2.7 VSEPR and Hybridization
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
The valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory predicts the:
geometries of molecules and polyatomic ions
The shape, or geometry, of a molecule is determined by:
lone pairs or bonds on the central atom of a molecule
Why is the shape or geometry of a molecule determined by the lone pairs or bonds on the central atom of a molecule?
these areas of electron density or “charge clouds” will minimize electron – electron repulsions by positioning themselves as far apart as possible.
Lone pairs of electrons repel more/less than bonds
more
Lone pairs of electrons tend to expand/compress the angle between bonding atoms.
compress
Lone pairs and bonds are called:
charge clouds
What should you do first when determining molecular geometry?
Draw lewis dot structure
Double and triple bonds should be counted as how many charge clouds?
one
Single electrons are counted as how many charge clouds?
one
How to determine geometry shape if there are more than 1 central atoms?
determine the geometric shape of each central atom individually
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 2 sigma bonds:
linear, sp, 180 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 2 sigma bonds

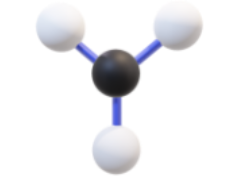
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 3 sigma bonds:
Trigonal planar, sp², 120 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 3 sigma bonds
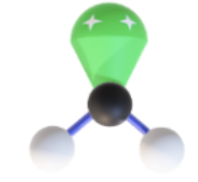
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pair
Bent, sp², <120 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pair
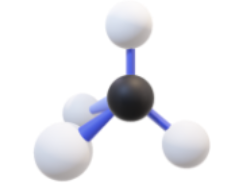
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 4 sigma bonds
Tetrahedral, sp³, 109.5 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 4 sigma bonds:
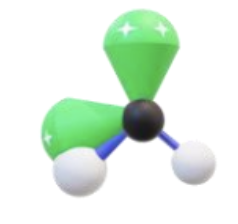
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 3 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pair
Trigonal pyramidal, sp³, <109.5 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 3 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pair

Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pair
Bent, sp³, <109.5 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pair
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 5 sigma bonds and 0 unshared electron pairs
Trigonal bipyramidal, sp³d, 90 degrees and 120 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 5 sigma bonds and 0 unshared electron pair
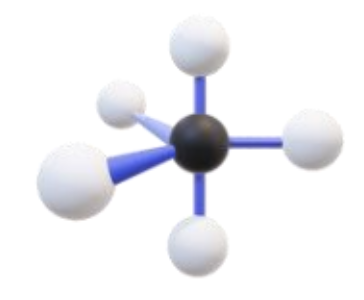
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 4 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pairs
See-saw, sp³d, 90 degrees and 120 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 4 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pairs
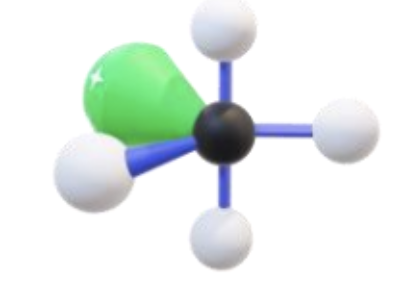
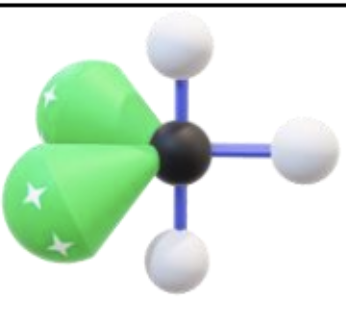
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 3 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pairs
T-shaped, sp³d, 90 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 3 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pairs
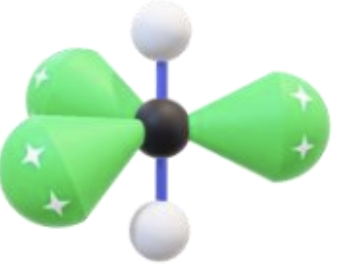
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 3 unshared electron pairs
Linear, sp³d, 180 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 2 sigma bonds and 3 unshared electron pairs
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 6 sigma bonds and 0 unshared electron pairs
Octahedral, sp³d², 90 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 6 sigma bonds and 0 unshared electron pairs
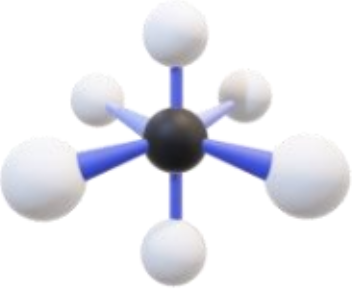
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 5 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pairs
Square pyramidal, sp³d², 90 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 5 sigma bonds and 1 unshared electron pairs
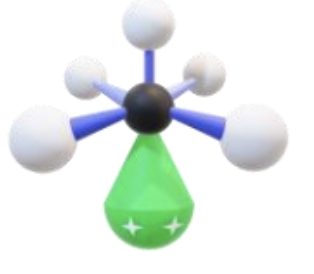
Name, hybridization, and bond angle for molecule with 4 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pairs
Square planar, sp³d², 90 degrees
Diagram for molecule with 4 sigma bonds and 2 unshared electron pairs
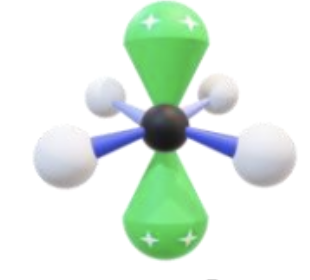
To explain molecular geometries, we assume that:
the atomic orbitals on an atom mix to form hybrid orbitals.
The shape of a hybrid orbital is a:
mix of the shapes of the original atomic orbitals such as s (spherical) and p (dumbbell).
The total number of atomic orbitals on an atom remains constant / changes
remains constant
the number of hybrid orbitals on an atom equals the:
number of atomic orbitals that are mixed
Why is the number of hybrid orbitals on an atom equal to the number of atomic orbitals that are mixed?
The total number of atomic orbitals on an atom remains constant
In methane, (CH4), the 2s and three 2p orbitals of carbon mix to form:
four sp3 hybrid orbitals
Relationship between the sum of the superscripts on the hybrid orbitals and the number of electron clouds around the central atom:
equal
The sum of the superscripts in sp3 equals:
4
Overlapping orbitals from a single bond are known as:
sigma bonds (σ)
Sigma bonds are ______ bonds
very strong
Double and triple bonds are formed from:
unhybridized p orbitals
Double and triple bonds are called:
pi bonds(π)
A double bond contains ______ sigma (σ) and ______ pi (π) bond(s).
one, one
A triple bond contains ______ sigma (σ) and ______ pi (π) bond(s).
one, two
The presence of pi bonds means that bonds are:
unable to rotate
The presence of pi bonds leads to:
geometric isomers
Why does the presence of pi bonds lead to geometric isomers?
The presence of pi bonds means that bonds are unable to rotate
Molecules have the same atoms but have different arrangements and are not superimposable.
Geometric isomer
As the number of bonds between two atoms increases, the bond increases/decreases in strength and energy
increases
As the number of bonds between two atoms increases, the bond increases/decreases in length
decreases
Pi bonds pull atoms closer together / push atoms farther apart
pull atoms closer together
The number of bonds between two atoms
Bond order
When the bond order increases, the bond length increases/decreases
decreases
When the bond order increases, the bond energy increases/decreases
increases
Bond order of single bond:
1
Bond order of double bond:
2
Bond order of triple bond:
3
For a molecule that exhibits resonance, we see that the bonds that have resonance are experimentally determined to:
be the same length
In an ozone molecule, is the single bond or the double bond longer?
Same
Bond lengths of single and double bonds in ozone molecules
Both halfway between a single and double bond length
Bond order of single and double bonds in ozone molecules
1.5
How to calculate bond order of molecules that exhibit resonance?
number of bonds shared divided by number of shared bonds between two atoms (could be any bond type)
When electrons are shared in a covalent bond, the shared electrons spend more time around the:
more electronegative element in the bond
Shared electrons spending more time around the more electronegative element in the bond gives it a:
partial negative charge (ẟ-)
Shared electrons spending more time around the more electronegative element in the bond gives the less electronegative element a:
slightly positive charge (ẟ+)
Covalent bonds form _____ molecules
polar
Why do covalent bonds form polar molecules?
Shared electrons form more time around more electronegative element, giving the more electronegative element a partial negative charge and the less electronegative element a slightly positive charge
In a polar molecule, the arrow in the diagram points to the:
More electronegative element
Is HCl a polar molecule?
Yes
Why is HCl a polar molecule?
It has a dipole moment that isn’t cancelled out
If a molecule is polar, it has a:
dipole moment
How to know if a molecule is polar:
know if the bonds are polar and the overall shape of the molecule
Drawing in the arrows pointing to the more electronegative element in equal and opposite directions demonstrates that the molecule has:
polar bonds but is overall a nonpolar molecule.
If the molecular geometry is bent, drawing the arrows indicates that the dipoles:
do not cancel
Why is water a polar molecule?
It has a bent shaped so dipoles do not cancel