Photosynthesis/Cellular respiration quiz
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Last updated 2:25 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
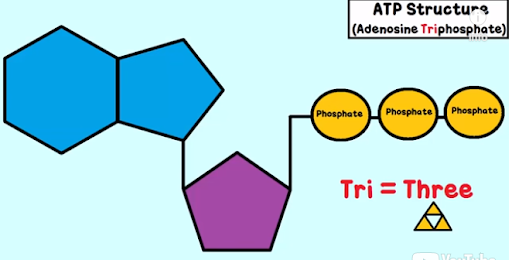
ATP
**stands for adenosine triphosphate**
* Adenosine is the base (blue)
* Tri- for the 3 phosphates (yellow)
* Ribose is the sugar (purple)
* Adenosine is the base (blue)
* Tri- for the 3 phosphates (yellow)
* Ribose is the sugar (purple)
2
New cards
How does ATP work?
* ATP is part of a cycle. ATP + H2O → ADP + P
* (ATP plus water converts to ADP plus a phosphate)
* ATP can **lose** *a phosphate,* __*so energy is released*__, and then becomes ADP (because it now has only 2 phosphates).
\n Then a process, like cellular respiration, can *provide the energy needed* to ***add a phosphate to ADP to make ATP again***
* (ATP plus water converts to ADP plus a phosphate)
* ATP can **lose** *a phosphate,* __*so energy is released*__, and then becomes ADP (because it now has only 2 phosphates).
\n Then a process, like cellular respiration, can *provide the energy needed* to ***add a phosphate to ADP to make ATP again***
3
New cards
How do animals get ATP?
During cellular respiration, animals break down the glucose they consume to make ATP.
4
New cards
What organisms need ATP?
all organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, protists, bacteria and archaea, need to make ATP.
5
New cards
What is cellular respiration?
a metabolic process. The cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
6
New cards
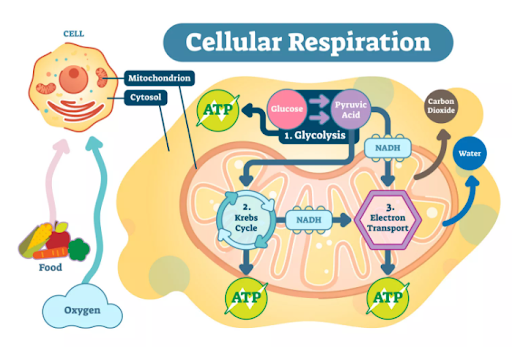
What are the steps of aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC).
7
New cards
Cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
8
New cards
What does **C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O**
mean?
mean?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
9
New cards
Where does glycolysis take place?
The cytoplasm
10
New cards
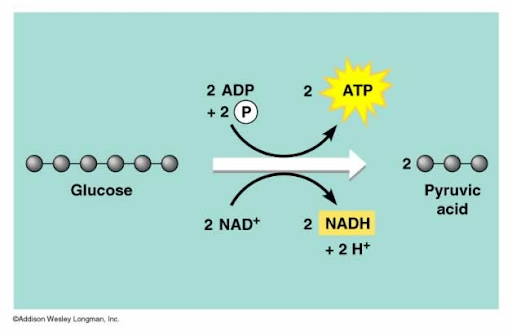
Glycolysis
This is the first step of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid and two NADH molecules.
11
New cards
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
the mitochondria
12
New cards
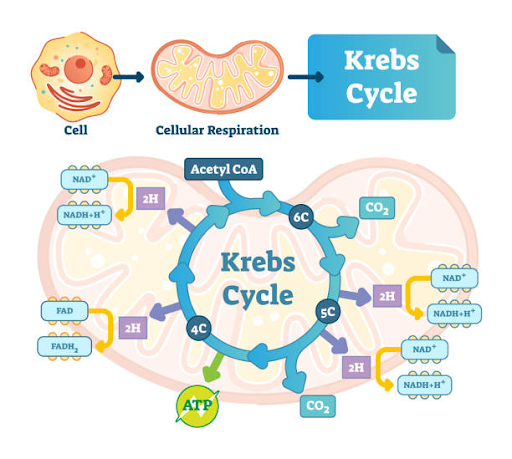
What is the Krebs cycle?
a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells **produce energy** in __aerobic respiration__. It uses oxygen and gives out **water** and **carbon dioxide** as products.
13
New cards
Where does the Electron Transport Chain occur?
Membrane of the mitochondria
14
New cards
What is the ETC?
The final stage of respiration. The parts of the electron transport chain are organized into four complexes labelled I to IV.
All of the electrons that enter the transport chain come from **NADH** and **FADH2** molecules produced during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle.
\
Energy is released when these electrons transfer across the electrochemical gradient, thus allowing ADP to gain a phosphorus, **making ATP**. This process also releases water.
All of the electrons that enter the transport chain come from **NADH** and **FADH2** molecules produced during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle.
\
Energy is released when these electrons transfer across the electrochemical gradient, thus allowing ADP to gain a phosphorus, **making ATP**. This process also releases water.
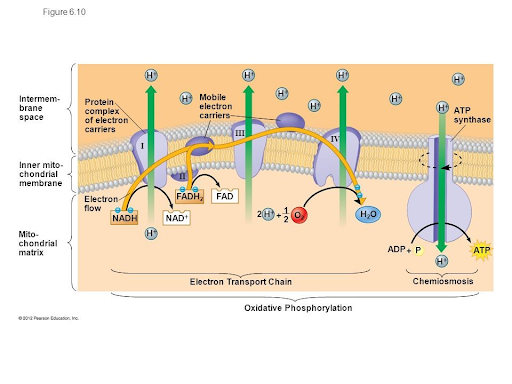
15
New cards
How many atp’s are produced from the ETC?
32
16
New cards
During Cellular Respiration how many ATP molecules are produced
During Cellular Respiration there are 36 ATP molecules produced
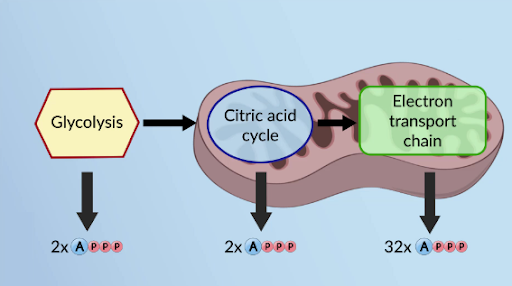
17
New cards
What is the main purpose of cellular respiration?
To produce ATP
18
New cards
What organic(made of carbon)molecule is broken down in cellular respiration?
glucose
19
New cards
Where in the cell does most of the process of cellular respiration take place?
mitochondria
20
New cards
What is about the total of energy that is produced in aerobic respiration?
36-38 ATP
21
New cards
Fermentation
Making ATP without oxygen is called fermentation. When oxygen is in short supply, some organisms use anaerobic respiration instead. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration.
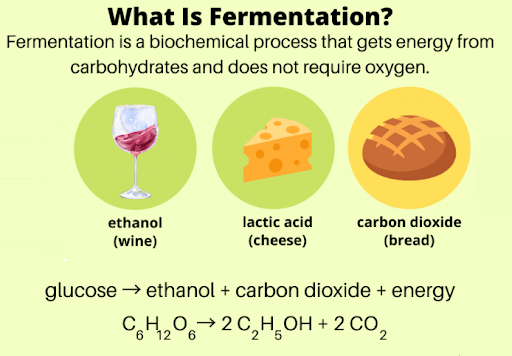
22
New cards
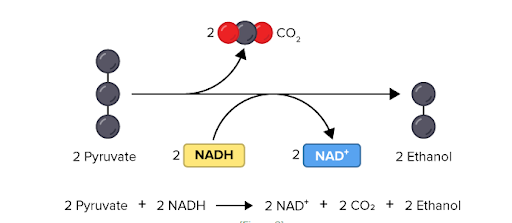
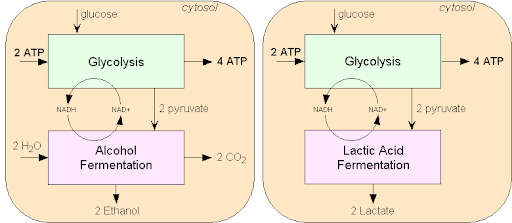
Alcohol fermentation
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate changes to alcohol and carbon dioxide. This is shown in the Figure below. NAD+ also forms from NADH, allowing glycolysis to continue making ATP. This type of fermentation is carried out by plants, yeasts and some bacteria. It is used to make bread, wine, and biofuels.
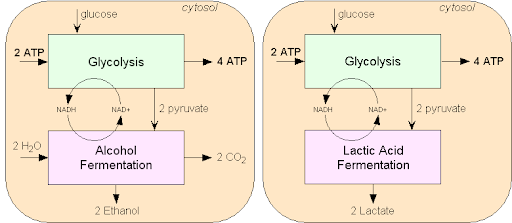
23
New cards
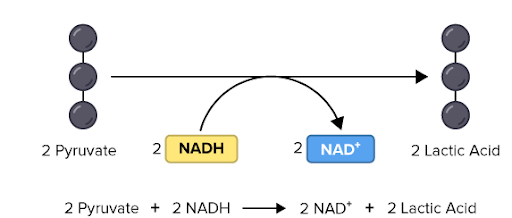
Lactic acid fermentation
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate (also known as pyruvic acid) from glycolysis changes to lactic acid. In the process, NAD+ forms from NADH. NAD+, in turn, lets glycolysis continue.
24
New cards
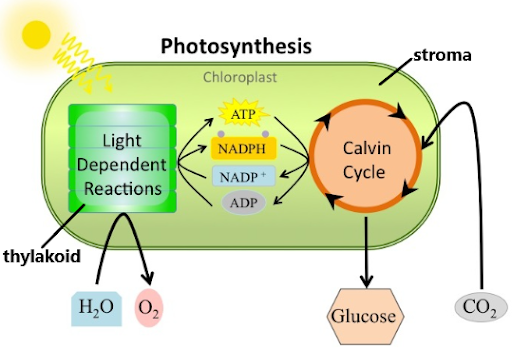
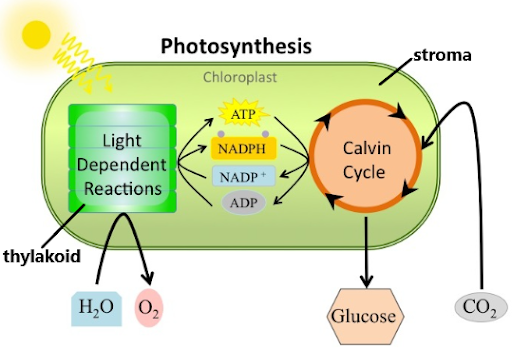
Light Dependent Reaction
**Where:** In the Thylakoid (in the chloroplast)(it contains the chlorophyll)
\
**What happens?**
Light energy is converted into ATP
\
**What is released?**
Oxygen
\
**What happens?**
Light energy is converted into ATP
\
**What is released?**
Oxygen
25
New cards
Light independent reaction
**Where:** In the stroma of the chloroplast
\
**What happens?**
ATP is used make glucose
\
**What happens?**
ATP is used make glucose
26
New cards
What part of the plant carries out photosynthesis?
leaves
27
New cards
What part of the plant **cell** performs photosynthesis?
chloroplasts
28
New cards
In which step is light energy captured and water molecules split?
light reactions
29
New cards
In which step is oxygen gas released?
light reactions
30
New cards
In which step is carbon dioxide turned into carbohydrates (glucose)?
light independent reaction
31
New cards
What is the function of chloryphyll?
it’s where light dependent reactions take place
32
New cards
Products of cellular respiration?
carbon dioxide, water, ATP
33
New cards
The reactants of cellular respiration include:
oxygen and glucose
34
New cards
What organelle of the cell works to produce ATP energy from small glucose molecules?
mitochondria
35
New cards
MAIN product of cellular respiration
ATP energy
36
New cards
T/F: During alcoholic fermentation carbon dioxide it released
true