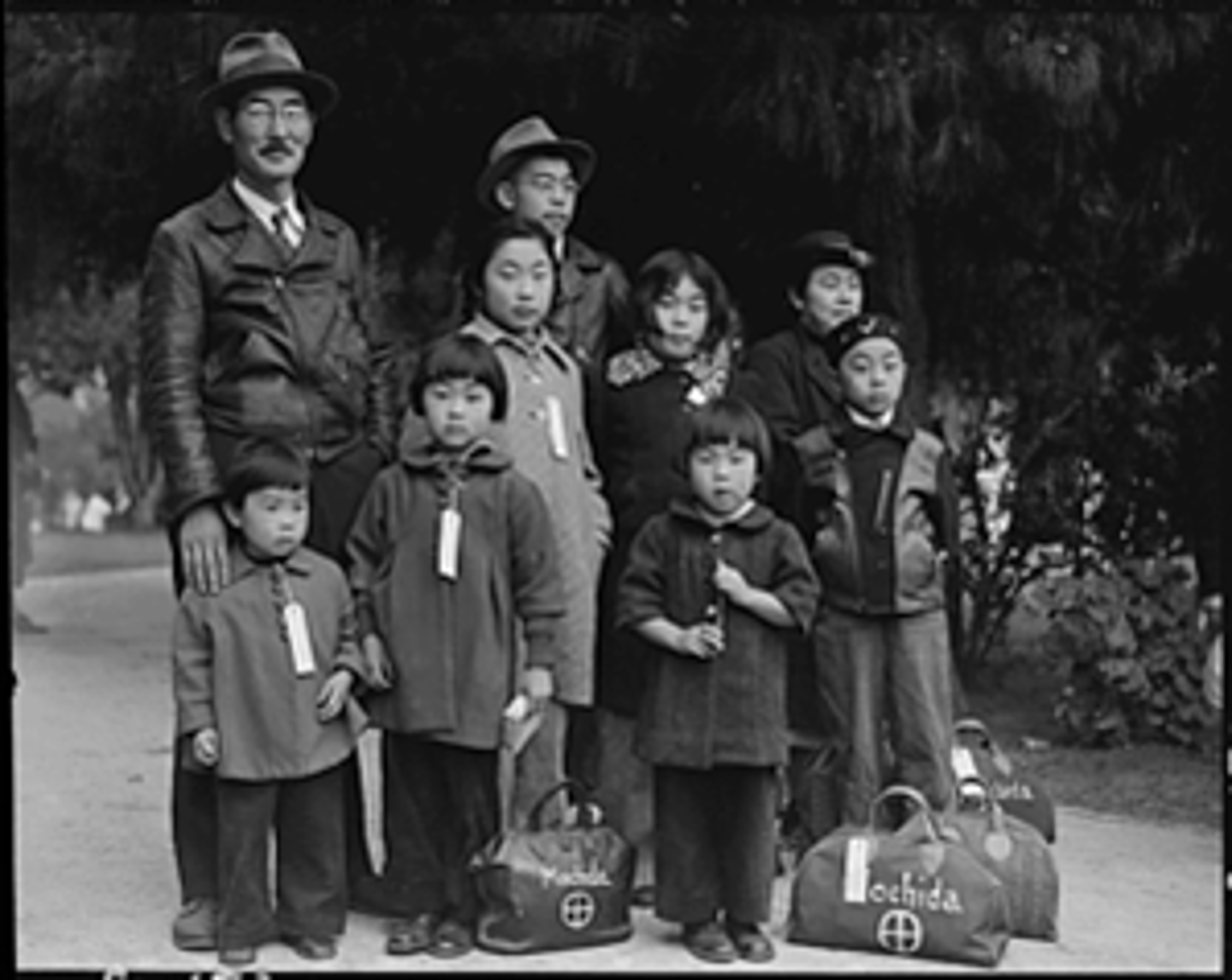
Japanese-American Internment
shortly after the bombing of Pearl Harbor by Japanese forces, Roosevelt signed a document Feb. 19,1942 stating that all people of Japanese ancestry from California and parts of Washington, Oregon, and Arizona, needed to be removed. Put them in internment camps because of their fear for another attack by the Japanese.

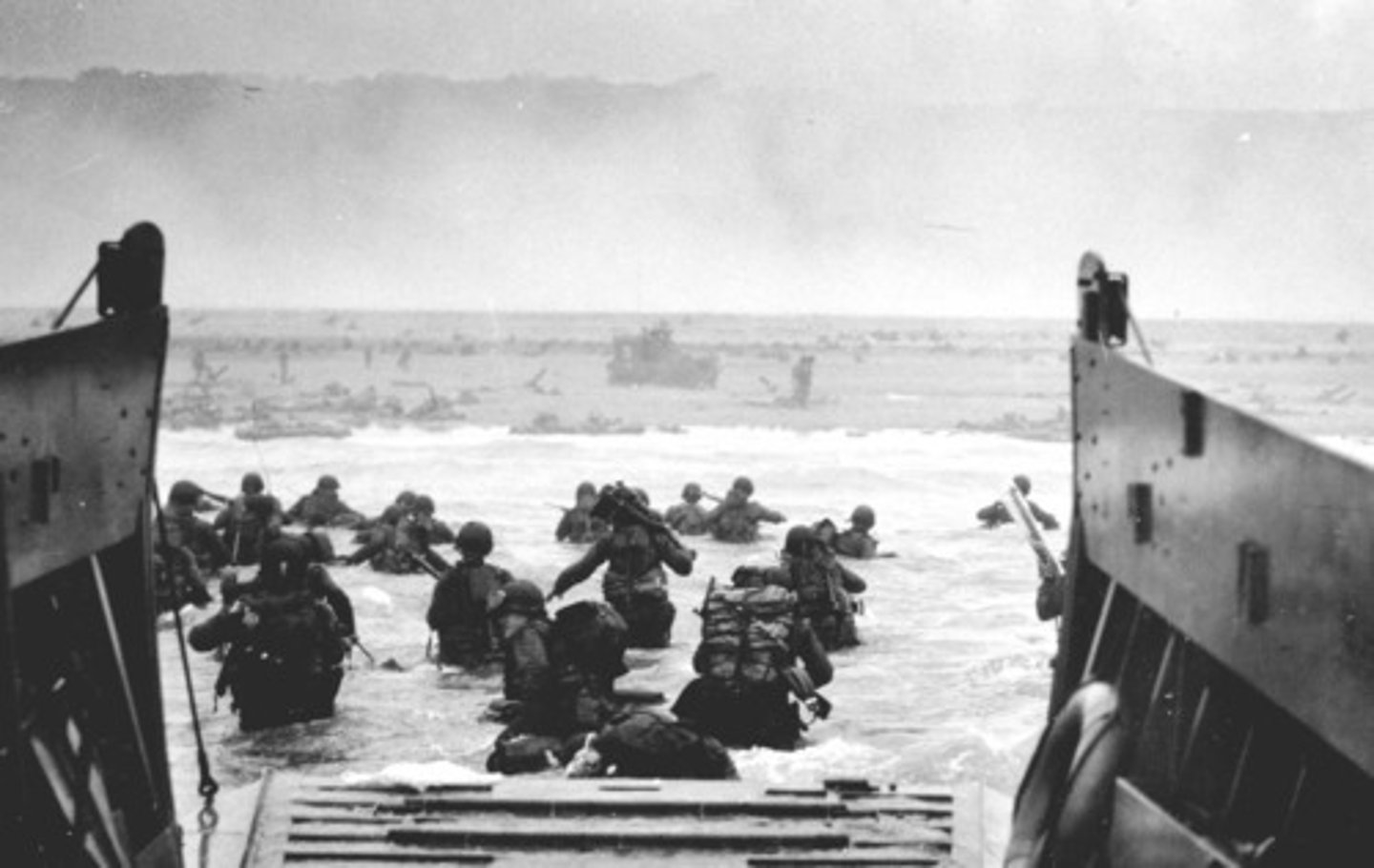
D-Day Invasion
June 6, 1944 when some 156,000 American, British and Canadian forces landed on five beaches along a 50-mile stretch of the heavily fortified coast of France's Normandy region. The invasion was one of the largest amphibious military assaults in history

"Island Hopping"
After the Battle of Midway, the United States launched a counter-offensive strike known as "island-hopping," establishing a line of overlapping island bases, as well as air control. The idea was to capture certain key islands, one after another, until Japan came within range of American bombers
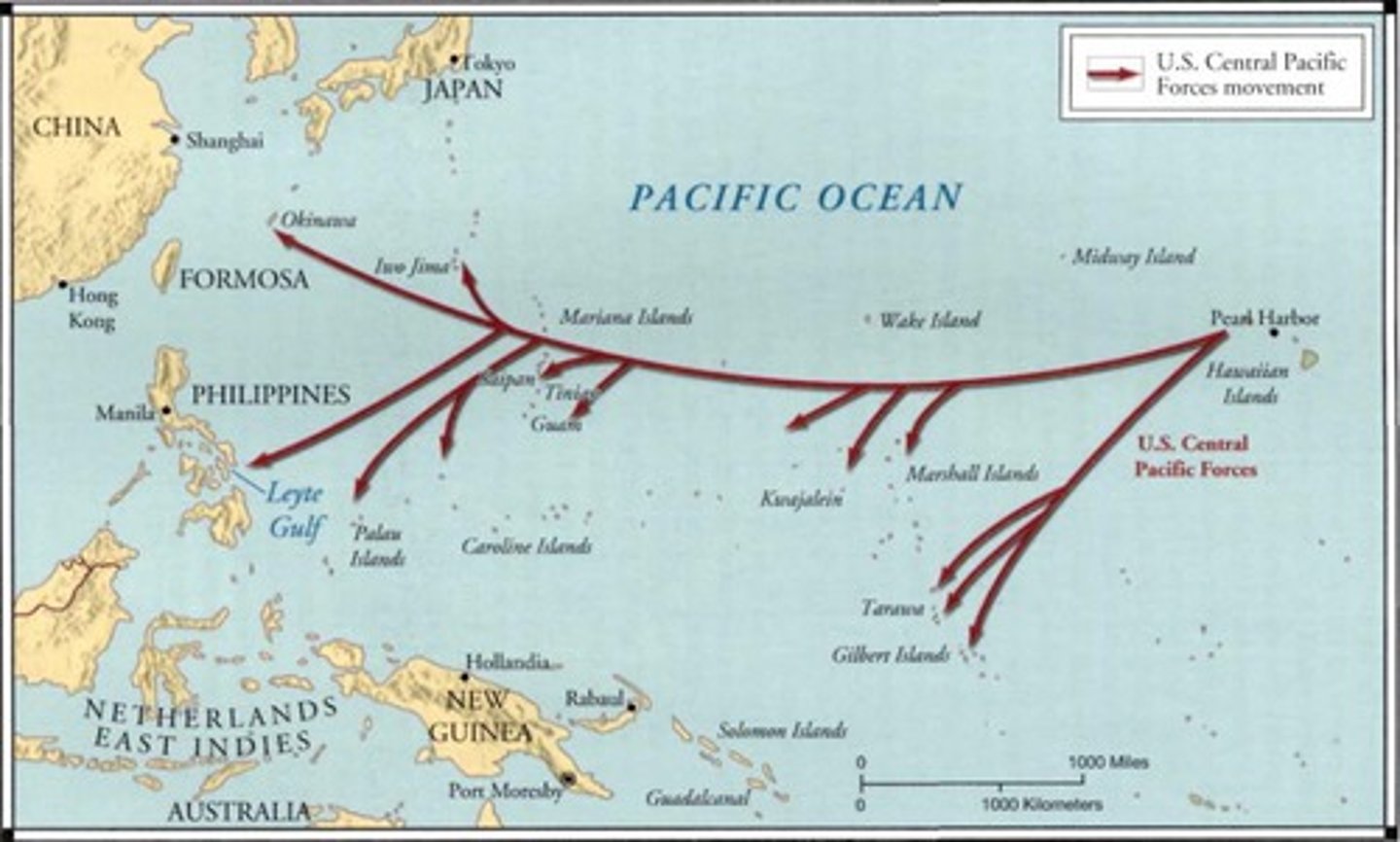
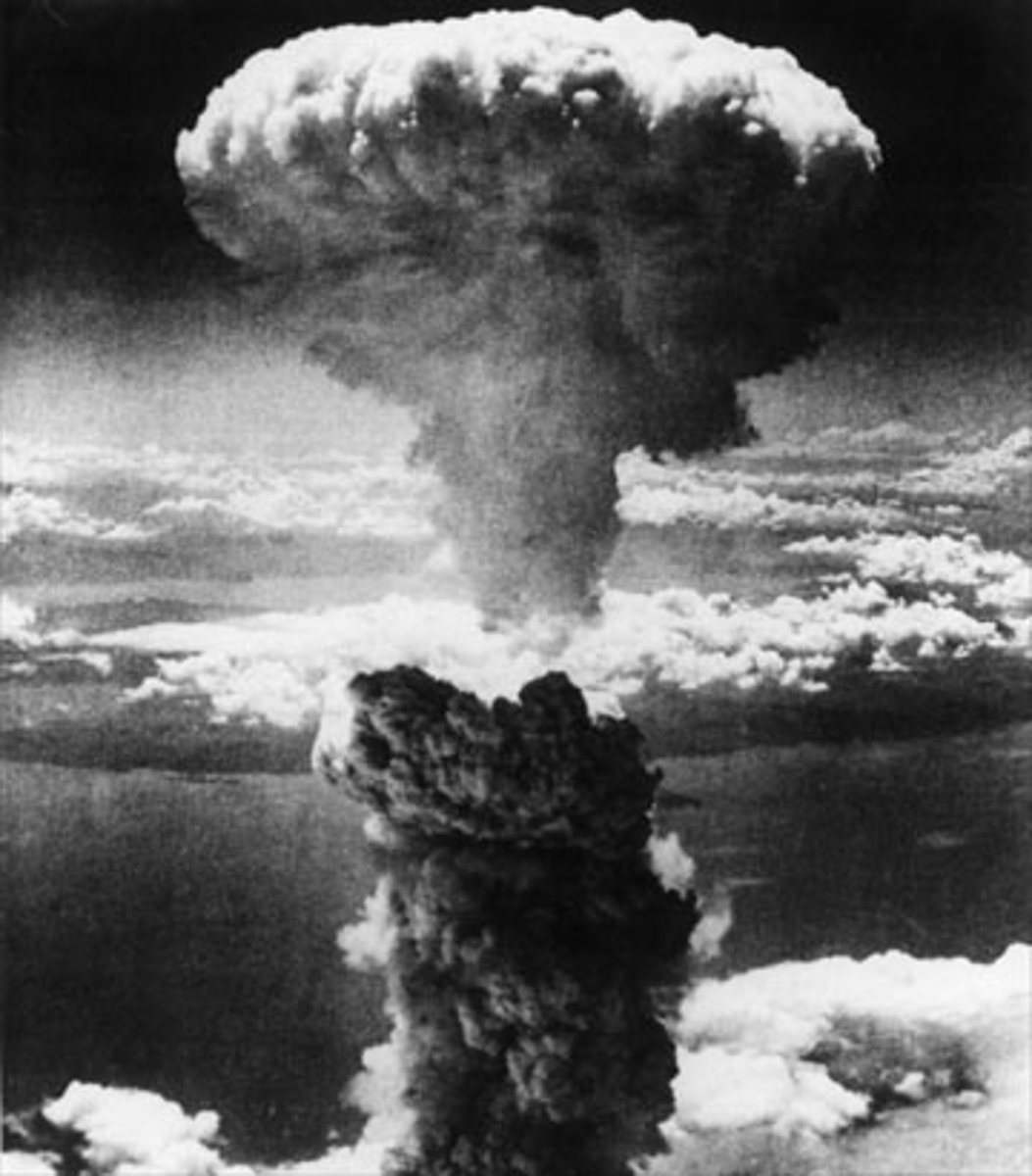
Atomic Bomb
on August 6, 1945, during World War II (1939-45), an American B-29 bomber dropped the world's first deployed atomic bomb over the Japanese city of Hiroshima
A weapon that produces tremendous power by splitting atoms

New Conservatism
Period 9
c. 1960's
A.K.A. Neoconservatism
The movement that was started by the liberals disenfranchised by the pacifist foreign policy of Democrats, including anti-Vietnam War and youth counterculture. Included many in George H.W. Bush's administration.

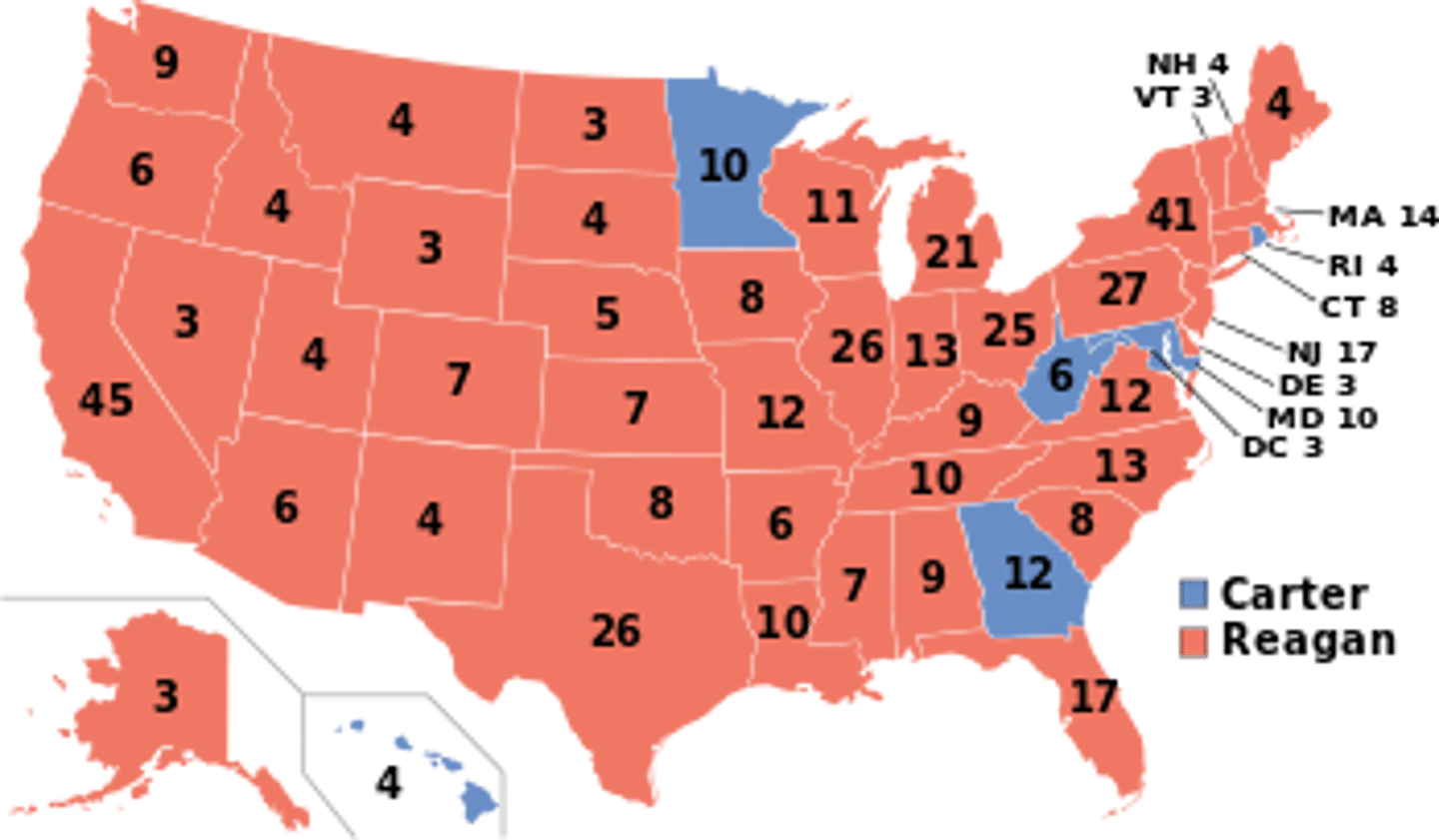
Election of 1980
Period 9
1980
United States presidential election was the 49th presidential election. Republican nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democrat Jimmy Carter.
Ronald Reagan
Period 9
President between 1981-1989

Deregulation
Period 9
c. 1980's
The lifting of restrictions on business, industry, and professional activities for which government rules had been established.

End of Cold War
Period 9
1947 - 1991
The end of the Cold War was the end of a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union with its satellite states, and the United States with its allies after World War 2.

Internet
Period 9
January 1, 1983
A global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities, consisting of interconnected networks using standardized communication protocols.

Climate Change
Period 9
Late 20th Century - Present
An awareness movement founded in analyzing the changes in global or regional climate patterns.

9/11 and the War on Terror
Period 9
2001 - Present
The terrorist attacks on American building and people and the responses from America in its aftermath.

"Republican Motherhood"
Period 3 (20th century term used to refer back to the 18th-19th century)
The emergence of recognition for educated and assertive women in US Society. One such example of this is Abigail Adams who advocated for women's rights through her "remember the ladies" letter to her husband regarding America's fight for independence from Britain

Articles of Confederation
Period 3 (1781-1789)
The first Constitution developed in the USA by the Constitutional Congress and ratified by the 13 colonies. This was later replaced by the Constitution for its overall weakness in preserving a larger federal government that could collect taxes and enforce national laws.

Constitutional Convention
Period 3 (May 25, 1787 - Sep 17, 1787)
The gathering of delegates across the colonies (excluding Rhode Island) and was led by Geroge Washington. The convention was meant to fix the problems of Articles of Confederation which led to the Constitution.

Consititution
Period 3 (ratified 1789)
The document that laid the groundwork for the United States government and how it was to operate. It provided basic laws and rights, many of which are still in effect today.

Federalists
Period 3 (1791-1824)
Led by John Adams,Alexander Hamilton, and more, this political party served the goal of strengthening national power and leaving the Constitution available to be interpreted.

Anti-Federalists
Period 3 (1791)
Led by Patrick Henry.Samuel Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and more, the Anti-Federalists believed in state power, so that the government couldn't become that of Britain's. They opposed the Constitution.
Federalist Papers
Period 3 (1788)
Written by James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay, the papers included various essays and articles promoting and explaining the Constitution.

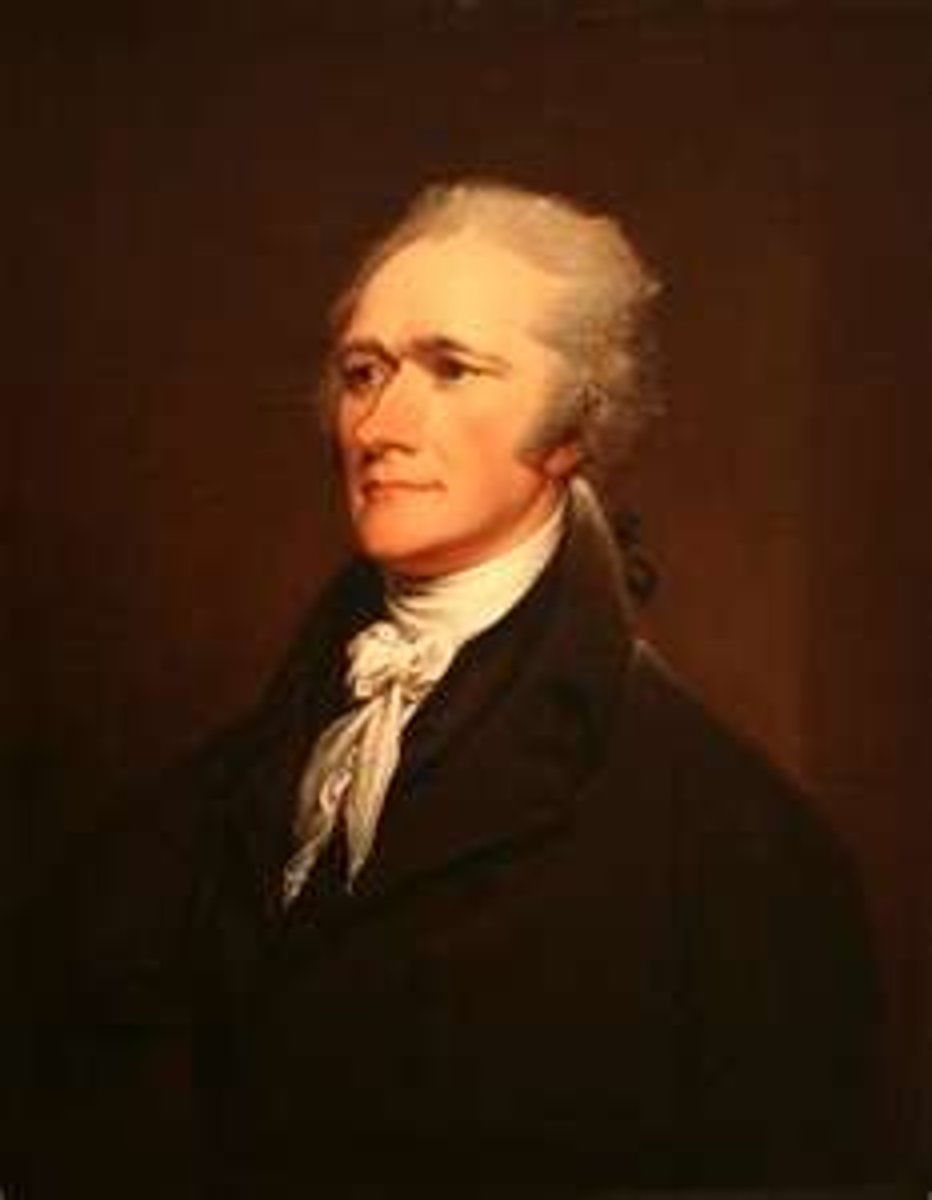
Alexander Hamilton
Period 3 (1757-1804)
First Secretary of Treasure and author of the Federalist Paper, Hamilton was dominant Federalist who helped shape foreign policy during the Washington Administration as well as establish the US Coast Guard.

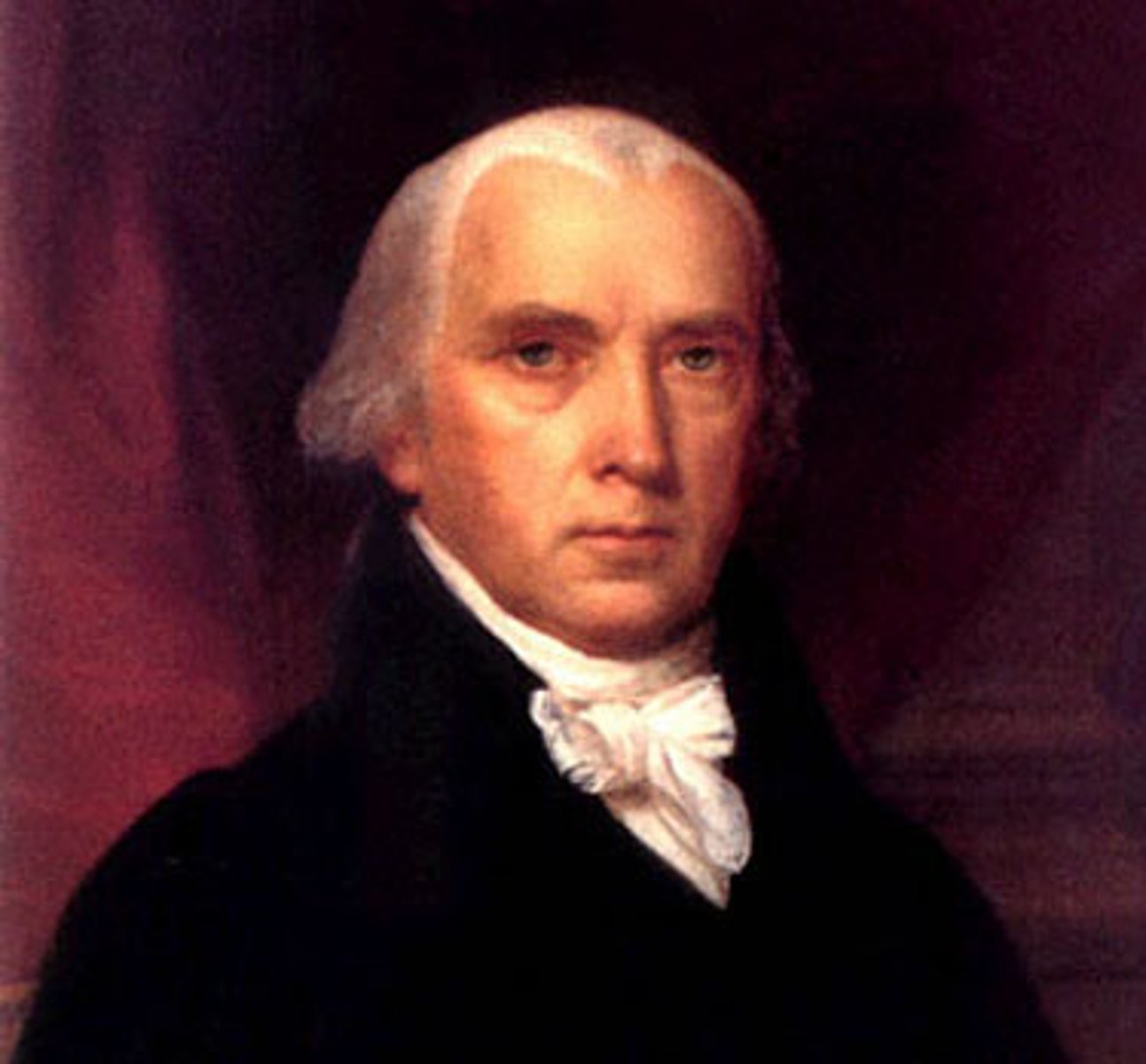
James Madison
Period 3 (1751-1836)
4th US president who write the first drafts of the Constitution, Federalist Paper, and Bill of Rights. He also created the Democratic-Republican Party alongside Thomas Jefferson.

Bill of Rights
Period 3 (ratified 1791)
The first 10 Constitutional Amendments that include the freedom of speech, right to bear arms, protected from unreasonable searches and seizures, and more.

George Washington
Period 3 (1732-1799)
1st US President who helped lead the United States to combative victory over the British during the Revolutionary War.

The Great Society
1964, LBJ's policies of fighting poverty and racial injustice

Civil Rights Act of 1964
1965 outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin
Gideon v. Wainwright (1963)
Extends to the defendant the right of counsel in all state and federal criminal trials regardless of their ability to pay.

Vietnam War
1954 A prolonged war between the communist armies of North Vietnam and the non-communist armies of South Vietnam.

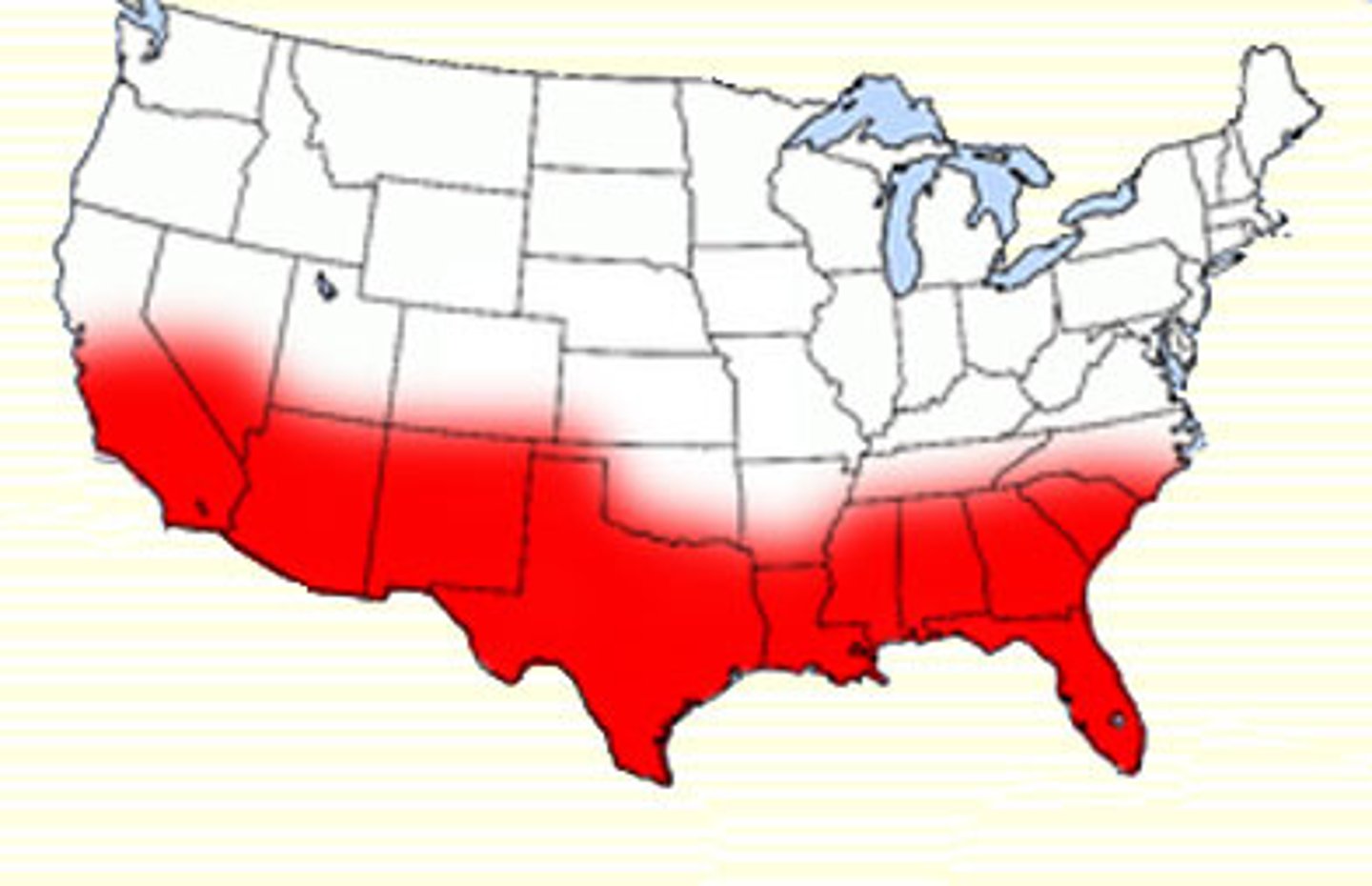
Sunbelt
states in the south and southwest that have a warm climate.
Immigration Act of 1965
1965 eliminated the quota restrictions in immigration, replaced by numerical limits that did not discriminate against specific countries; provided that the relatives of legal US residents could be admitted outside of the numerical limits
