Lecture 10: Vascular Disorders: Hemorrhage, Emboli, & Shock
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1. When does hemorrhage occur and what are the four major factors which influence hemostasis?
Hemorrhage or loss of/abonormal function to one or more of the four major factors that influence hemostasis results in hemorrhage which are the following; Endothelium, Blood Vessel, Platelets, and Coagulation factors.
2. What are the causes of hemorrhage? With each example provided understand the cause of the hemorrhage and be able to identify hemorrhage grossly.
Causes of hemorrhage can be
Trauma
Infectious Agents (bacterial, viral, fungal, immune complexes ie. FIP, endotoxemia)
Collagen Disorders
Thrombocytopenia,
DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation)
Neoplasia
Severe Liver Disease (loss of clotting factors, includes toxins, anticoagulants- inhibit vitamin K dependent clotting factors
Shock: reduced vascular perfusion, then it reperfuses and hemorrhage occurs
3. What are causes of thrombocytopenia?
4. What are causes of decreased platelet function?
5. What is Virchow’s triad? Be able to name the three major mechanism which lead to thrombosis and why each mechanism is important. Which is the most important mechanism?
6. What are the major morphologic differences between arterial and venous thrombi? How can you differentiate a thrombus from a post mortem blood clot?
7. How are thrombi resolved?
8. What are emboli? Be able to name the types of emboli. Understand why a saddle thrombus is an embolus.
9. What is shock? What are the three types of shock? How do they differ?
10. What are the clinical and morphologic features of shock?
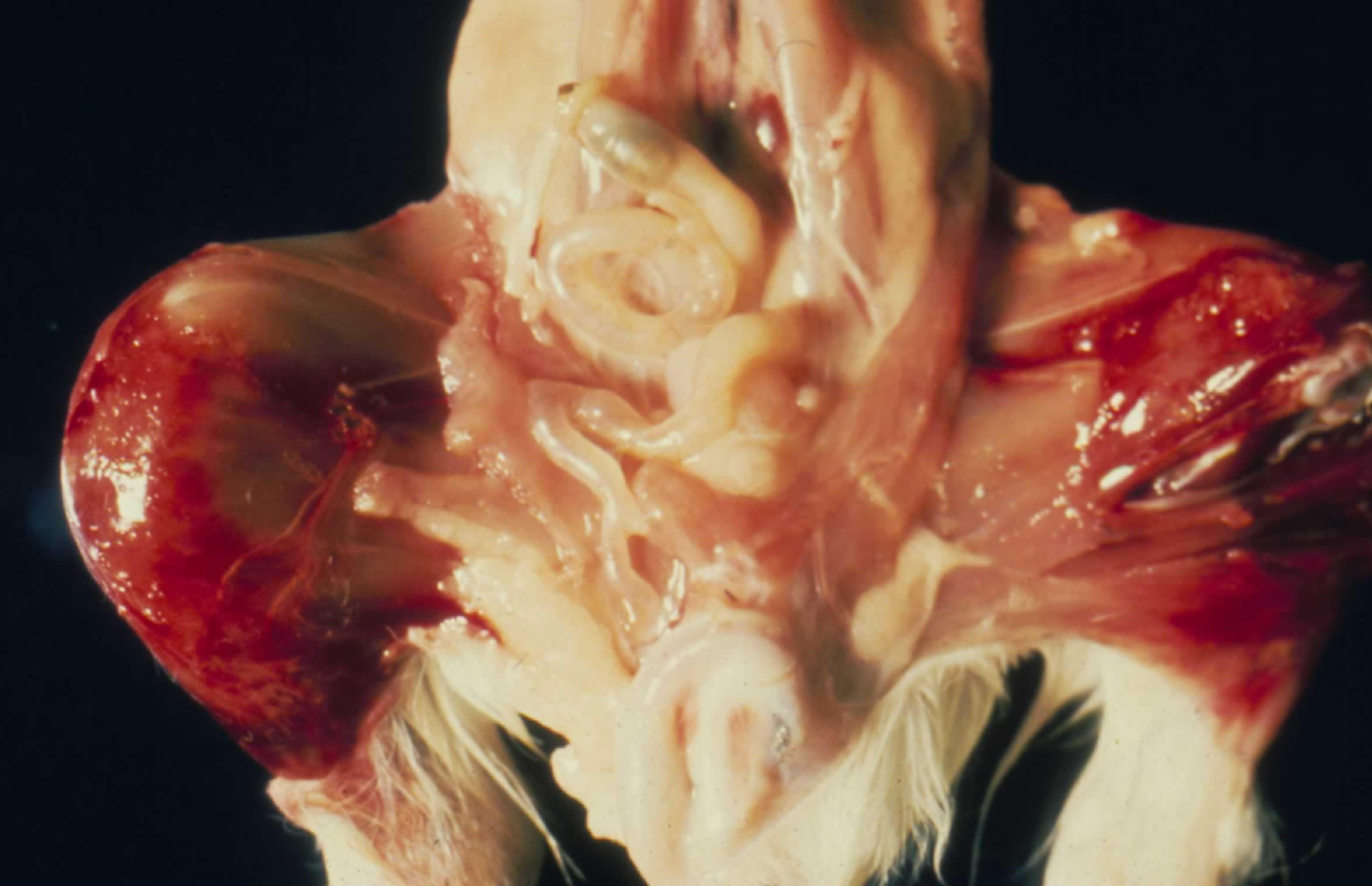
You have a guinea pig on nercropsy, history of
Lethargy, hunched posture
Stiff, painful gait with reluctance to move (suspected lameness)
Gingival hemorrhage and loose teeth
Rough coat and poor grooming
Small skin wounds that failed to heal properly
You also see this on post-mortem examination, what is your differential diagnosis and what is the cause?
Possible causes include vitamin C deficiency, leading to scurvy, which is common in guinea pigs. This is due to vitamin C being required to produce the cofactor to produce type 1 collagen. This causes fragile vasculature and tissues with collagen