Chapter 30 Population Ecology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Population ecology
the study of how and why populations change over time
What population characteristics are measured
population density and size, geographic range which is determined by the boundaries of distribution, habitat (specific environment) population dispersion is the distribution of individuals in space, age structure (relevant number of individuals of dif ages), generation time is the average time between birth and birth of its offspring, sex ratio, reproducing individuals in a population.
3 kinds of mark and recapture
hair-snares (put cat nip on a round brush, animals rub on it, their hair is snared), remote cameras, scat surveys
3 patterns of spatial dispersion
Clumped, random (pretty rare), uniform
Demography
statistical study of processes that change a population size and density through time
population growth factors
Birth and imigration
population decline factors
death and emigration
Life tables
Summarize the demographic of a population. Age-specific mortality, Age-specific survivorship, Age-specific fecundity
cohort
group of individuals of similar age
What do organisms use their energy budget for?
Growth, Maintenance, and reproduction. one function is invested in there is less energy for other functions. adjusted to maximize living offspring
Type 1 curve
high survivorship until late in life
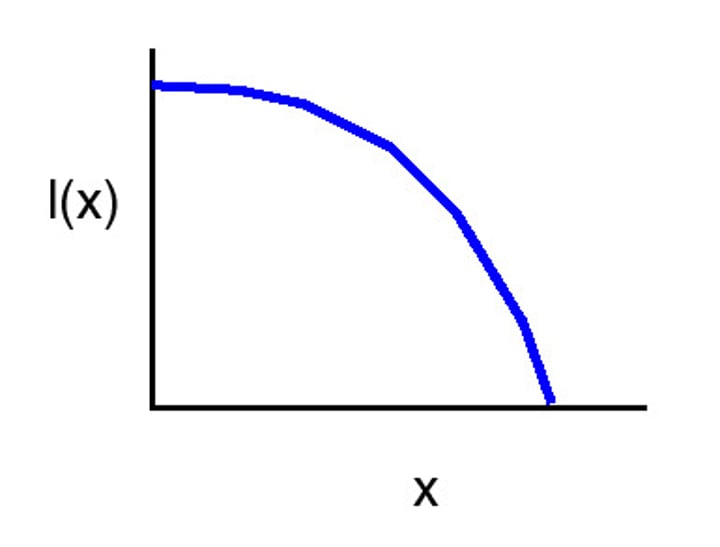
Trade-off between fecundity versus parental care How often to breed: once or repeatedly? Age at first reproduction: when to start reproducing
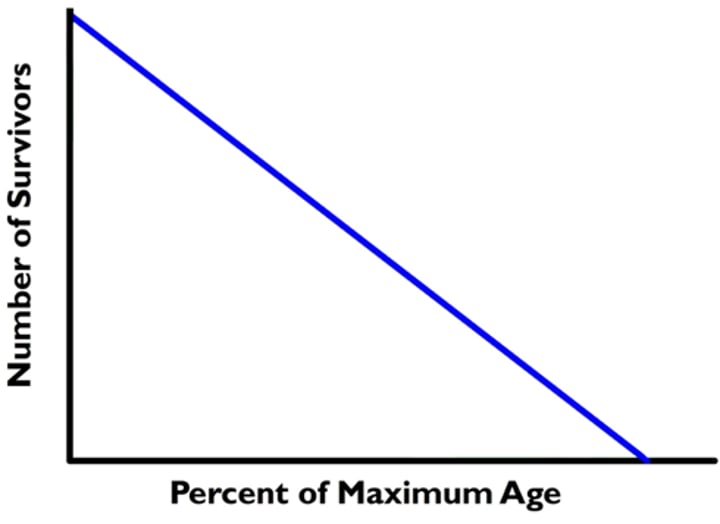
type 2 curve
constant mortality rate at all ages
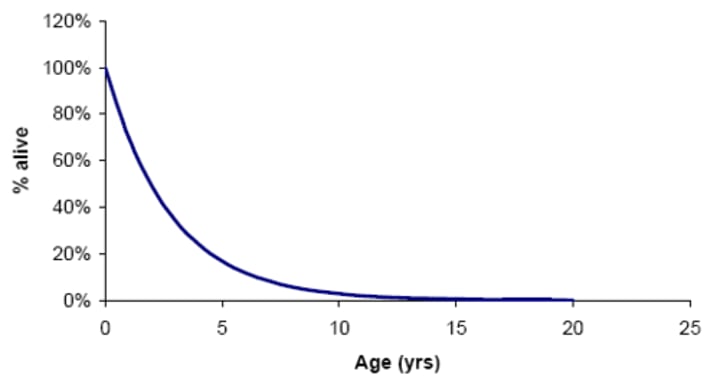
type 3 curve
high juvenile mortality rate followed by low mortality after critical age
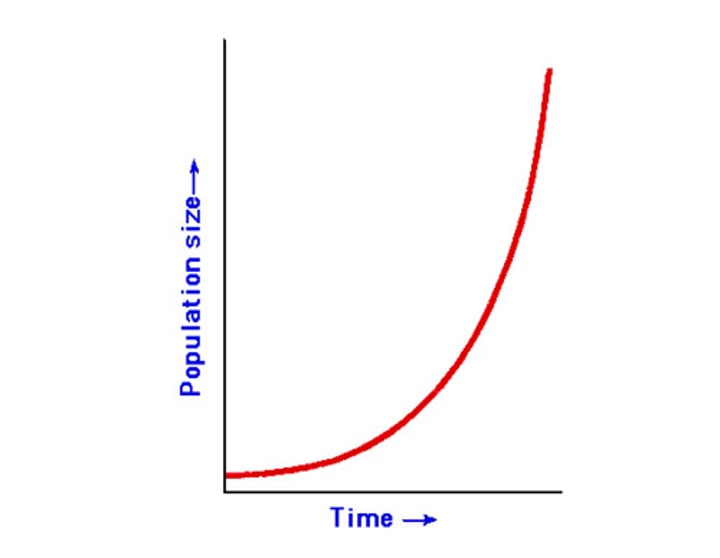
Exponential model
unlimited growth
Logistic models
limited recourse and carrying capacity. Includes effects of resource limitations (intraspecific competition). Carrying capacity (K): Maximum population size that environment can sustain. Per capita population growth rate (r) decreases as N approaches K
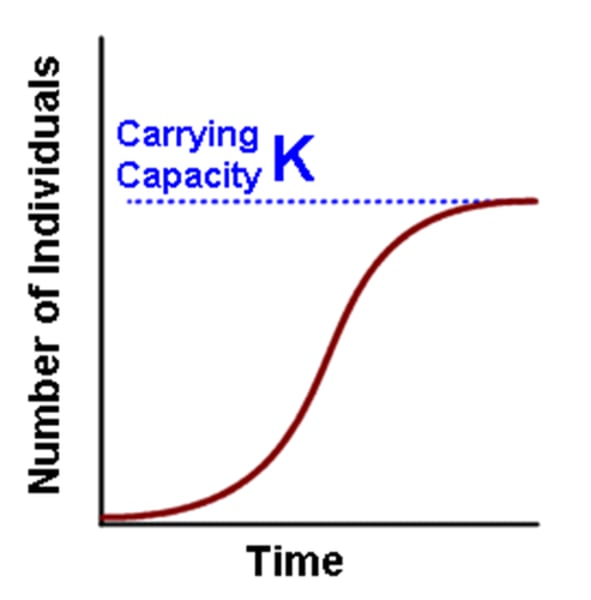
what is this -> dN/dt = rmaxN(K − N)/K
Logistics model equation
Population regulation
Density dependent and independent factors. sometimes population density effects mortality
Density independent factors
reduce population growth regardless of populations size (abiotic environmental factors)
Density dependent factors
Crowding decreases individual growth rates, adult size, and survivorship. Also decreases fecundinty (fertility).
Other density population factors (5)
Competition within populations or between species, Sometimes increases in migratory responses, Predator-prey interactions, Parasites, Infectious diseases can cause density-dependent population regulation
Cyclic fluctuations
periodic changes in the frequency of diseases and health conditions over time. some animal populations experience cyclic fluctuations in population size.
Intrinsic Control
Hormonal and behavioral changes
Extrinsic Control
Relationship between a cycling species and other factors (food or predators)
potential drivers of the hare cycle
Weathe/Climate, Forest Succession, Food Availability and Quality (abundance, plant secondary compounds), Predation (direct and hormones)
Human population growth
Past 200 years: Humans overcame usual density-dependent population regulation; populations now grow exponentially, Expanded into most terrestrial habitats, Increased carrying capacity, Reduced death rates with improved medical care and sanitation
how long did it take the human population to reach 1 billion? 2 billion? 5 billion?
Took 2.5 million years for human population to reach 1 billion 80 years to reach second billion 12 years to jump from 5 billion to 6 billion