Newton's Laws of motion
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Newton’s first law
when no net force acts on an object then
if the object is at rest, it will remain at rest
if the object is moving, it will continue to move in a straight line at a constant speed
no net force→no acceleration
if no net force and object is at rest then it will continue to be at rest, if no net force and object is moving then it will continue to move at a constant speed.
summarize newton’s first law
no net force→no acceleration
remember: no net force→no acceleration
the weight and the normal force have equal mags and opp directions so they cancel out
remember: the weight and the normal force have equal mags and opp directions so they cancel out
Newton’s second law
the net force acting on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration
F→net = m×a→
fnet = ma
apply Newtons second law (fnet = ma) to each component separately (to x component and then to y component, NOT all together)
remember: apply Newtons second law (fnet = ma) to each component separately (to x component of accel and then to y component of accel, NOT all together)
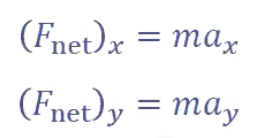
problem-solving strategy
1) draw free-body diagram
2) break up the forces into their components
3) apply newton’s second law:
fnet = 0 for objects not accelerating
fnet = ma for object that are accelerating
1) draw free-body diagram 2) break up forces into their components 3) apply newtons second law
summarize the problem-solving strategy
Fnet = 0
if the object is not accelerating the net force is what?
Fnet = ma
if the object is accelerating the net force is what?