Kidney Diseases, UTI
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
•Kidney diseases are a leading cause of death in the United States.
•About 37 million US adults are estimated to have CKD, and most are undiagnosed.
•40% of people with severely reduced kidney function (not on dialysis) are not aware of having CKD.
•In the United States, diabetes and high blood pressure are the leading causes of kidney failure, accounting for 3 out of 4 new cases.
•In 2019, treating Medicare beneficiaries with CKD cost $87.2 billion, and treating people with ESRD cost an additional $37.3 billion.

T
Some health consequences of CKD include:

•Anemia or low number of red blood cells
•Increased occurrence of infections
•Low calcium levels, high potassium levels, and high phosphorus levels in the blood
•Loss of appetite or eating less
•Depression or lower quality of life

Kidney structure
•The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found onthe left and right sides of the body in vertebrates
•
•They are located at the back of the abdominal cavity
•
•In adults they are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) inlength

blood flows into → glomerulus, and fluid is
absorbed in the tubule
fluid and substances needed by body returned to blood in
vessels along the tubule
Tubule funciton
passes water material → bladder
Capillary walls are pierced with openings, known as
fenestrations
The nephron utilizesfour processes to modify the bloodplasma.

•Filtration
•Reabsorption
•Secretion
•Excretion

The kidneys are essential for maintaining the homeostasis of the body:

•Regulation of extracellular fluid and osmolarity
•
•Electrolyte concentrations
•
•Regulation of pH. The kidneys prevent blood plasma from becoming too acidic or basic by regulating ions.
•
•Excretion of wastes and toxins.
•
•The kidneys filter out a variety of water-soluble waste products and environmental toxins into the urine for excretion.

Kidney •Production of hormones

•Erythropoietin (red blood cell synthesis)
•Renin (salt and water balance, blood pressure)

GFR
The measurement of volume filtered through the glomerular capillaries and into the Bowman’s capsule per unit of time.

•Creatinine is a

breakdown product of dietary meat and creatine phosphate found in skeletal muscle.
Aging in the kidney is generally characterized by a spontaneous progressive decline in renal function accompanied by

histological alterations including focal glomerulosclerosis.
•Changes in renal function with age are well documented both in human and animal models.
•
•Baseline homeostasis of fluids and electrolytes is maintained with normal aging
•
•Progressive decline in renal reserve
•
•Impaired salt or water load or deficit all cause
→
Renal complications during acute illnesses

Hypertension accelerate age-related loss of renal reserve and increased vulnerability

T
Structural or functional abnormalities of thekidneys for >3 months, as manifested byeither:
•Kidney damage, with or without decreasedGFR, as defined by
•pathologic abnormalities
•markers of kidney damage, includingabnormalities in the composition of the bloodor urine or abnormalities in imaging tests
•GFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2, with or withoutkidneydamage
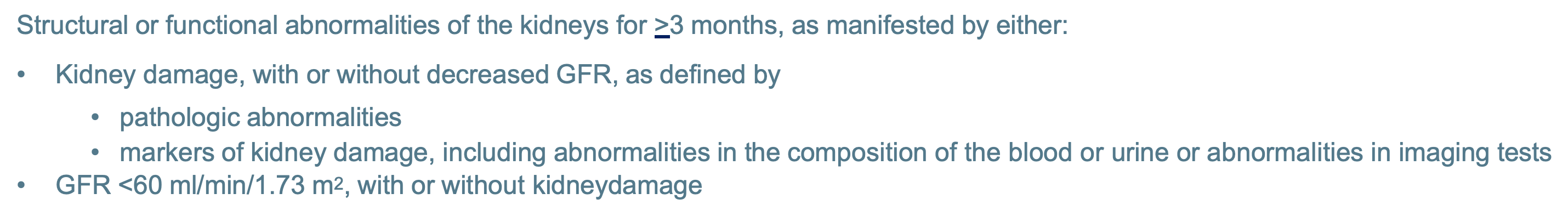
Chronic Kidney Failure
Edema as a result of
renal dysfunction can affect all parts of the body
•Pyuria is generally defined by the

presence of 10 or more white blood cells (WBC/mm3) per high-power field (hpf) in a urine sample, suggesting inflammation of the genitourinary tract.
The presence of bacteria in urine is often asymptomatic and regarded as colonization ( sometimes no treatment required, in some cases antibiotics)

Asymptomatic Bacteriuria:
