3: Software Fault Tolerance
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Detector - Pseudocode
If a predicate (e.g. safety condition) is not met, exit if we prioritise safety over liveness.
Corrector - Pseudocode
If a predicate (e.g. safety condition) is not met, then it is enforced.
May prioritise liveness over safety.
Uses enforcement techniques to ensure the invariant is satisfied again.
Fault Tolerance Techniques - List
Runtime checks
Exception handlers
Forward Error Recovery
Backward Error Recovery
Runtime Checks
Used for detecting errors.
Runtime Checks - Examples
Replication checks - compare outputs of matching modules
Timing checks - use of timers to check timing constraints
Reversal checks - reverse output and check against inputs
Coding checks - parity, Hamming codes, etc.
Reasonable checks - semantic properties of data
Structural checks - redundancy in data structures
Validity checks - divide by 0, array bounds, overflow
Exception Handlers
Detectors raise exceptions (interrupt signals)
Exceptions - Examples
Interface exception
Local/internal exception
Failure exception
Interface Exception
Invalid service request detected by interface detectors and corrected by the service requester.
Local/internal Exception
Problems with internal operations detected by local detectors, and corrected by local correctors.
Failure Exception
Internal errors propagate to the interface and detected by detectors - global correction may be needed.
Forward Error Recovery
Upon error detection, the program attempts to get into a non-erroneous state.
Backward Error Recovery
Upon error detection, the program rolls back to a previously “recorded” good point then restart execution.
Checkpoints
A snapshot of a program’s state in a given point of time, restarting from there if a failure is met.
Recovery Line
A set of checkpoints across all processes to which the programs can be rolled back in the event of a failure.
Checkpoints - Best Practices
OK to checkpoint after a message send
Not OK to checkpoint before a message receive
Recovery Lines - Consistency Requirement
There are no messages that originate after the line and terminate before it (there are no receives without corresponding sends).
Recovery Blocks
A mechanism that runs a series of algorithms in different implementations before running them through an acceptance test.
1 hardware channel, N software channels
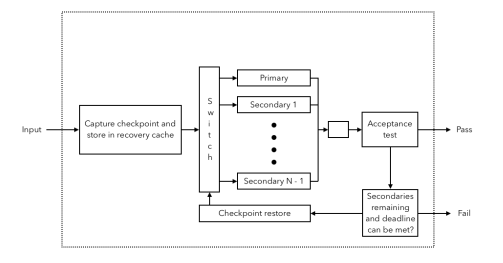
Recovery Blocks - Process
First primary algorithm is run.
If the algorithm execution is error-free, test against the acceptance test.
If the evaluation of the acceptance test is error-free and yields true, the test is satisfied.
If the execution/evaluation was not error-free, where the program will then restore to a state prior to execution
After that, an alternative algorithm is attempted
Recovery Blocks - Possible Failure Reasons
Error in the module operation
Timeout has expired
Raised exception
N-Version Programming
N different developers build different implementations to solve a problem without sharing their approach, and all implementations are run at the same time before being decided on the correct one.
Lack of agreement indicates a problem occurred.
N hardware channels, N software channels
N-Version Programming - Axiom
Will not work if all versions fail on the same inputs.
Will not work if they fail in similar ways.
Fault Injection Analysis
Subjects a system to abnormal conditions, such as introducing faults and errors to assess behaviour.
N-Version Programming - Selection Process
Analyses output, and selects the “best” output - done with a diagnostic program.
N-Version Programming - Problem Handling
Can restart or retry
Neither liveness nor safety critical
Transition to a predefined state followed by later retries
Not recommended when liveness is critical
Designating a version as being more reliable
Liveness is preserved