Cognitive Psychology - Determinants of Selective Attention
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
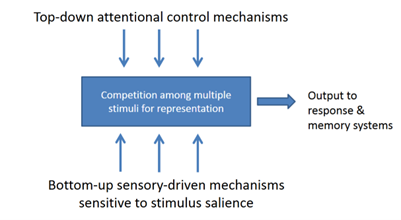
Biased Competition Theory (Desimone & Duncan, 1995)
Theory suggesting Top-Down Attentional Control Mechanisms + Bottom Up Sensory driven mechanisms contribute towards competition among multiple stimuli for representation, leading to a response (output).
What kinds of stimuli can “capture” our attention?
High Salient (Noticeable) Stimuli
Movement
Stimuli relevant to us
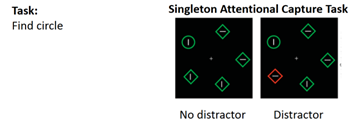
Salient “Singletons” Task (Theeuwes, 1992)
Task involving searching for an “odd one out” (e.g. circle not square). coloured “singletons” that aren’t the target result in reaction time being slowed. Shows top-down mechanisms does not only focus on shapes.
Stimulus Driven Selection Theory (Theeuwes)
Theory suggesting an initial bottom-up sweep is performed, where particularly salient stimuli draws attention. Selection takes place within an attentional window.
What can vary the size of Attentional Windows?
Spatial Cues
Saliency Map
An image that shows how salient each pixel is for a given task, such as object recognition.
Contingent Capture Theory (Folk & Remington, 1992)
Theory suggesting attention is captured by stimuli relevant to goals. (not stimulus-driven)
Cue-Capture Task
Task where invalid cues slows reaction time. But it was contingent on relation to the task (colour captured attention when target was defined by colour)
What did Bacon & Egeth (1994) propose about cue capture tasks?
Suggested that we have a strategy of spotting the “odd one out” so colour may be relevant to top-down goals. Theeuwes argued against this saying they were reducing salience of singletons.
Abrupt Onsets
Suggests suddenly appearing stimuli can produce stimulus-driven capture. Yantis et al found onsets produced attentional capture but colour did not.