Organic Compounds & DNA Quiz
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
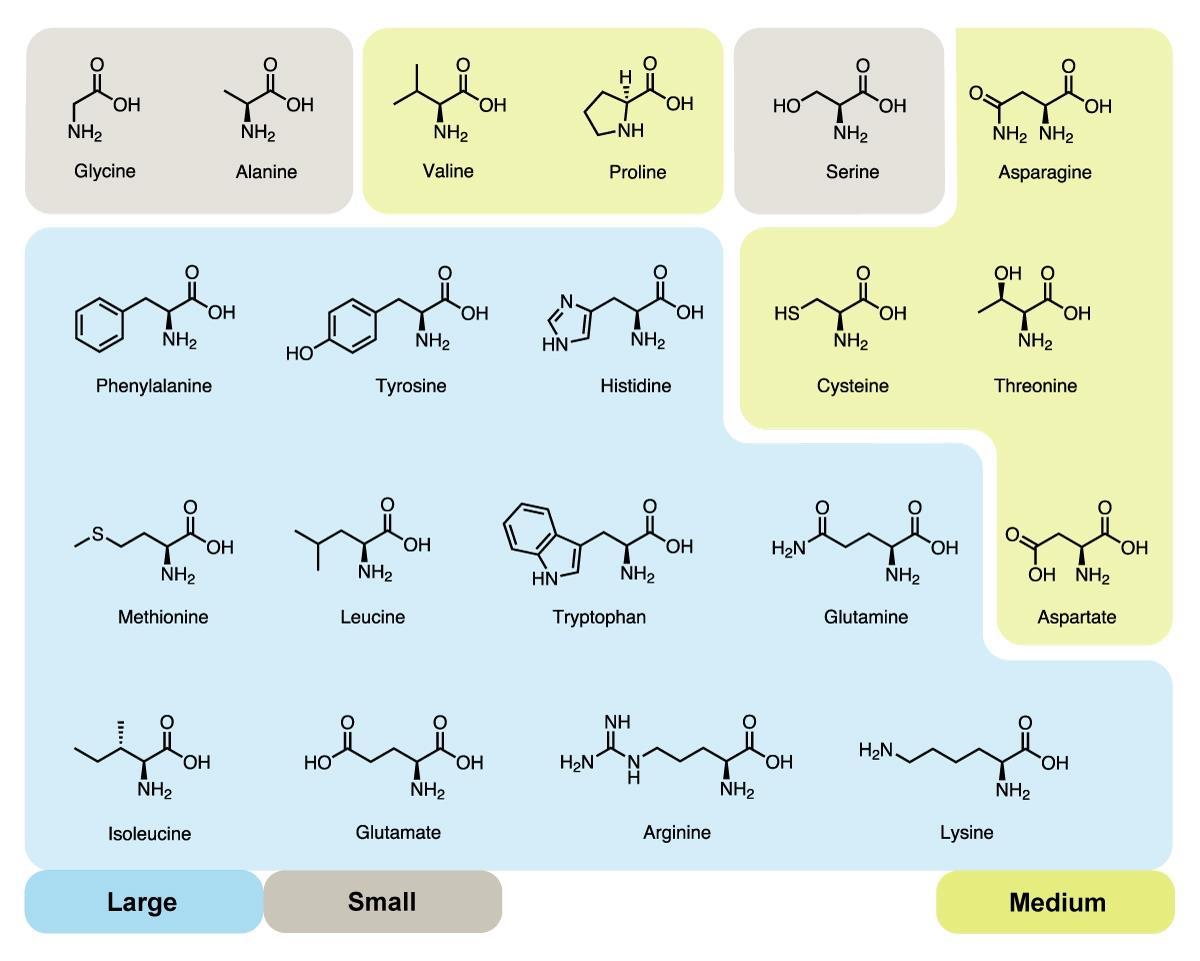
amino acid
Contains an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH).
Makes up building blocks for protein.
There are 20 different amino acids containing a different R group.
All amino acids have the same chemical structure.
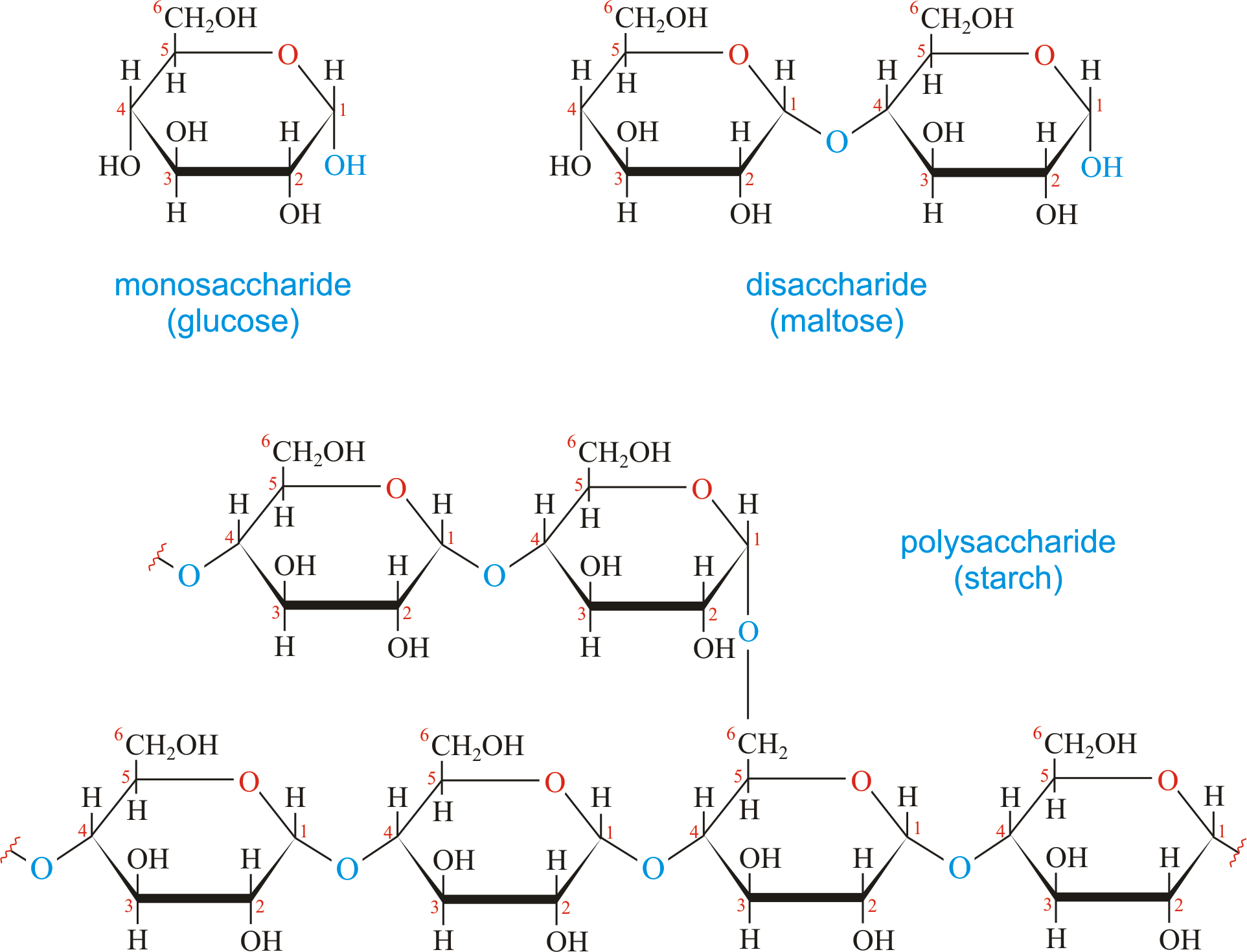
animal vs plant carbohydrates
Plants store excess sugar (polysaccharides) in the form of starch.
Animals store their excess sugar (polysaccharides) in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles.
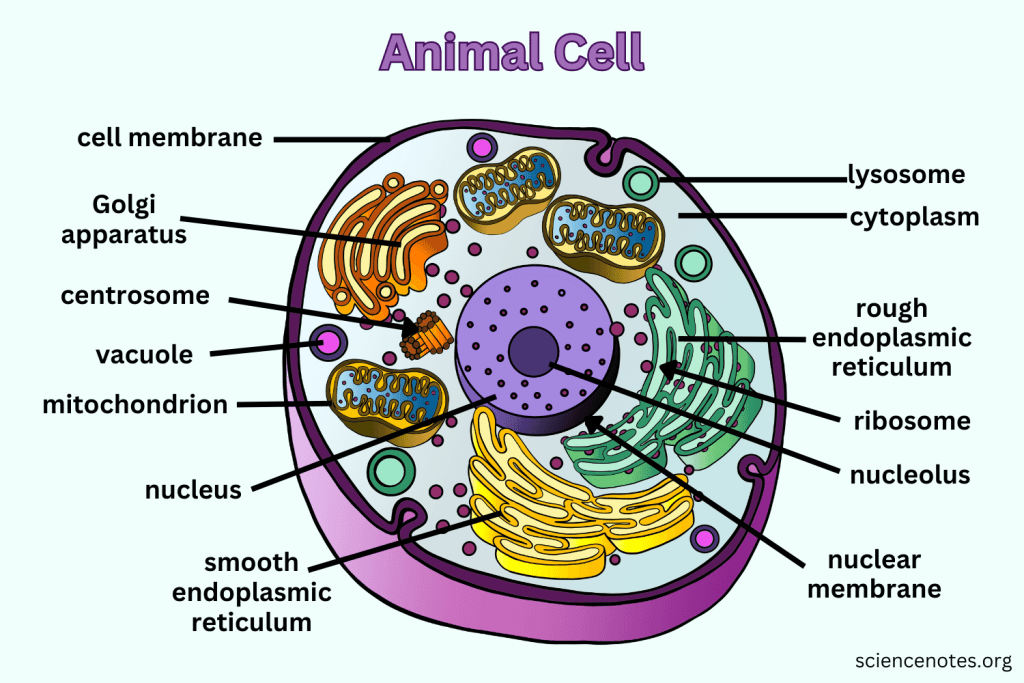
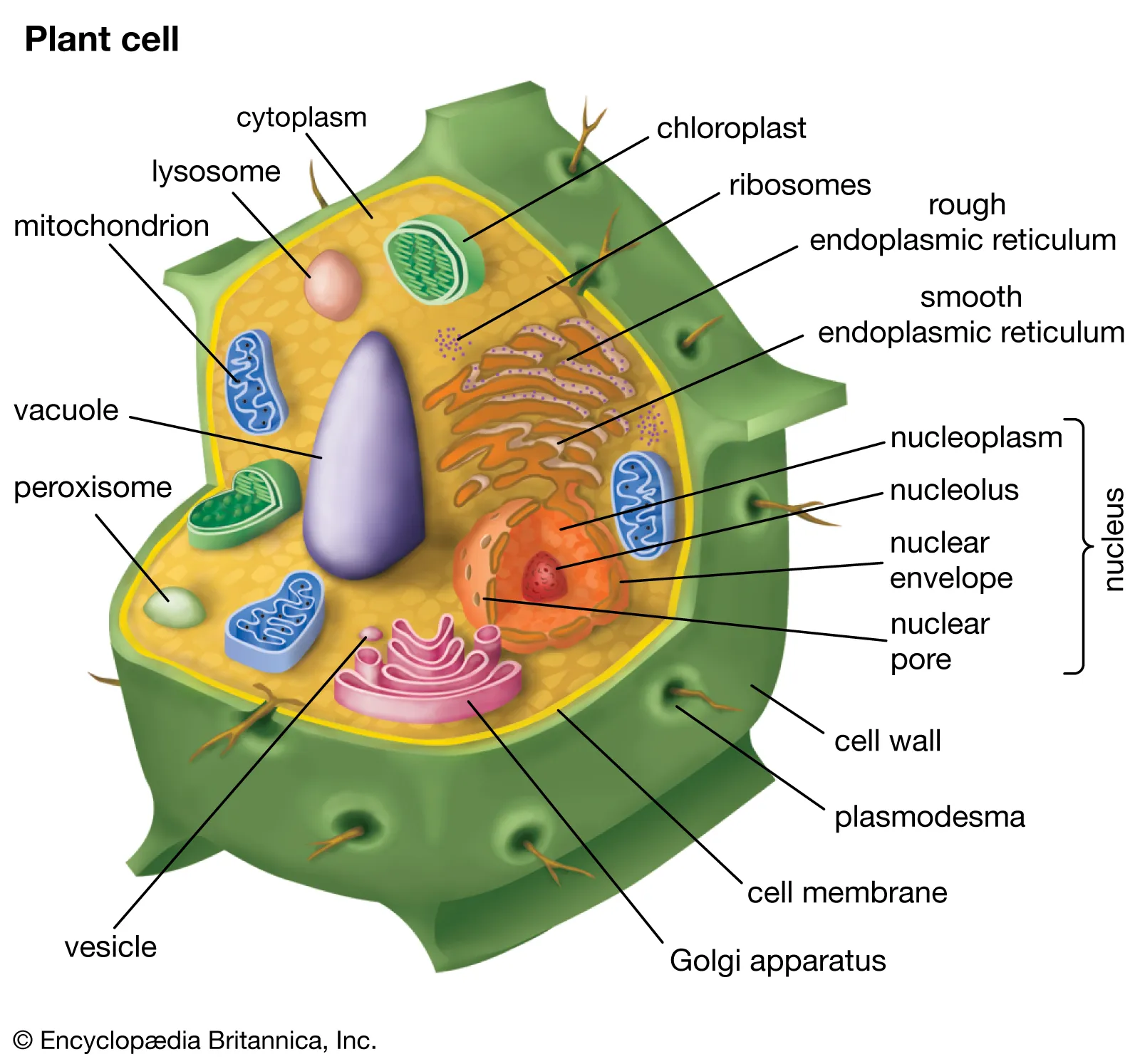
animal vs plant cell differences
Cells in animals, plants, and related organisms have 3 basic structures: cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm.
Animal cells: lysosome, centriole.
Plant cells: chloroplast, cell wall, plastid (leucoplast), and plastid (chromoplast).
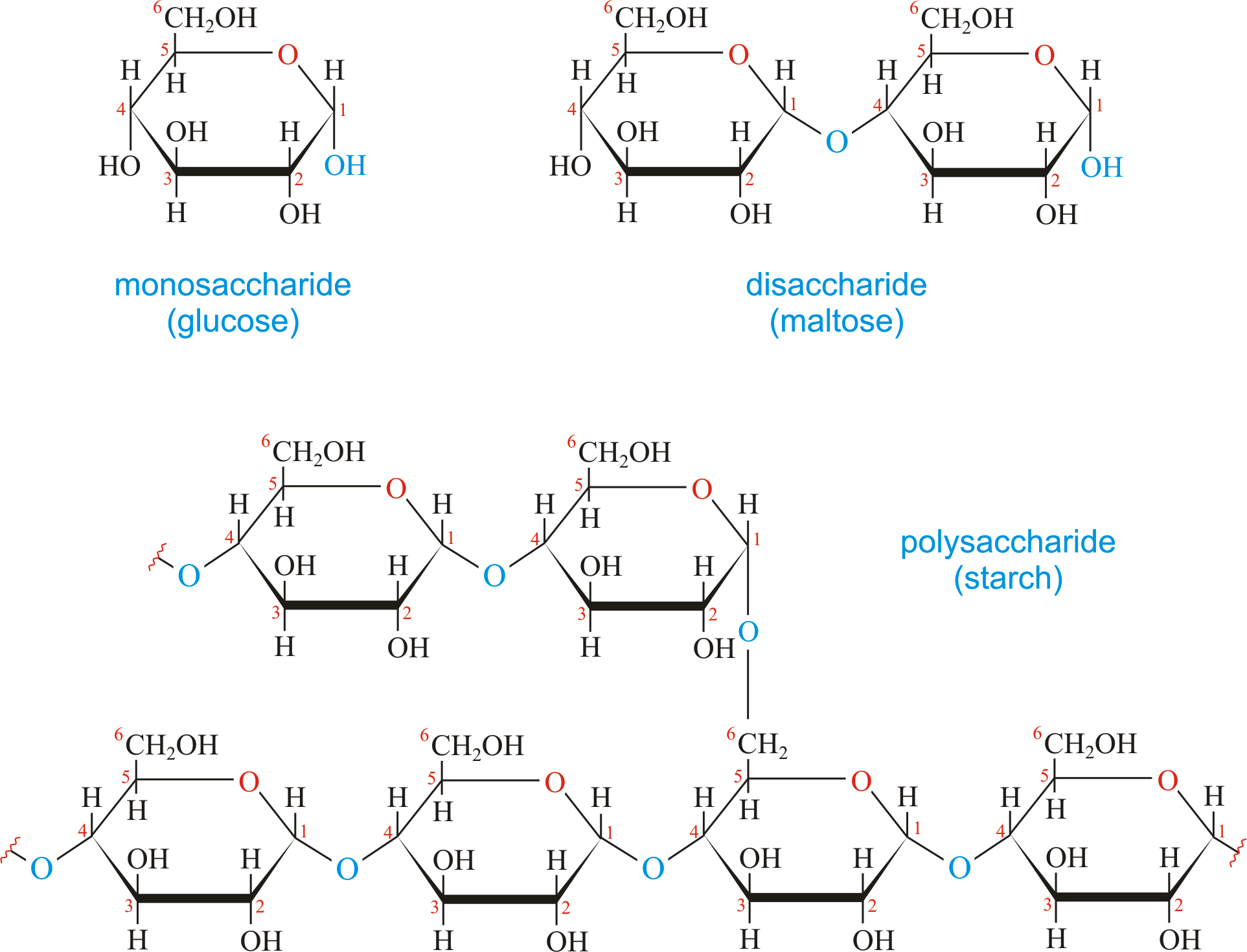
carbohydrate
Organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio (C6H12O6).
Source of energy for humans’ bodies.
4 types of carbohydrates: sugar, starch, glycogen, cellulose.
Monosaccharide: Single sugar (glucose, galactose, and fructose).
Disaccharides: Double sugar (sucrose, maltose - malt sugar, lactose - milk sugar).
Polysaccharides: formed by many monosaccharide units (starch, glycogen, cellulose).
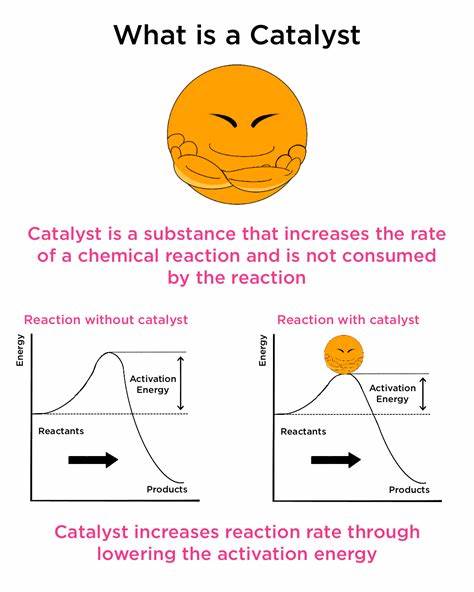
catalyst
A substance that speeds up the chemical reaction.
Stays unchangeable during the reaction.
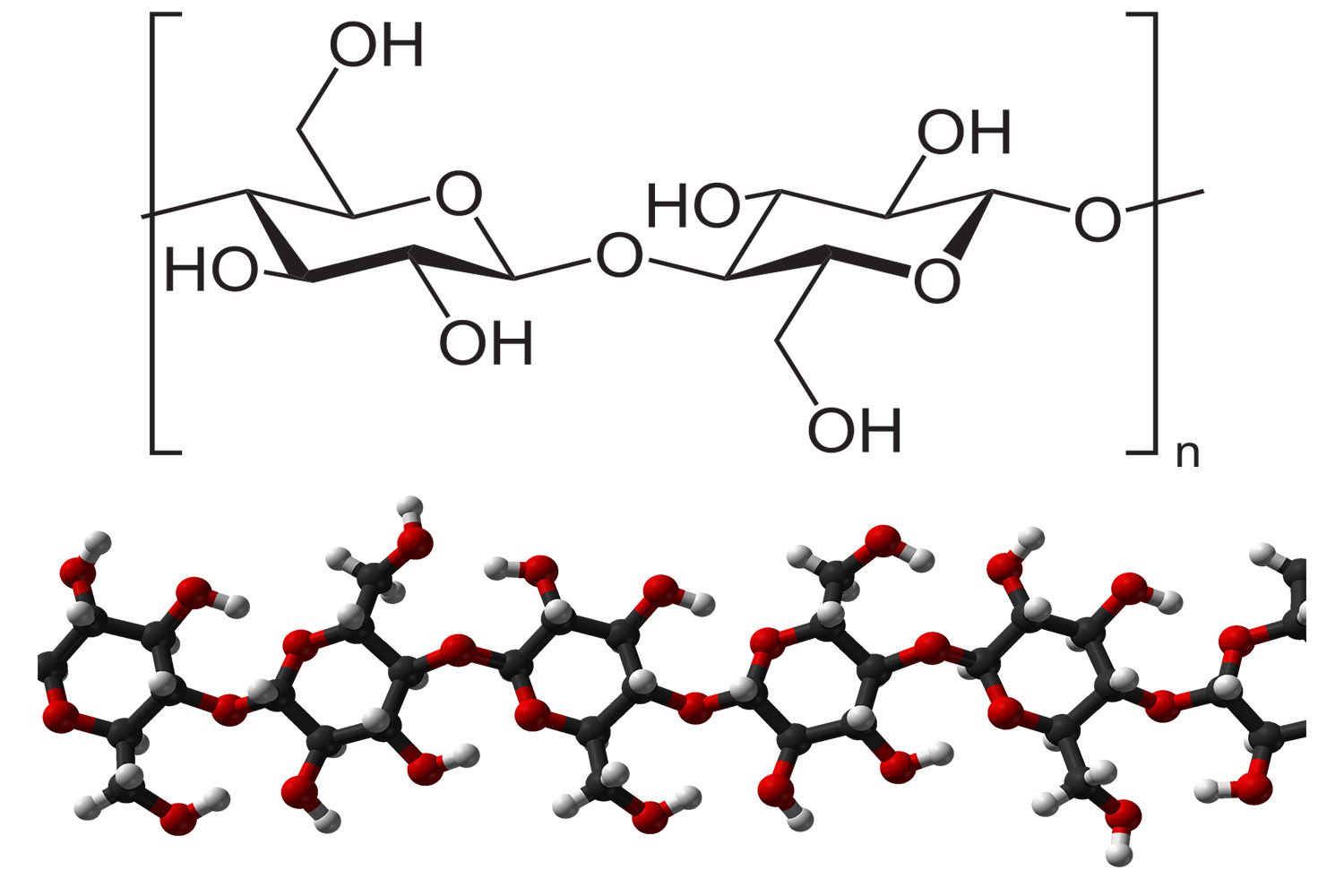
cellulose
A type of polysaccharide.
Exists only in plants.
Support plants by giving them strength and rigidity.
Major component of wood → Woods are used to make building and printing materials.
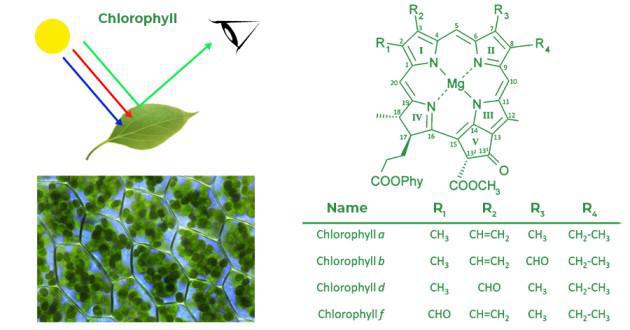
chlorophyll
Principal pigment in the cells of photosynthesis autotrophs that capture light energy.
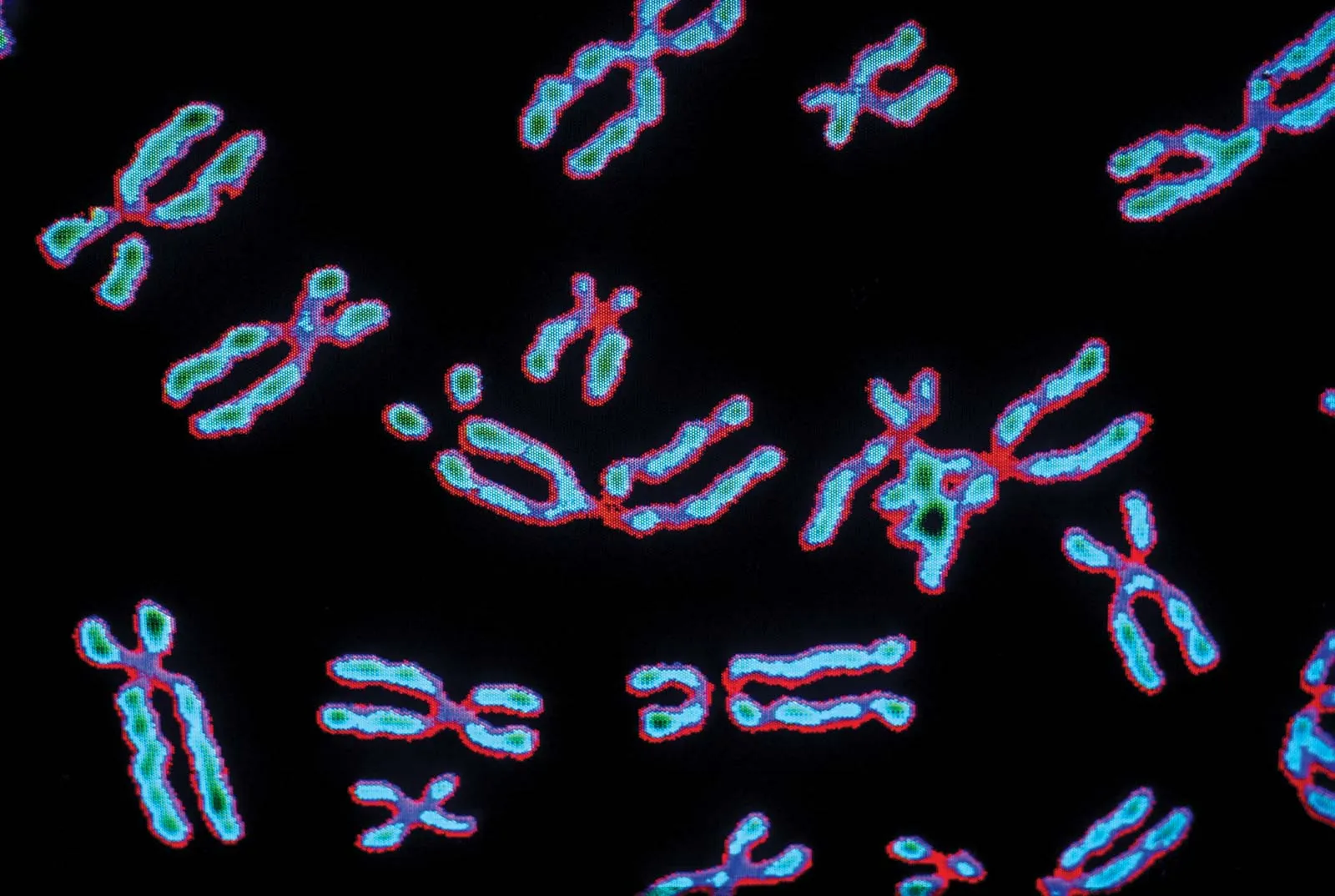
chromosome
Threadlike structure in a cell contains the genetic information (DNA) passed on from one generation of cells to the next.
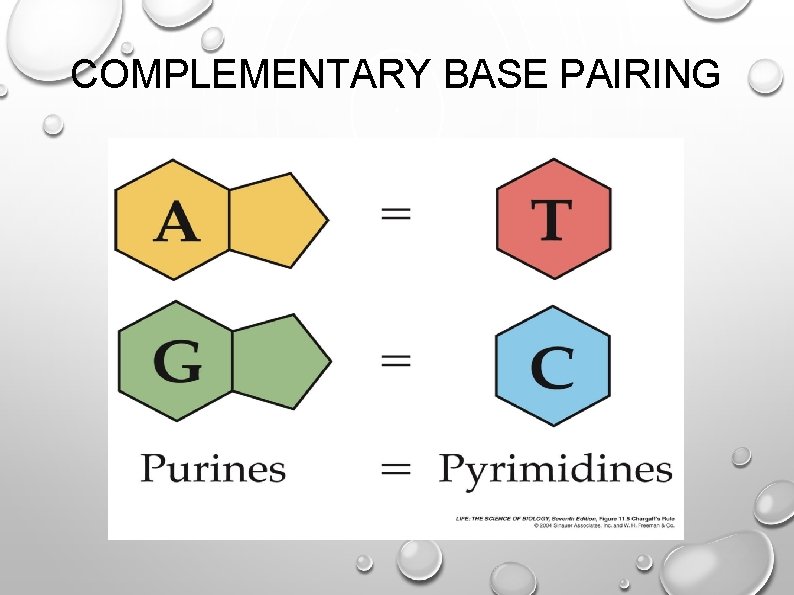
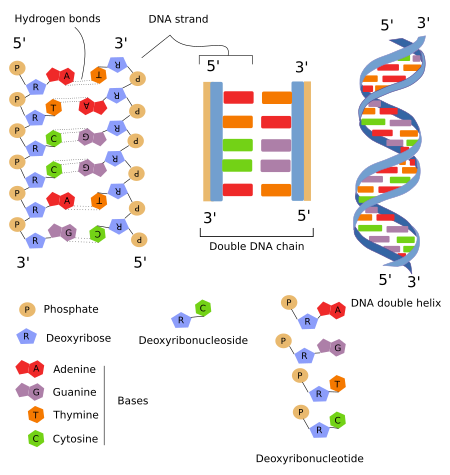
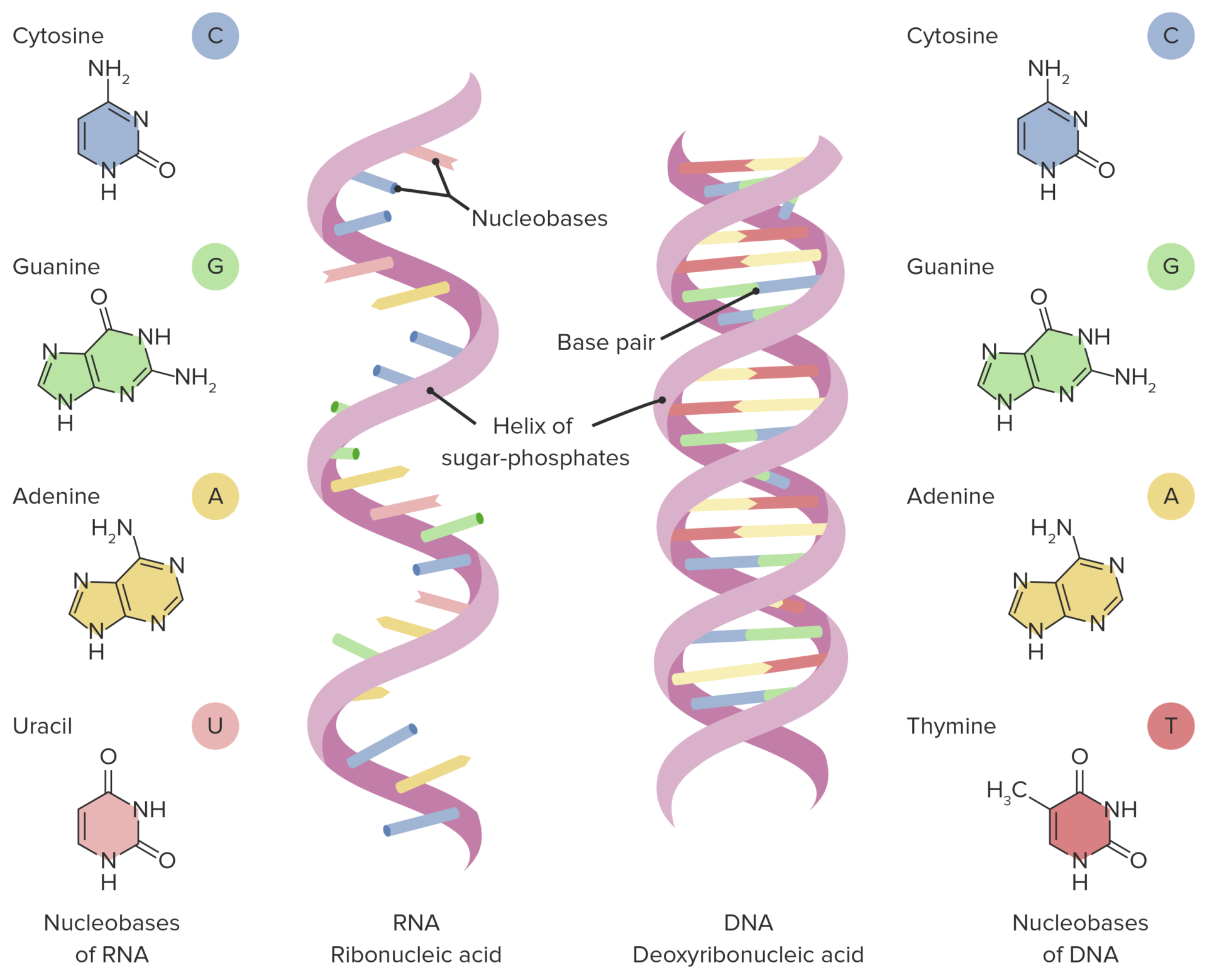
complementary bases
Pair of nitrogenous bases.
Adenine always pairs up with Thymine.
Cytosine always pairs up with Guanine.
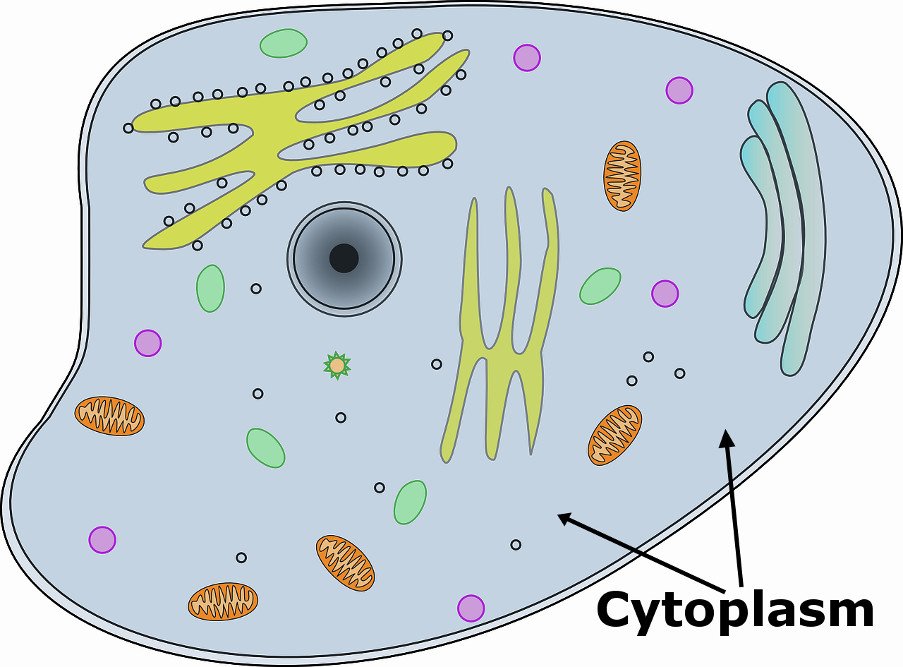
cytoplasm
Area between the nucleus and the cell membrane in an eukaryotic cell.
Contains many important structures such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes, etc.
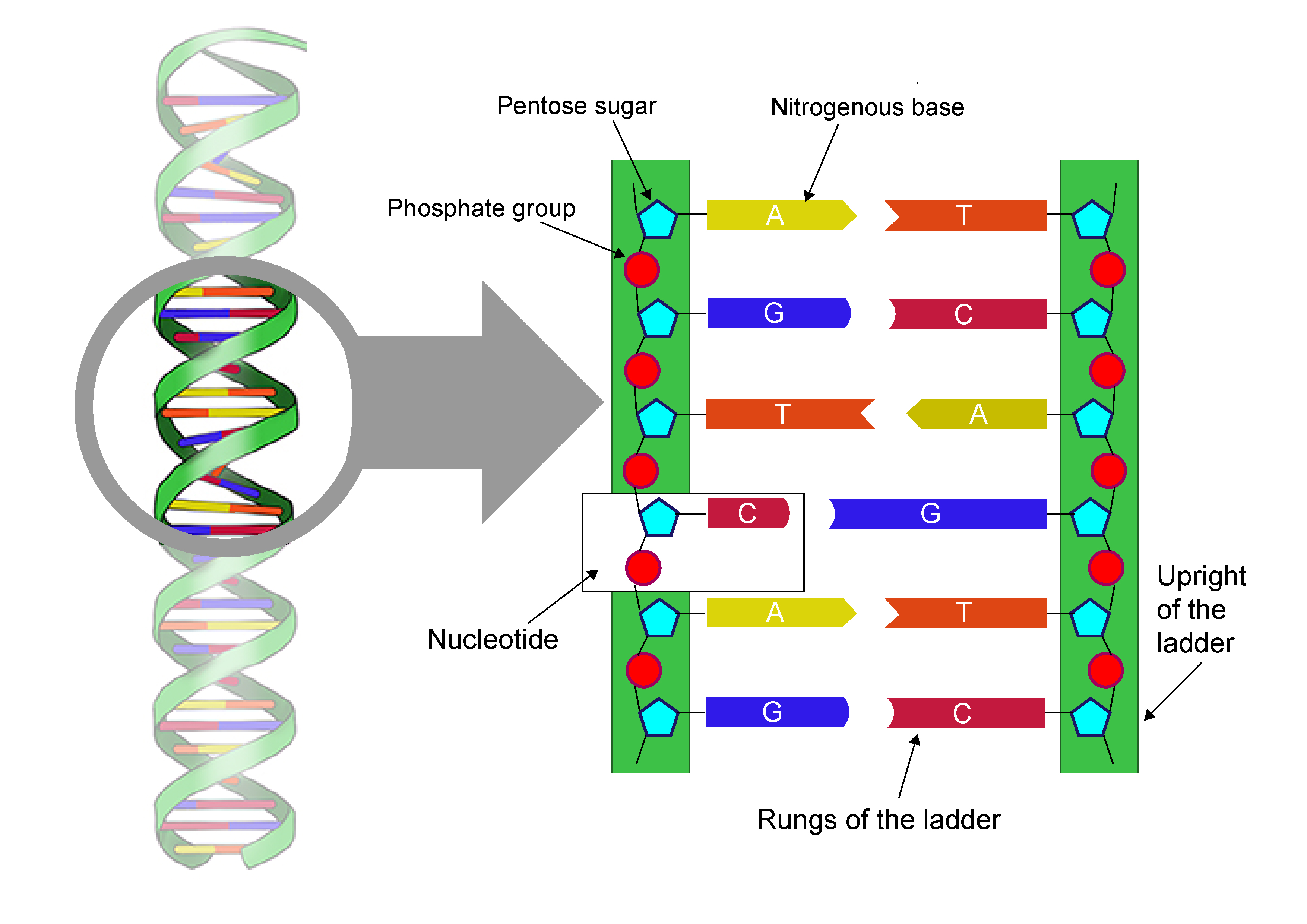
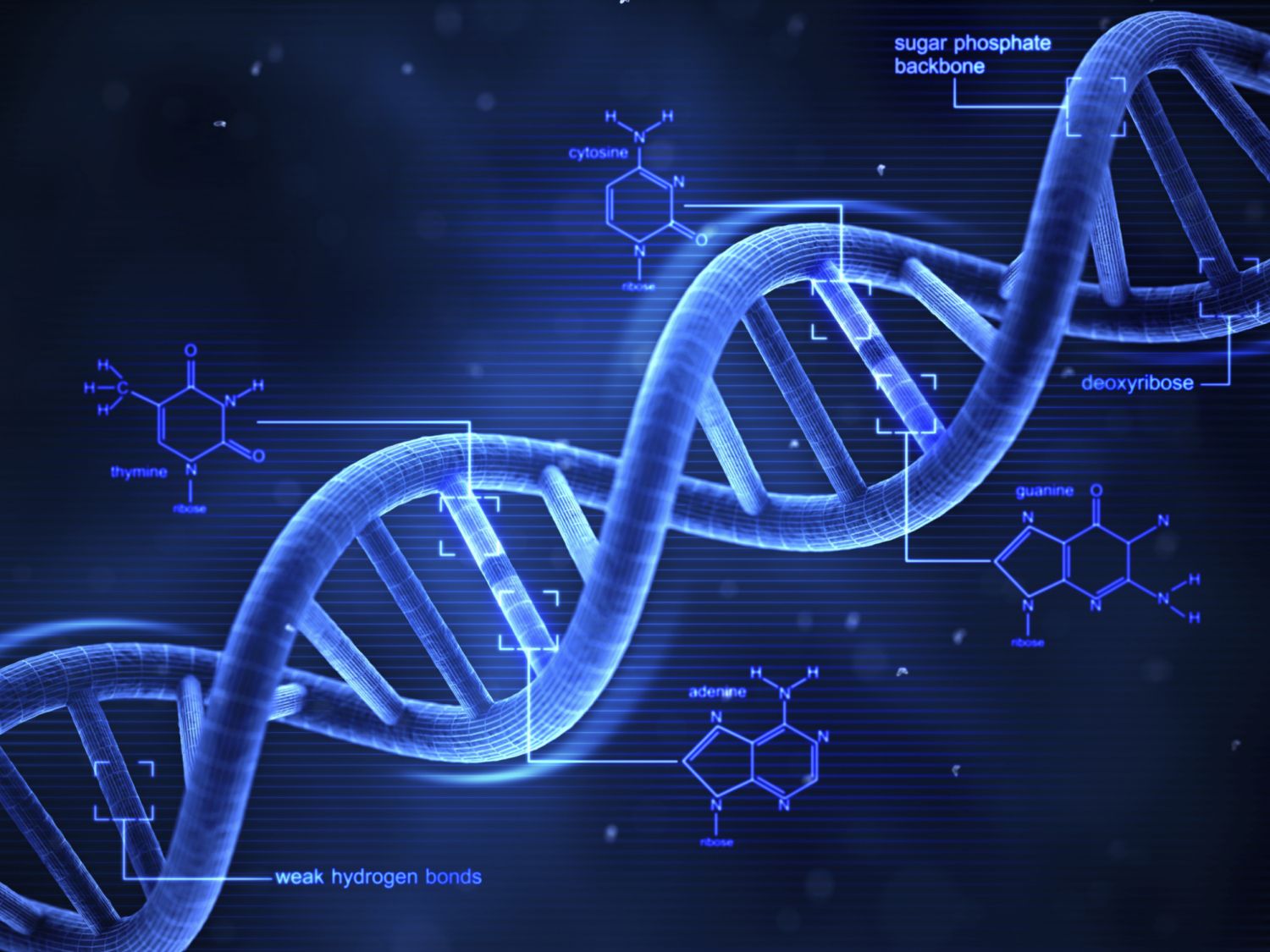
DNA ladder
Nucleic acid stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next.
2 DNA strands were twisted around each other → DNA was shaped as a double helix.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA vs RNA
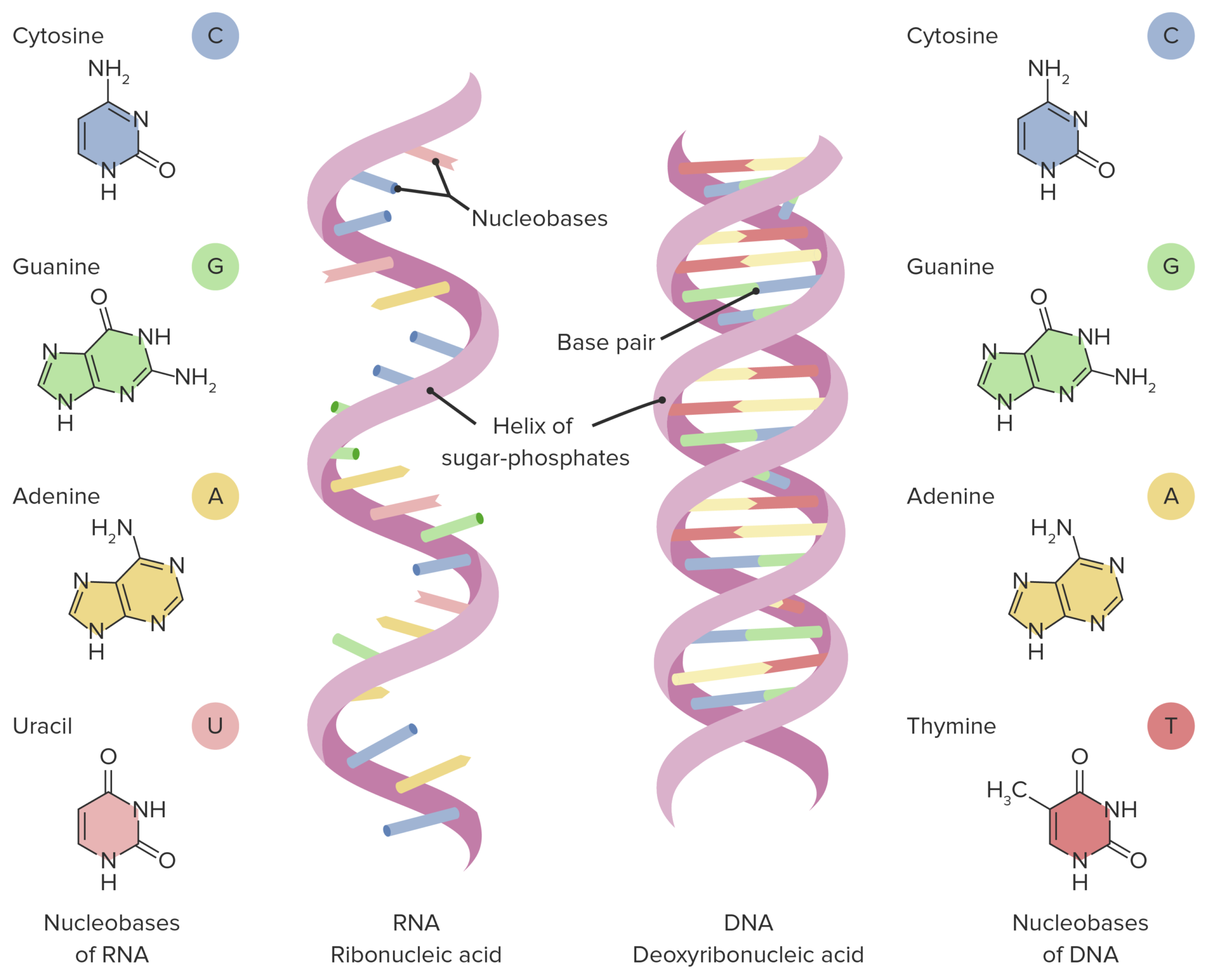
Sugar in RNA is ribose, whereas sugar in DNA is deoxyribose.
RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotide, while DNA is double-stranded.
Nitrogenous bases of DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, while RNA contains adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine.
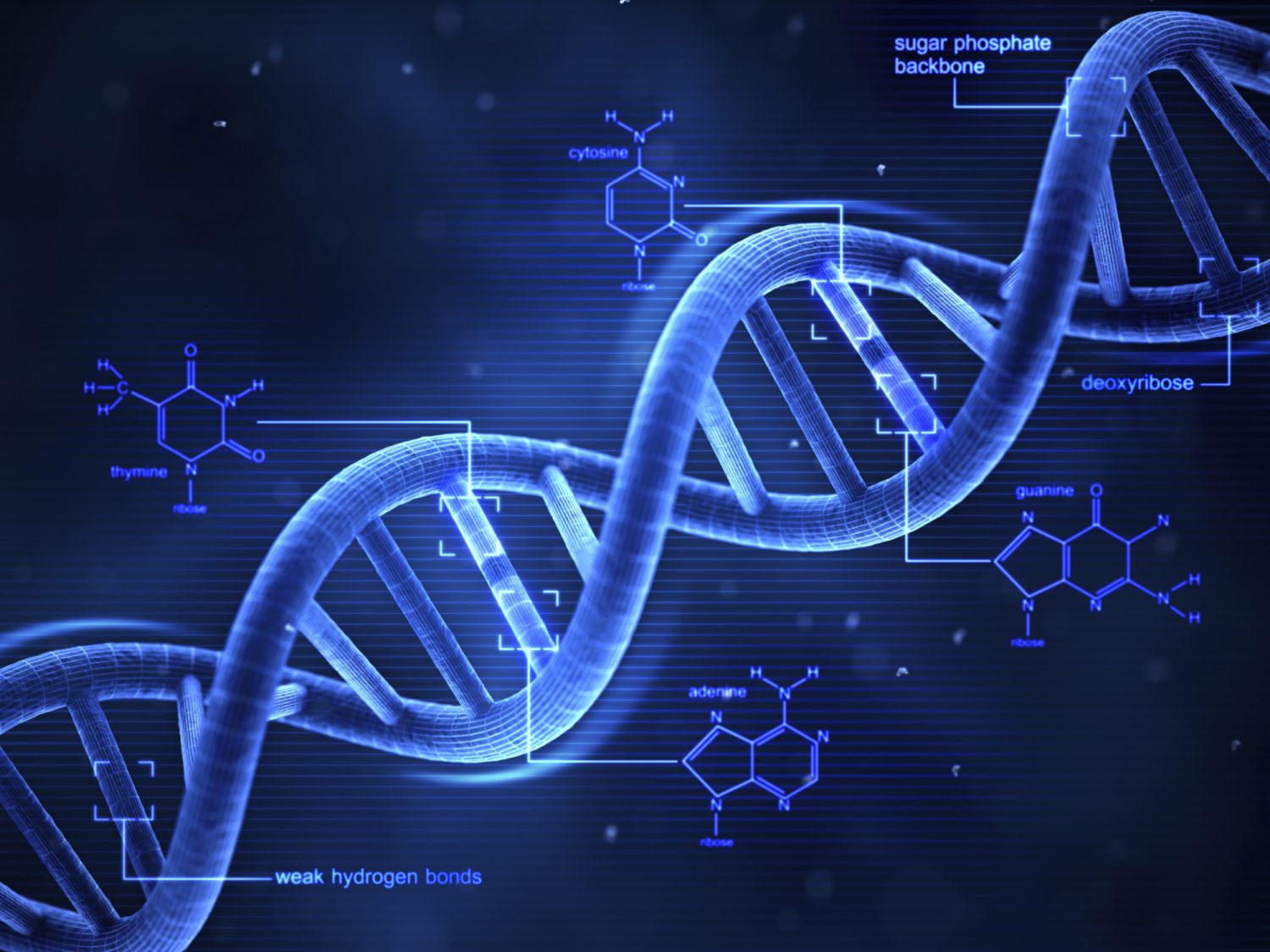
double helix
Similar to a spiral, or the way the threads are arranged in a screw.
Two strands are twisted around each other, forming a double helix.
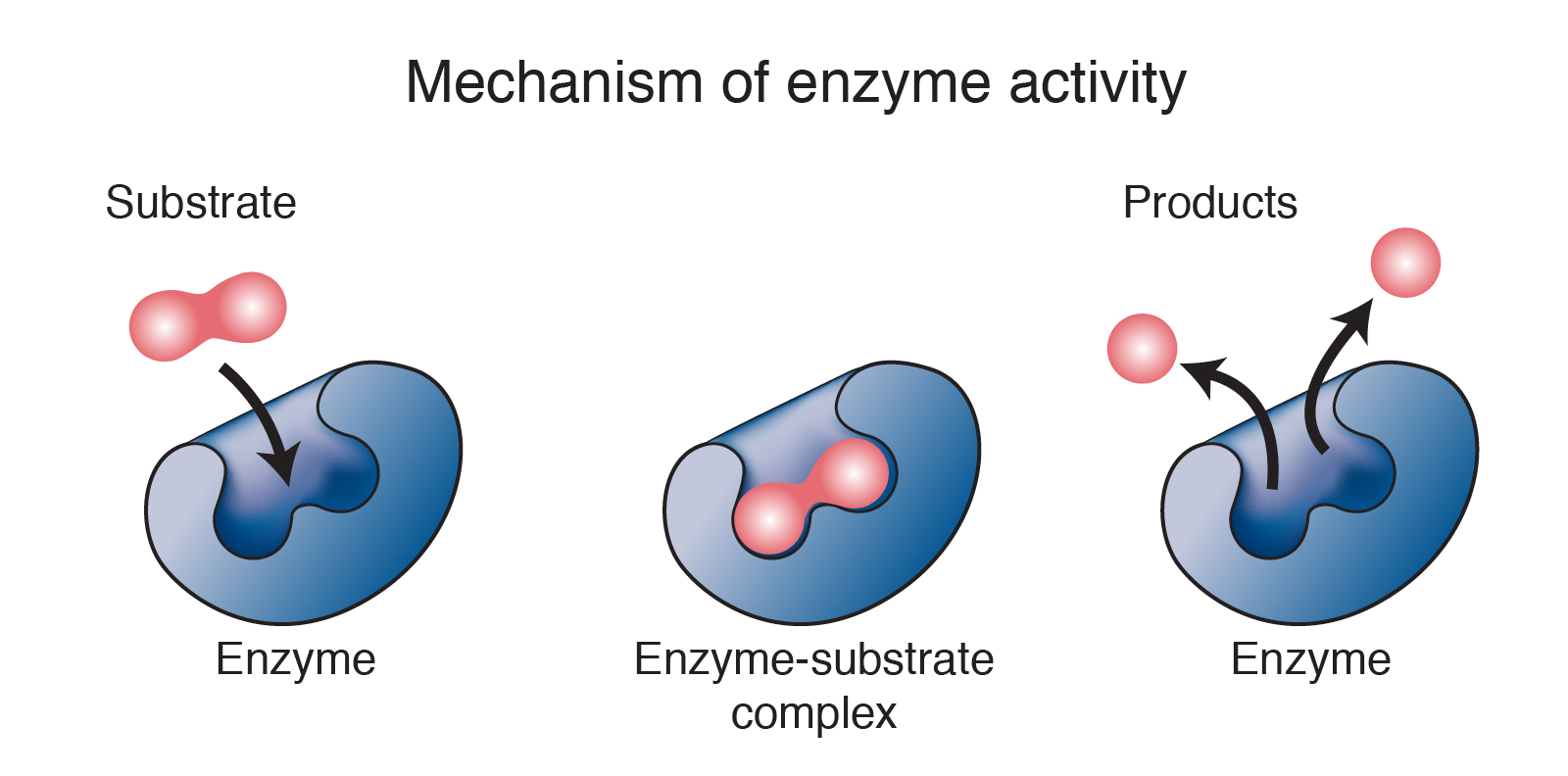
enzyme
One of many special protein catalysts contained in living organisms.
Enzymes are important in regulating chemical pathways, synthesizing materials needed by cells, releasing energy, and transferring information.
Necessary for DNA synthesis: separate the DNA strands, insert appropriate bases, produce covalent sugar-phosphate links, and proofread the bases that have been inserted.
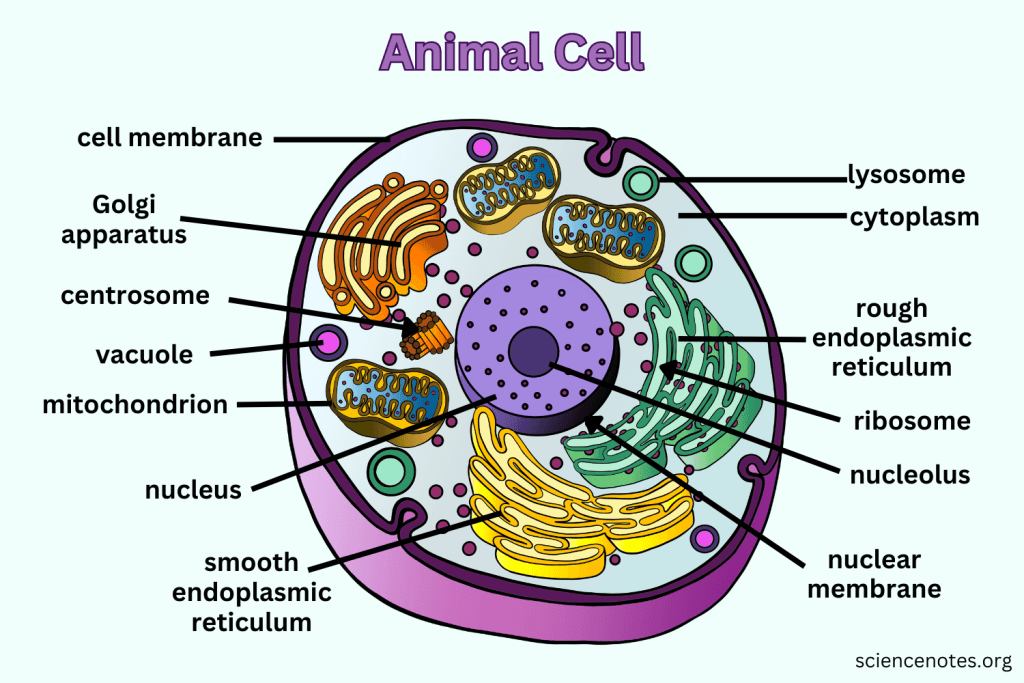
Eukaryotic cell
Cells that contain clearly defined nucleus.
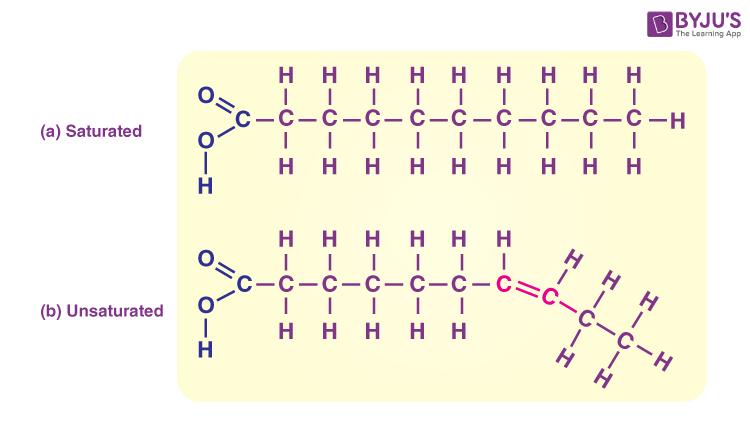
fat
A common name for lipid.
Fats are solid at room temperature.
Healthy fat (unsaturated): avocado, oily fish
Unhealthy fat (saturated): fats from pigs, cows, beef, tuna
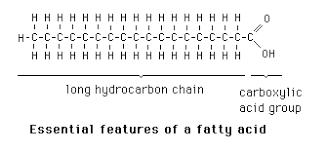
fatty acid
A factor that forms lipids.
Long chains of hydrogen and carbon atoms that have a carboxyl group attached at one end.
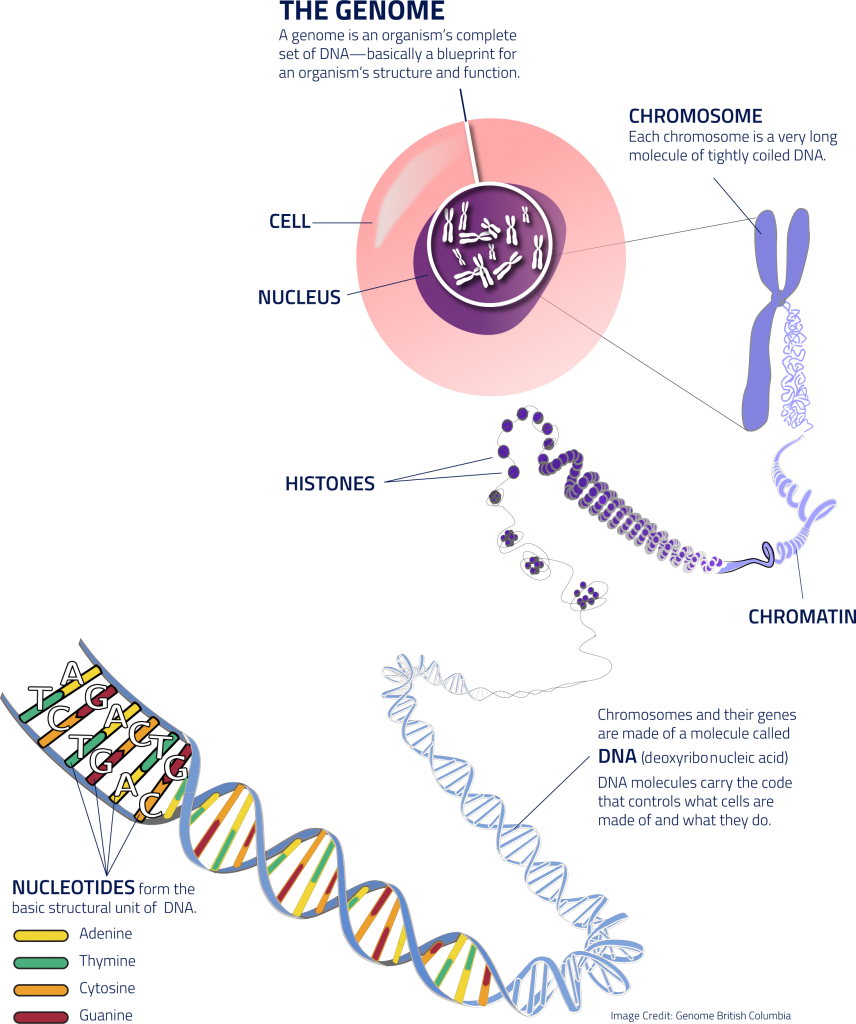
genome
All the genes possessed by an organism.
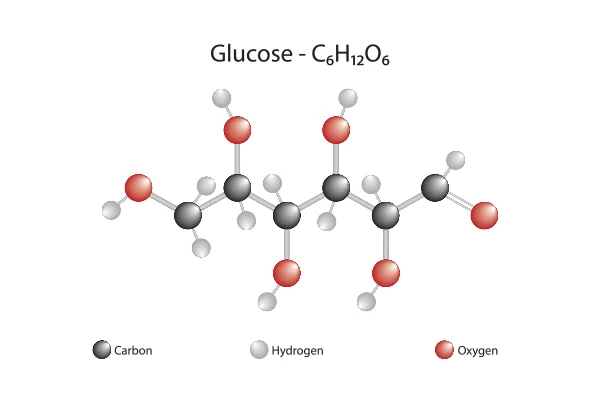
glucose
Sugar with formula C6H12O6 is a product of photosynthesis; and can be broken down for energy.
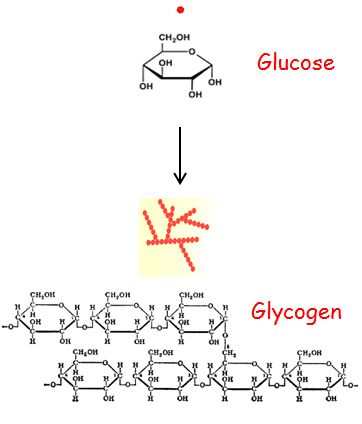
glycogen
Multibranched polysaccharide of glucose.
A form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria.
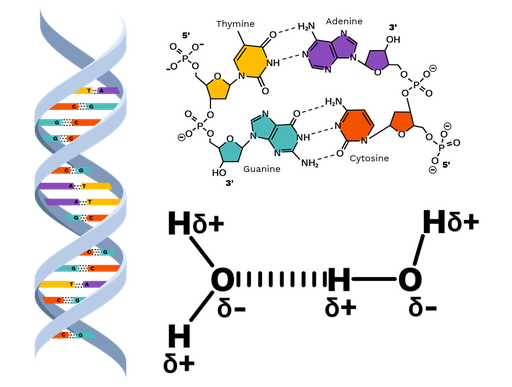
hydrogen bonds
Hold the two strands of DNA together.

kinds of compounds
Inorganic compounds: compounds that do not contain carbon (CO2 is an exception).
Organic compounds: carbon-containing compounds
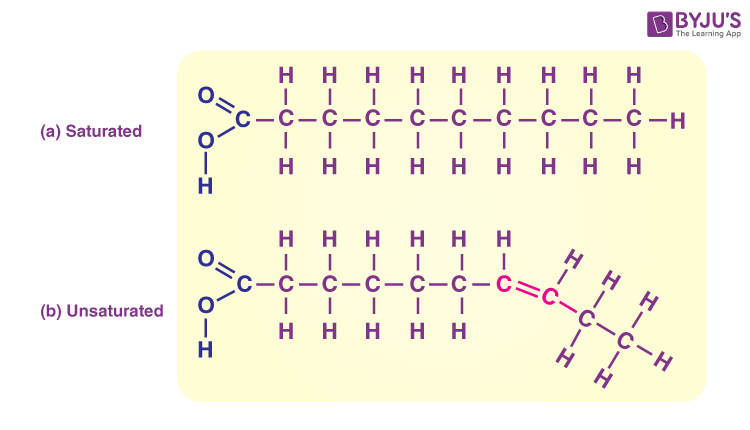
lipid
Organic compounds that are waxy or oily.
Lipids store energy, form biological membranes, and act as chemical messengers.
Many important lipids are formed from combinations of fatty acids and glycerol.
Types of lipids: saturated, unsaturated, sterols, and phospholipids
Means of storing energy.
When lipids are broken down, they produce more energy gram for gram than carbohydrates do → lipids are healthier.
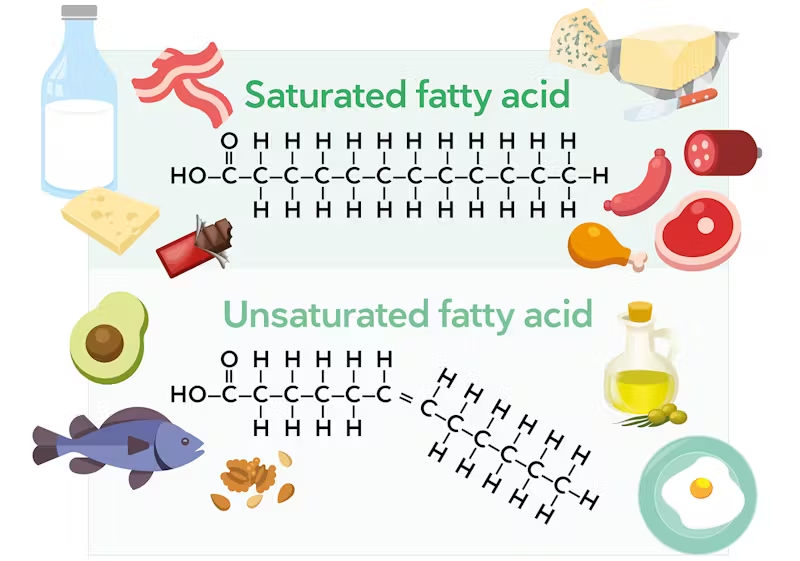
saturated lipids
Carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain are joined together by a single bond.
Contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms.
Less healthy
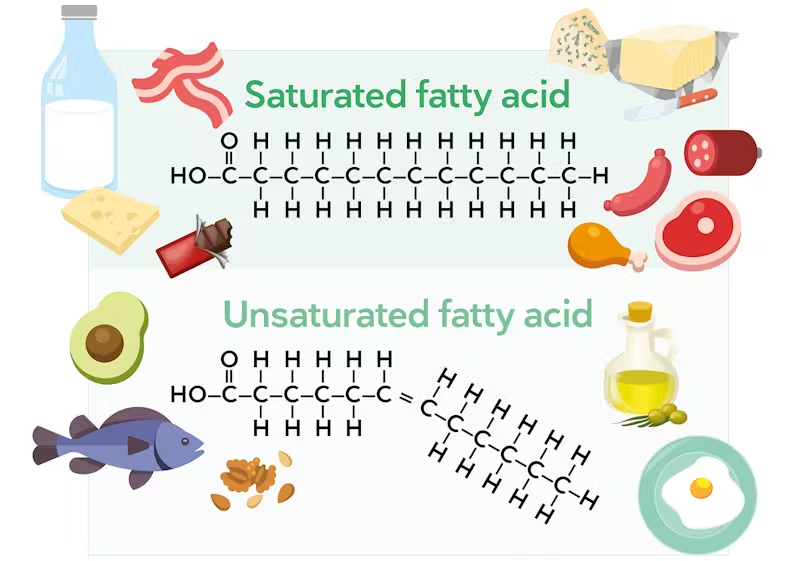
unsaturated lipids
Fatty acids contain several double bonds.
Does not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms.
Healthier → help prevent heart diseases
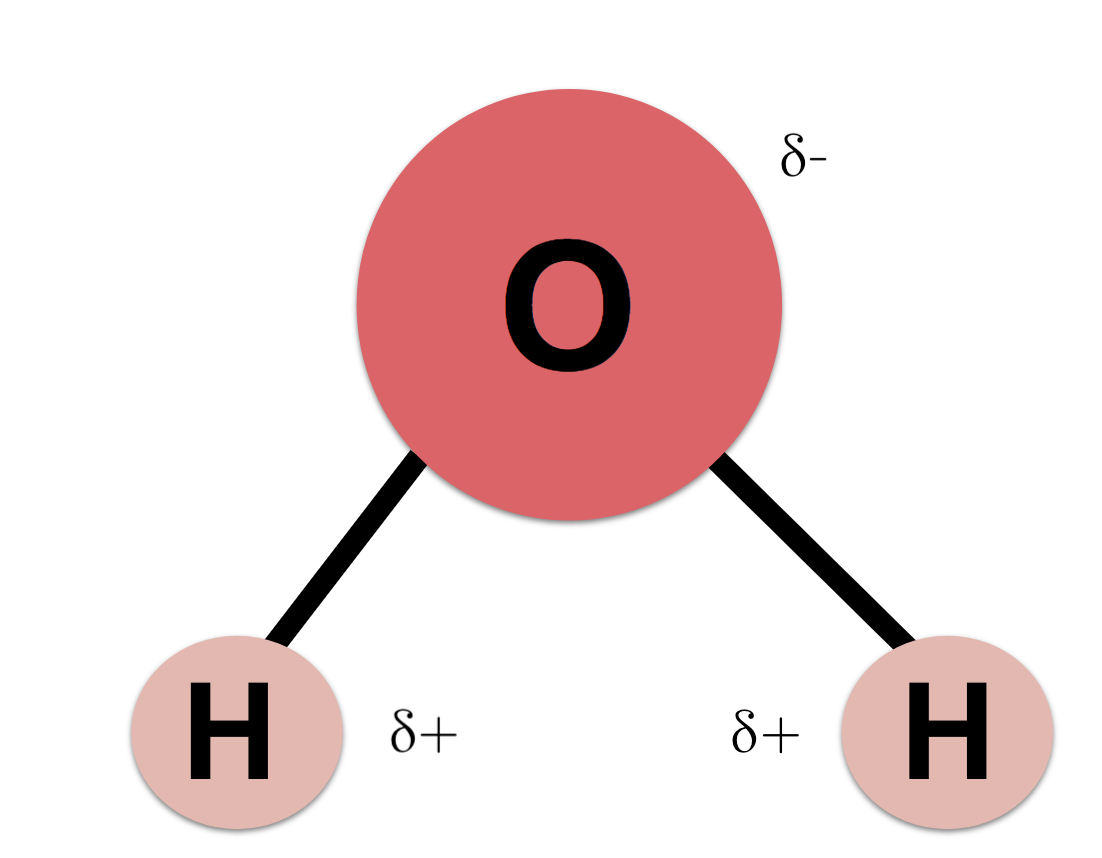
most abundant compound in a cell
Water is the most abundant molecule in the cells, accounting for 70% or more of total cell mass.
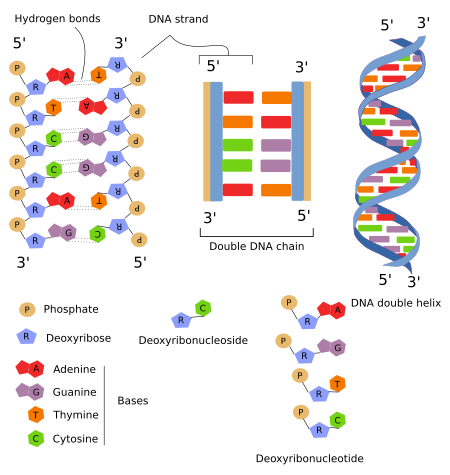
nitrogenous bases
DNA contains 4 nitrogenous bases.
Purines: adenine and guanine.
Pyrimidines: cytosine and thymine.
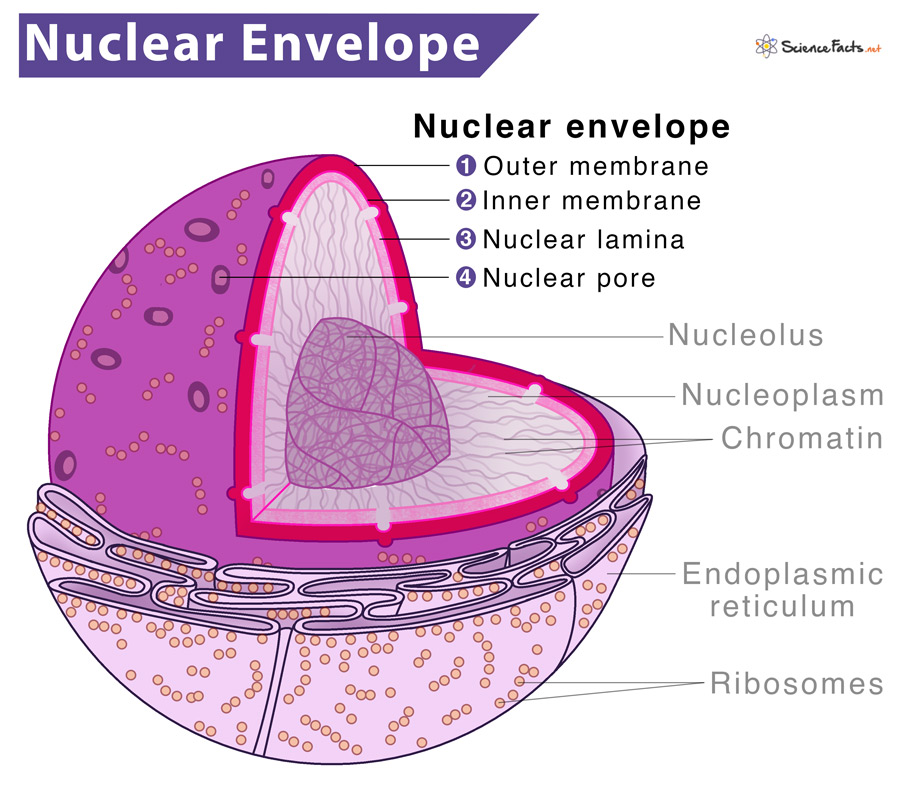
nuclear membrane / nuclear envelope
A membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell.
In the nuclear envelope are thousands of nuclear pores, or small openings.
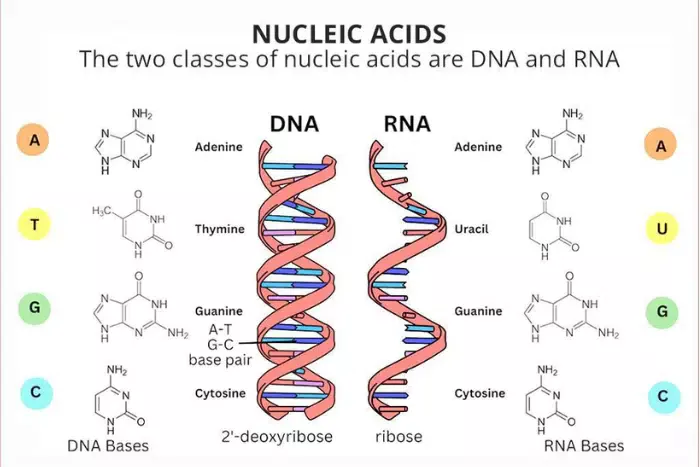
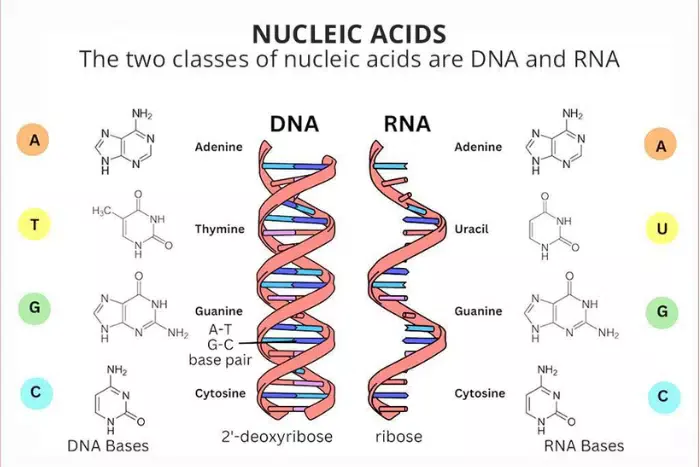
nucleic acid
Complex organic molecules comprise carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms.
Polymers of individual monomers are known as nucleotides.
2 kinds of nucleic acids: RNA (ribonucleic acid), and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
Store and transmit the genetic information that is responsible for life itself.
nucleotide
Monomers of nucleic acids
Built up of 3 basic parts: a special 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
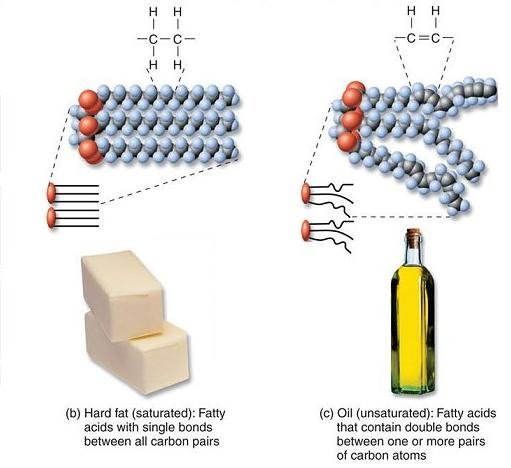
oil
A common name for lipids.
Liquid
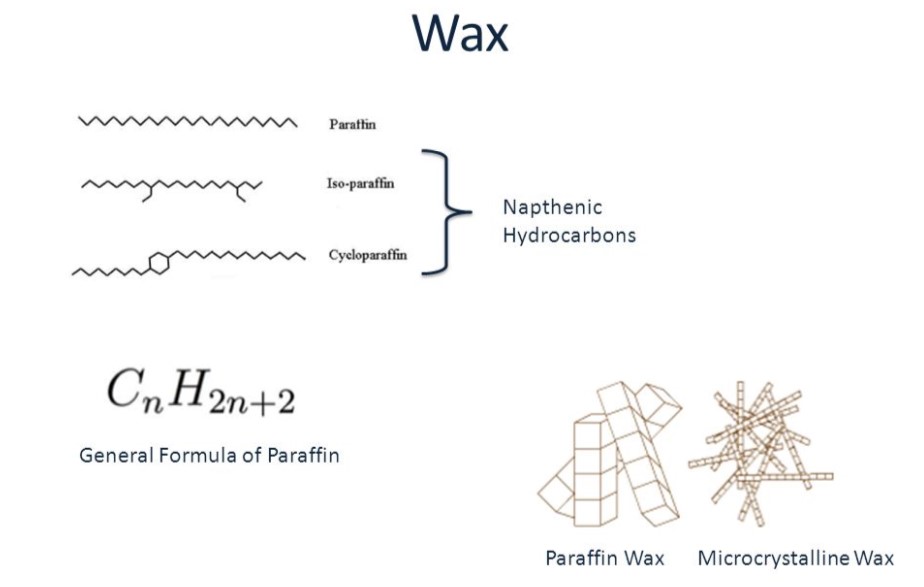
wax
Another common name for lipids.
Solid at room temperature.

organic compound
Carbon-containing compounds.
Carbon is a unique element because of its remarkable ability to form covalent bonds that are strong and stable.
4 groups of organic compounds: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
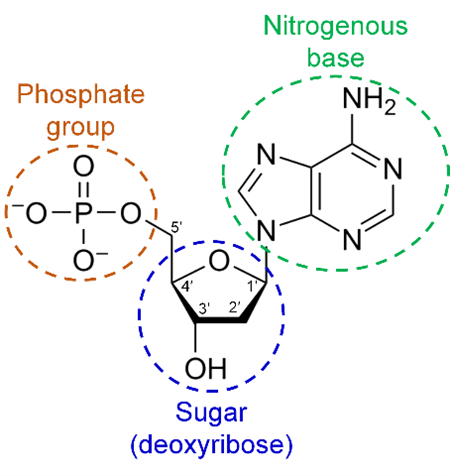
phosphate group
A phosphorus atom is bound to four oxygen atoms.
Makes of nucleic acids along with sugars and nitrogenous bases.
Provides energy for moving our muscles.
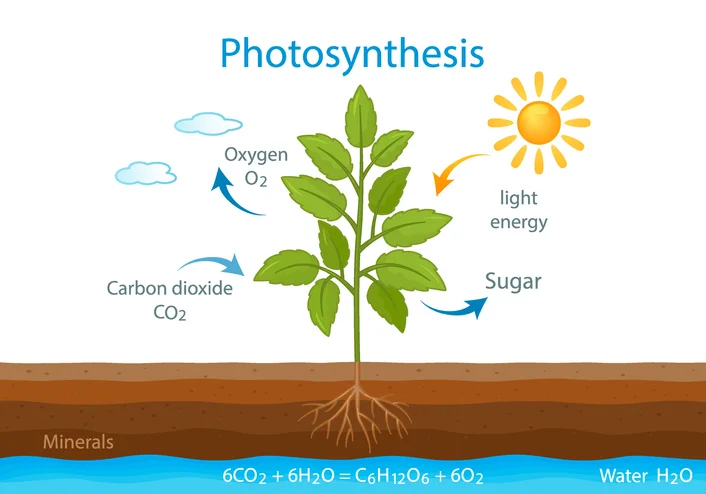
photosynthesis equation / purpose
In the process of photosynthesis, plants use the energy of sunlight to produce carbohydrates.
6CO2 + 6H2O → (light) C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide + Water → (light) Glucose + Oxygen
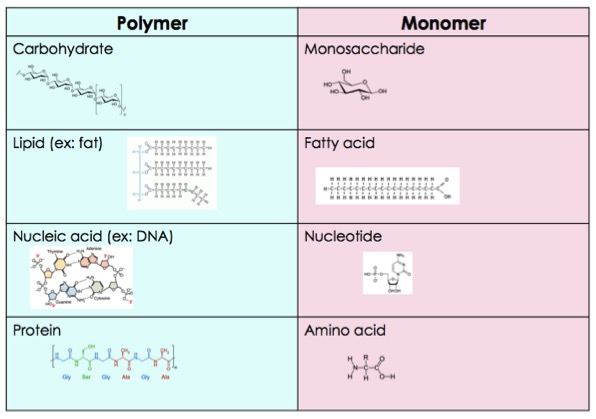
monomer
Small compounds can be joined together with other small compounds to form polymers.
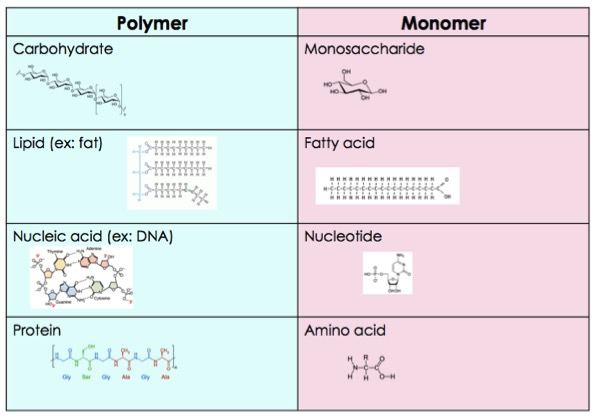
polymer
Large compounds are formed by combinations of monomers.
Many polymers are so large that they are called macromolecules.
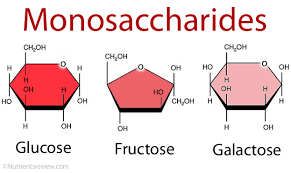
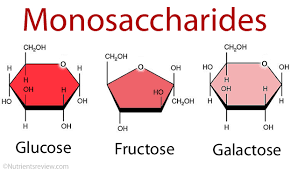
monosaccharides
Simple carbohydrate, also known as single sugar.
Examples of monosaccharides: glucose, galactose, and fructose.
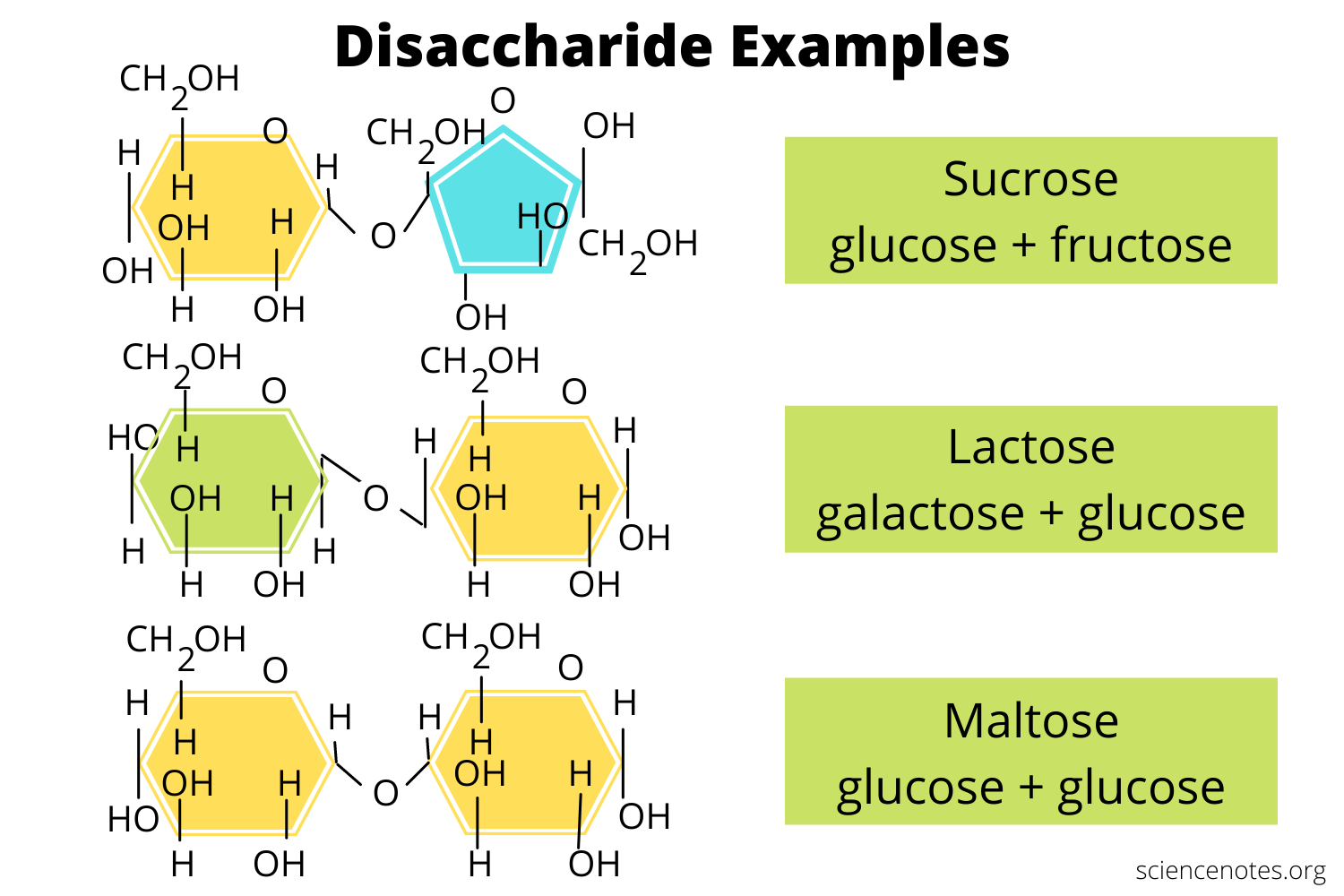
disaccharides
Compound formed from the joining of two single sugars in dehydration synthesis.
Examples of disaccharides: sucrose, maltose, and lactose.
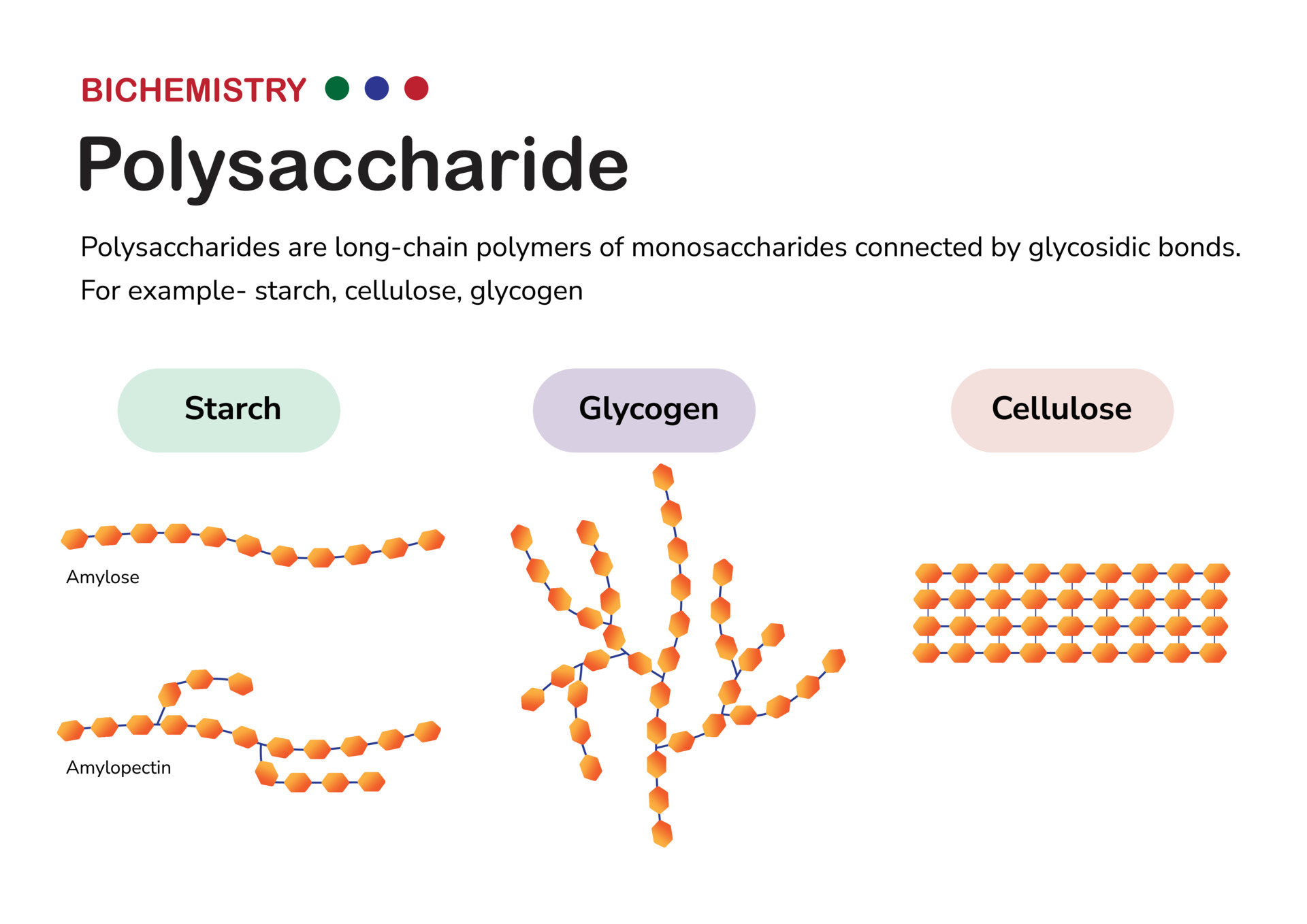
polysaccharide(s)
Very large molecules can be formed by joining together many monosaccharide units.
Examples of polysaccharides: starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
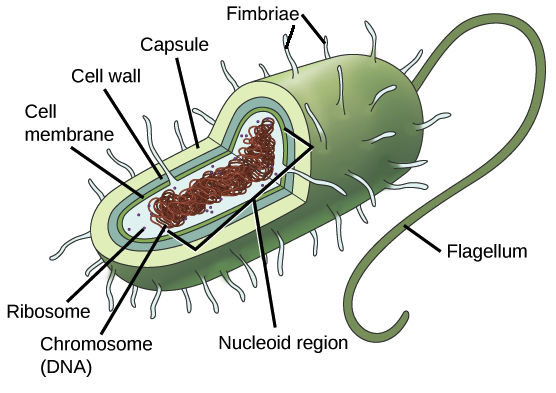
Prokaryotic cell
A single-cell organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
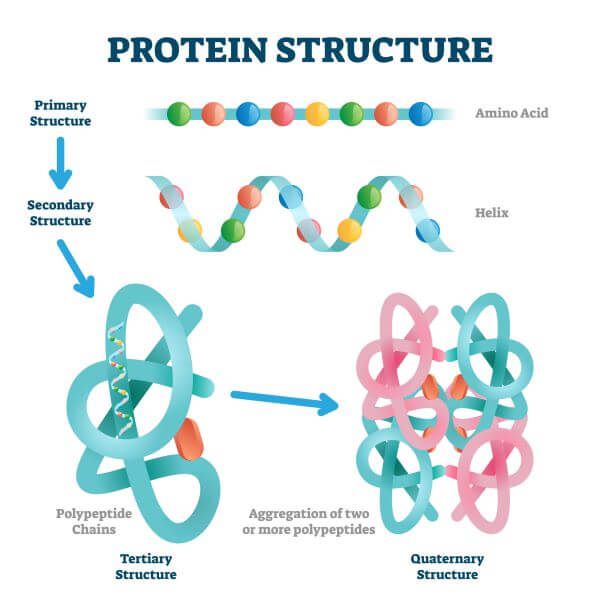
protein
Organic compounds that contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Polymers of amino acids.
Peptide bond: a covalent bond that joins two amino acids.
Has numerous roles: carrying out chemical reactions, pumping small molecules in and out of cells, and being responsible for cell moving.
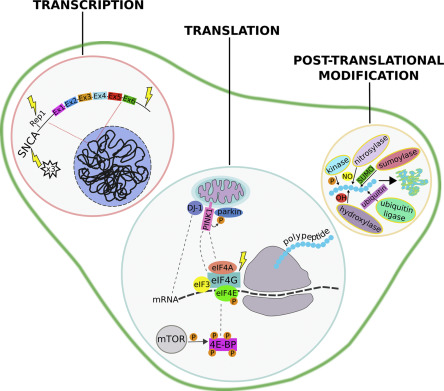
protein synthesis
Information that DNA transfers to messenger RNA is in the form of a code.
Messenger RNA binds to the ribosomes on which ribosomal RNA is found.
Amino acids in the cytoplasm are picked up by transfer DNA and are carried to messenger RNA.
The anticodons in transfer RNA attach to the proper codons in messenger RNA.
→ Amino acids are brought together in the correct sequence to form a protein molecule.
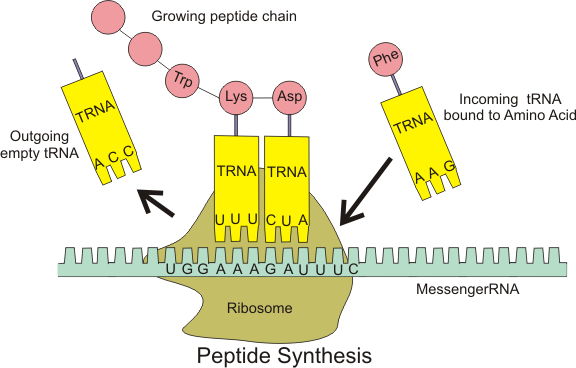
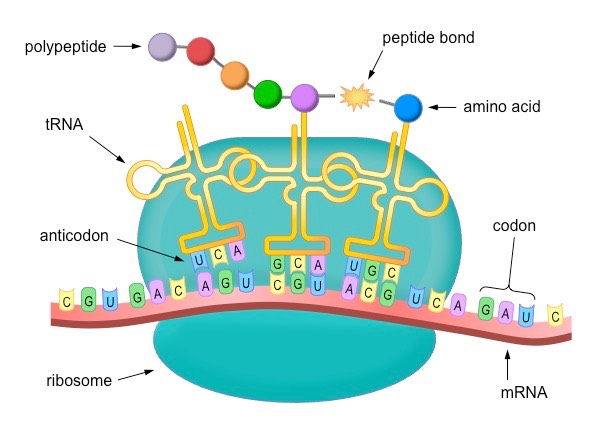
codon
Combination of three nucleotides on the messenger RNA.
Each codon specifies a particular amino acid that is to be placed in the polypeptide chain.
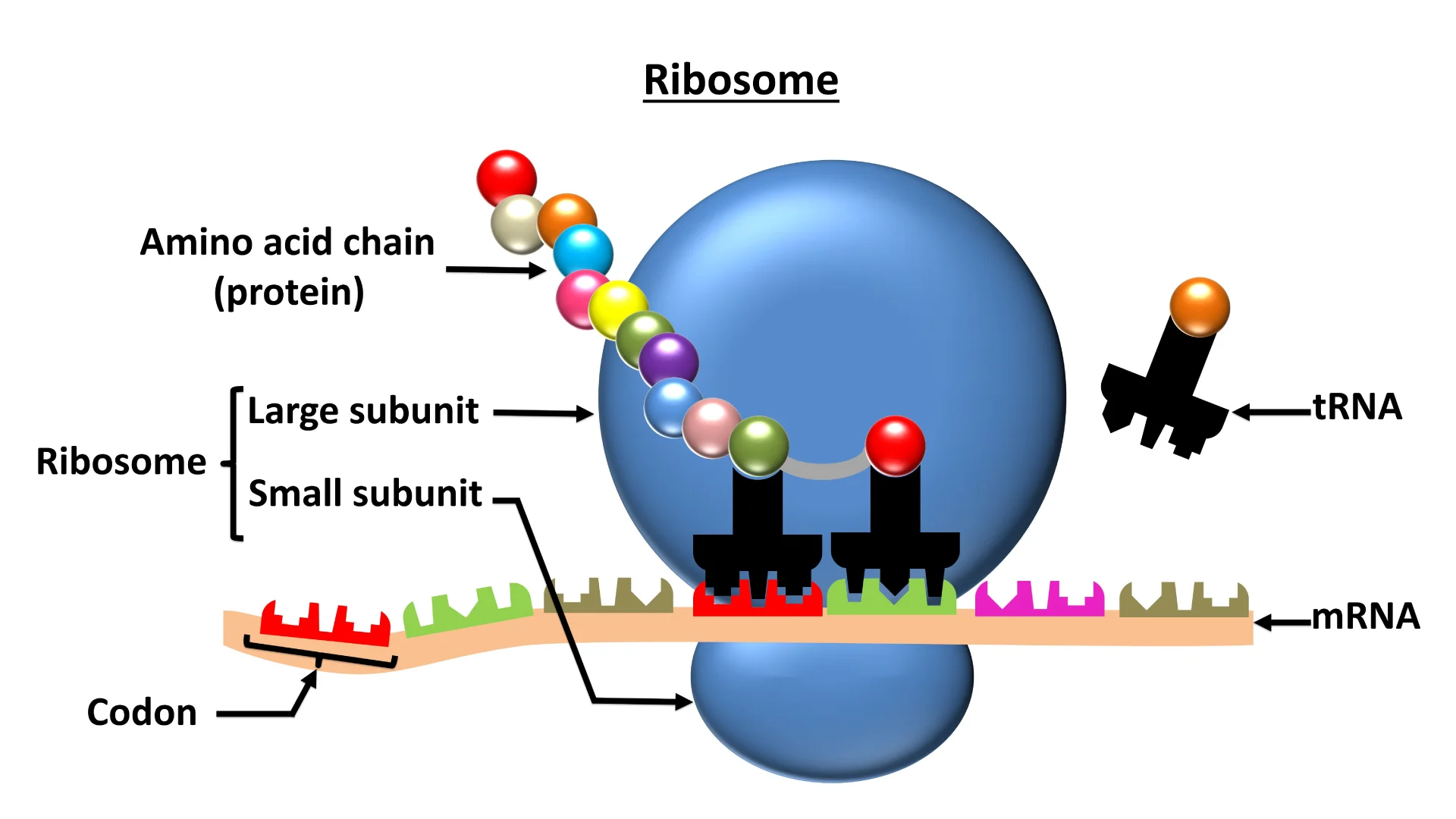
ribosome
Organelle in which proteins are made.
Ribosomes are made up of two subunits, a large one and a smaller one.
Protein synthesis takes place in ribosomes.
RNA
Nucleic acid that acts as a messenger between DNA and the ribosomes.
Carries out the process by which proteins are made from amino acids.
Consists of a long chain of macromolecules made up of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide is made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
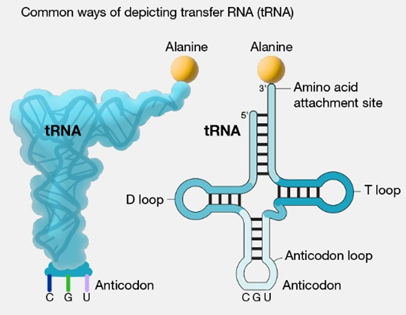
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Carries amino acids to the ribosomes, where the amino acids are joined together to form polypeptides.
3 transfer RNA nucleotides are called anticodon.
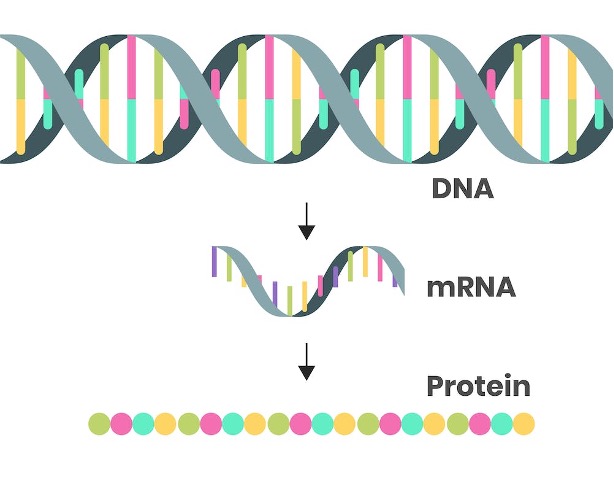
messenger RNA (mRNA)
Bring the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus out to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
translation
The decoding of a messenger RNA into a polypeptide chain (protein).
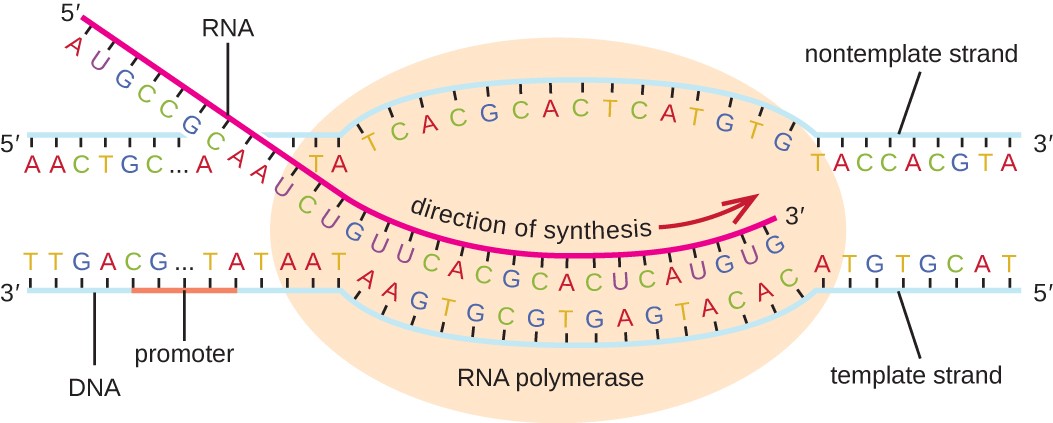
transcription
The process by which a molecule of DNA is copied into a complementary strand of RNA.
simple sugar & purpose
Contains a great deal of energy.
Energy stored in bonds will make up the carbohydrate molecules.
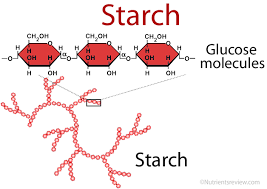
starch
A very large molecule is formed by joining together hundreds of glucose molecules.
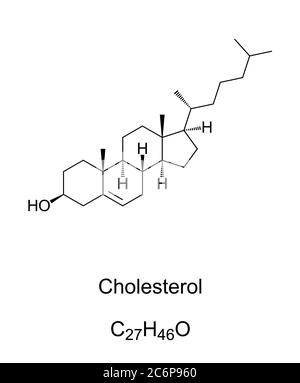
sterols
One kind of lipid living in organisms.
The most common sterol is a molecule called cholesterol.
Cholesterol is an important part of many cells, but excessive cholesterol in the diet is a risk factor for heart disease.
Steroid lipids play many important roles in building cells and carrying messages from one part of the body to another.

phospholipids
Another kind of lipid living in organisms.
Molecules consist of parts that dissolve well in water and parts that do not dissolve well in water.
Phospholipid molecules are mixed with water will form liposomes.
polymerization
Many carbon-based compounds are formed in which large compounds are constructed by joining together smaller compounds.