Week 9: IKE + SSL/TLS
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
What does IKE stand for?
Internet Key Exchange
What is IKE?
A protocol that establishes keys and security associations
What types of things does IKE define for key exchange?
- Protocol format
- Cryptographic + hashing algorithm
- Keys
What is a master key?
A pre-shared key
What is the difference between an encryption and signature key?
Encryption keys are used for encryption and decryption, whilst signature keys are used for signing and signature verification
What protocols did IKE evolve from?
- Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP)
- Oakley
What is the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol?
A framework and generic negotiation protocol for establishing security associations and cryptographic keys
What is Oakley?
A suite of key agreement protocols that enable two parties to generate a key at the same time
How does IKE build on Oakley and ISAKMP?
IKE combines the packet format of ISAKMP and protocol exchanges of Oakley
What protocol is IKE, ISAKMP, and Oakley based on?
Diffie-Hellman protocol
What are the 2 phases of IKE?
1. Two parties negotiate a security association
2. Security association in Phase 1 is used to create actual child security associations that encrypt and authenticate individual conversations
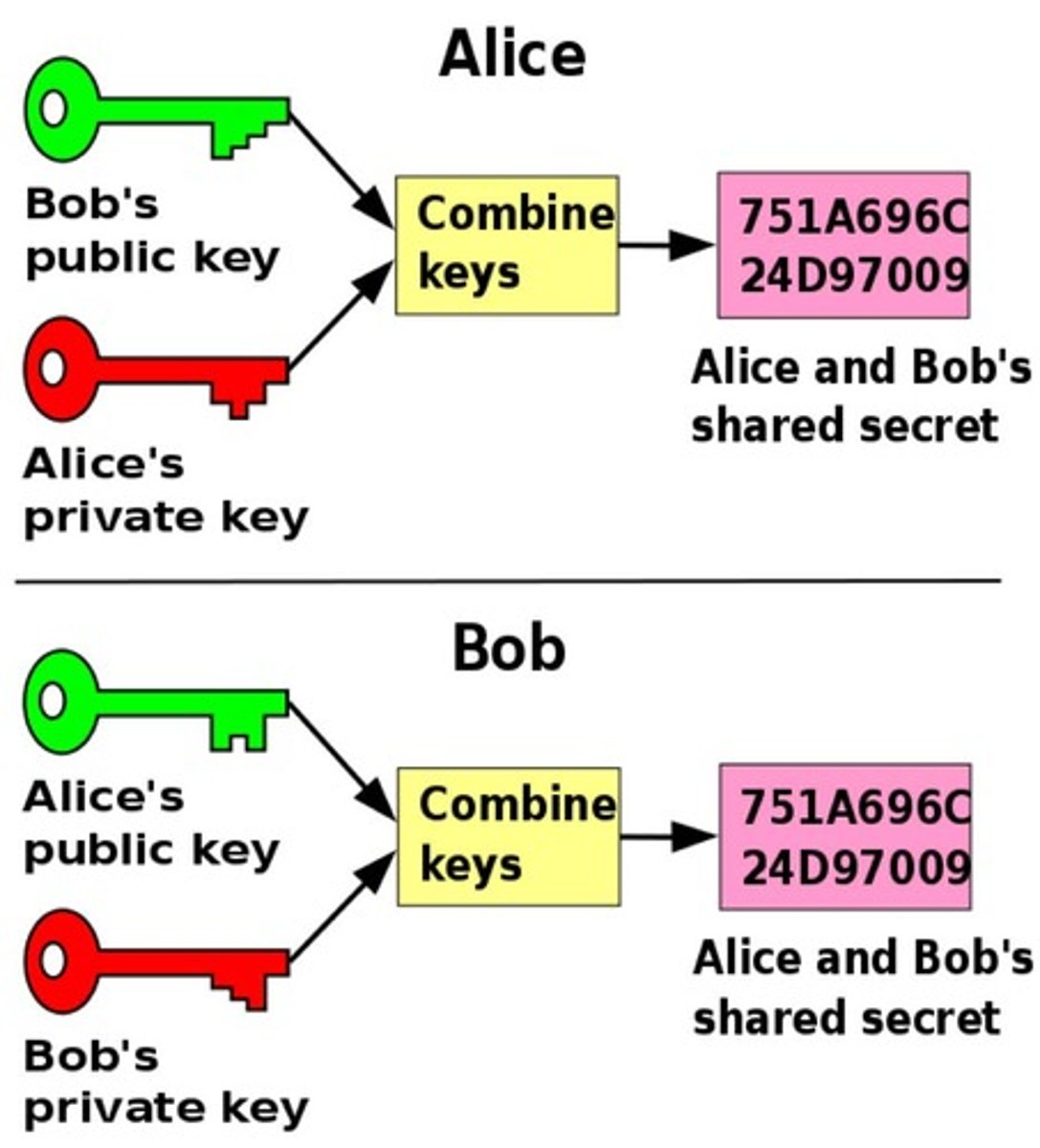
What is Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
A public key exchange that exchanges symmetric shared public variables as well as some hidden private keys used to generate the same key between two hosts
What is the 1st step of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
Two parties (Alice and Bob) decide on two public variables: a prime q and a, where a < q, and a is a primitive root of q

What is the 2nd step of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
Alice and Bob generate a private key Xa and Xb each, such that Xa < q and Xb < q
What is the 3rd step of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
Alice calculates a public key Ya = a^(Xb) % q, Bob calculates a public key Yb = a^(Xb) % q
What is the 4th step of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
Alice and Bob send their respective public keys Ya and Yb to each other
What is the 5th step of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
Alice and Bob both calculate their shared secret key K
- Alice does K = (Yb)^(Xa) % q
- Bob does K = (Ya)^(Xb) % q
What does the Diffie-Hellman protocol achieve?
Diffie-Hellman protocol achieves perfect forward secrecy
What is perfect forward secrecy?
A property of key agreement protocols that ensures a session key derived from a set of master keys cannot be compromised if any master key is compromised

How does Diffie-Hellman key exchange achieve perfect forward secrecy?
The private keys used by each party can be randomised since we just need a random value of q and a
What is Phase 1 of IKE?
Establishes a secure channel for Phase 2 negotiations to be done in private
In Phase 1 of IKE, what is negotiated with Diffie-Hellman key exchange?
An ISAKMP security association (master key) is negotiated
In Phase 1 of IKE, what 3 things are needed to negotiate an ISAKMP security association?
- Cookies
- Identifier
- Authenticators
What are the 2 modes of IKE Phase 1?
- Main mode
- Aggressive mode
How many messages are sent during IKE Phase 1 if it is in main mode?
6 messages
How many messages are sent during IKE Phase 1 if it is in aggressive mode?
3 messages
What is the key difference between IKE Phase 1 main mode and aggressive mode?
- Main mode provides identity protection whilst aggressive mode does not provide identity protection
- This means that aggressive mode is faster than main mode
What is the 1st step of IKE Phase 1 in main mode?
Initiator generates an initial cookie
What is the 2nd step of IKE Phase 1 in main mode?
Initiator sends the cookie and a cryptographic proposal
What is the 3rd step of IKE Phase 1 in main mode?
If the responder agrees to any of the cryptographic proposal, then it sends the initial cookie, its own cookie, and its own cryptographic proposal to the initiator
What is the 4th step of IKE Phase 1 in main mode?
Diffie-Hellman key exchange occurs to generate a secret shared cryptographic proposal
What is the 5th step of IKE Phase 1 in main mode?
After key exchange, both the initiator and the responder sends the ciphertext and authenticators {ID, AUTH}
What is the cryptographic proposal generated in IKE Phase 1?
The Internet Security Association and Key Management (ISAKMP) security association data
What is the contents of the initial cryptographic proposal sent by the initiator in IKE Phase 1?
A series of proposals and their corresponding algorithm
What is the contents of the cryptographic proposal sent by the responder back to the initiator in IKE Phase 1?
A series of proposals accepted by the responder with their corresponding algorithm
What happens if the responder does not support any of the initiator's proposals during IKE Phase 1?
The exchange is rejected
What are cookies used for in IKE Phase 1?
Cookies prevent DoS attacks since they verify every subsequent request that the initiator makes to the responder
How are cookies created for IKE Phase 1?
Cookies are independently hashed using a fast hash algorithm e.g. MD5 over the IP source and destination addresses
Why are cookies hashed?
To prevent attackers from obtaining a cookie with real IP address details, which can be used in flooding attacks
In the 2nd step of IKE Phase 1 (main mode), why does the initial cookie get sent back to the initiator?
To verify that the responder received the initial packet
What are nonces used for in IKE Phase 1?
To generate identifiers for each host
Why is {ID, AUTH} sent between the initiator and responder after key exchange?
- The pair {ID, AUTH} allows each host to identify the other party
- AUTH is authenticated data used to verify data integrity
What is IKE Phase 2?
The security association generated in Phase 1 is used to encrypt individual sessions where the initiator and responder communicate
What are the 2 modes of IKE Phase 2?
- Quick mode
- New group mode
What is IKE Phase 2 quick mode?
Quick mode establishes new security associations for Authentication Header (AH) or Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocols
What is IKE Phase 2 new group mode?
New group negotiates new parameters or security associations on existing proposals
How does IKE Phase 2 quick mode allow for perfect forward secrecy?
IKE Phase 2 alters the Diffie-Hellman key exchange to send a unique identifier for each message sent between an initiator and responder

What does SSL stand for?
Secure Socket Layer
What does TLS stand for?
Transport Layer Security
What is SSL?
A protocol that provides communication privacy over the Internet
What 3 things does SSL prevent during a client/server communication?
- Eavesdropping
- Tampering
- Message forgery
Does SSL satisfy all three of the CIA triad?
Yes it does!
What are the 3 main goals of SSL?
- Secrecy
- Integrity
- Authentication (if both parties want it)
How does SSL work?
SSL configures a one/two way authentic channel for secret communication
How does SSL ensure the tunnel it creates is authentic?
By using public key certificates
What are 2 SSL/TLS sub-protocols?
- TLS handshake
- TLS record
What is the TLS handshake?
- Initialises new/restarts existing connections
- Establishes a channel with the desired channel properties
What is the TLS Record Protocol?
- Protocol for sending application data
- Describes how data is compressed and authenticated
- Describes how the payload is encrypted
How does the TLS record describe how data is authenticated?
With the Message Authentication Code header
What is the difference between the purpose of a TLS connection and TLS session?
TLS connection provides secure communication between two peers, whilst TLS session provides a definition for shared cryptographic parameters
What is the difference between the relationship between TLS connections and TLS sessions?
TLS connections are peer-to-peer, whilst TLS sessions are client-server relationships
What is the difference between the lifetime of a TLS connection and TLS session?
TLS connections are transient and per communication, whilst TLS sessions are persistent and can cover multiple communications
What is the difference between the creation of a TLS connection and TLS session?
TLS connections are created when they are needed, whilst TLS sessions are indirectly created from a TLS handshake
What is the difference between the association of a TLS connection and TLS session?
TLS connections are tied to 1 session, whilst TLS sessions support multiple TLS connections
What is the difference between the role of a TLS connection and TLS session in encryption?
TLS connections use session parameters to encrypt/decrypt, and TLS sessions store encryption algorithms and secrets
What is the difference between the efficiency of a TLS connection and TLS session?
TLS connections have more overhead if a new session is required for each connection, whilst TLS sessions can reuse parameters across multiple connections
What does the TLS Record Protocol provide?
- Confidentiality
- Message integrity
How does the TLS Record Protocol provide confidentiality?
Defines a shared secret key used for TLS payload encryption
How does the TLS Record Protocol provide message integrity?
Defines a shared secret key used to form the Message Authentication Code
What are the 3 main steps of TLS Handshake Protocol?
- Negotiation
- Identification
- Establishment
What is a server certificate?
- A certificate signed by a trusted third party
- Contains the name and public key of the server
What are 2 assumptions made on the initial key exchange in a TLS Handshake?
- Simplification shows key exchange as one message
- Server may request for client certificate, but this is rarely used in practice
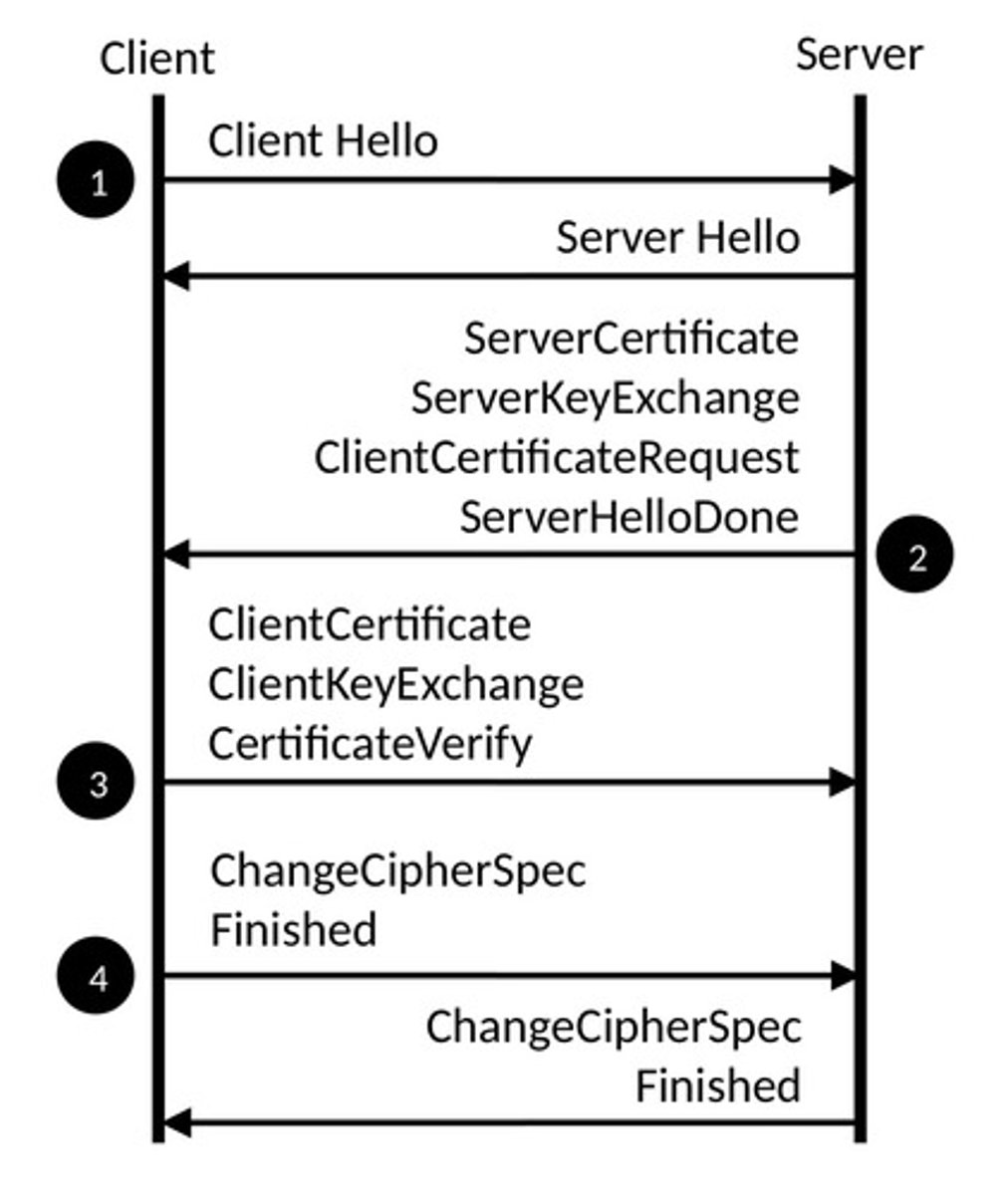
What are the steps to a TLS Handshake?
1. Client Hello
2. Server Hello
3. Server Certificate
4. Client Certificate (opt)
5. Client Key Exchange
6. Client Certificate Verification (opt)
7. Client Finish
8. Server Finish
During client authentication in the TLS Handshake, what is the PMS used for?
To generate new keys for the client authentication
What does PMS stand for?
Pre-master secret
During the initial hellos between client and server in the TLS Handshake, what is exchanged?
Nonces are exchanged during initial hellos
How do web browsers use TLS?
- HTTPS for applications using credit card numbers or customer data, required!
What are 4 UI vulnerabilities with SSL/TLS?
- Users don't understand the meaning of the lock
- Users never click on the lock
- Users don't understand certificates
- Warning messages are confusing
What does PKI stand for?
Public Key Infrastructure
What does PKI provide?
Authentication
What are 2 examples of bad SSL users on the Internet?
- F-Secure
- Phishing
How does F-Secure use SSL poorly?
- F-Secure is a company that sells software
- Buying from the company generates an SSL connection, but the certificate is issued to another company
- This is a clear example of an untrustworthy connection, so users shouldn't buy from here
How does SSL prevent phishing?
It doesn't because phishing is a server-side problem (trustworthiness of legitimate users)
What is a possible solution to phishing with SSL?
Multiple communication channels, server sends user a temp authorisation number to prove their identity
What is a drawback to multiple communication channels to tackle phishing?
Clients need to have an existing relationship with the server e.g. the server needs to know their legitimate phone number
What is security's worst enemy?
Complexity!
Are many flaws of IKE known?
No, but that's because IKE is too complex to find everything...