Animal + Plant Transport
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is abiotic stress?Give an example
Non-living environmental factor that could harm a plant, e.g mineral deficiency,drought,depleted oxygen supply,pollution
How do plants respond to abiotic stress and herbivory? [4]
Produce anti-freeze enzymes
May contain bitter-tasting tannins
May contain bitter-tasting nitrogen compounds called alkaloids
Release cell-signalling pheromones to trigger defensive responses in other organisms
How does Mimosa pudica respond to being touched?
The leaves fold due to seismonasty
What is a plant tropism?
Directional growth response of plants
What is phototropism?
Response to light
What is geotropism?
Response to gravity
What is hydrotropism?
Response to water
What is thermotropism
Response to temperature
What is thigmotropism?
Response to touching a surface or object
How is leaf loss in deciduous plants controlled? [3]
As leaf ages, cytokinin and auxin levels lower,ethene level increases
Triggers production of cellulase enzymes which weaken leaves by breaking down cell walls in abscission layers
Leaves break from branch, and Suberin layer forms to prevent entry of pathogens
List the functions of gibberellins [4]
Stimulates germination
Elongation at cell internodes
Fruit growth
Rapid growth/flowering
How is germination stimulated? [4]
Seed absorbs water, activating embryo to secrete gibberellins
Gibberellins diffuse to aleurone layer,which produces amylase
Amylase diffuses to endosperm layer to hydrolyse starch.
Hexose sugars act as respiratory substrate to produce ATP as ‘energy currency’
List the functions of auxins [4]
Involved in trophies responses
Control cell elongation
Suppress lateral buds to maintain apical dominance
Promote root growth e.g in rooting powder
Outline the positive phototropic response shown by shoots [5]
IAA diffuses to shaded side of shoot tip
This causes active transport of H⁺ Into cell wall
Disruption to H-bonds between cellulose molecules plus the action of expansins makes the cell more permeable to water
Cells on shaded side elongate faster due to higher turgor pressure
Shoot bends towards light
Outline the gravitropic response of roots [3]
Gravity causes IAA to accumulate on lower side of the root
IAA inhibits elongation of root cells
Cells on the upper side of the root elongate faster, so the root tip bends downwards
How do hormones stimulate stomata to close? [4]
Abscisic acid binds to complementary receptors on guard cell membrane, causing Ca²⁺ Ion channels on tonoplast to open. Ca²⁺ Ions diffuse from vacuole into cytosol
Positive feedback triggers other ion channels to open, causing them to diffuse out of the guard cell
Water potential of guard cell becomes more positive. Water diffuses out via osmosis.
Guard cells become flaccid so stomata close
What hormones maintain apical dominance?
Maintained by the action of auxin, abscisic acid and cytokinins
Explain the experimental evidence that auxins maintain apical dominance
When the site of auxin production, the apex, was removed, these two things happened:
Auxin levels drop,causing abscisic acid levels to drop
Cytokinins diffuse evenly to promote bud growth in other parts of plant, causing lateral buds
Explain the experimental evidence that gibberellins control stem elongation and germination. [2]
Stem elongation-Tall plants have higher gibberellins concentration than dwarf plants
Germination-Mutant seeds with non-functional gibberellins gene do not germinate unless gibberellin is applied externally
How are auxins used commercially? [3]
Rooting powder
Growth of seedless fruit
Herbicides
How are cytokinins used commercially? [2]
Prevents yellowing of lettuces leaves
Promotes shoot growth
How are gibberellins used commercially?
Delate senescence in citrus
Elongation of stalks
Speeding up seed formation
How is ethene used commercially?
Speeds up ripening
Promotes lateral growth
Promotes fruit drop
Outline the gross structure of the mammalian nervous system using a flow diagram
Name the two main divisions of the nervous system
Central nervous system and nervous system
Name the two main divisions of the peripheral nervous system
Somatic
Autonomic
Name the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
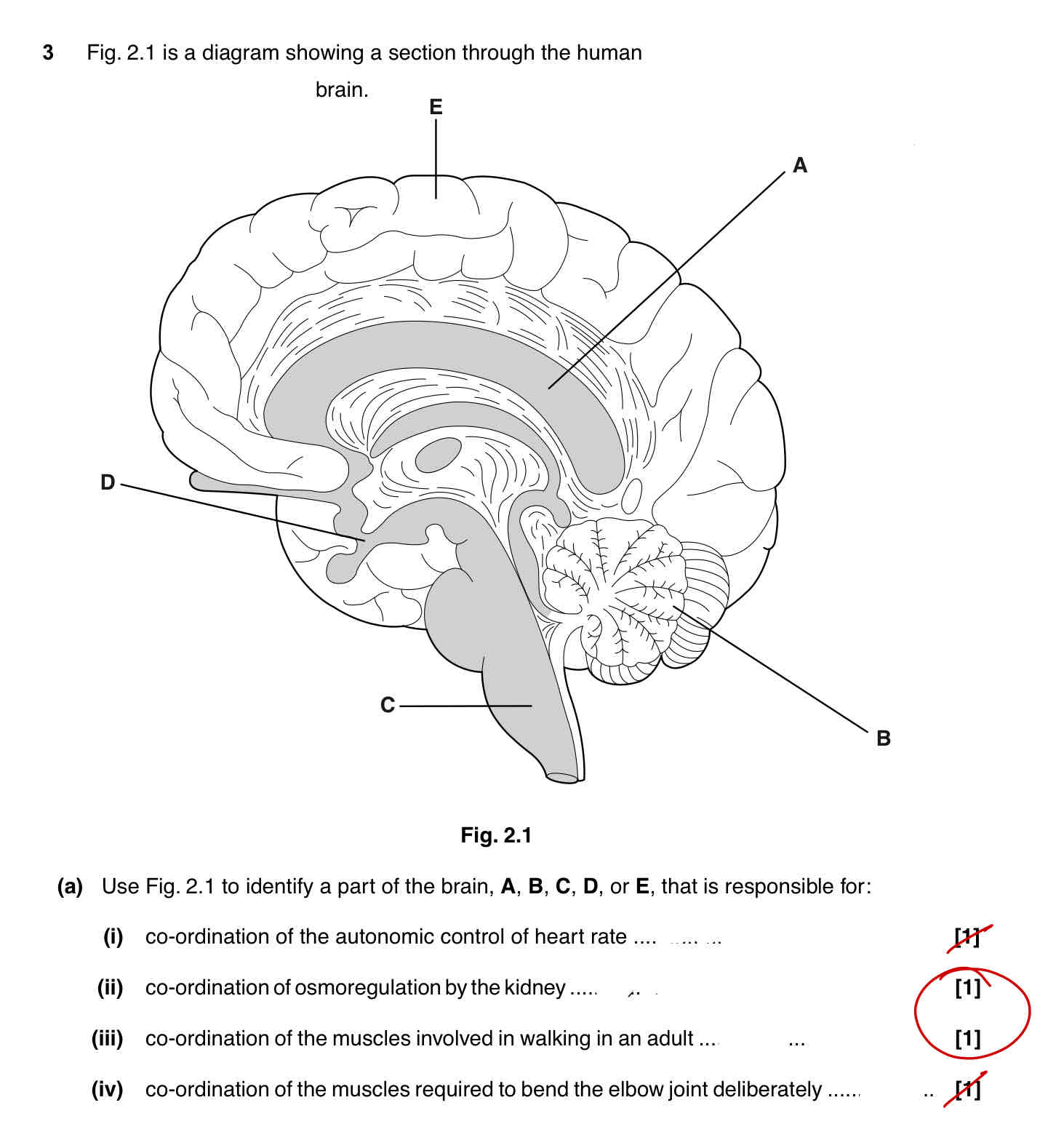
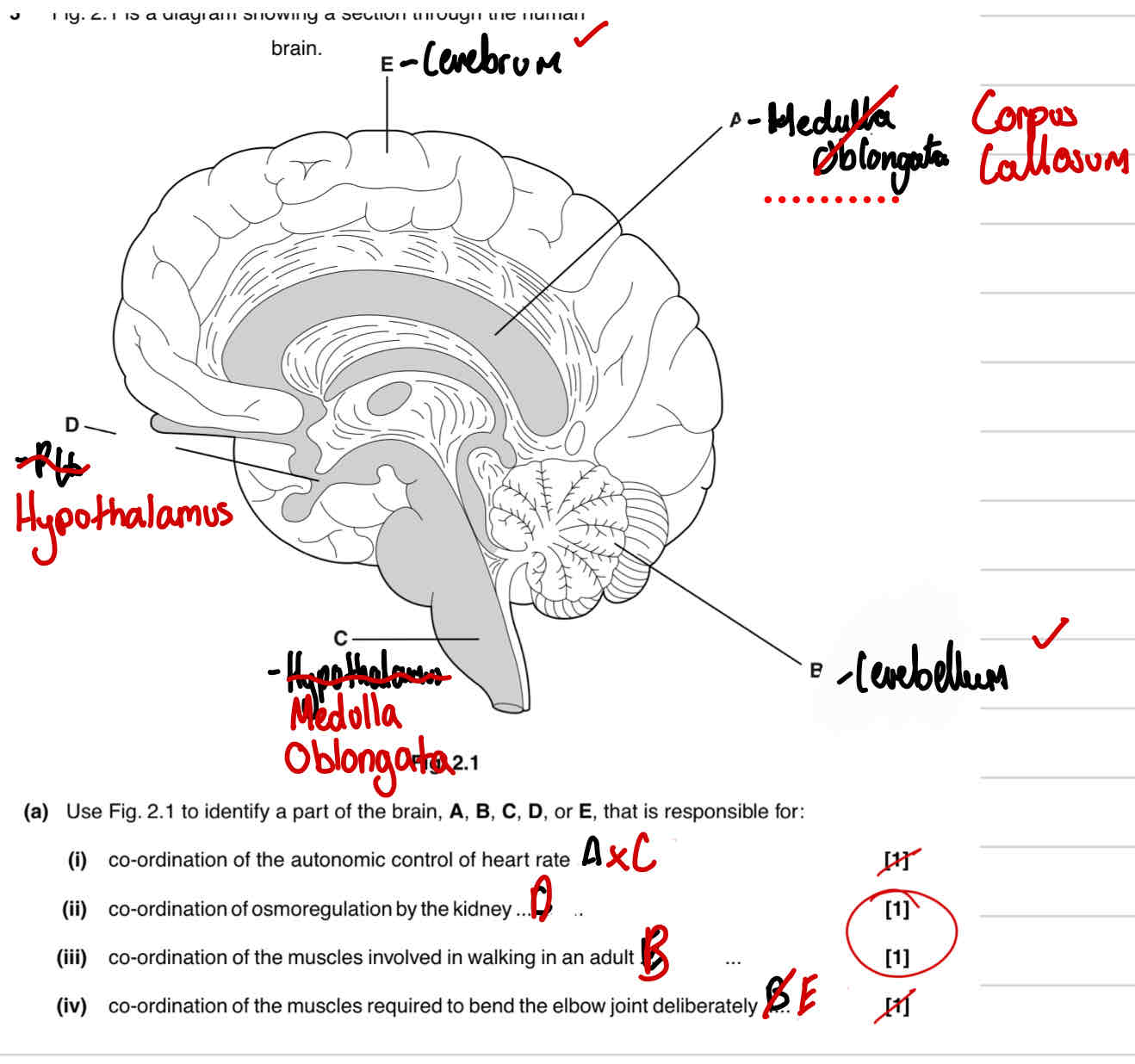
Describe the gross structure of the human brain, including the lobes and their function [4]
2 Hemispheres joined by band of nerve fibres divided into lobes
Parietal lobe-top of the brain-movement,orientation,memory and recognition
Occipital lobe-back of the brain-visual cortex processes signals from the eye
Temporal lobe-beneath the temples-processes auditory signals
What is the function of the cerebllum?
Controls execution of movement, and potential role in cognition
Identify the function of the medulla oblongata
Controls a rage of autonomous functions, including breathing rate and heart rate
Identify the function of the cerebrum
Controls voluntary functions
Identify the functions of the hypothalamus
Includes anterior pituitary gland and is involved in thermo and osmoregulation
Outline what happens in a simple reflex arc
Receptor detects stimulus → sensory neuron → relay neuron in CNS coordinates response → response by effector
What is the survival benefit of a reflex arc?
Rapid response to potentially dangerous stimuli since only 3 neurons are involved
Describe the knee jerk reflex
Tapping patellar tendon stimulates stretch mediated receptors
Impulse travels sensory → motor neuron
Quadriceps contract,inhibiting antagonistic hamstring contraction
Describe the blinking reflex and the reflex arc
Consensual response since both eyelids close when just 1 cornea is stimulated
Sensor neuron of trigeminal nerve → spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve → interneurons→ facial motor nerve → effector muscled orbicularis oculi
What is the fight or flight response?
A stress response to a perceived threat triggering a series of physiological response to prepare the body
Use the secondary messenger model to explain how adrenaline works [5]
Adrenaline is the 1st messenger, forming a hormone-receptor complex
Conformational change to receptor activates G-protein
Activates adenylatye cyclase, which converts ATP → cAMP
cAMP works as 2nd messenger activating the protein kinase A pathway
Results in glycogenolysis
What are the three types of muscle tissue
Skeletal, smooth and cardiac
Describe skeletal muscle function
Antagonistic muscle pairs enable movements
Describe the function of smooth muscle
Enables contraction of walls of blood vessels and intestines
Describe the structure and function of cardiac muscle
Consists of branched uninucleated cells
Myogenic contractions cause a heartbeat
Describe the gross structure of skeletal muscle
Muscle cells are fused together to form bundles of parallel muscle fibres called myofibrils
Each bundle is surrounded by endomycium:loose connective tissue with many capillaries
Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle
Myofibrils: site of contraction
Sarcoplasm: shared nuclei and cytoplasm with lots of mitochondria and ER
Sarcolemma: folds inwards towards sarcoplasm to form transverse T tubules
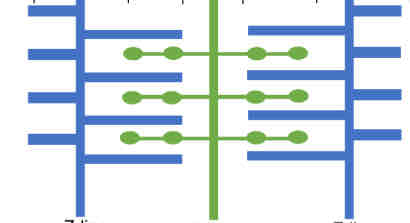
Label this diagram with the zones and bands of a myofibril
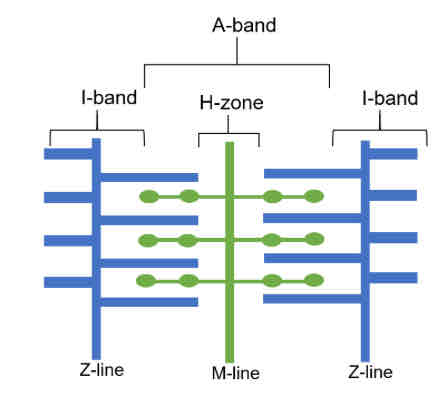
What is the Z line?
Boundary between sarcomeres
What is the I band
The ‘light’ band containing only actin
What is the A band
The ‘dark’ band which overlaps actin and myosin
What is the H-zone
A zone that only contains myosin
How is muscle contraction stimulated? [5]
Action potential arrives at neuromuscular junction, opening voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels open
Vesicles move towards & fuse with presynaptic membrane
Exocytosis of acetylcholine, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft
Ach binds to receptors on Na⁺ channel proteins on skeletal muscle cell membrane
Influx of Na⁺ Causes depolarisation
Explain the role of Ca²⁺ in muscle contraction [3]
AP moves through T-tubules in sarcoplasm, opening Ca²⁺ Channels in sarcoplasm in reticulum
Ca²⁺ binds to troponin, triggering conformational change in tropomyosin
Exposes binding sites on actin filaments so action myosin bridges can form
Outline the ‘sliding filament theory’ [5]
Myosin head with ADP attached forms cross bridge with actin
Power stroke: myosin head changes shape & loses ADP, pulling actin over myosin
ATP attaches to myosin head, causing it to detach from actin
ATPase hydrolyses ATP→ADP + Pi, returning mysoin head to original position
Myosin head re-attaches further along filament
How does sliding filament action cause a myofibril to shorten? [3]
Mysoin heads flex in opposite directions = actin filaments are pulled towards each other
Distance between adjacent sarcomere Z lines shortens
Sliding filament action occurs up to 100 times per second in multiple sarcomeres
Explain the role of creating phosphate in muscle contraction
Phosphorylase’s ADP directly to ATP when oxygen for aerobic respiration is limited
State the name and location of the 2 nodes involved in heart contraction
Sinoatrial node (SAN) : within the wall of the right atrium
Atrioventricular node (AVN): near the lower end of the right atrium in the wall that separates the 2 atria
Name the receptors involved in changing HR and state their location?
Baroreceptors: carotid body
Chemoreceptors: carotid body and aortic body
How does the body respond to an increase in BP? [3]
Baroreceptors send more impulses to the cardioinhibitory centre in the medulla oblongata
More impulses to SAN down vagus nerve via parasympathetic nervous system
Stimulates release of Ach, which decreases HR
How does the body respond to a decrease in blood pressure? [3]
Baroreceptors send more impulses to cardioacceleratory centre in the medulla oblongata
More impulses to SAN via sympathetic nervous system Stimulates release
Stimulates release of noradrenaline, which increases heart rate and strength of contraction
How does the body respond to an increase in CO₂ Concentration? [3]
Chemoreceptors detect pH decrease and send more impulses to cardioacceleratory centre of medulla oblongata
More impulses to SAN via sympathetic nervous system
HR increases, so rate of blood flow to lungs increase, increasing rate of gas exchange and ventilation
Describe the structure of a neuromuscular junction and its function
Synaptic cleft between a presynaptic motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
Acts as the end of neural pathway and always stimulates an excitatory response