Fetal Pig Dissection
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
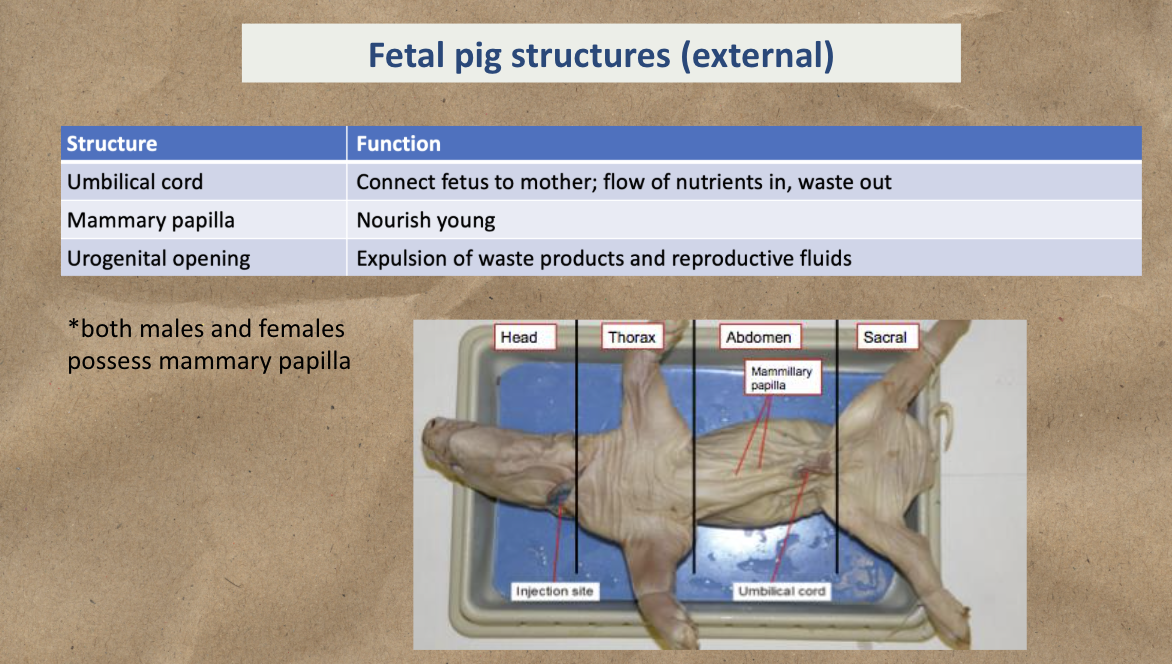
Fetal pig external structures include
Umbilical cord - Connect fetus to mother, flow of nutrients in, waste out
Mammary papilla (present in both male/female) - Nourish young
Urogenital opening - Expulsion of waste and productive fluids
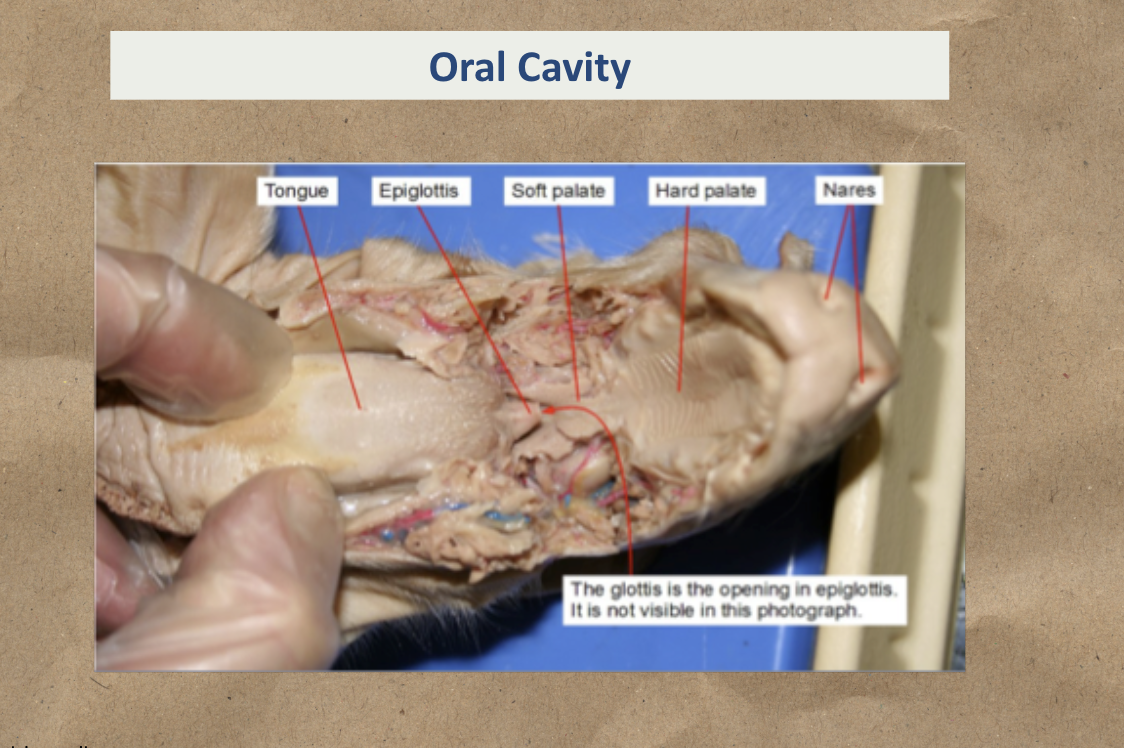
Mouth cavity and pharynx include
Hard palate - separates nasal cavity from oral cavity; food manipulation
Soft palate - separates nasal cavity from oral cavity; food manipulation
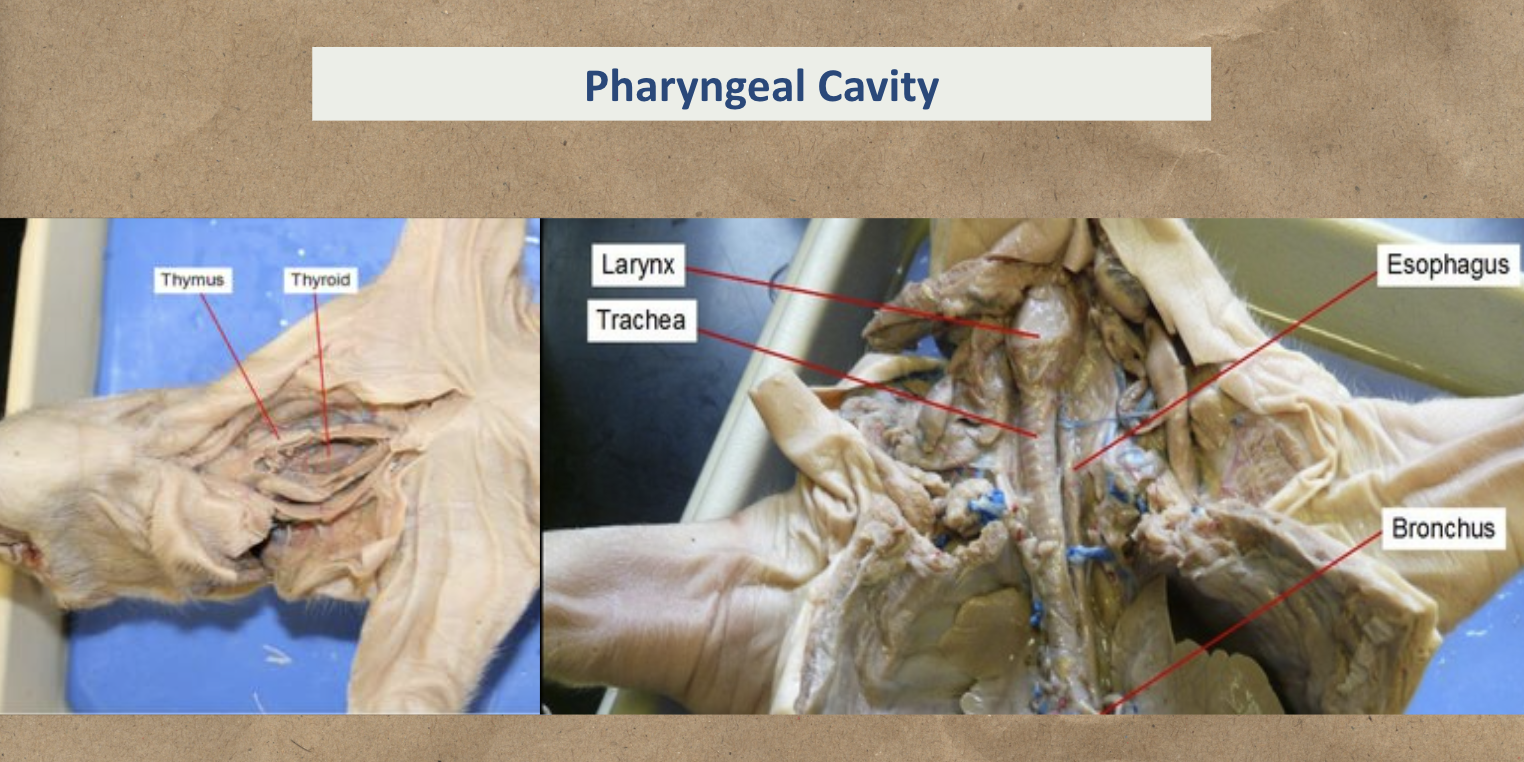
Larynx - voice box; connect pharynx and trachea
Esophagus - connect pharynx to stomach
Epiglottis - Prevent food and liquid from entering airways
Thymus - T cell maturation
Trachea - conduct air to and from lungs
Thyroid gland - Oval gland and responsible for hormones in body
Oral cavity
Study the image
Pharyngeal Cavity
Study the image
Fetal pig thoracic & abdominal cavities include
Lungs - respiration
Heart - Circulates of blood
Diaphragm - Contraction expands lungs for respiration
Spleen - Site of immune cell interactions
Umbilical vein - carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
umbilical arteries - carries deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
Kidneys - control volume and composition of blood
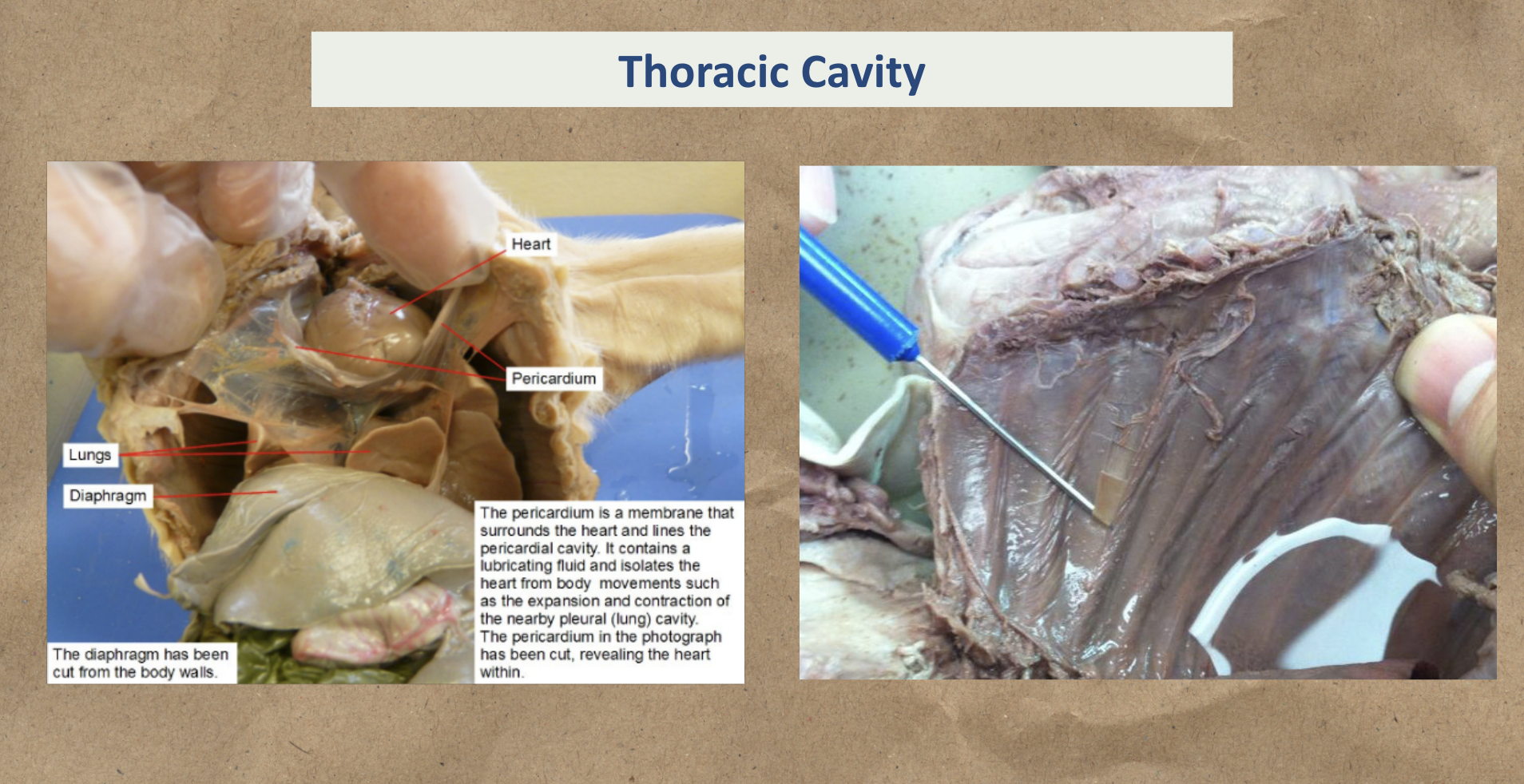
In the thoracic cavity are the following:
Heart
Lungs
Diaphragm
Pericardium - membrane that surrounds and protects the heart
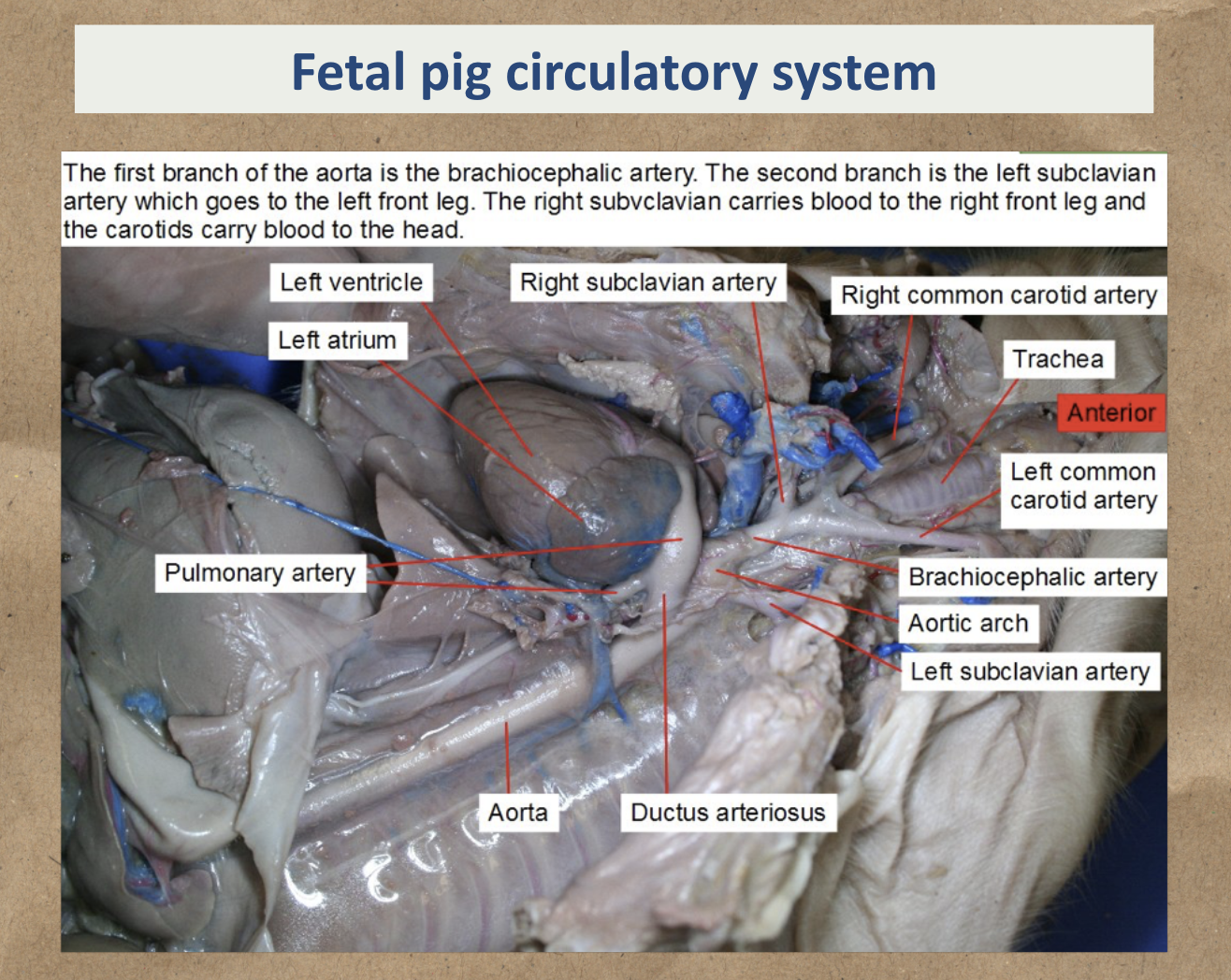
Fetal pig circulatory system
Study the image
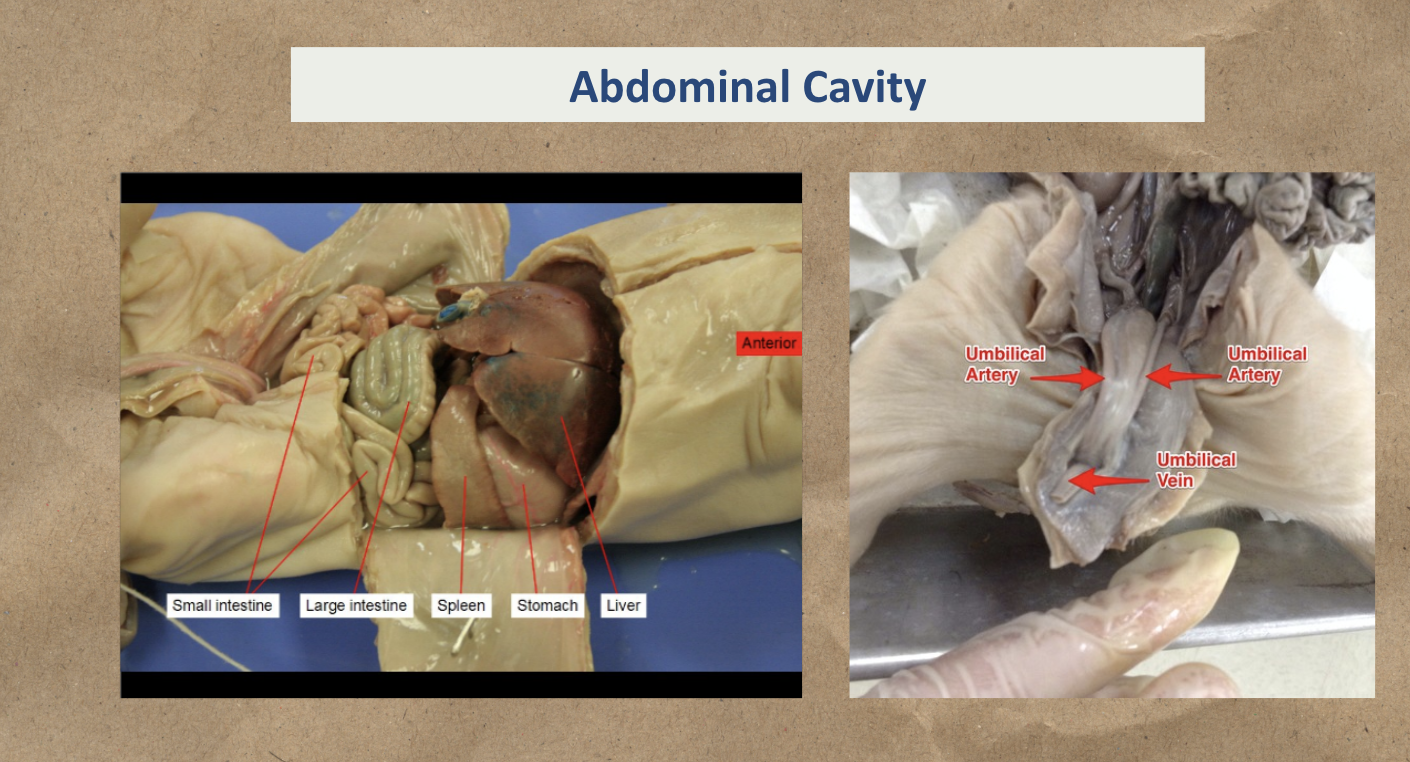
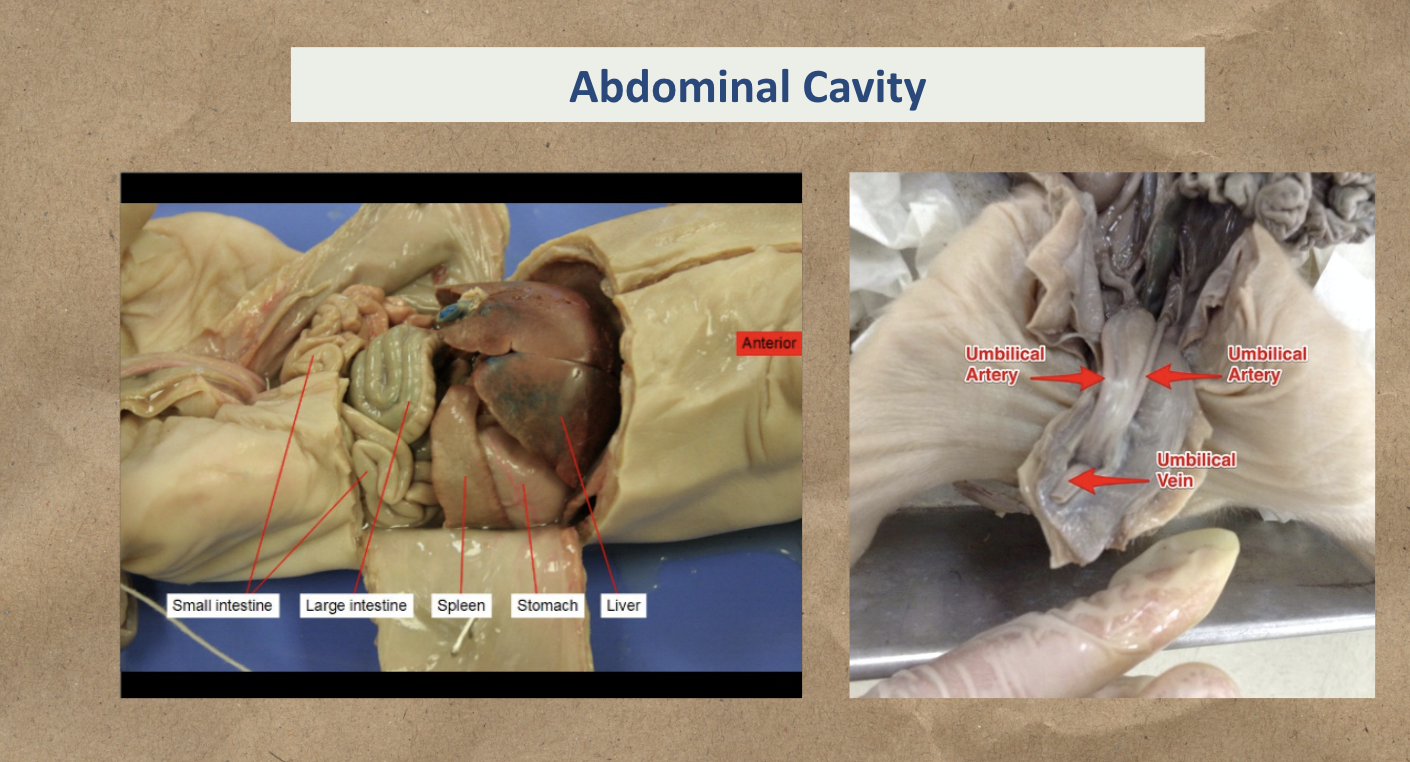
Abdominal Cavity:
Liver
Stomach
Spleen
Large intestine
Small intestine
Umbilical Artery
Umbilical Vein
Study the image
Fetal pig digestive tract include:
Esophagus - carry food to stomach
Stomach - food storage, mechanical and chemical digestion
Small intestine - chemical digestion, nutrient absorption
Large intestine - water and inorganic ion reabsorption
Rectum - last segment of large intestine
Liver - Bile production
Gallbladder - Bile storage
Pancreas - Digest enzymes produces
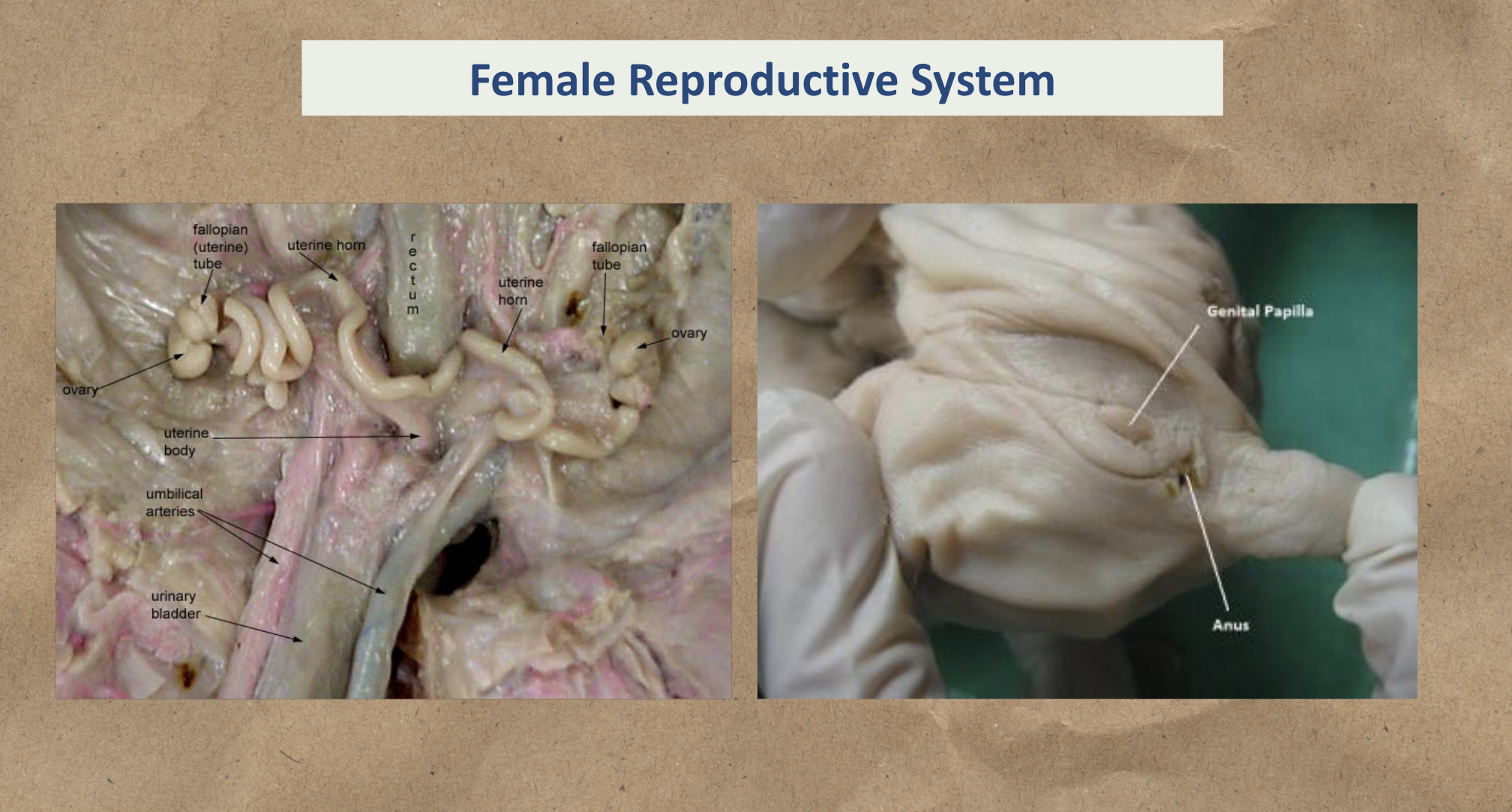
Female Reproductive System
Study the image
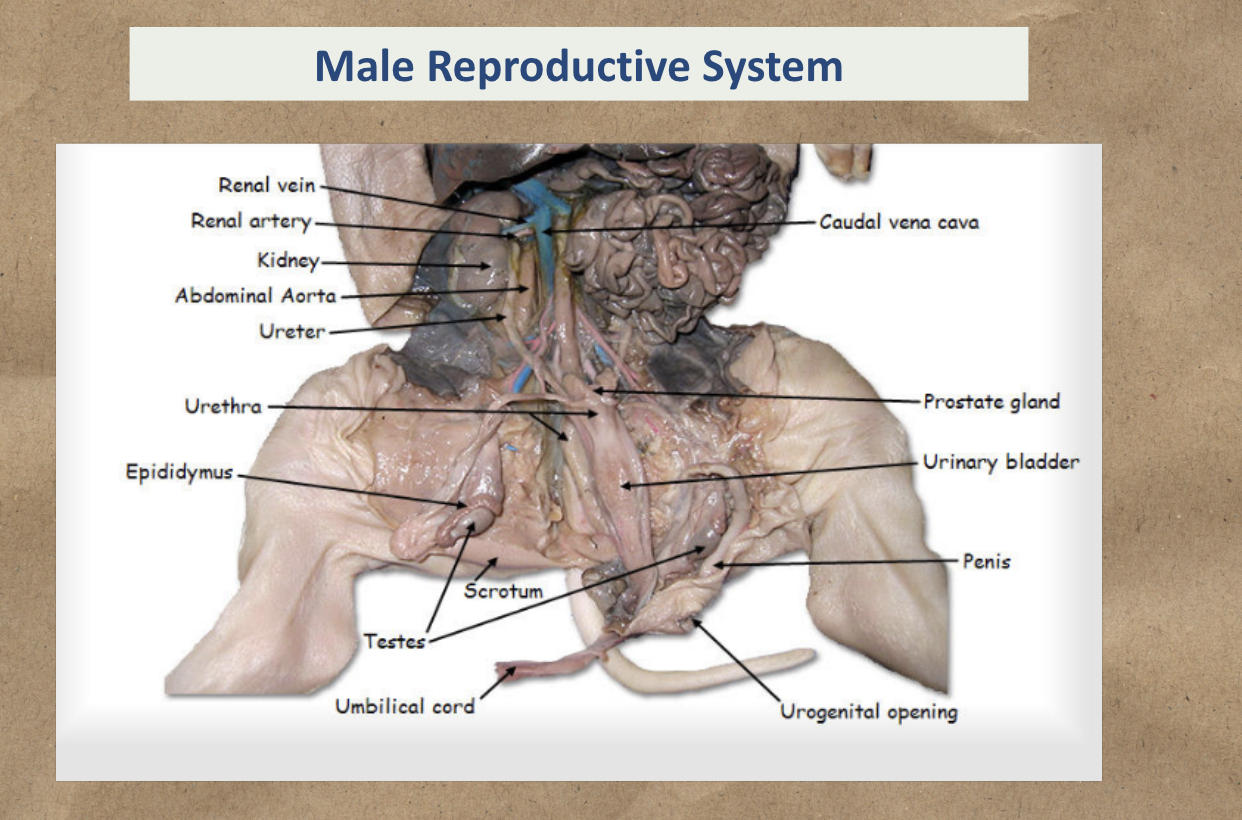
Male reproductive system
Study the image