4. Period 3 oxide reactions with water
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What happens to the O2- ions in the sodium and magnesium oxides, when these compounds react with water?
The O2- ions accept protons from the water molecules to form hydroxide ions.
Which compound has a higher alkalinity?
2NaOH because it is more soluble in water and so therefore forms a more alkaline solution.
Word and symbol equation for sodium oxide with water.
sodium oxide + water → sodium hydroxide
Na2O (s) + H20 (l) → 2NAOH(aq)
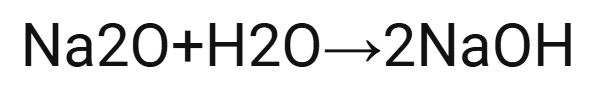
Word and symbol equation for magnesium oxide with water.
magnesium oxide + water → magnesium hydroxide.
Mg0 (s) + H20 (l) → Mg(OH)2 (aq)
What is produced when non-metals react with water?
Acids
Phosphor with water:
Word equation
Symbol Equation
Dissociation of Period 3 acid in water.
Phosphoric(V) acid
H3PO4(aq) → 3H+ (aq) + PO43- (aq)
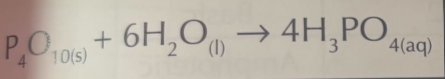
Sulfur dioxide with water
Word equation
Symbol Equation
Dissociation of Period 3 acid in water.
sulfurous aicd
H2SO3 (aq) → 2H+ (aq) + SO3 2- (aq)
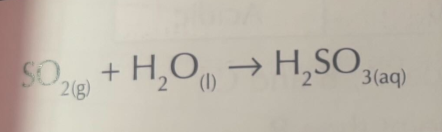
Sulfur trioxide with water
Word equation
Symbol Equation
Dissociation of Period 3 acid in water.
sulfuric (VI) acid
H2SO4 (aq) → 2H+ (aq) + SO4 2- (aq)
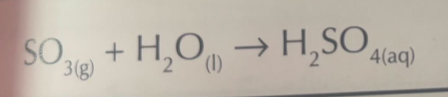
why is silicon dioxide classified as an acid?
due to it’s giant covalent structure, it is insoluble, but it still reacts with bases to form salts, so it is therefore classified as an acid.
what is aluminium oxide knows as?
amphoteric
amphoteric meaning
it can act as a acid or base. partially ionic and covalently bonded.