evolution of life
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
definition for life
no universal defenition
in biology: physical entities that have biological processes (eg. metabolism & birth)
to be functionally alive 3 parts are required:
information that is physically represented (= DNA & RNA)
Machinery that uses energy to make copies of the information (= replication)
structure that houses the information and the machinery
modern ‘tree’ of lfie
Eukaria
single or multicellular
eukaryotes: DNA in nucleus
most complex
Archaea
single celled
prokaryotes: no nucleus
can adapt to extreme environments
Bacteria
single celled
prokaryotes: no nucleus
most succesful form of life
phylogenetics
study of the evolutionary history of life
first it used only phenotype (anatomical similarities & differences) & later also genotype (genetic similarities & differences)
Which principle is used in phenotypical comparisons in phylogenetics
PARSIMONY PRINCIPLY = phylogeny that requires the least amount of evolutionary changes is most likely to be correct
Complications with parsimony principle
1) hard to distinguish analogous and homologous traits
similar adaptions can evolve independently to solve similar environmental challenges
2) nature does not always work in simplest possible way
came clear with advances in genetics
some species look totally different but are closely related (eg. platypus and hedgehog - vogelbekdier en egel)
earth has not been a stable environment
environmental conditions on this planet have been extremely diverse during its history → organisms have been shaped acordingly during different periods
1) earth’s position in space in relation to the sun
eliptical orbit
variation of tilt
axial wobble
2) regular incidents (eg. movements of tectonic plates)
3) unpredicted incidents (eg. meteorites)
eon
history of life is divided into eons → ‘similar’ environmental conditions and dominant groups of species within 1 eon
between eons = drastic environmental changes that triggered mass extinctions
When did different forms of life evolve
precambrian eon (archean area): simple life (3.8-3.6 bya)
where?→ we don’t know only hypotheses (eg. deep ocean / thermal vents…)
what kind? → simple life
Proterozoic eon: multicellular eukaryotic organisms (2bya)
cambrian eon: multicellular animals (600 mya)
Ordovician period: first chordates from which vertebrates evolved (460 mya)
2 facts about early earth
sun ignited ± 5 billion years ago
hadean eon: earth changed from liquid to solid & crust cooled
early eath was different
less oxygen (>1%)
violent volcanic activity
faster rotation speed
hostile environment for life
Prime candidate to be the first form of life (but…)
self replicating RNA
but they do not leave fossils → no traces of themselves…
life has changed the environment on earth and environmental changes have changed life
give an example of the first
bacteria started with fotosynthesis → O2 in atmosphere → protective ozone layer around the planet
What’s good in extinctions?
large number of species dissapears → ecological richness open up → species that survived can employ this ecological niches
adaptive radiation
eg different type of mammals & birds: dinos went extinct → new ecological niches opened → new species of mammals & birds started to diversify from those species that survived the evolutionary bottle neck that killed the dinos
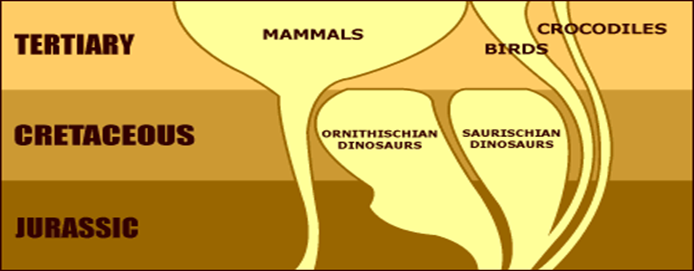
last common ancestor
the last common ancestor of two species is the species in the past form which the two species started to differentiate
common ancestor for all known life (when + name)
last UNVIERSAL common ancestor
3800 mya
‘LUCA’
timeline of lives
5 billion ya: sun is born & pretty soon after that the solar system (earth & moon) formes
How did the moon formed? → earth had a sister planet (Thea) & she ran into earth splitting the planet in 2 → moon
In the early solar system the moon was much closer to earth & it is gradually drifting away as it orbit is distancing from the planet => earth spin is constantually slowing & slowing as the gravitational pool of the moon gets weaker & weaker
3.8 billion ya: first forms of life are born (cells without nuclei)
3.5 billion ya: fotosyntheses => rise of oxygen in the atmosphere => ozone layer
2 billion ya: eukaryotes (first cells with nuclei)
Cambrian explosion: multicellular animals
300 million years ago: reptiles → dinos
250 millions ya: birds & mammals
Only after dinos went extinct, birds & mammals started massive adaptive radiation into different species
10 millions ya: primate evolution
However, the modern human (homosapien) only have been around for the last 200 000 years (= short in evolution time scale)