Physics AQA Gcses Paper 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
what are the eight energy stores?
thermal
kinetic
gravitational potential
elastic potential
chemical
magnetic
electrostatic
nuclear
how can energy be transferred?
mechanically (force doing work)
electrically (work done by moving charges)
by heating
by radiation (light, sound etc)
what happens when a system is changed?
(system is a single object/group of objects)
energy is transferred
(into or away from the system, between different objects in the system or different energy stores)
what are closed systems?
systems where neither matter nor energy can enter or leave
(the net change in the total energy of a closed system is always zero)
how can energy be transferred by heating?
water in a kettle:
energy is transferred electrically to the thermal component of the kettle, which transfers energy by heating to the water’s thermal energy store
what are examples of doing work?
initial force of throwing a ball upwards (chemical - kinetic)
gravitational force of dropping a ball (gravitational potential - kinetic)
friction between car brakes + wheels as it slows down (kinetic energy - thermal in the surroundings)
collision between car and solitary object (kinetic - other)
what has kinetic energy and what does this depend on?
anything that is moving - energy is transferred TO this store when an object speeds up and transferred AWAY when an object slows down
the energy in the kinetic store depends on the object’s mass + speed - greater the mass and the faster it’s going, the more energy there will be in this store
what has gravitational potential energy and what does this depend on?
raised objects - lifting an object in a gf requires work, which -causes a transfer to the gpe store of the object (the higher the object is lifted, the more gpe it has)
the energy in the gpe store depends on the object’s mass, its height and the strength of the gravitational field
what energy transfers happen when something falls?
gravitational potential energy store → kinetic energy store
energy lost from gpe store = energy gained in kinetic store (with no air resistance)
air resistance causes some energy to be transferred to other stores (e.g thermal)
what is specific heat capacity?
specific heat capacity is how hard it is to heat something up
(different materials have different specific heat capacities eg. water needs 4200J to warm 1kg by 1C but mercury only needs 139J)
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - investigating specific heat capacities
you will need a block of chosen material with two holes in it (for heater and thermometer to go in)
measure the mass of the block and wrap it in an insulating layer, then insert the heater and thermometer
measure the initial temperature of the block, set the voltage of the power supply to be 10V, then turn on the power supply and start the stopwatch
as the block heats up, take readings of the temp and current, every minute for 10 minutes
use P = VI to calculate the power supplied to the heater
calculate how much energy has been transferred to the heater using E = Pt (t is the time in seconds since it began)
plot a graph based on the results, and then find the gradient of the straight part (temp change / change in thermal energy)
the specific heat capacity of the material is 1/ (gradient x mass of the block)
what is the conservation of energy principle?
energy can be transferred usefully, stored or dissipated, but cn never be created or destroyed
what is power?
power is the rate of energy transfer, or the rate of doing work
power is measured in watts (one watt = one joule of energy transferred per second)
a powerful machine is one which transfers a lot of energy in a short space of time
what is conduction + where does it occur?
the process where vibrating particles transfer energy to neighbouring particles - occurs mainly in solids
(particles in an object being heated vibrate and collide with each other, causes energy to be transferred between particles’ kinetic energy stored - thermal conductivity is how quickly this happens)
what is convection + where does it occur?
where energetic particles move away from hotter to cooler regions - occurs only in liquids and gasses
(similar to conduction, but unlike in solids, particles in liquids and gases are able to move - when heated particles move faster and space between them increases, density decreases - warmer and less dense region will rise above cooler denser regions)
how can we reduce unwanted energy transfers?
lubrication - reduces frictional forces
insulation - reduces rate of thermal transfer
what is efficiency?
most energy transfers involve some waste energy - the less energy that is wasted, the more efficient the device is
useful energy output is not equal to total energy input as no device is 100% efficient (usual wasted energy → unwanted thermal stores)
what are non-renewable energy sources?
fossil fuels - oil, coal, natural gas
nuclear fuel - uranium, plutonium
these will run out some day and do damage to the environment, but they are reliable
what are renewable energy sources?
solar
wind
waves
tides
hydro-electricity
biofuel
geothermal
these will never run out, they do less damage to the environment but are less reliable and don’t provide as much energy
wind, solar and geothermal resources
wind - turbine that have a generator in them, the spinning blades generate electricity
solar cells - depends on solar rays, so only can be used in the daytime
geothermal power - uses underground thermal stores in volcanic areas (slow decay of radioctive elements) - reliable
hydro-electricity, waves and tides
hydro-electricity - falling water in valleys using dams -
waves - wave powered turbines
tidal barrages - uses the sun and moon’s gravity
bio-fuels and non-renewables
bio-fuels - made from plants and waste - large costs
non renewables - reliable but cause environmental problems such as carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burnt - nuclear waste is dangerous and potential major catastrophe
what is current?
the flow of electrical charge
(current can only flow with a source of potential difference, in a closed circuit current has the same value everywhere, measured in amperes - A)
what does the total charge in a circuit depend on?
current and time - the size of the current is the rate of flow of charge
what is an ammeter?
it measures the current (in amps) flowing through a wire
must be placed in series with whatever you’re investigating
what is a voltmeter?
it measures the potential difference (in volts) across a wire
must be placed in parallel with whatever you’re investigating - not around any other bit of of the circuit (e.g battery)
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - resistance and wire length
attach a crocodile clip to the wire level with 0cm, then attach a second crocodile clip a certain distance away from the first (e.g 10 cm)
close the switch, then record the current through the circuit through the wire and the pd across it
open the switch and move the second clip another distance along the wire, then close it and record current and pd again
repeat this for a number of lengths of the test wire
use measurements of current and pd to calculate resistance using R = V / I for each length of wire
plot a graph of resistance against wire length and draw a line of best fit, graph should be a straight line through origin
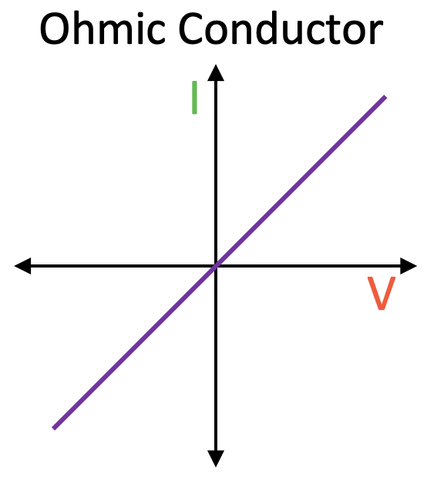
what are ohmic conductors?
components of a circuit that have a constant resistance (not changed as the current is changed)
e.g a wire or resistor
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - I-V characteristics
set up a test circuit with a battery, variable resistor, voltmeter, ammeter and a component that you will change
begin to vary the variable resistor - alters the current flowing through the circuit and pd across the component
take several readings from the voltmeter and ammeter to see how the pd varies as the current changes
swap over the wires connected to battery so the current is reversed and take readings
plot a graph of current against voltage for the component
what is the I-V characteristic for a filament lamp?
as the c__urrent increases__, the temperature of the component increases, so the resistance increases - means less current can flow per unit pd - graph gets shallower, hence the curve
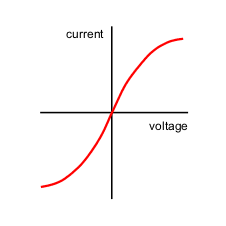
what is the I-V characteristic for an ohmic conductor?
the current through this conductor is directly proportional to potential difference - straight line
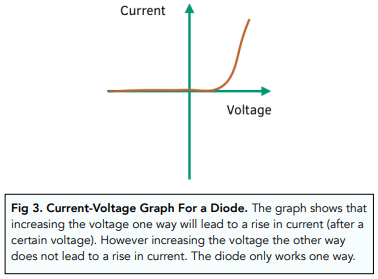
what is the I-V characteristic for a diode?
current will only flow through this component in one direction - the diode has very high resistance in the reverse direction
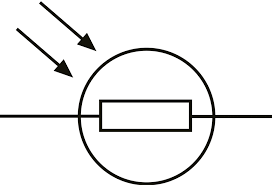
what is an LDR?
light dependant resistor - dependant on the intensity of light
bright light - resistance falls
darkness - resistance is highest
what is a thermistor?
temperature dependant resistor
hot conditions - resistance drops
__coo__l conditions - resistance goes up
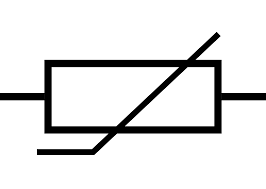
what is a series circuit + what happens to resistance, pd and current?
different components are connected line to line, end to end between the +ve and -ve of the power supply - if you remove/disconnect a component, the circuit is broken
current - the same everywhere
pd - shared - pds around the circuit always add up to the source pd
resistance - adds up - total resistance of two components is the sum of their resistances
what is a __paralle__l circuit + what happens to current, pd and resistance?
each component is separately connected to the +ve and -ve of the power supply - if you remove one component, it will hardly affect the others at all
current - shared between branches - total current is equal to the total of all currents through the separate component
pd - same across all components
resistance - adding a resistor in parallel reduces the total resistance
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - investigating adding resistors in series
find at least four identical resistors - build a circuit with a battery, ammeter and resistor
make note of pd and measure current to calculate resistance
add another resistor and measure current and pd to calculate resistance with the added resistor
repeat until you have added all your resistors
plot a graph of the numbers of resistance against the total resistance of the circuit
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - investigating adding resistors in parallel
use the same equipment as in series and build the same initial circuit
measure total current and calculate resistance again
add another resistor in parallel with the first
measure total current and pd of the battery to calculate the overall resistance of the circuit
repeat until you have added all your resistors in parallel
plot a graph of numbers of resistors against the total resistance
what are the two supplies of electricity in the home?
ac - alternating current - constantly changing direction, produced by alternating voltages, - mains supply
dc - direct current - flowing in the same direction, produced by direct voltage - batteries and cells
what is the frequency and potential difference of the UK mains supply?
frequency - 50Hz
potential difference - 230V
what are the three separate wires in a plug?
live - brown - provides the alternating pd from the mains supply - 230V
neutral - blue - completes the circuit, current flows through the live and neutral wires - 0V
earth - green and yellow - protecting the wiring, stops the appliance from becoming live if faulty - 0V
what is static electricity and how is it caused?
when certain insulating materials are rubbed together, negatively charged electrons will be scraped off one material and dumped on the other
this leaves the materials electrically charged, with a positive or negative charge on the two materials
which way the electrons are transferred depends on the two materials involved
they cause a shock or spark when moved
what creates an electric field?
electric charges:
an electric fields is created around any electrically charged object
the closer you get, the stronger the force is
you can show an electric field around an object using field lines
what happens when a charged object is placed in an electric field?
it feels a force
the force causes attraction or repulsion
the force is caused by the electric fields of each charged object interacting with each other
the force on an object is linked to the strength of the electric field it’s in
as you increase the distance between charged objects, the strength of the field decreases and the force between them gets smaller
what causes sparking?
when there is a high enough pd between a charged object and the earth/an earthed object
a high pd causes a strong electric field between the charged and the earthed object
the strong electric field causes electrons in the air particles to be removed (known as ionisation)
air is normally an insulator,but when it is ionised it is much more conductive, so a current can flow through it - sparks
what is density?
a measure of the compactness of of an object - relates the mass to how much space it takes up - in a dense object particles are packed tightly together
what are the three states of matter?
solid - fixed, regular particles that don’t have much energy, density is highest, strong forces of attraction between particles
liquids - particles are close together, can move past each other and form irregular arrangements, more energy than solid, weaker forces between particles, less dense
gas - free to move in random directions at high speeds, low density, more energy than liquids and solids, almost no forces between particles
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - investigating density in solids
use a balance to measure its mass
regular solid - measure its length, width and height, then calculate its volume
irregular solid - submerge in a eureka can filled with water, and it will transfer the displaced water by the solid into a measuring cylinder - this is the volume of the solid
use the its volume and mass to calculate the density
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - investigating density in liquids
place a measuring cylinder on a balance and zero it
pour 10ml into the cylinder, repeating until the cylinder is full and measure the mass and volume each time
use the density formula
what is internal energy?
energy stored by the particles making up a system
they have energy in their kinetic energy stores as particles vibrate
also have gpe depending on their positions
heating the system transfers energy to its particles so increases the internal energy
what is specific latent heat?
the energy needed for a 1kg mass of a material to change state without changing its temperature
for cooling, it is the energy released by a change of state
between a solid and a liquid - slh of fusion
between a liquid and a gas - slh of vaporisation
what creates pressure in a gas?
colliding gas particles:
when collision happens a force is exerted
increasing temperature will increase the pressure (if volume is kept constant)
pressure and volume are inversely proportional
pV = constant
what are isotopes?
different forms of the same element but with a different number of neutrons - atomic mass increases
what are alpha particles + alpha radiation?
a helium nucleus - 2 protons + 2 neutrons
alpha radiation is when a helium nucleus is emitted from an atom
__strongl__y ionising
not very penetrative - stopped by paper
what are beta particles + beta radiation?
high speed electron released by the nucleus
moderately ionising
moderately penetrative - stopped by aluminium foil
for every beta particle emitted, a neutron in the nucleus has turned into a proton
what is gamma radiation?
electromagnetic waves with a short wavelength
weakly ionising
very penetrative + can travel long distances - stopped by thick lead or concrete
what happens to the nucleus during alpha decay?
changes the mass of the nucleus
atomic number reduces by 2
mass number reduces by 4
what happens to the nucleus during beta decay?
increases the charge
a neutron changes into a proton
an __electro__n is released
atomic number increases
mass number does not change
what is half-life?
time taken for the number of radioactive nuclei in an isotope to halve
short half-life - activity falls quickly - less dangerous
long half-life - activity falls slowly - more dangerous
what are the sources of background radiation?
radon gas
rocks (uranium salts in graphite)
food (bananas)
cosmic rays
radioactive waste or fallout
what is irradiation?
exposure to radiation - irradiating something does NOT make it radioactive
what is contamination?
unwanted radioactive atoms getting onto/into an object - contaminating atoms might then decay, releasing harmful radiation
what are the uses of radiation?
radiotherapy - cancer cells killed by ionising radiation
medical tracers - iodine-123
what are the risks of radiation usage?
can enter living cells and ionise atoms and molecules within them - causes tissue damage
high doses can kill many cells at once, causing radiation sickness
what is nuclear fission?
the splitting of a large, unstable nucleus
the atom has to absorb a neutron before splitting
atom splits and forms two lighter elements
two or three more electrons are released when an atom splits, causing a chain reaction - the energy produced from this heats water which turns turbines
uncontrolled causes lots of energy - nuclear weapons
what is nuclear fusion?
the joining of two small nuclei
two light nuclei collide at a high speed to create a larger, heavier nucleus
heavier nucleus does not have as much mass as the two separate nuclei
fusion releases lots of energy
fusion happens in stars with helium and hydrogen
Definition of a wave
Waves carry energy or information from one place to another
Transverse waves
e.g. light waves
Travel perpendicular to the direction of energy travel
Up and down movements
Longitudinal waves
e.g sound waves
Travel parallel to the direction of energy travel
Across movements
What is the term for short and long wavelengths in a Longitudinal Wave
Short: compression
Long: Rarefaction
What frequency can humans hear?
20 - 20,000 Hz
Definition of Frequency
The number of waves passing a point in a second
Definition of ‘period’
P - time period
Time taken to pass a point (seconds)
Time taken for one complete oscillation
Variables for the speed of ripples on water practical
Control - Travel length, height dropped from
Dependant - Time to travel 2m
Independent- Water Depth
Equation for speed
S=D/T
Speed = Distance / Time
What is the ‘normal’?
A line drawn perpendicular to the mirror/surface to help measure the angle
When light reflects off a flat surface in a straight line, what is this called?
specular
When light reflects off a rough surface in different directions, what is this called?
Diffused
Info about sound waves
Longitudinal (across)
Vibrations travel through air
Vibrations move to our ear drums which vibrate and cause the sensation of sound
Ultrasound
Above 20,000Hz (above human hearing)
Wave is partially reflected at the boundary between materials
What is ultrasound used for and how does it work?
Medical (foetus scan) - Sound waves bounce off skin, organs etc at different speeds. These echos are converted into images with a transducer.
Industrial (under oceans) - Time taken for reflections to reach a detector can be used to determine how far away a boundary is
Dog training (whistles)
S - waves
Secondary Waves
Transverse
Can’t travel through liquid
P - waves
Primary Waves
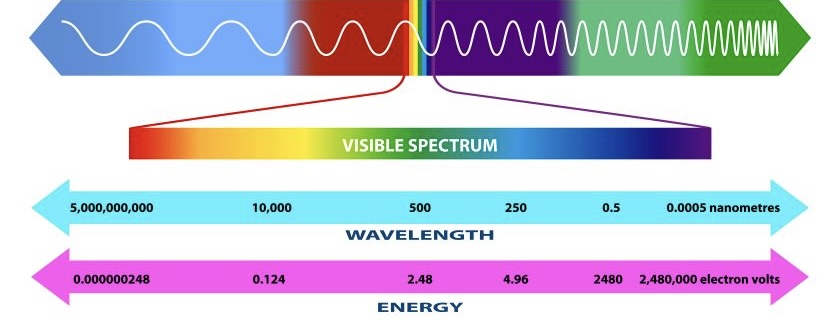
What is the Electromagnetic spectrum?
Moves energy from a source to an absorber
Lowest Freq:
Radio waves
Microwaves
Inferred Radiation
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma waves
Highest Freq
Wavelength
The distance from a point on a wave to the equivalent point on the next wave
(metres)
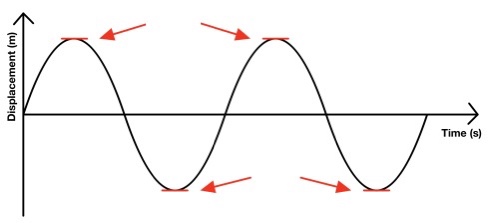
What Is the highest and lowest point on a wave called?
Peaks
Troughs
What can happen when a wave meets a boundary
Reflection
Transmission
Absorption
Refraction
What happens when waves are reflected off a surface
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
What does Refracted mean?
Wave is reflected off a surface and changes direction
What happens when light travels from a material with a low to one with higher refractive index?
The light bends towards the normal
What happens when light travels from a material with a high to one with lower refractive index?
The light bends away from the normal
Why does Refraction happen?
When a light wave enters a medium in which it travels slower at an angle,
The first part of the wave to enter slows down
The rest continues at a higher speed
the waves changes direction towards the normal
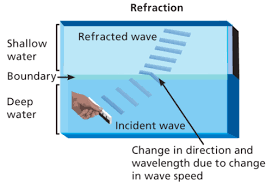
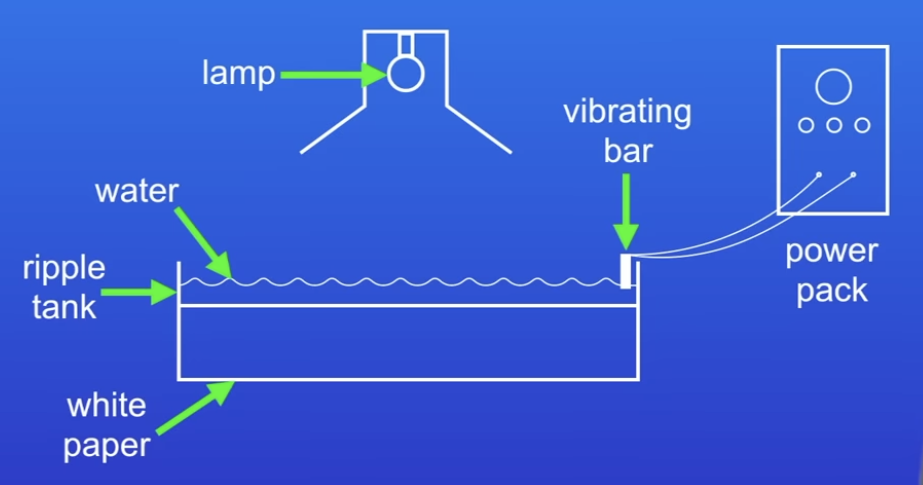
Label this ripple tank
Wave speed equation
v=f x λ
wave speed = freq x wavelength
Label this diagram
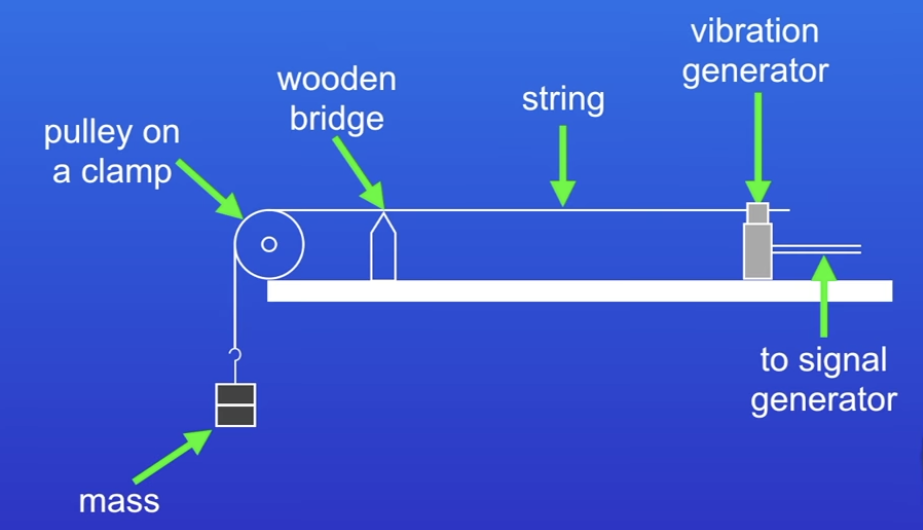
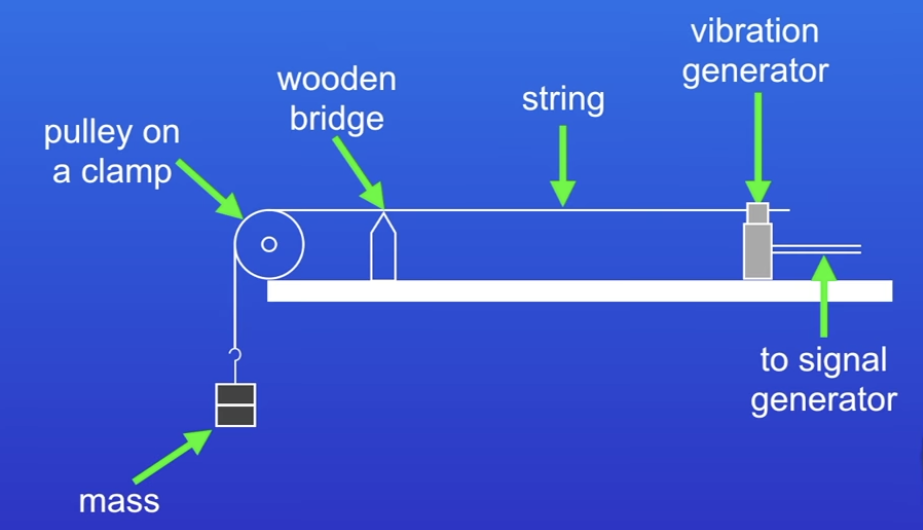
How to determine wavelength with this practical
Total Length / number of half wavelengths x 2
How to draw the reflected ray?
What is a convex lens?
How do you show this?

Method for angle of refraction with ray box
• place a glass block on a piece of paper
• draw around the glass block
• use the ray box to shine a ray of light through the glass block
• mark the ray of light entering the glass block
• mark the ray of light emerging from the glass block
• join the points to show the path of the complete ray through the block
• and draw a normal line at 90 degrees to the surface
• use a protractor to measure the angle of incidence
• use a protractor to measure the angle of refraction
• use a ray box to shine a ray of light at a range of different angles (of incidence) • increase the angle of incidence in 10 degree intervals
• from an angle of incidence of 10 degrees to an angle of incidence of 70
degrees.