Unit 1 世界地理和人类起源 What is Sociology and early civilizations
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1.社会学 (shè huì xué)
Sociology: The study of society, social institutions, and social relationships.
2. 文明 (wén míng)
Civilization: A complex human society that has developed cities, social structures, and cultural achievements.
3. 国家 (guó jiā)
Country/Nation: A politically organized area with a defined territory, government, and population.
4. 地球 (dì qiú)
Earth: The third planet from the sun, where humans live.
5. 东南西北 (dōng nán xī běi)
East, South, West, North: The four cardinal directions.
6. 农业 (nóng yè)
Agriculture: The practice of cultivating soil, growing crops, and raising animals for food, fiber, and other products.
7. 灌溉 (guàn gài)
Irrigation: The artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops.
8. 社会阶级 (shè huì jiē jí)
Social Class: A division of society based on social and economic status.
9. 地理 (dì lǐ)
Geography: The study of Earth's physical features and human-environment interactions.
10. 历史 (lì shǐ)
History: The study of past events, particularly in human affairs.
11. 政府 (zhèng fǔ)
Government: The governing body of a nation, state, or community.
12. 宗教 (zōng jiào)
Religion: A system of faith and worship, often involving a belief in a higher power or gods.
13. 文化 (wén huà)
Culture: The social behavior, norms, and practices of a particular group of people or society.
14. 清真寺 (Qīngzhēnsì)
Mosque: A place of worship for Muslims.
15. 教堂 (Jiàotáng)
Church: A place of worship for Christians.
16. 寺庙 (Sìmiào)
Temple: A building used for the worship of a god or gods, especially in religions like Hinduism and Buddhism.
17. 习俗 (xí sú)
Custom: Traditional practices or behaviors followed by a particular group or society.
18. 建筑 (jiàn zhù)
Architecture: The art and practice of designing and constructing buildings.
19. 位置 (wèi zhì)
Location: A specific place or position.
20. 绝对位置 (jué duì wèi zhì)
Absolute Location: The precise point where a place is located on Earth, usually given in latitude and longitude.
21. 相对位置 (xiāng duì wèi zhì)
Relative Location: The position of a place in relation to another place.
22. 东 (dōng)
East: One of the four cardinal directions, opposite of west.
23. 西 (xī)
West: One of the four cardinal directions, opposite of east.
24. 南 (nán)
South: One of the four cardinal directions, opposite of north.
25. 北 (běi)
North: One of the four cardinal directions, opposite of south.
26. 经线 (jīng xiàn)
Longitude: Imaginary lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, used to measure distance east or west of the prime meridian.
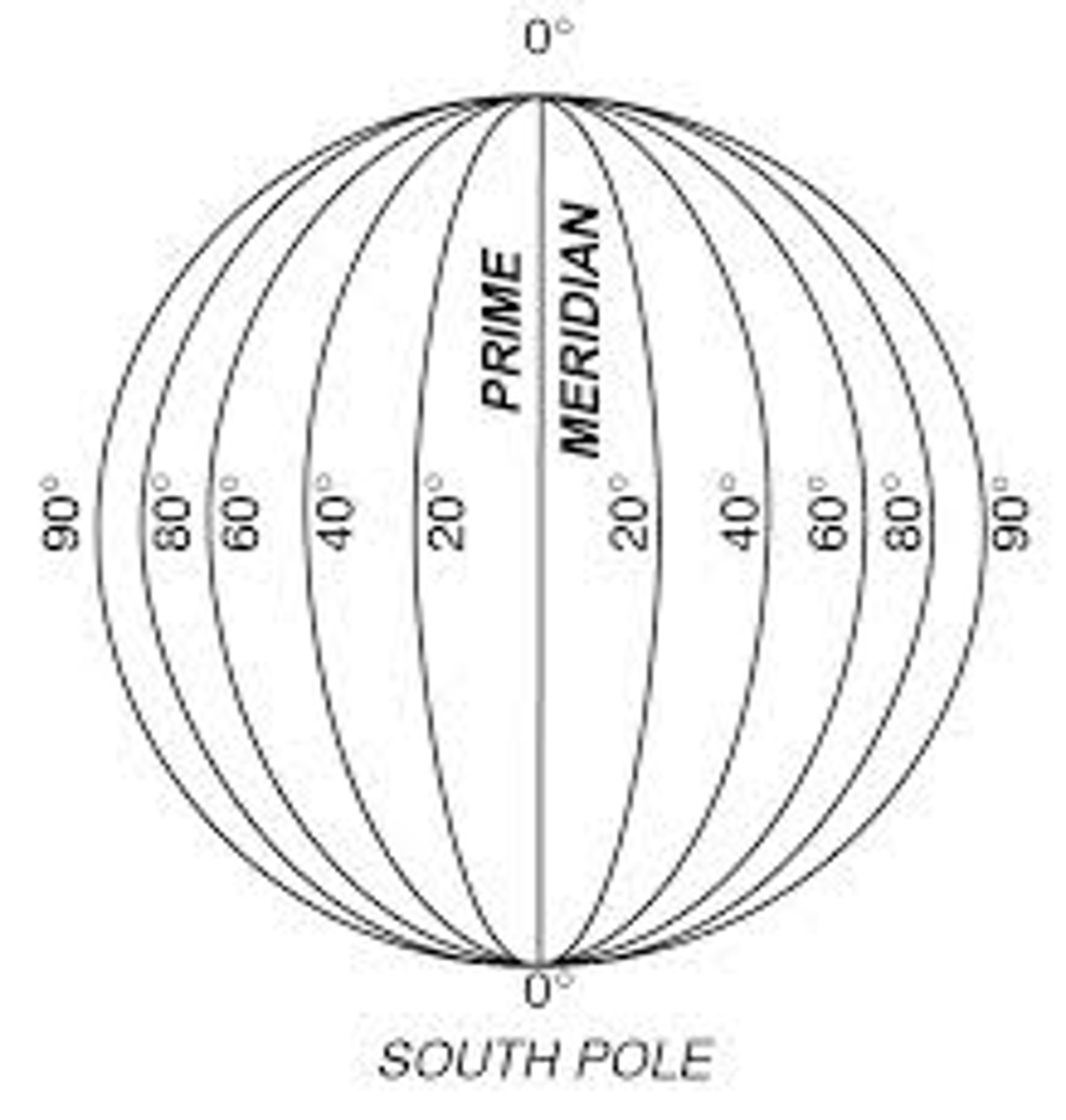
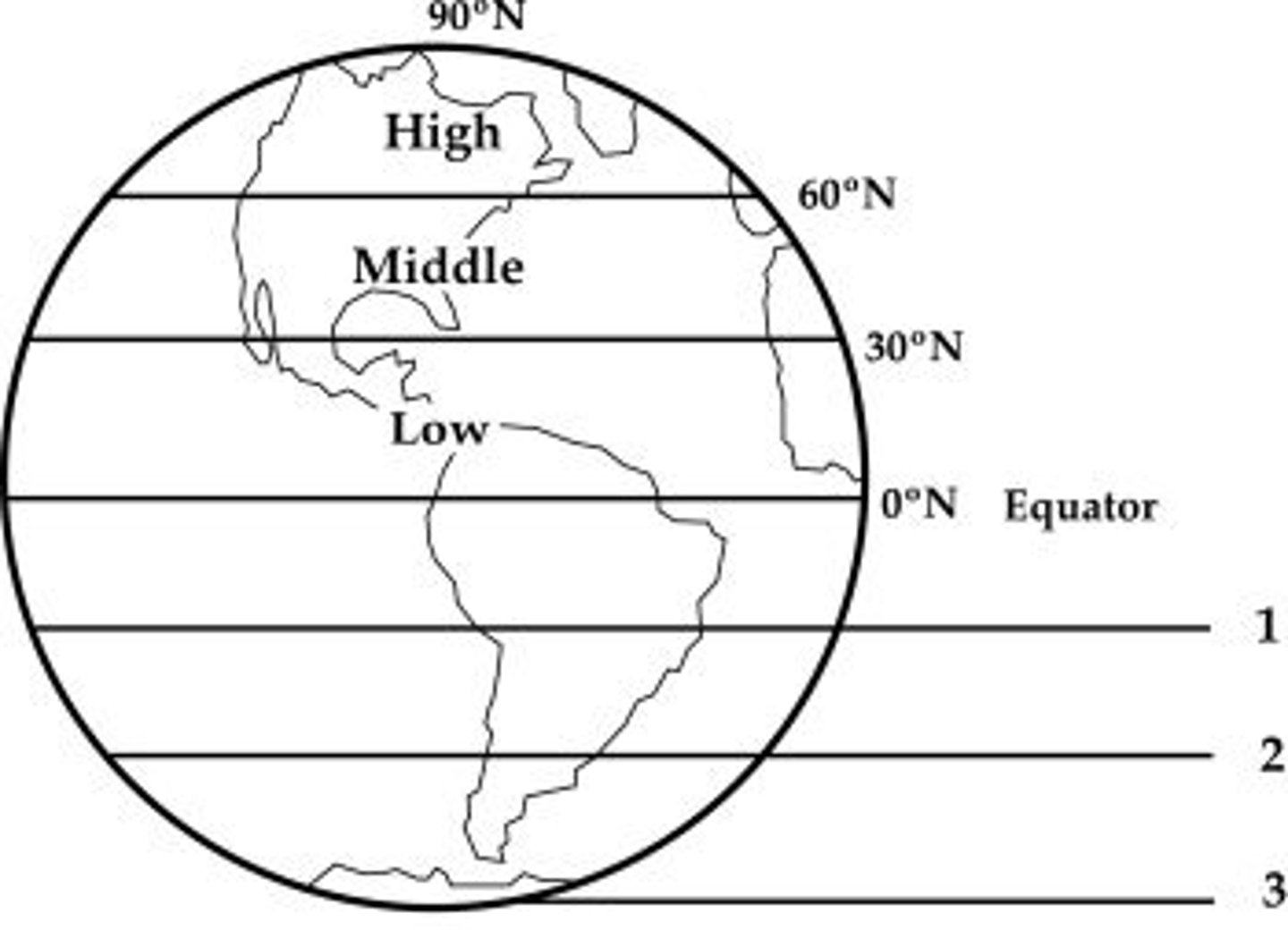
27. 纬线 (wěi xiàn)
Latitude: Imaginary lines that run parallel to the equator, used to measure distance north or south of the equator.
28. 地点 (dì diǎn)
Place: A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular characteristic.
29. 自然特征 (zì rán tè zhēng)
Natural Features: Physical characteristics of the Earth, such as mountains, rivers, and lakes.
30. 人造特征 (rén zào tè zhēng)
Human-made Features: Elements created by humans, such as buildings, roads, and bridges.
31. 特征 (tè zhēng)
Feature: A distinctive attribute or aspect of something.
32. 人和环境 (rén hé huán jìng)
Human and Environment: The interaction between humans and the natural world.
33. 山 (shān)
Mountain: A large landform that rises prominently above its surroundings, usually having a peak.
34. 河 (hé)
River: A large, flowing body of water that usually empties into a sea or ocean.
35. 土地 (tǔ dì)
Land: The part of the Earth's surface that is not covered by water.
36. 桥 (qiáo)
Bridge: A structure built to span a physical obstacle, like a river or valley, for transportation.
37. 大坝 (dà bà)
Dam: A barrier constructed to hold back water and raise its level, forming a reservoir.
38. 采矿 (cǎi kuàng)
Mining: The process of extracting minerals or other geological materials from the Earth.
39. 种植 (zhòng zhí)
Planting: The act of placing seeds or plants in the soil for growth.
40. 运动 (yùn dòng)
Movement: The act of changing physical location or position.
41. 地区 (dì qū)
Region: An area or division, especially part of a country or the world, having definable characteristics but not always fixed boundaries.
42. 亚洲 (Yà zhōu)
Asia: The largest continent, located primarily in the Eastern and Northern Hemispheres.
43. 非洲 (Fēi zhōu)
Africa: The second-largest continent, located south of Europe and bordered to the west by the Atlantic Ocean.
44. 欧洲 (Ōu zhōu)
Europe: A continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere.
45. 大洋洲 (Dà yáng zhōu)
Oceania: A geographic region comprising Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
46. 北美洲 (Běi měi zhōu)
North America: A continent in the Northern Hemisphere, bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the Caribbean Sea, and to the west by the Pacific Ocean.
47. 南美洲 (Nán měi zhōu)
South America: A continent in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
48. 南极洲 (Nán jí zhōu)
Antarctica: The Earth's southernmost continent, containing the geographic South Pole.
49. 太平洋 (Tài píng yáng)
Pacific Ocean: The largest and deepest ocean on Earth, extending from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south.
50. 大西洋 (Dà xī yáng)
Atlantic Ocean: The second-largest ocean, separating the Americas from Europe and Africa.
51. 印度洋 (Yìn dù yáng)
Indian Ocean: The third-largest ocean, bordered by Asia to the north, Africa to the west, and Australia to the east.
52. 北冰洋 (Běi bīng yáng)
Arctic Ocean: The smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans, located around the Arctic Circle.
53. 地图 (dì tú)
Map: A visual representation of an area, showing physical features, political boundaries, or other specific data.
54. 地球仪 (dì qiú yí)
Globe: A spherical representation of Earth, showing continents, oceans, and geographic features.
55. 故事 (gù shì)
Story: A narrative, either true or fictitious, designed to interest, amuse, or instruct.
56. 古代 (gǔ dài)
Ancient Times: A period of history that refers to the time long past, especially the time before the fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476.
57. 历史学家 (lì shǐ xué jiā)
Historian: A person who studies and writes about the past.
58. 时间线 (shí jiān xiàn)
Timeline: A graphical representation of a chronological sequence of events.
59. 公元前 (gōng yuán qián)
Before Common Era (BCE): A time period before the year 1 in the Gregorian calendar.
60. 公元 (gōng yuán)
Common Era (CE): A time period starting from the year 1 in the Gregorian calendar, used as a secular alternative to Anno Domini (AD).
61. 资料 (zī liào)
Information/Data: Facts or details about a particular subject.
62. 石器时代 (shí qì shí dài)
Stone Age: A prehistoric period when tools and weapons were made of stone.
63. 游牧民族 (yóu mù mín zú)
Nomadic Peoples: Groups of people who move from place to place instead of settling permanently in one location.
64. 性别角色 (xìng bié jué sè)
Gender Roles: The behaviors, tasks, and responsibilities that a society considers appropriate for men and women.
65. 打猎 (dǎ liè)
Hunting: The act of pursuing and killing wild animals for food or sport.
66. 采集 (cǎi jí)
Gathering: The act of collecting food or resources from the natural environment.
67. 工具 (gōng jù)
Tools: Implements or devices used to perform tasks or work.
68. 冰河时代 (bīng hé shí dài)
Ice Age: A period of long term reduction in Earth's temperature, resulting in the expansion of continental ice sheets and alpine glaciers.
69. 新时期时代 (xīn shí qí shí dài)
Neolithic Era: The later part of the Stone Age, characterized by the development of agriculture and the making of polished stone tools.
70. 种植 (zhòng zhí)
Planting: The act of putting seeds or plants into the soil for growth.
71. 养殖 (yǎng zhí)
Breeding/Raising: The practice of raising animals or cultivating plants for food, resources, or other purposes.
72. 文明 (wén míng)
Civilization: A complex human society with cities, social hierarchy, and cultural development.
73. 美索不达米亚 (Měi suǒ bù dá mǐ yà)
Mesopotamia: An ancient region located in the eastern Mediterranean, largely corresponding to present-day Iraq and parts of Syria, Turkey, and Kuwait.
74. 中东地区 (Zhōng dōng dì qū)
Middle East: A region that includes Western Asia and parts of North Africa, often associated with historical and cultural significance.
75. 两河地区 (Liǎng hé dì qū)
The Land Between Two Rivers: A region in ancient Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
76. 幼发拉底河 (Yòu fā lā dǐ hé)
Euphrates River: A major river in Western Asia that, along with the Tigris, defines Mesopotamia.
77. 底格里斯河 (Dǐ gé lǐ sī hé)
Tigris River: A river that flows through Turkey and Iraq, forming the eastern boundary of Mesopotamia.
78. 水源 (shuǐ yuán)
Water Source: A place or entity from which water originates, such as a river, lake, or spring.
79. 影响 (yǐng xiǎng)
Influence: The capacity to have an effect on the character, development, or behavior of someone or something.
80. 灌溉 (guàn gài)
Irrigation: The artificial application of water to land to assist in the growing of crops.
81. 农业 (nóng yè)
Agriculture: The practice of farming, including the cultivation of the soil for growing crops and the rearing of animals for food, wool, and other products.
82. 空中花园 (kōng zhōng huā yuán)
Hanging Gardens: One of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, believed to be a series of tiered gardens built in ancient Babylon.
83. 神庙 (shén miào)
Temple: A building used for religious or spiritual activities, particularly in ancient cultures.
84. 汉谟拉比法典 (Hàn mò lā bǐ fǎ diǎn)
Code of Hammurabi: One of the earliest and most complete written legal codes, proclaimed by the Babylonian king Hammurabi.
85. 法律 (fǎ lǜ)
Law: A system of rules that a society or government develops to regulate behavior, with penalties for violations.
86. 教士 (jiào shì)
Priest: A person authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and deities.
87. 贵族 (guì zú)
Nobility: A social class normally ranked immediately below royalty, with privileges such as land ownership and titles.
88. 贫民 (pín mín)
Commoners: Ordinary people without noble rank or status, often engaged in labor or trade.
89. 统治阶级 (tǒng zhì jiē jí)
Ruling Class: A class of people who hold power and authority in a society, typically the wealthy and influential.
90. 被统治阶级 (bèi tǒng zhì jiē jí)
Subjugated Class: The class of people who are governed or controlled by others.
91. 奴隶 (nú lì)
Slave: A person who is legally owned by another person and is forced to work without pay.