Business Management - Topic 3
1/194
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
What is finance?
The process of acquiring and managing money for a business
What is accoutning?
The process of recoding money flows and assets for a business
What is procurement?
The act of purchasing goods and services for a business
What is the job of a finance department?
Allocating funds for other departments, ensuring the business stays within budget and meets financial targets, planning financial future and monitoring external changes
What is capital expenditure?
Spending on the company’s fixed assets
What are fixed assets?
Something that will be used for more than 1 year and usually requires long-term investment (land, buildings, factories, machines, tech, production equipment, vehicles)
How are fixed assets funded?
Through long-term finances as they tend to be expensive
What is revenue expenditure?
Spending on a company’s general operational costs/things that have to be paid daily, weekly, or monthly (utility, wages, salaries, taxes, debts)
How are revenue expenditure funded?
Short or medium-term finances
What are the time periods of short, medium, and long-term finance?
Short-term is repaid within a year, medium-term is 1 to 5 years, long-term is more than 5 years
What is the purpose of short-term sources of finance?
Solve cash flow problems or to pay for revenue expenditure
What is the purpose of medium-term sources of finance?
Finance capital expenditures or purchase a fixed asset
What is the purpose of long-term sources of finance?
Finance large capital expenditures
What are internal sources of finance?
Money that is raised from the business’s or owner’s existing assets, doesn’t have to be repaid
What are benefits of internal sources of finance?
Less risk, maintains controlW
What are the 3 internal sources of finance?
Personal funds, retained profits, sales of assets
When are personal funds used?
Start of business or when in crisis
Why would a business want to sell an asset?
Need quick money or want to use the money to replace the asset
What are disadvantages of internal sources of finance
Slower to get funds, use of personal funds is risky for the owner, using retained profits results in a lower dividend value, selling assets has opportunity costs
What are external sources of finance?
Finance that comes from outside the business
What is equity finance?
The provider of finance receives part ownership of the business in exchange for the finance
What is an advantage of equity finance?
Don’t have to be repaidW
What are disadvantages of equity finance?
Loss of ownership and control
Who are business angels?
A successful, wealthy person who invests their money into a new business to provide funding to a business that is not yet listed on the stock exchange
What to business angels want out of a business?
High growth and large returns on investment
What is an advantage of having a business angel?
They can be mentors
What is a disadvantage of having a business angel?
Conflicts may occur if parties want to set up a business differentlyW
Who are venture capitalists?
Companies that use money from clients to fund a new business
What do venture capitalists want out of a business?
They want the business to grow so that they can sell their stake at a higher price
What is share capital?
Money raised through shares on the stock market, shareholders get a portion of profits as dividends
What is the benefit of share capital?
Easy to access large amounts of financial capital
What is debt finance?
Money that is borrowed from a bank or other financial institutions
What is the benefit of debt finance?
Ownership is maintained
What is the disadvantage of debt finance?
Money must be paid back, likely to have interest
What is loan capital?
Medium to long-term finance used to buy fixed assets
What must the business give up to get a loan?
Provide a collateral, an asset, in the event that the business doesn’t pay back the loan
What is a mortgage?
A special type of loan used to purchase land or buildings, tend to be repaid over 25 years
What are advantages of loan capital?
Money is available immediately, repaid in small chunks, used to buy profit-generating assets which will repay itself
What are overdrafts?
High cost, short term loans attached to a bank account which allows the account holder to withdraw more money than they have in their account
What is microfinancing?
Providing financial services to individuals who have very limited income and assets and are not able to get services from traditional banks
What is microcredit?
Small loans that can allow someone to start or continue to finance a small-scale business
What are the benefits of microcredit?
No collateral, low interest rates
What are disadvantages of microcredit?
Loans are small, loan period is short
What is trade credit?
A business receives goods and services from a supplier immediately but pays at a later date, normally 30, 60, or 90 days with no interest
Why would both parties benefit from trade credit?
Customers stay happy, business will have extra cash on hand for production, business will want to pay in a timely manner to maintain good relationships
What is leasing?
Renting a fixed asset over a period of time instead of buying it
Why would a company want to lease?
Don’t need to worry about maintenance or repair, lower cost of production, can always lease the latest model
What is crowdfunding?
Many people investing small amounts of money to fund a project
What is peer-to-per lending?
Investors provide a loan that earns interest
What is equity crowdfunding?
Investors acquire a small share of ownership in the business
What is rewards-based crowdfunding?
Investors receive a non-financial reward at a later date, normally a good or service produced by the business
What is donation-based crowdfunding?
Donors don’t receive anything in return
Where does crowdfunding occur?
A platform that a business pays a fee to use
What is taken into consideration when choosing a source of finance?
Ownership type and size of business
Purpose of the business
What finance is needed for
Risk tolerance
What are costs?
All the expenses needed to produce a good or service
What are variable costs?
Costs that vary with output (materials, packaging, delivery, piece-rate wages, commission)
What is variable cost per unit?
The variable cost of making 1 product
What is total variable cost?
The sum of all variable costs for the entire output (variable cost x output)
What are fixed costs?
Costs that don’t vary with output (insurance, rent and mortgage payment, machines, and salaries and wages that aren’t dependent on output)
What are semi-variable costs?
Costs with a fixed and variable element (utility bills, staff who are paid a basic salary and a bonus)
What are direct costs?
Costs that can be tracked back to an individual project, product, or department (staffing costs of a particular department, utilities of a store, material costs of a product line)
What are indirect costs?
Costs that can’t be tracked to the production or sale of any single product (nationwide campaigns, expenses of a central HR department)
What is revenue?
Income earned from selling goods and services
How do you calculate total revenue?
Selling price x quantity sold
What are revenue streams?
Methods through which a business will get revenue
What is the effect of having more revenue streams?
Makes the business more resilient to external changes
What is the break-even point?
The quantity or output where total revenue equals total costs
How is contribution per unit calculated?
Selling price - variable costs per unit
How is total contribution calculated?
Contribution per unit x output
How is BEP (units) calculated?
Fixed costs ÷ contribution per unit
How is the margin of safety (units) calculated?
Current output - BEP
How is profit at a certain level of output calculated?
(Output x contribution per unit) - fixed costs
How is a break-even chart made?
Calculate BEP
Draw fixed cost line
Draw total cost line (starting at FC line and increases with output)
Draw total revenue line (starting at 0 and increases with output)
Mark BEP, where TC and TR intersect
Mark current or planned output and indicate margine of safety
Shade area of profit and loss
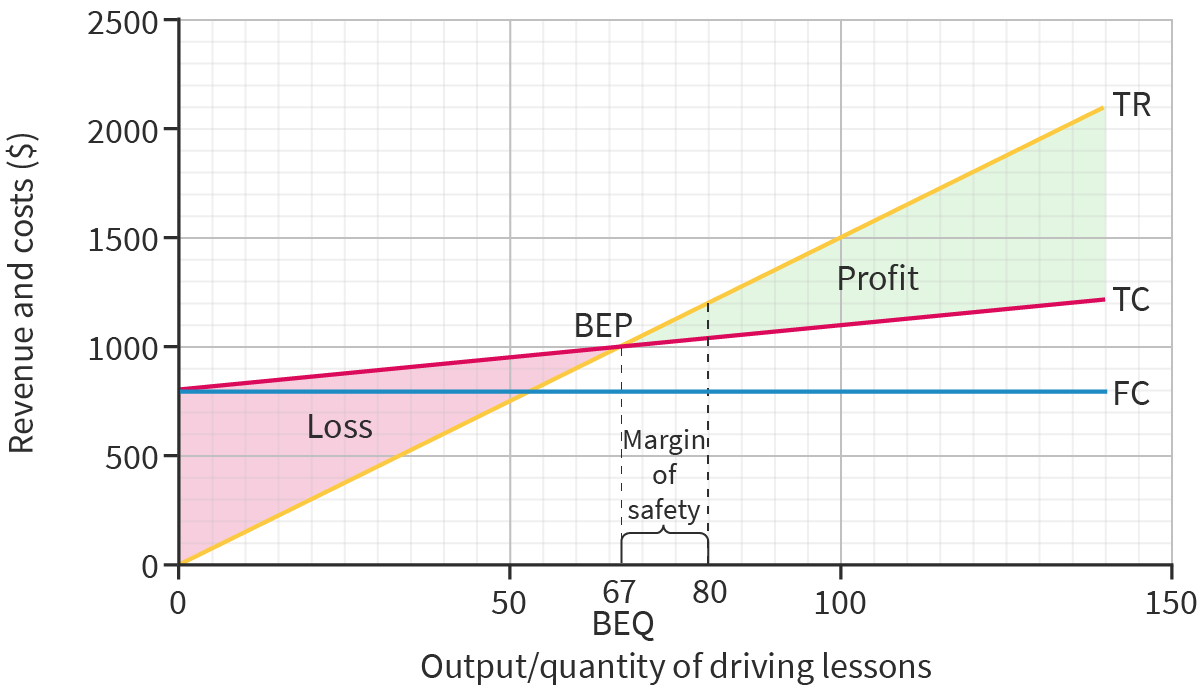
What is a break-even chart used for?
Help understand what output is needed to earn a profit
Used by banks and investors to judge a risk of a loan or investment
Examine cost and revenue scenarios when considering change
What are the limitations of break-even?
Costs and revenue change regularly, need to update often
Assumes costs and revenue are linear
Time-consuming to analyze for each product
What are decisions trees?
Tool that helps businesses make decisions by putting an estimated value on various options, often used to choose between investment decisions
What are elements of a decision tree?
Decision node (square)
Probability node (circle)
Crossed-out lines to indicate an option is rejected
How is a decision tree made?
Calculate the expected revenue of each outcome (probability x revenue)
Calculate the total expected value of each outcome for each option (successful + unsuccessful expected revenue)
Calculate the net expected value of each option by subtracting initial costs, written next to the decision node
Cross out rejected option
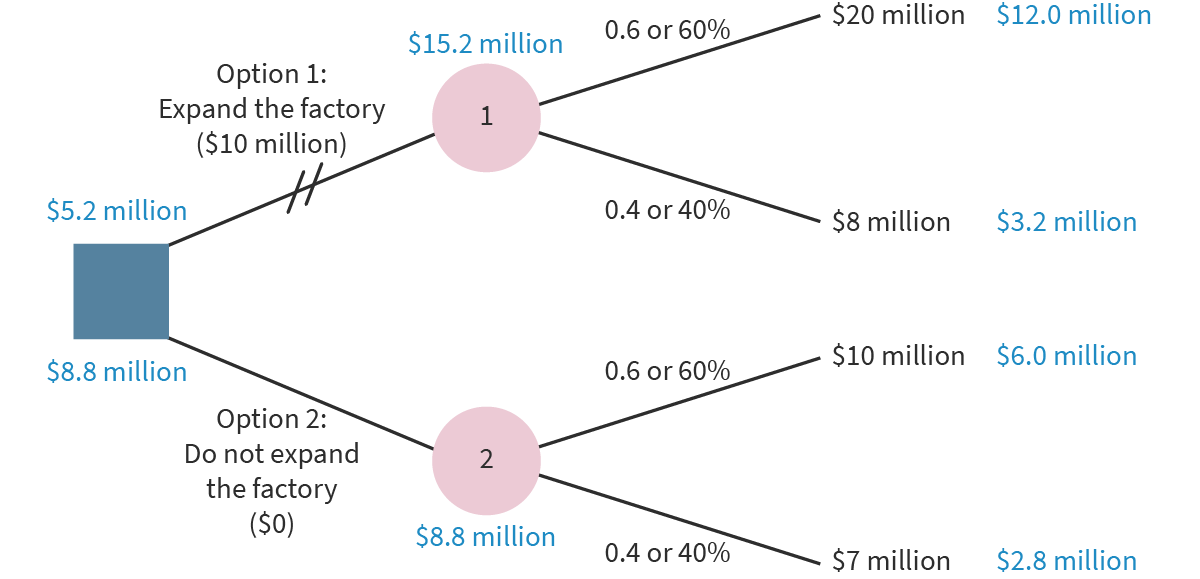
What are advantages of decision trees?
Clear and easy visual representation of complex problems
Integrates uncertainty (risks) into analysis
Considers all options
What are disadvantages of decision trees?
Don’t take qualitative factors into account
Probabilities and revenues are estimated, can lead to false results
Estimated figures are prone to bias
How does management use final accounts?
See changes in the business and develop new strategies, identify how easily short and medium-term debts are covered, how profits are earned, values of assets, and amount of money invested by shareholders
How do owners and shareholders use final accounts?
Identify how effectively their money is invested and how much they will receive in dividends
How do employees use final accounts?
Know financial stability of a business and how secure their jobs are, negotiate wages based on profits
How does the government use final accounts?
Assess taxes, health of a business, identify when a business needs financial support
How do competitors use final accounts?
Assess overall financial strength, compare profits
How do banks use final accounts?
Check ability to pay loans
How do suppliers use final accounts?
Check how effectively a business can pay for goods on credit
How does the local community use final accounts?
Check how financially stable a company is and if the business can continue to provide jobs and goods/services
How is a statement of profit and loss/income statement for a for-profit enterprise made?
Calculate gross profit (sales revenue - cost of sales)
Cost of sales = opening stock + purchases - closing stock
Calculate profit or loss
Profit before interest and tax = gross profit - expenses
Calculate profit before tax (profit before interest and tax - interest)
Calculate profit for period (profit before tax - tax)
List how profits are distributed (dividends and retained profits)
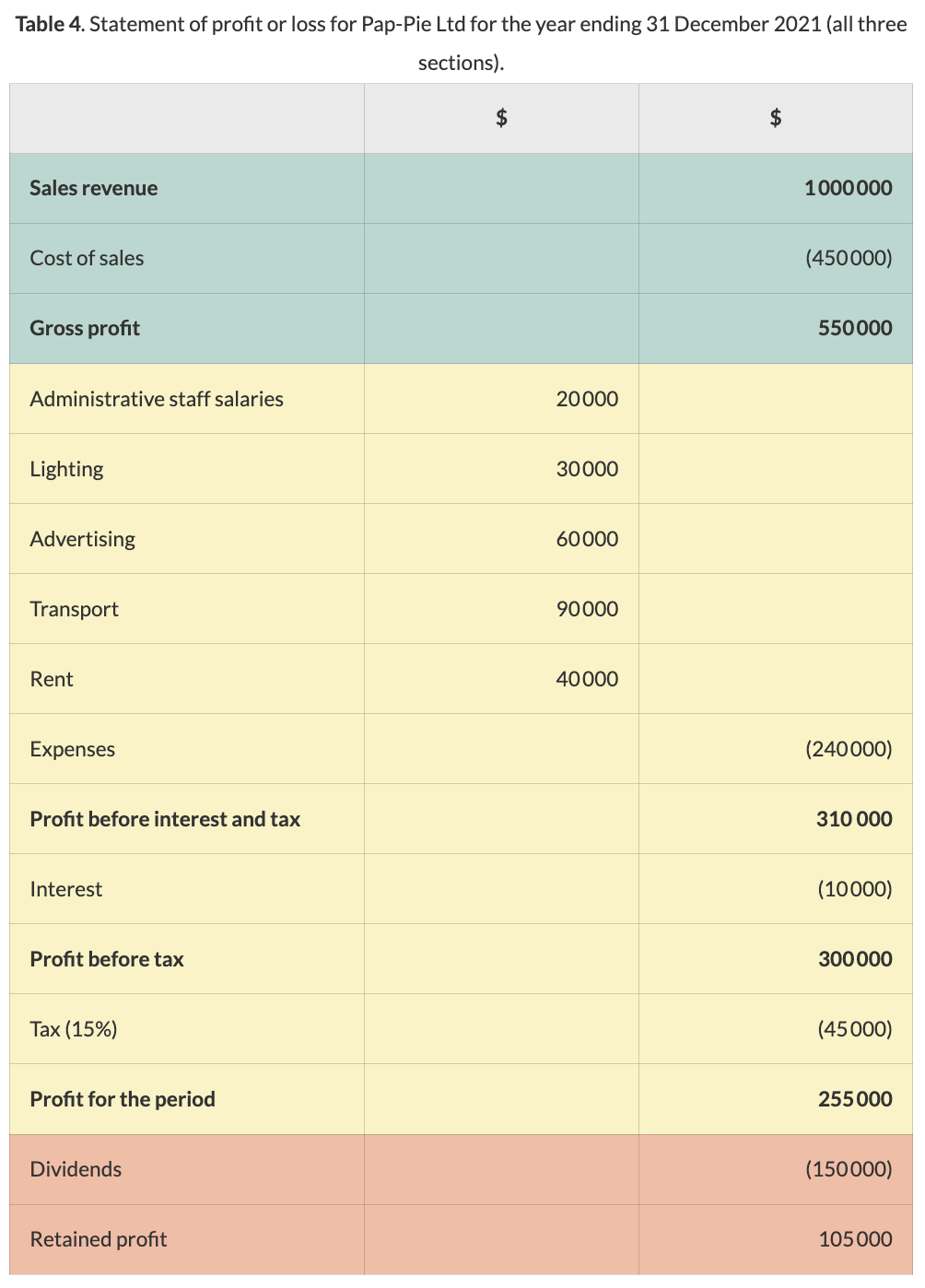
What is the difference between a profit and loss statement for a profit and non-profit enterprise?
Surplus instead of profit, no taxes, no dividends
What is a statement of financial position/balance sheet?
States the company’s assets and liabilities and shareholder’s investment or equity in the business
What is the structure of a balance sheet for a for-profit enterprise
Current assets
Cash
Debtors
Stock
Non-current assets
Total assets
Non-current liabilities
Current liabilities
Total liabilities
Net assets
Equity
Share capital
Retained earnings
Total equity
Net assets = total equity
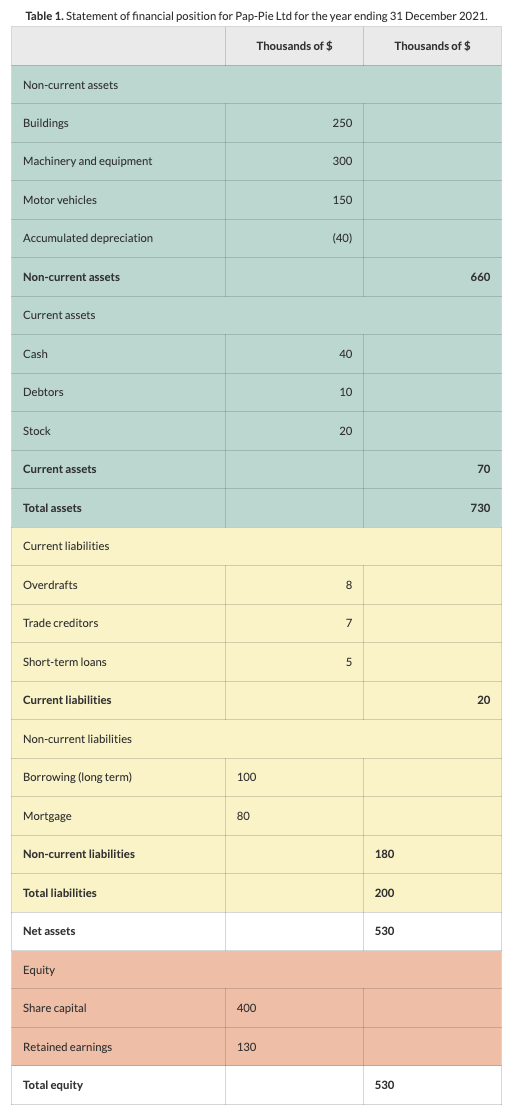
What is the difference between a balance sheet for a profit and non-profit enterprise?
No shareholders so no share capital
What are intangible assets?
Non-physical items of value owned by a company that has a lifespan of more than a year
What are patents?
Legal protection given to inventors of products to prevent copying for a certain number of years
Why are patents beneficial for businesses?
They grant temporary monopoly or production, businesses can earn large revenue
Incentive to develop or innovate even with high costs
What is copyright?
A form of legal protection given to producers of literary or artistic works to protect their exclusive right to publish, reproduce, perform, distribute, and sell
How long does copyright last?
50-70 years after the creator’s death, once expired work enters the public domain
What is a registered trademark?
A distinctive mark, sign, or symbol a company or individual uses to identify or brand itself
What is goodwill?
The intangible value of a company derived from its ‘good nature’ in business, public’s perception of a business