Musculoskeletal - work in progress
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are four components to a small animal musculoskeletal exam?
gait
standing palpation
recumbent palpation
sit test
orthopedic
A unilateral lameness is more suggestive of a lameness due to an ___________ issue (orthopedic/neurologic)
proprioceptive deficits: abnormal scuffing or swinging of limb
a two engine gait: thoracic limbs move faster or slower than pelvic limbs
What two things would suggest to you that lameness is due to a neurologic cause, and not orthopedic, upon gait evaluation?
symmetry
any muscle atrophy
joint effusion/swelling
pain/discomfort
etc.
What are some things you assess/palpate for upon a standing or recumbent palpation exam?
Crepitus
Range of motion
Effusion
Pain
Instability
CREPI is the acronym applied for the recumbent palpation exam in the small animal. what does each letter in this acronym stand for?
1-5
What is the grading scale for lameness in small animals?
Lameness is consistent at a trot under some circumstances
What is a grade 2 lameness, as defined by the AAEP?
Lameness is consistently observable at a trot under all circumstances.
What is a grade 3 lameness, as defined by the AAEP?
Lameness is obvious at a walk.
What is a grade 4 lameness, as defined by the AAEP?
Lameness produces minimal weight bearing in motion and/or at rest or a complete inability to move. In other words - Non or minimal weight-bearing at a rest or walk.
What is a grade 5 lameness, as defined by the AAEP?
0-3
of 1-5
What are the two different lameness scales for cattle?
normal, the animal walks normally, with no apparent lameness or change in gait. The hind feet land in a similar location to the front feet.
How would you describe a 0/3 grade lameness in cattle?
The animal exhibits a shortened stride when walking, dropping its head slightly. The animal exhibits no limp when walking.
How would you describe a 1/3 grade lameness in cattle?
The animal exhibits an obvious limp, favoring an affected limb or limbs which still bear(s) weight. A slight head bob and arched back are present when the animal is walking.
How would you describe a 2/3 grade lameness in cattle?
The animal applies little or no weight to the affected limb and is reluctant or unable to move. While walking, the animal will drop and bob its head, arch its back and exhibit a limp.
How would you describe a 3/3 grade lameness in cattle?
down on the sound
the head will be greatly lifted when weight is placed on the lame limb (in an effort to reduce the weight placed on the limb)
What motion of the head can give you an indication as to which forelimb is lame? in any species
shortened stride on that side
hip hike on side of affected limb
reduced fetlock sinking in the affected limb.
What are three things that can help you determine which pelvic limb is lame in a horse?
Digital tendon sheath
Fetlock joint
What structures are in the region of the fetlock that could be a potential source of lameness in the horse if they are inflamed?
Diagnostic nerve blocks
If you have no financial limitations, what would be one of your first steps in diagnosing lameness in the horse related to the distal limb?
Grade 1
What grade lameness matches this description for cattle? on the 1-5 scale: Walks easily and readily. Bears full weight on foot and limb but has an observable gait alteration. Stands on all 4 limbs squarely. Spine in normal position.
Grade 2
What grade lameness matches this description for cattle? on the 1-5 scale: Walks with encouragement, but has an obvious shortened stride during weight-bearing on lame leg, inconsistent head bob, does not bear full weight on lame leg while standing. Inconsistent lordosis of spine.
Grade 3
What grade lameness matches this description for cattle? on the 1-5 scale: Reluctant to walk, but bears some weight on leg while walking. Noticeable and consistent head bob. Lame leg has altered weight-bearing during standing. Greater time spent in recumbency. Consistent lordosis of spine.
Grade 4
What grade lameness matches this description for cattle? on the 1-5 scale: Walks only with stimulus. Bears minimal weight on leg, only toe touching. Pronounced head bob and lordosis of spine. Spends majority of time in recumbency.
Grade 5
What grade lameness matches this description for cattle? on the 1-5 scale: If walking, refuses to bear weight on leg. Some animals are unable or unwilling to rise as a result of lameness.
head bob - down on the sound
placement of limb directly under themselves or not.
What observations upon observing the gait of cattle (and most species) as to which forelimb is lame?
sup. & deep digital flexor tendons and their sheaths
navicular bone and its bursa
digital cushion
synovial joints of fetlock, pastern, and coffin joints
etc.
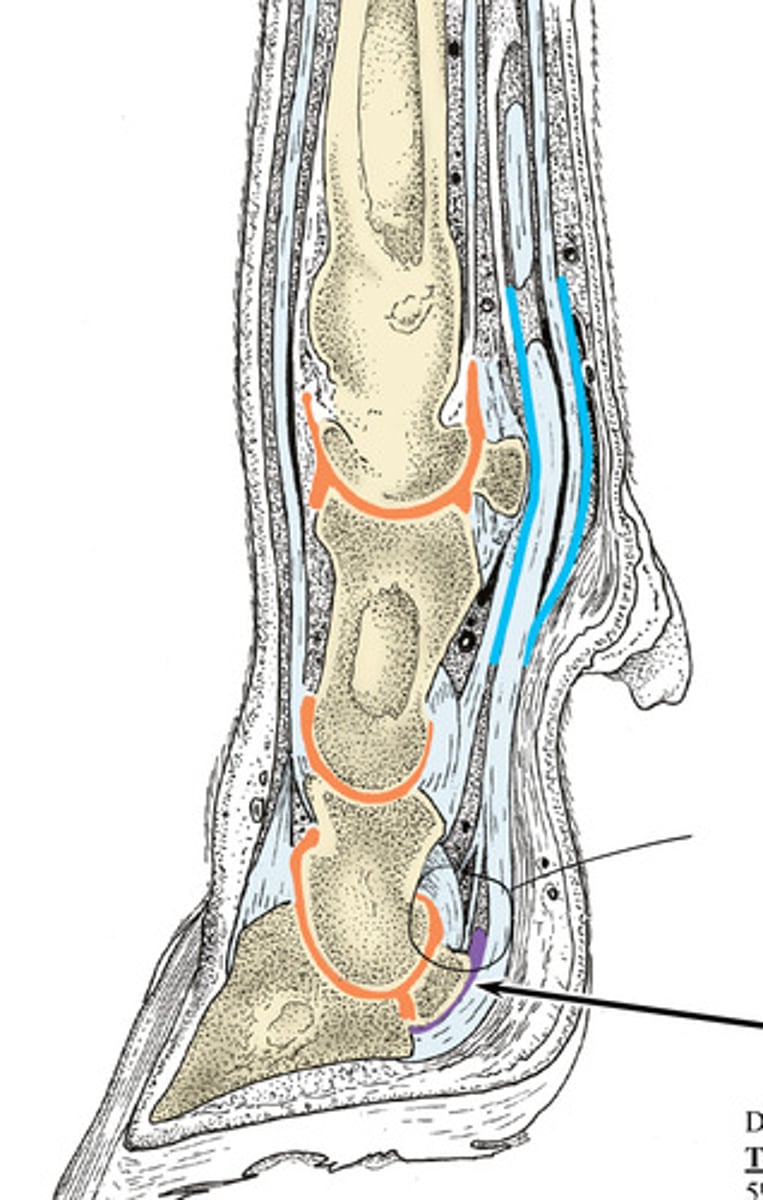
Remember the structures in the bovine/ruminant foot. Engrain this image in your brain. What structures do ya see?
herd
individual
Locomotion scoring usually helps assess a(n) __________, whereas lameness grading helps as a(n) ___________.
Radiographs
Arthrocentesis
What are a couple of diagnostic tools you may utilize to find the source of lameness in a cow with lots of swelling in its digits?
amputation of claw
synovial lavage
blocks
What are potential treatments for lameness in cattle related to the digits? (depending on cause of lameness)