14. Upper respiratory tract diseases: nose, nasal cavity, oropharynx, trachea
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What are the two main types of cough?
Dry: painful, irritation. Tx: antitussives
Wet: Tx: mucolytic, expectorants
What are the two main types of cyanosis?
Central: hypoventilation, airway obstruction, metHB
Peripheral: vessel obstruction, heart failure, shock
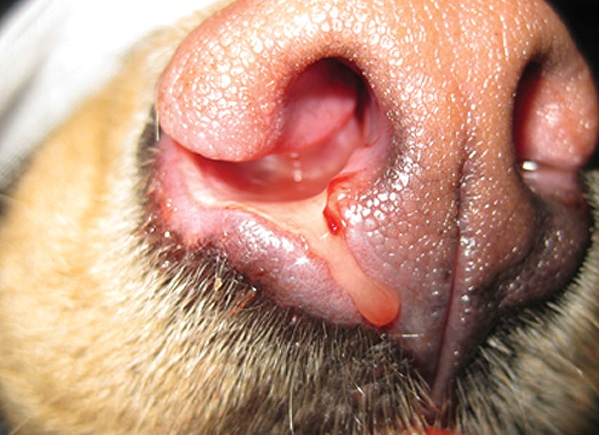
What are the different types of nasal discharge?
Serous (clear liquid): allergy, Kennel cough, foreign body in ear
Muco-purulent (thick, yellow-green): bacterial, fungal, parasitic, neoplasia,
Epistaxis (bleeding): trauma, rodenticides, neoplasia, oro-nasal fistula, dental problems,
Milk: palatoschisis- cleft palate
What are some abnormal lung sounds?
Wheezes (small airway disease)
Crackles (fluid in lungs)
Bronchi (bronchial disease)
Dullness (consolidation)
Absence of sound (pleural disease)
What is induction of cough used for in respiratory examinations?
To assess the nature and productivity of the cough, irritability of respiratory tract
What are some causes of rhinitis?
Infectious
Viral (Kennel cough, Calicivirus, herpesvirus)
Bacterial (Bordetella, chlamydia, mycoplasma),
Fungal (cryptococcus, aspergillosis)
Parasites – Mite: Pneumonyssoides caninum)
Allergy
Tooth root abscess
Oronasal fistula (cleft palate)
Deformed turbinates
Nasal tumours (polyps)
Foreign material (grass seeds/straw)
What are some clinical signs of rhinitis?
Nasal discharge (unilateral or bilateral, serous/purulent/haemorrhagic), sneezing, reverse sneezing, gagging, coughing (dry or wet), lethargy, and oral ulcers
What are the most common pharyngeal disorders in dogs?
Brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome (BOAS) and soft palate disorders
What are examples of diseases of the larynx?
Laryngeal paralysis
Laryngeal collapse
Obstructive laryngitis
Laryngeal neoplasia (rare, more common with adjacent tumours like thyroid carcinoma)
What is laryngeal paralysis?
Loss of normal function of the larynx due to paralysis of the muscles controlling the arytenoid cartilages and vocal cords during inspiration
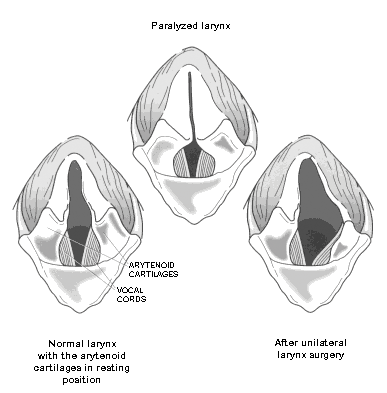
What are some treatments for laryngeal paralysis?
Surgery (laryngoplasty)
Medical management (prednisone)
Conservative management (avoiding exercise)
What is laryngeal collapse?
Weakening of the laryngeal cartilages due to chronic negative pressure from increased inspiratory effort
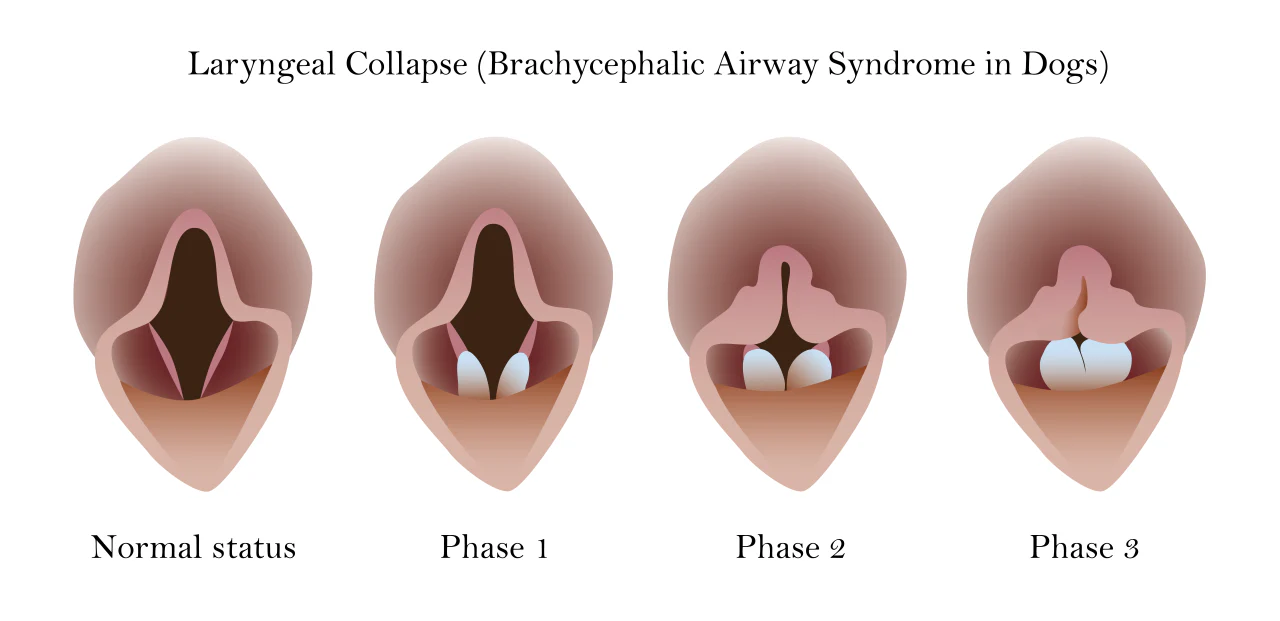
What are examples of tracheal diseases?
Tracheal collapse
Tracheobronchitis
Foreign body
Tracheal rupture
Tracheal tumour
What causes tracheal collapse?
Weakening of tracheal rings or the dorsal ligament
Weakening and stretching of the trachea muscle
Can be congenital, due to obesity, nutritional factors, bacterial infection, neurological issues, chronic airway disease, or idiopathic
What are the grades of tracheal collapse?
1-4
What are some treatments for tracheal collapse?
Cough suppression (butorphanol or codeine),
Bronchodilators
Weight loss
Surgical correction (tracheal prosthetic rings)
Antibiotics (to reduce complications)
What must be considered before administration of butorphanol/cough suppression?
The heart of the patient must be able to handle it
How is a wet cough treated?
Mucolytics
What is the most likely cause of sudden onset of sneezing?
Grass seeds or foreign bodies
With which type of nasal discharge should ATB be used?
Mucopurulent
How can problems in the nasal cavity be visualised?
Rhinoscopy, caudal rhinoscopy, x-ray, CT, MRI
What is epistaxis, and what are differential diagnoses for uni/bilateral epistaxis?
Epistaxis: bleeding from one or both nostrils
DDx: trauma, clotting disorders, foreign body, neoplasia