PNB 2265 Practical #1
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
erythrocytes function
transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and CO2 from the tissues back to the lungs for exhalation
thrombocytes function
stop bleeding and help wounds heal
erythrocytes
red blood cells
thrombocytes
platelets
leukocytes
white blood cells
leukocytes
protect against infections and disease; identify forgein invaders- bacteria and viruses
hereditary condition; abnormal hemoglobin is produced (which disease)
sickle cell anemia
infectious mononucleosis
viral disease; increased production of monocytes and lymphocytes
polycythemia
overproductino of RBCs; result of bone marrow cancer
hemoglobin
critical protein found on surface of RBC; made of 4 globin subunits and 4 hem groups; each group has an IRON molecule that binds oxygen
hematocrit
multiple different disorders can be seen in a hematocrit; polycythemia; dehyration; anemai
A= elc equation
%saturation= (A-B)/ (A-C) x 100%
a=
aborbance after complete deoxygenation (after removing oxygen)
b=
abrobance after each deoxygenation stop (between)
c=
absorbance before deoxygenation (before removing oxygen)
right shift oxygen affinity
lower
easier to unload what shift
right
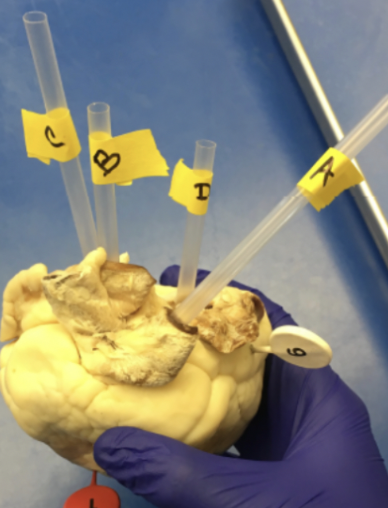
A
pulmonary trunk
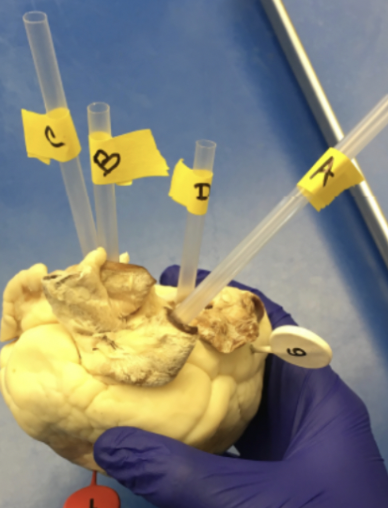
b
aorta
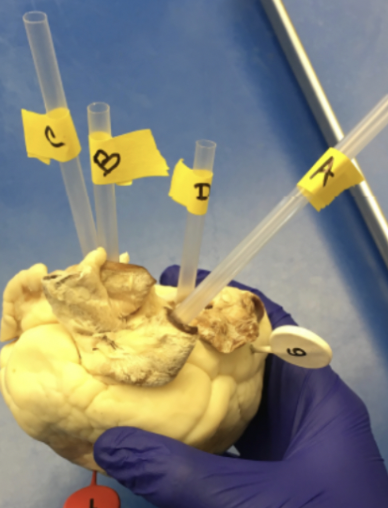
c
superior vena cava
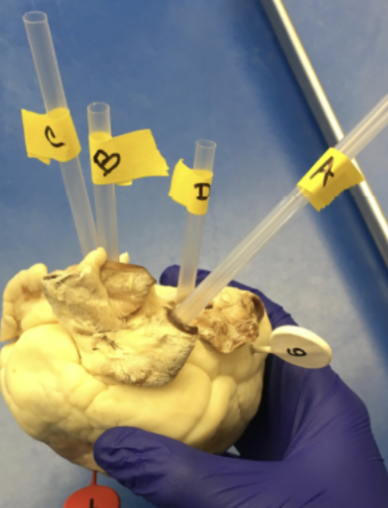
D
pulmonary vein
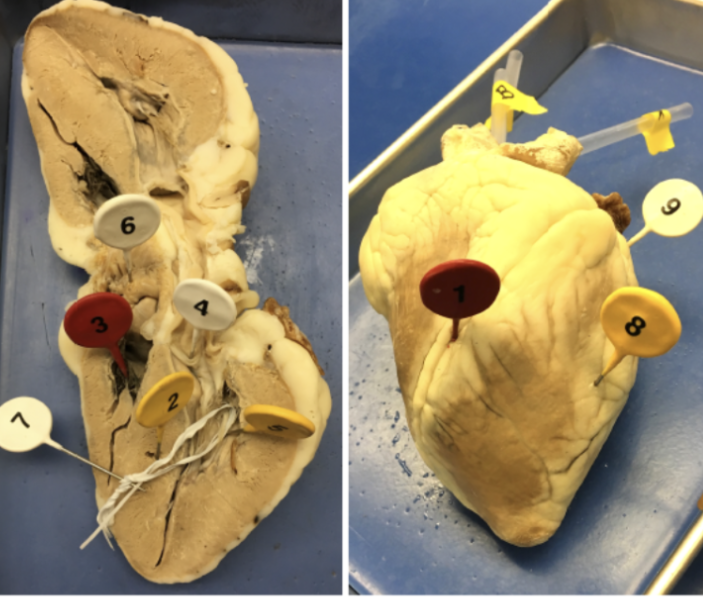
1
interventricular sulcus
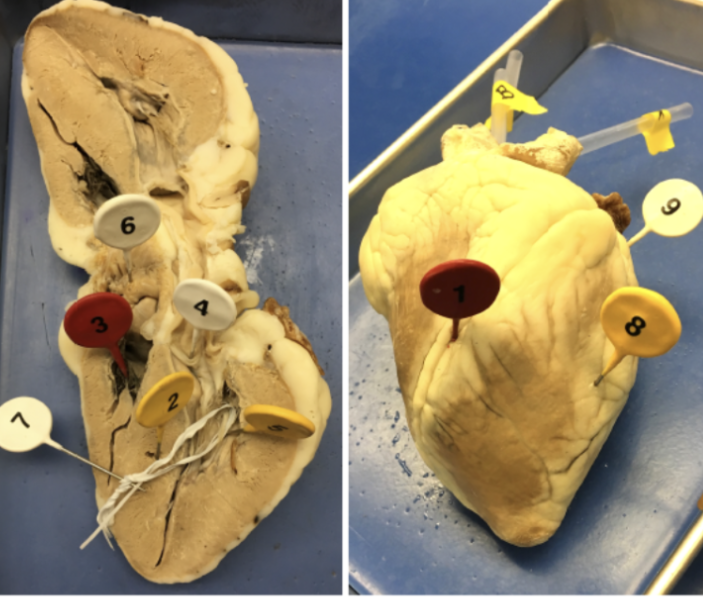
2
interventricular septum
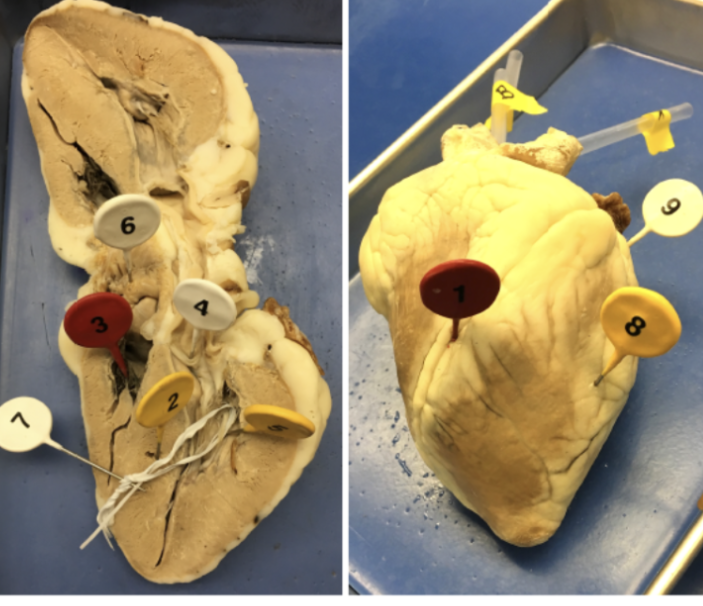
3
tricuspid valve
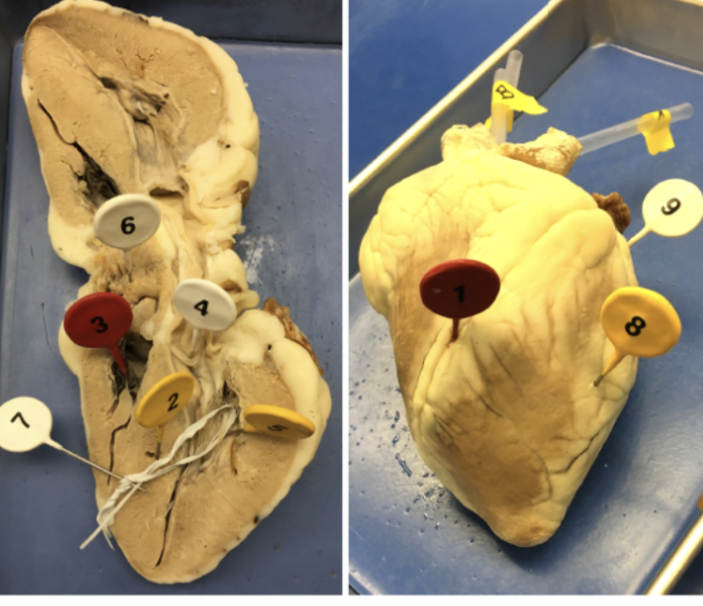
4
bicuspid valve
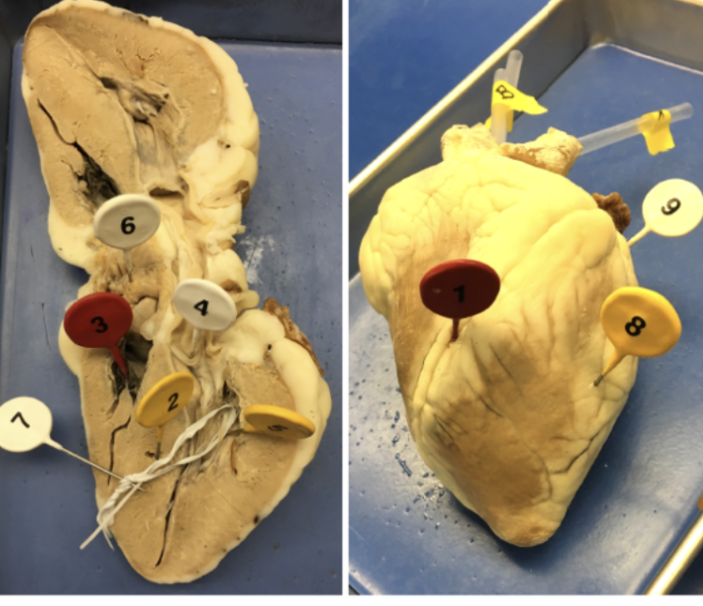
5
papillary muscle
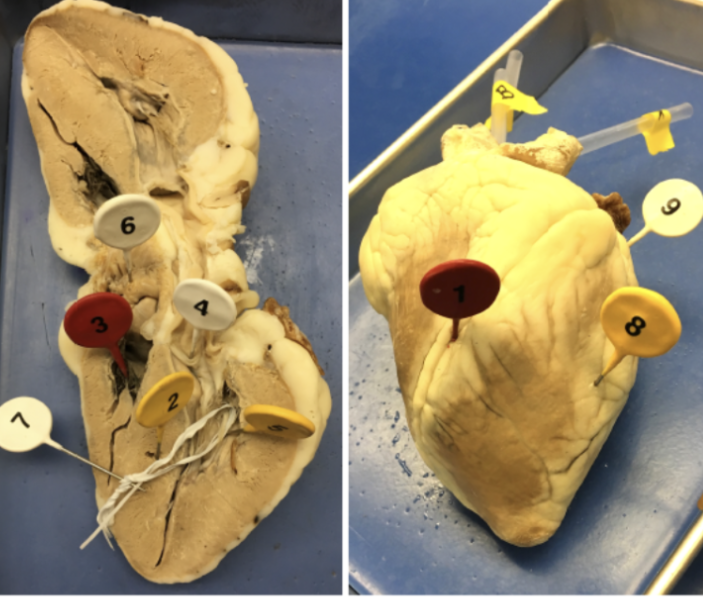
6
pectinate muscle
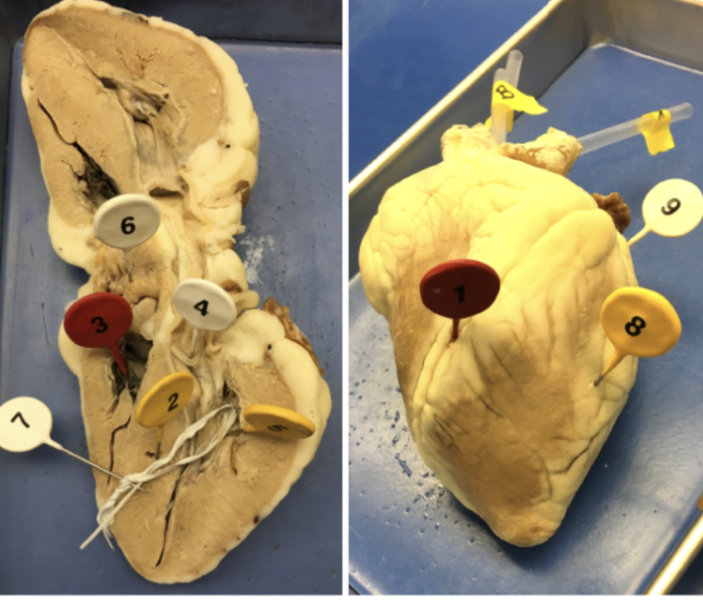
7
chordae tendinae
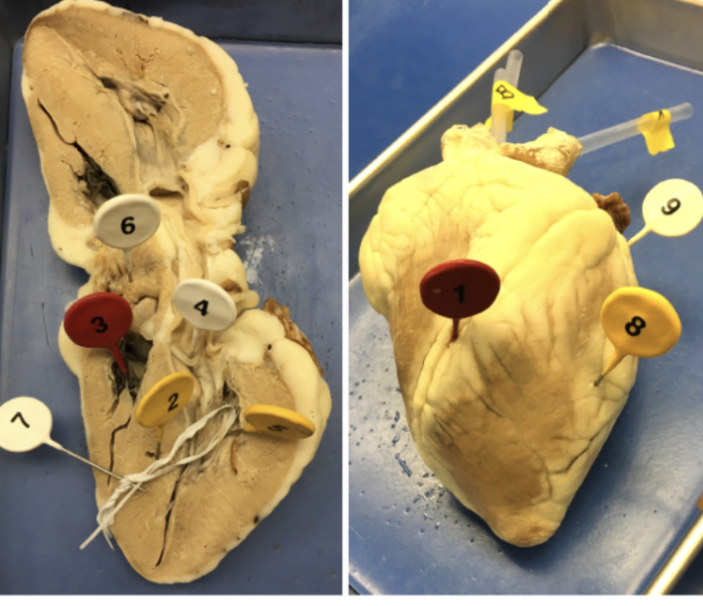
8
ventricle
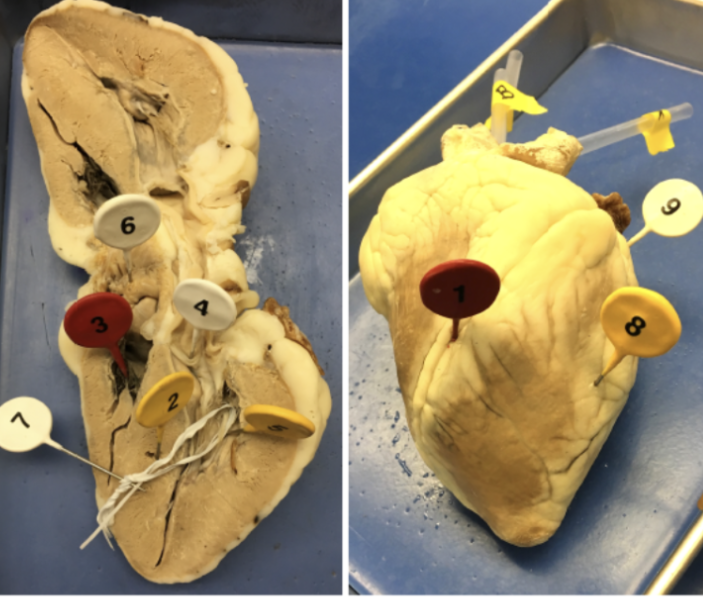
9
atrium
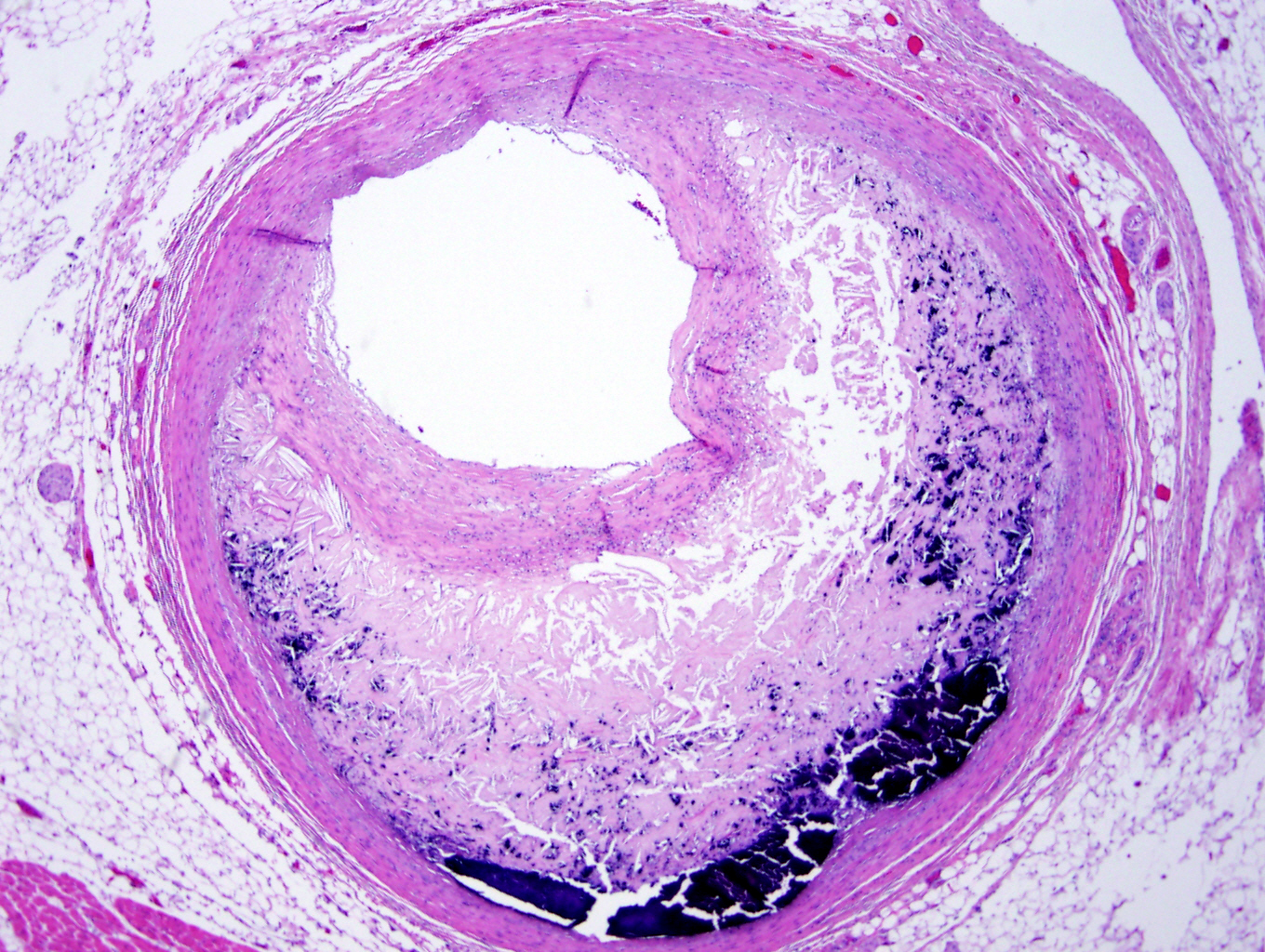
which
artherosclerosis
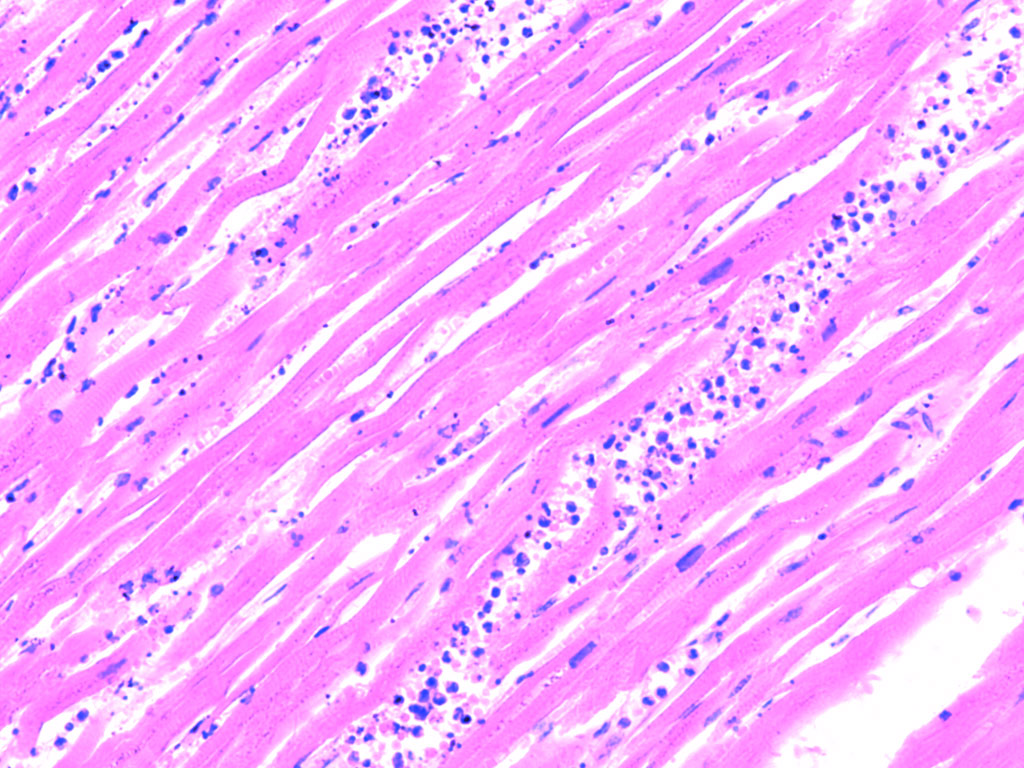
which
MI
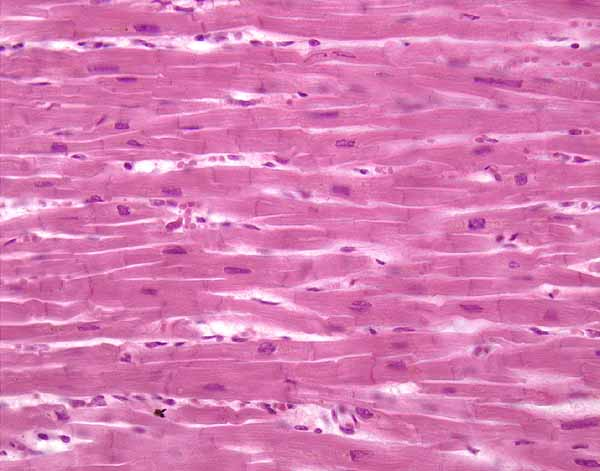
which
cardiac muscle
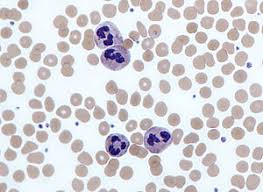
which
neutrophil
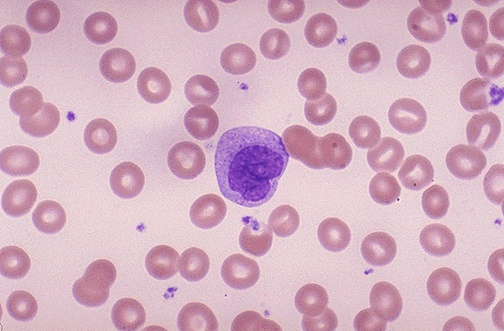
which
monocytes
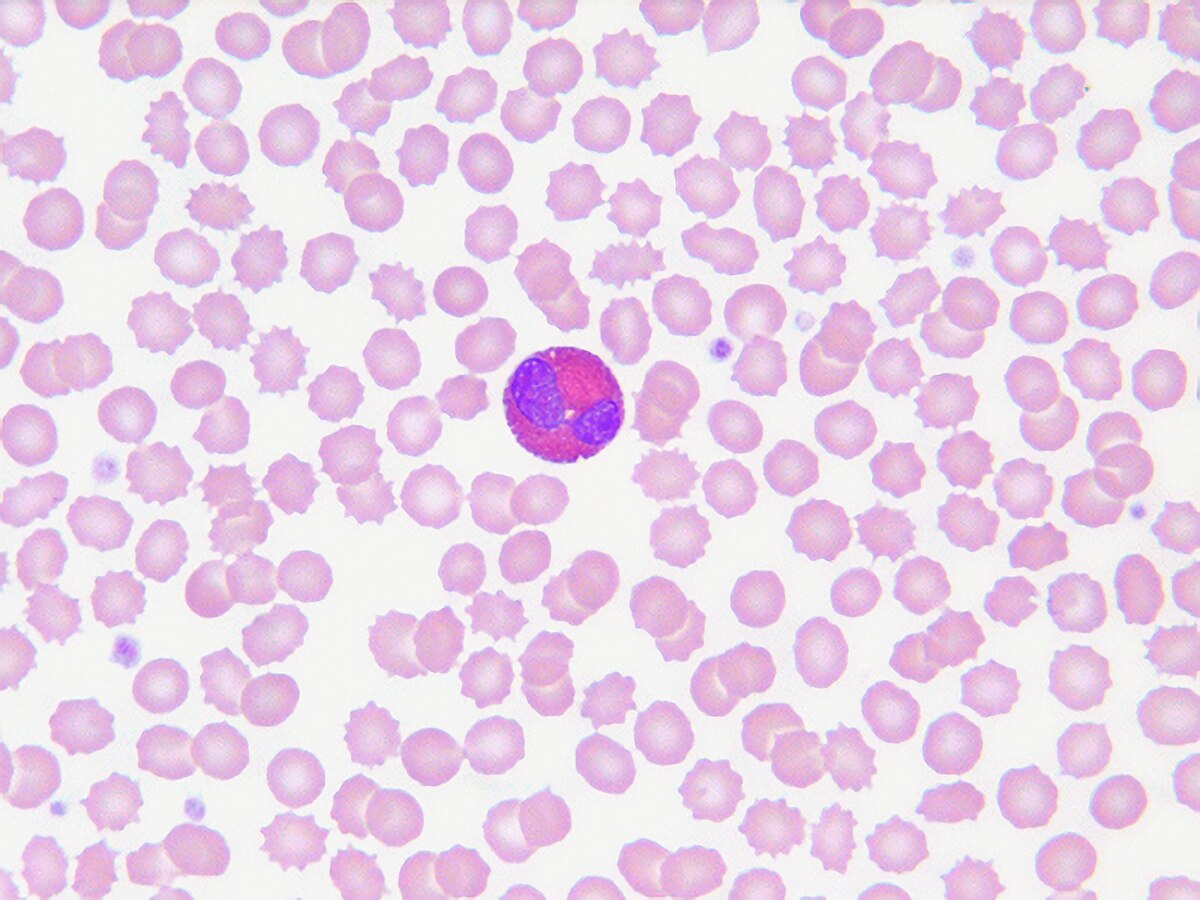
eosinophils
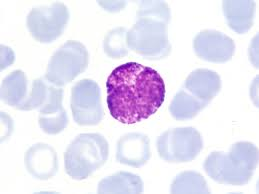
basophils
pulmonary trunk (blood flow)
from the heart
pulmonary arteries blood flow
from the heart
aortic arch blood flow
from the heart
brachiocephalic trunk
from the heart
left common cortotid artery. blood flow
from the heart
descending thoracic aorta blood flow
from the heart
R/L subclavian arteries
blood flow to the upper limbs
r/l axillary artery
blood flow to the upper limbs
r/l brachial artery
blood flow to the upper limbs
r/l radial artery
blood flow to the upper limbs
descending abdominal aorta
descending abdominal aorta
abdominal blood flow
celiac trunk
abdominal blood flow
superior mesenteric artery
abdominal blood flow
inferior mesenteric artery
abdominal blood flow
r/l common iliac arteries
blood flow to the lower limbs
r/l internal iliac artery
blood flow to the lower limbs
r/l external iliac artery
blood flow to the lower limbs
r/l femoral artery
blood flow to the lower limbs
frog heart number of chambers
3; 2 atria and one ventricle
mechanism of Ach
slows heart rate
mechanism for NE
speeds up heart rate
expected observation for increase of calcium
obvious increase in force with little or no increase in heart rate
expected observations for increseae in potassium (K+)
increase in HR then decrease in HR, no change in force
increased potassium reasoning
depolarizes the membrane potential of pacemaker cells and decreases driving force
reasoning for potassium concentration
depolarizes the membrane potential of pacemaker cells and decreases driving force
decrease in temp expected observations
decrease in HR
reasoning behind decrease HR
proteins and enzymes require optimal temp to work efficiently
isuprel expected observations
increase HR and contractile force
isuprel reasoning
activate beta-1 adrenergic receptor, “fight or flight”
Ach expected observations
decrease heart rate
Ach resoning
activate muscinaric receptors, “rest or digest”
atropine then Ach expected observations
normal HR and force
reasoning for atropine then Ach
plant alkaloid, block muscinaric receptors
mechanical stretch expected observations
increase contractile force, no decline phase due to pericardium
mechanical stretch reasoning
Frank-starling law