Kinetics - 6, 16
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:17 PM on 9/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Collision Theory
1. reactant particles must collide with the **correct orientation**
2. reactant particles must collide with sufficient E(a)
2
New cards
Activation Energy
Minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must require for a reaction to occur.
3
New cards
E(a)
energy between reactants - energy in transition state
4
New cards
Transition state
highest energy state on a reaction coordinate, point at which new bonds are being formed and old bonds are being broken
5
New cards
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
In an ideal gas, the kinetic energy of the molecules is spread over a range of values
6
New cards
Total area under the Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution =
Total number of particles in the sample
7
New cards
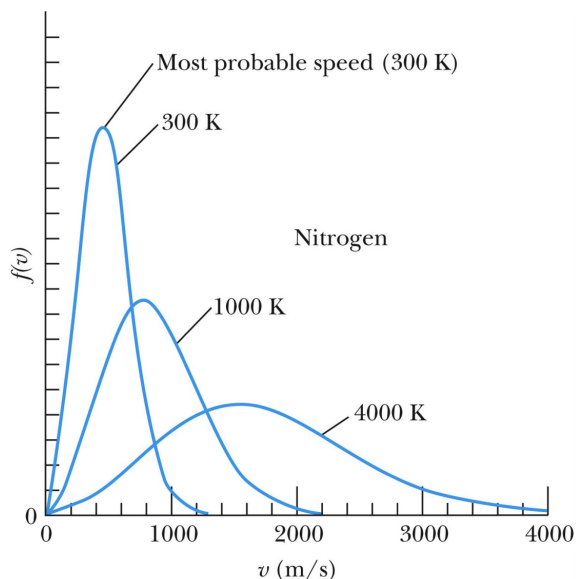
MBDC - When temperature increases
Curve flattens out
8
New cards
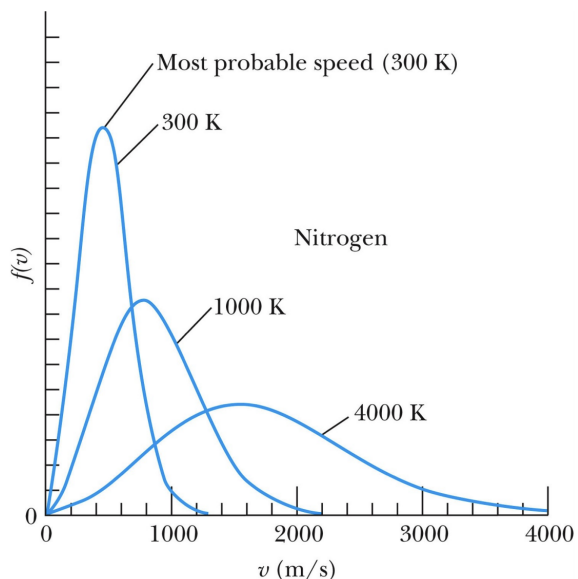
MBDC - When temperature decreases
curve is taller and leaner
9
New cards
MBDC - When lower molar mass
Higher speed, curve flattens
10
New cards
MBDC - When heavier molar mass
slower, taller & leaner
11
New cards
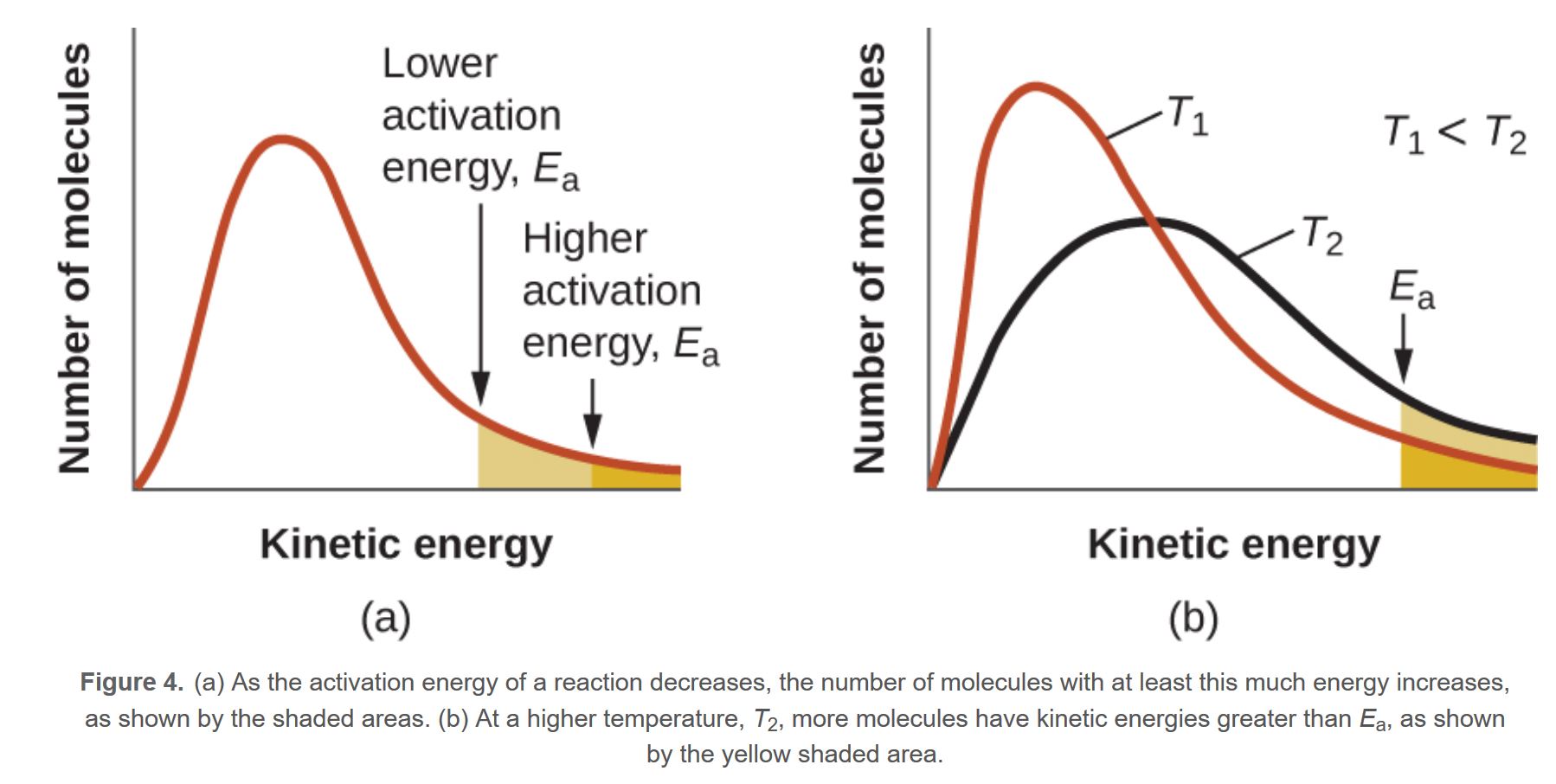
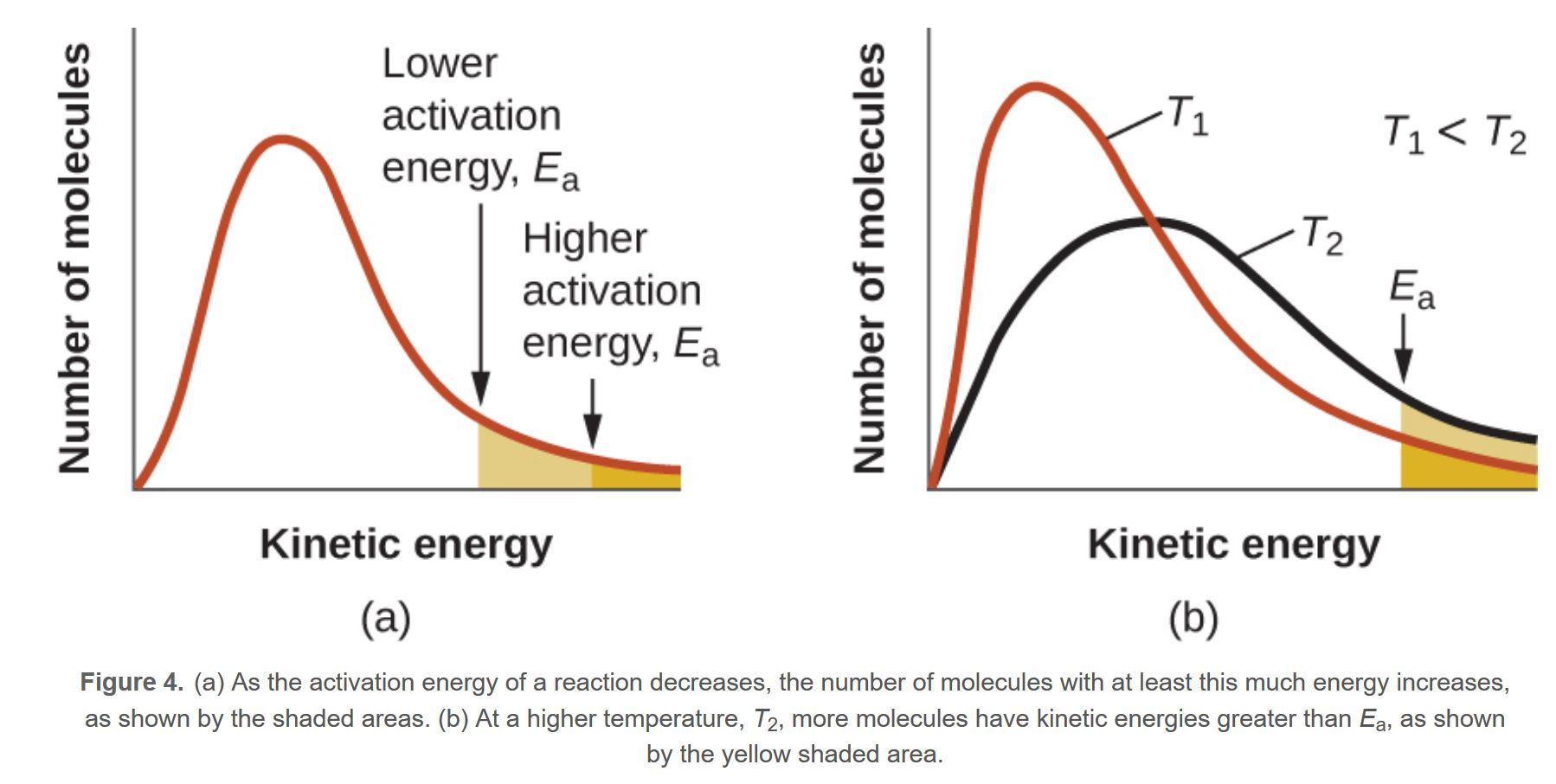
MBDC - Activation Energy
The lower the activation energy the more particles are eligible to take part in the reaction, shaded region larger
12
New cards
Find Activation Energy: Formula
lnK = (-E(a)/R) x (1/t) x lnA \*divide by 1000 as R is in J
13
New cards
Comparing 2 conditions
ln(k1/k2) = -Ea/R (1/T2 - 1/T1)
14
New cards
ROR
Change in concentration or pressure of a reactant or products per unit of time.
15
New cards
Calculate average rate of reaction for a gaseous rxn carried out in a 2.5 dm^3 vessel if 0.04 mol of product was produced in 20 seconds.
1. c = n/v = 0.04/2.5 = 0.016
2. ROR = Δc/Δt = 0.016/20 seconds
3. average ROR = 8 x 10^-4 **mol/dm^3/s**
16
New cards
ROR =
Δc/Δt
17
New cards
How to calculate Instantaneous rate
1. Draw a tangent to the curve at a particular time
2. divide Δy/Δx to find gradient
18
New cards
Metal + Acid
Salt + H2
19
New cards
Metal Hydroxide + acid
Salt + water
20
New cards
Metal carbonate + acid
salt + CO2 + H2O
21
New cards
Metal Oxide + acid
Salt + water
22
New cards
FAROR: Concentration
1. as concentration increases
2. number of collisions increase
3. between reactant particles
4. leading to greater successful collisions
23
New cards
FAROR: Temperature
1. as temperature increases
2. particles gain kinetic energy
3. leading to frequent collisions
4. leading to greater successful collisions
24
New cards
FAROR: Surface Area
1. as surface area increases
2. more reactant particles are exposed to other reactant particles
3. leading to greater successful collisions
25
New cards
FAROR: Pressure
1. As pressure in a system increases
2. distance between reactant particles decreases
3. leading to more frequent collisions
4. leading to greater successful collisions
26
New cards
FAROR: Catalyst
1. substance that **alters ROR**
2. by **lowering its activation energy**
3. through an **alternate path**
4. without **getting used up** during the reaction
27
New cards
Transition Metals as catalysts
1. surface of transition metals are slightly positive due to transition metals
2. lone pairs in reactant particles are attracted to slightly positive charge.
3. temporary polar bonds formed till other reactant particles collide with it.
4. lowering activation energy
28
New cards
First Order Reaction, units
s^-1
29
New cards
Second order Reaction units
mol^-1dm^3s^-1
30
New cards
Third order Reaction units
mol^-2dm^6s^-1
31
New cards
Arhennius Factor ‘A’ =
frequency of collisions & probability that collisions are in the correct orientation.
32
New cards
Find Ea graphically
Graph of lnK vs 1/T where m = -Ea/R
33
New cards
Plausible Reaction mechanisms
1. Elementary steps must add up to give the overall balanced equation
2. Reaction mechanisms must be consistent with experimental data
34
New cards
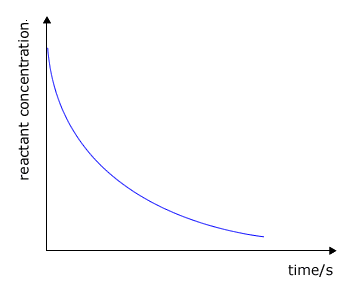
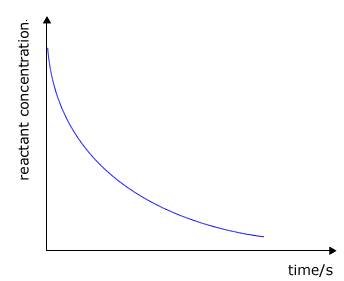
Reactants - concentration/pressure vs time
35
New cards
Products - concentration/pressure vs time
36
New cards
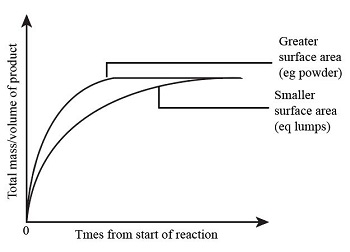
Surface area = powder vs granules on product conc.