APEX AP Macroeconomics Unit 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Economics
the study of human behavior constrained by scarcity
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole
Microeconomics
the study of the economic behavior and decision making of small units, such as individuals, families, and businesses
Resources (factors of production, inputs)
land, labor, and capital (sometimes entrepreneurship)
Land
all the natural resources that come from the earth
Labor
all human effort, physical and mental
Capital
all the machinery, equipment, buildings, and human skills used to manage and produce goods and services
Physical Capital
includes machinery, buildings, and equipment
Human Capital
includes the knowledge and skill used to make goods and services, but not natural ability
Entrepreneurship
the process of starting, organizing, managing, and assuming the responsibility for a business
Market system
The price of a good or service depends on its scarcity. Items with high prices are generally more scarce, and items with low prices are generally less scarce. The US is an example of a market system.
Scarcity depends on...
availability and value
Free goods
When the amount of a good available exceeds the amount that people want, it is a free good. It has a zero price.
Market
"A place where buyers and sellers exchange goods or services for a price they agree on." For economists, a market exists whenever and wherever an exchange takes place.
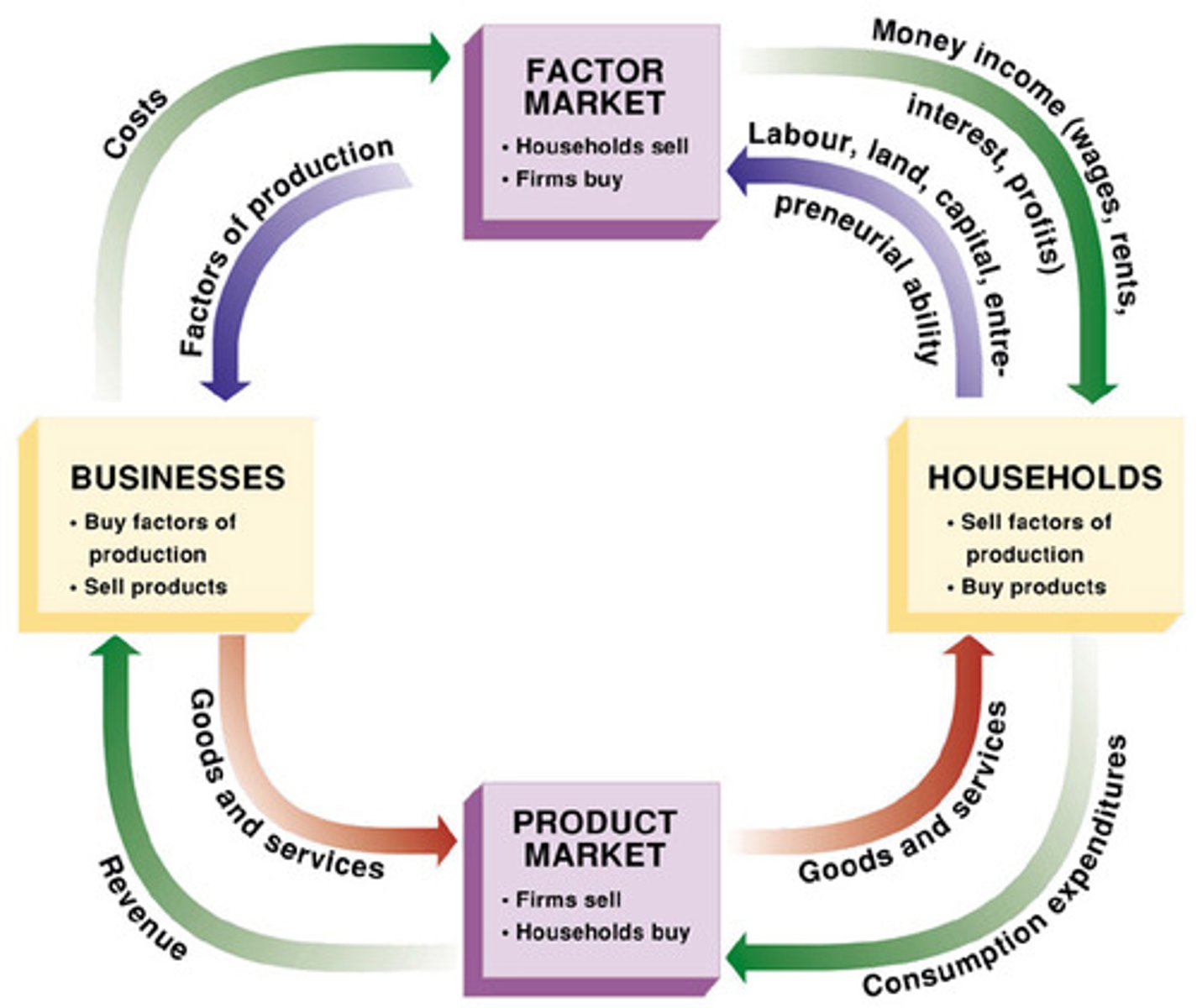
Factor Markets (Resource Market)
Resources and semi-finished products are exchanged in the factor market. Resource owners receive rent for their land, wages for their labor, and interest for their capital.
Product Market
Goods and services are exchanged in the product market. Sellers receive the selling price for goods and services.
Circular Flow of Economic Activity
Resource owners sell their resources to business owners in the factor market. In exchange they get rent, wages, or interest. The business owners then use the resources they bought to make goods or services. Finally, they sell these goods and services in the product market, to the resource owners.
Three Fundamental Economic Questions
• What goods and services will be produced?
• How will those goods and services be produced?
• Who will get those goods and services?
The answers to these questions determine the production and allocation of resources, goods, and services.
Traditional Economy
Decisions are based on the decisions, customs, or religious practices of ancestors. Ex: India
Command Economy
An economic system that is centrally planned. The country's resources and means of production are publicly owned, and government officials make the economic decisions
Market Economy
buyers and sellers use prices as a medium to exchange goods in free markets. In other words, price is used to indicate the value that buyers and sellers place on goods and services in unregulated markets. In a pure-market economy, people act in their own best interest, producing whatever gives them the most profit, buying whatever gives them the most satisfaction. Based on ideas of Adam Smith
U.S. Economy
U.S. economy is based on the idea of a market economy. It promotes the ideas of capitalism and free markets, and most of the means of production are privately owned. It also includes aspects of both command and traditional economies (i.e., the U.S. Postal Service and the custom of tipping). Government regulation of private businesses is another command element in the U.S. economy.
Four Economic Goals
1. Economic efficiency
2. Economic security (maintain stable prices)
3. Economic equity (full employment)
4. Economic growth
The Fallacy of Composition
the incorrect belief that what is true for the individual, or part, must necessarily be true for the group, or the whole
Assuming Association is Causation
The incorrect belief that if 2 variable happen at about the same time, one causes the other.
Bad Sample Selection
Using statistical analysis on a sample of the population that's not representative of the whole.
faulty ceteris paribus
The incorrect assumption that variables are constant when they aren't.
Ignoring Secondary Effects and Unaccounted Variables
This happens when investigators forget to look at some effect of changes in a variable or don't take into account variables that have an influence on the outcome.
measurement error
Changes in experimental results that can be attributed to slight differences in how measurements are taken.
Ceteris Paribus
a Latin phrase that means "all other things held constant"