Cognitive Psych Concepts & Definitions for Paper 1
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
1
New cards
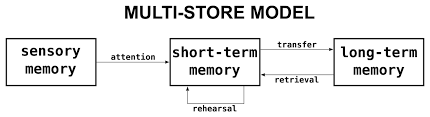
Multi Store Model of Memory
Claims memory progresses according to a linear model: stimuli first enters sensory memory, moving to short term memory once attention is paid, then moving to long term memory once rehearsed adequately. Each phase has its own capacity, duration, and encoding processes.
2
New cards
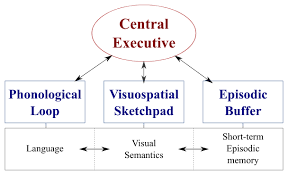
Working Memory Model
Claims working memory is delegated by the “Central Executive” to one of three components: the phonological loop (auditory input), the visuospatial sketchpad (visual input), or the episodic buffer (moving images). Claims that multiple tasks can be completed simultaneously IF the tasks use separate components.
3
New cards
Schema Theory
Claims that humans integrate new information with their existing schemas (self, social, AND scripts). Schemas influence our cognitive abilitiesm & biases, i.e. paying more attention to details that fit our existing schemas.
4
New cards
Thinking & Decision Making
Dual Process Theory proposes 2 systems of thinking: System 1 (quick, intuitive, bias-prone) and System 2 (slow, rational, considers multiple perspectives). Claims people use each system depending on the task/situation.
5
New cards
Reconstructive Memory Theory
Claims memories are reconstructed at the time of retrieval, thereby prone to bias. Ties to schema theory: details consistent with your schemas may be more likely to be remembered than details inconsistent with your schemas.
6
New cards
Biases in Thinkng and Decision Making (Confirmation Bias)
Confirmation Bias claims people pay greater attention to information than confirms their beliefs and less attention to information that contradicts their beliefs.
7
New cards
The Influence of Emotion on Cognitive Processes (Flashbulb Memories)
Flashbulb Memory theory claims that experiences of intensified emotion lead to exceptionally vivid memories. Research has not found these memories to be any more accurate than other memories.
8
New cards
Digitization
Refers to the effect of modern technology on cognitive processes. The Google Effect claims we remember where to find information more readily than we remember the information itself. Video games and virtual reality exposure therapy have demonstrated positive effects on visual processing and PTSD recovery.