ANAT 100 - Module 1 (Foundations of the Human Anatomy)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Anatomy
- Anatomy is the study of structure
- "To cut apart" (Greek)
- Parts of an organism are "cut apart" to ascertain their position, relations, structure and function
4 Areas of Anatomy
1. Histology (microscopic features)
2. Gross anatomy (macroscopic features)
3. Neuroanatomy
4. Embryology
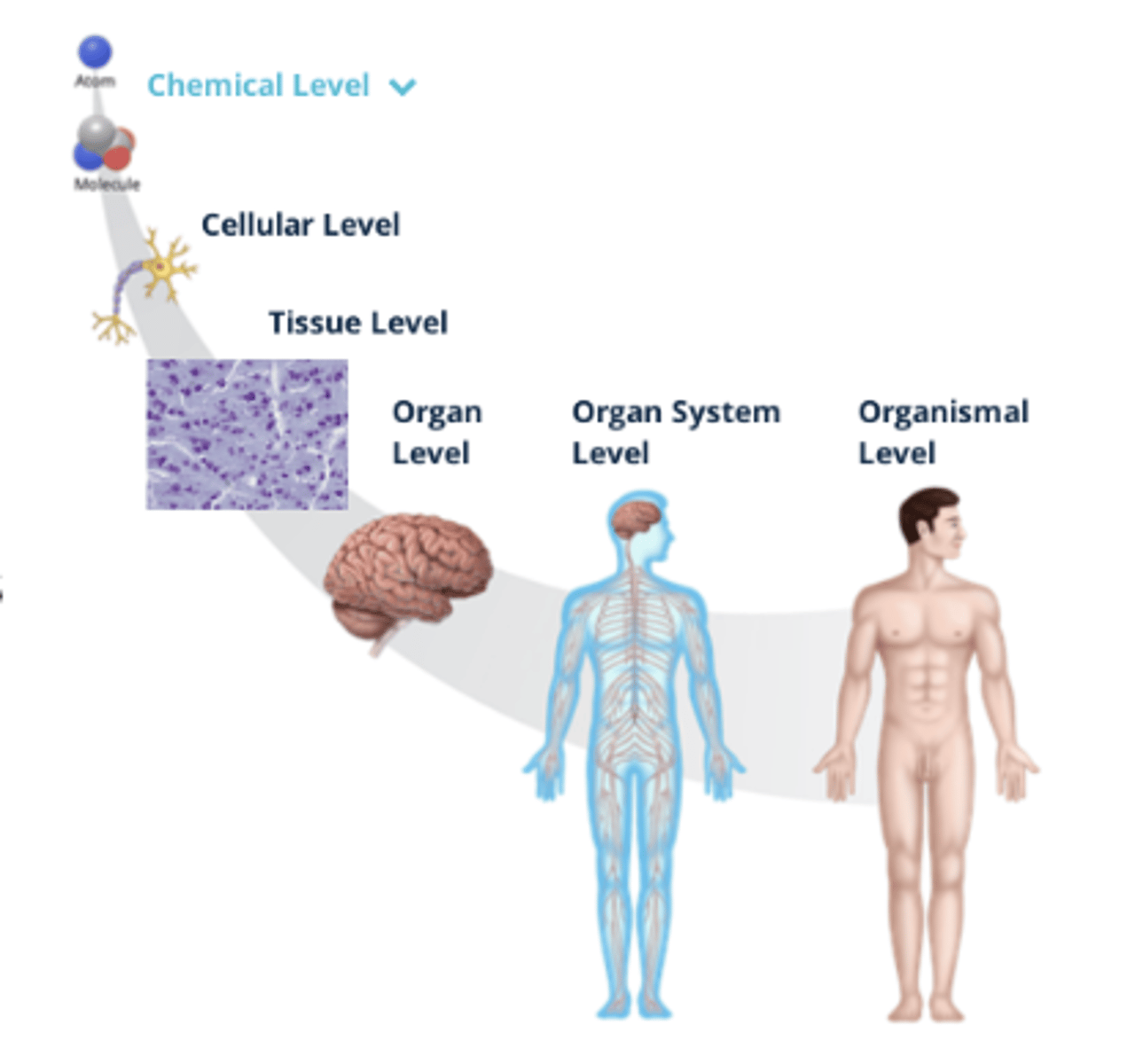
Organization of the Human Body
- There are microscopic (small) and macroscopic (large) structures of the human body that can be organized by fundamental levels, ranging from small molecules and cells to the organ system
1. Organismal Level
2. Organ System Level
3. Organ Level
4. Tissue Level
5. Cellular Level
6. Chemical Level
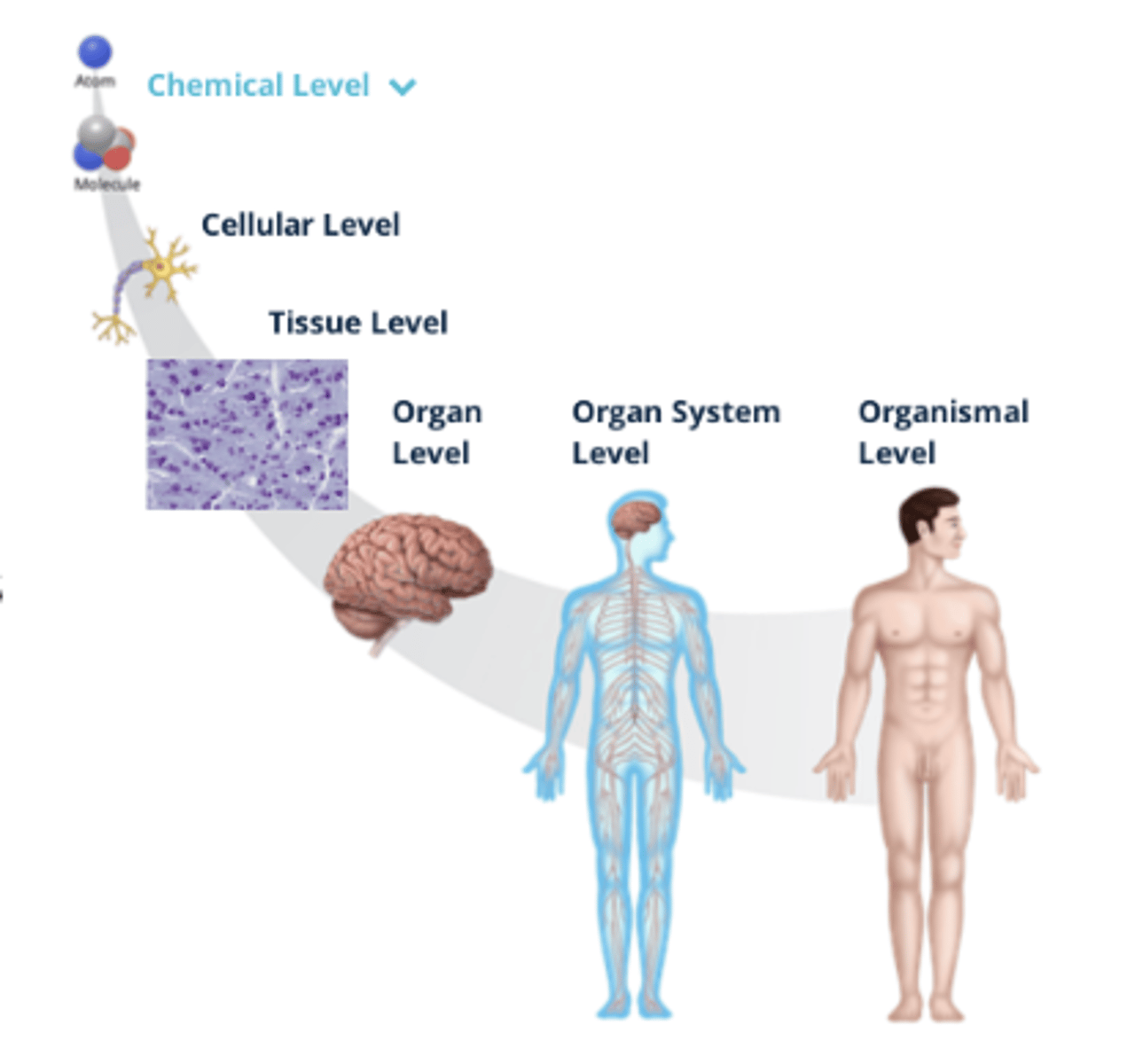
Organismal Level (Organization)
All body systems function interdependently in a single living human
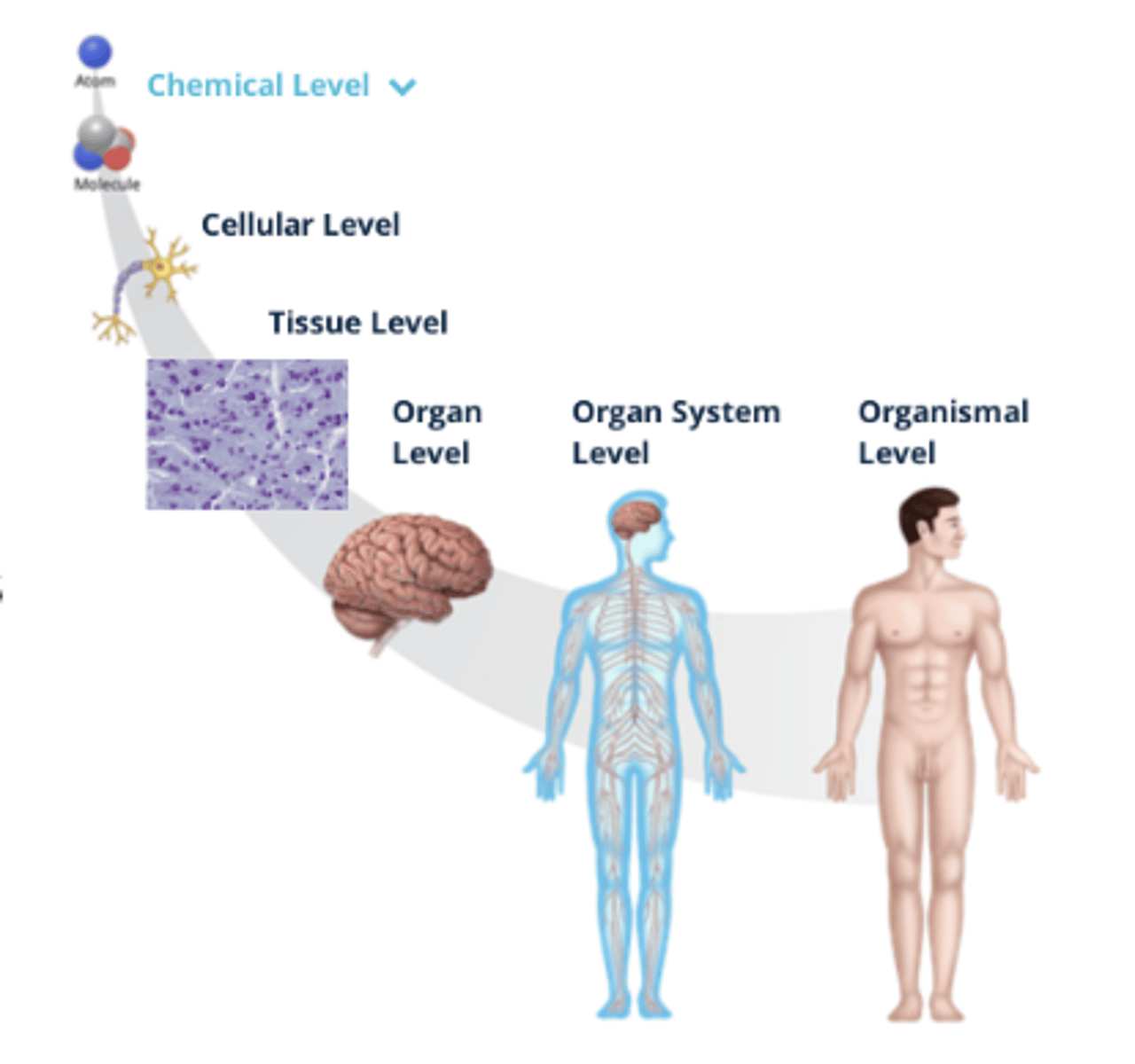
Organ System Level (Organization)
Consists of related organs that work together to coordinate activities and achieve a common function
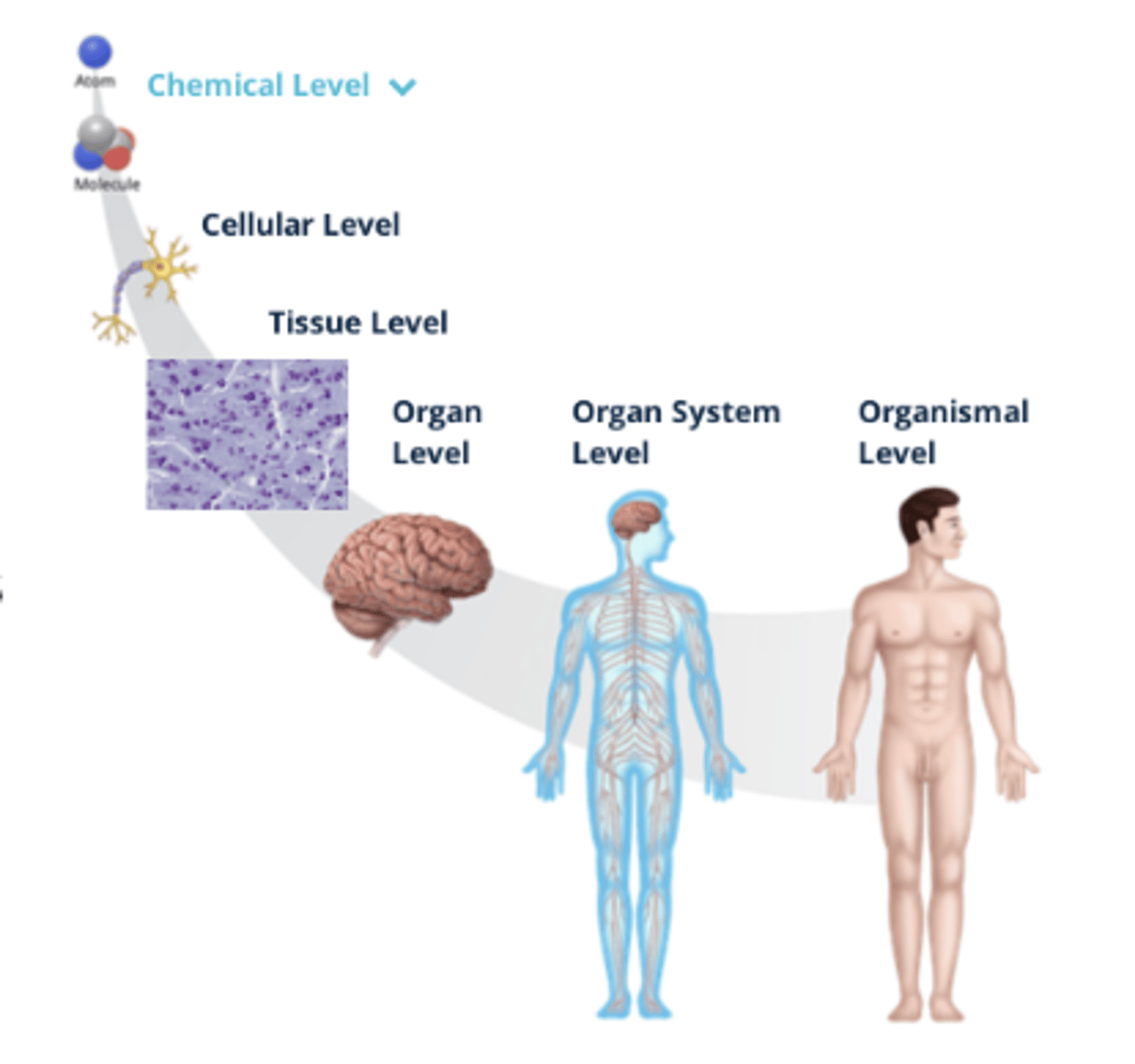
Organ Level (Organization)
Two or more tissues that work together to perform complex functions
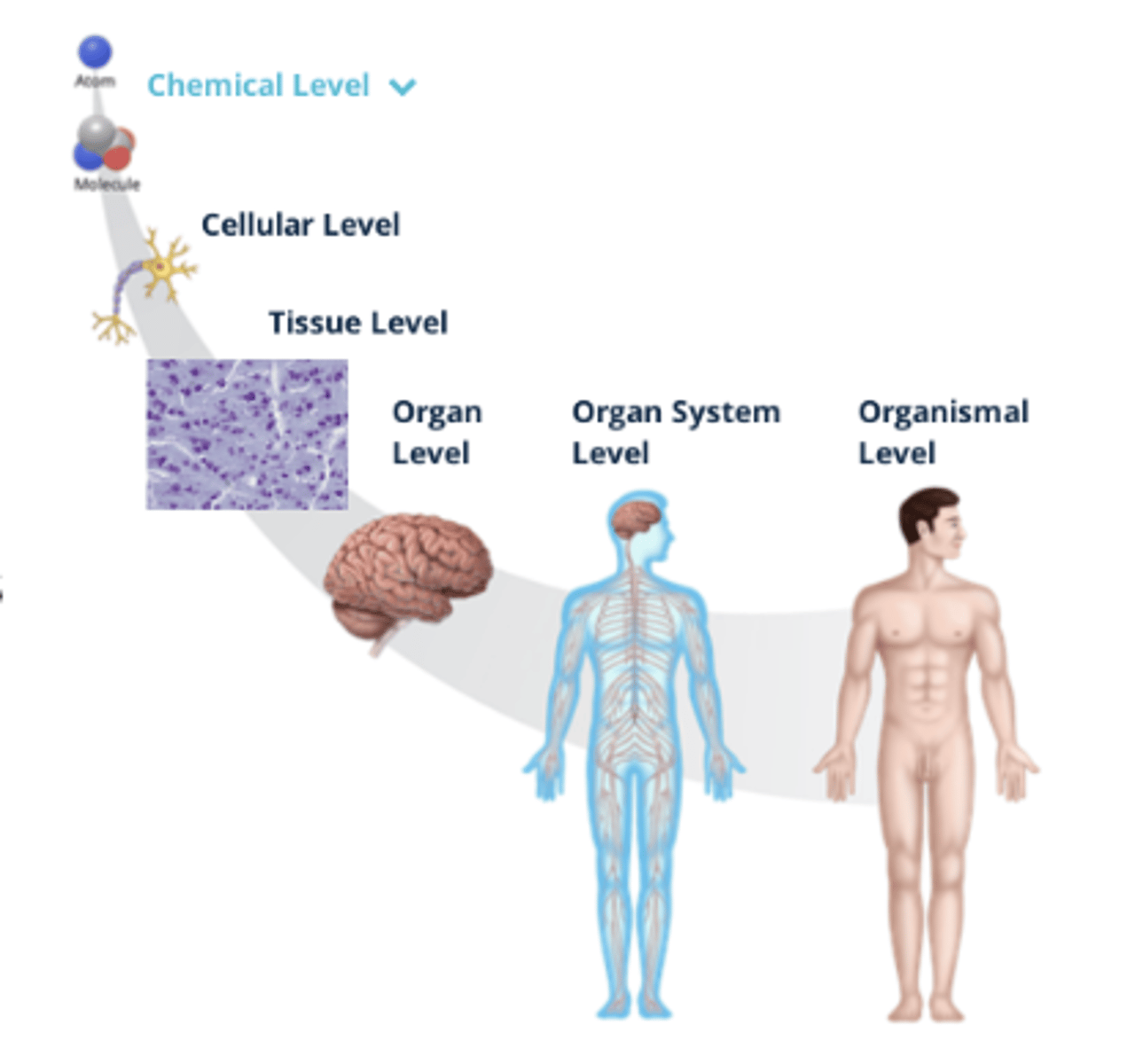
Tissue Level (Organization)
Tissues are similar cells that perform specialized functions
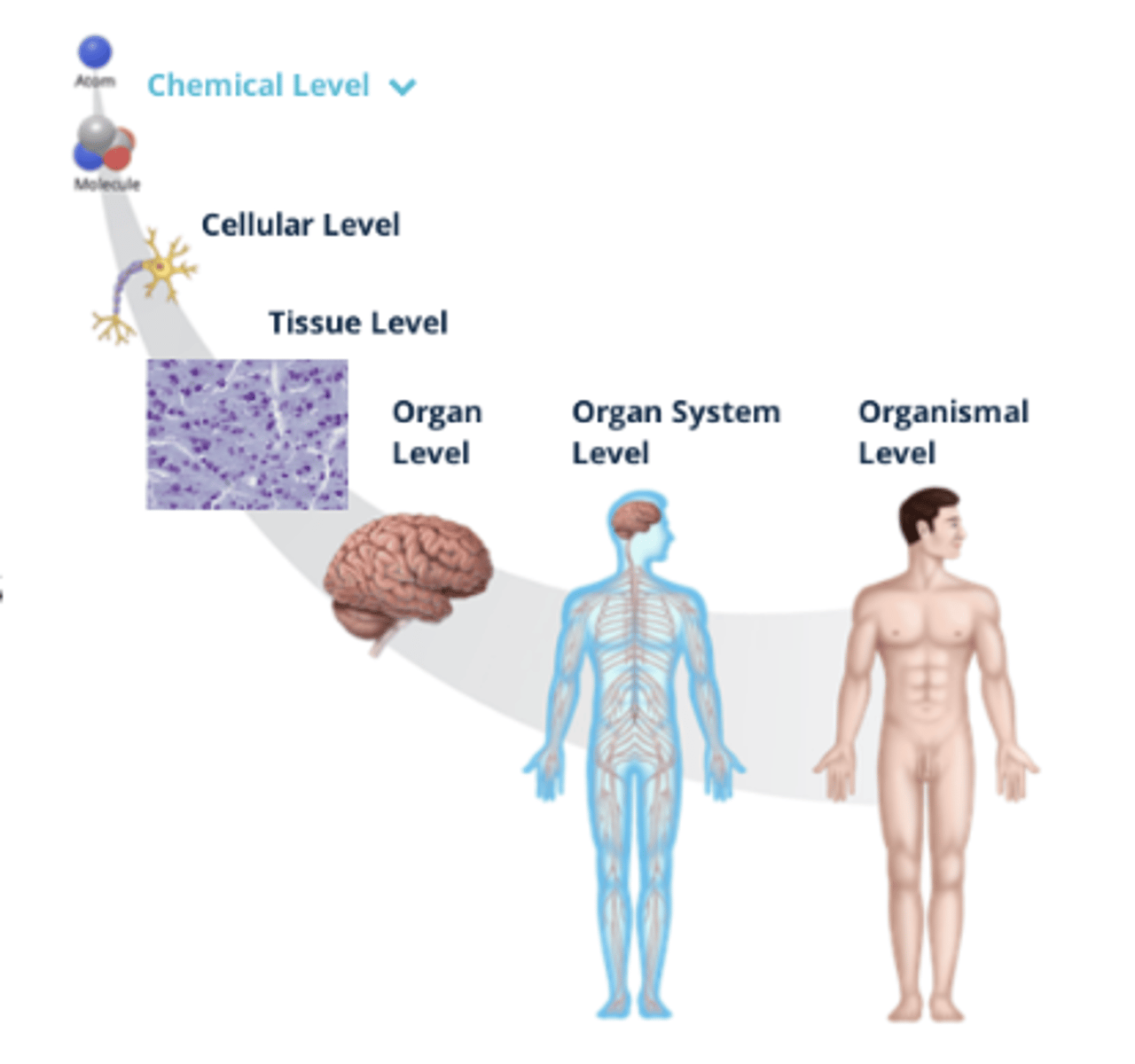
Cellular Level (Organization)
Cells are the smallest living structure and are formed from atoms and molecules
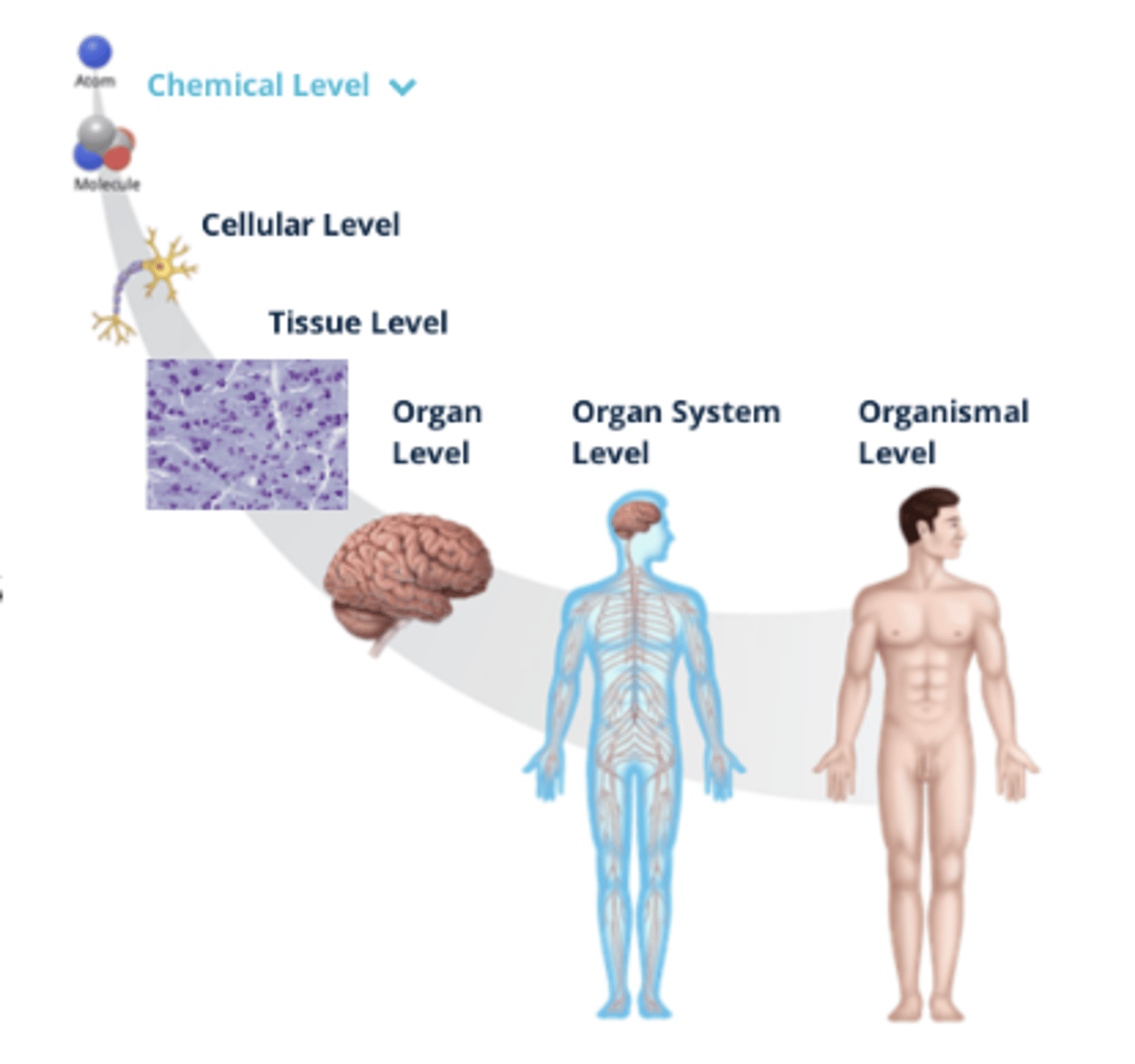
Chemical Level (Organization)
A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together
Axial (Body Divisions)
- Forms the main vertical axis of the body
- Includes head, neck, trunk
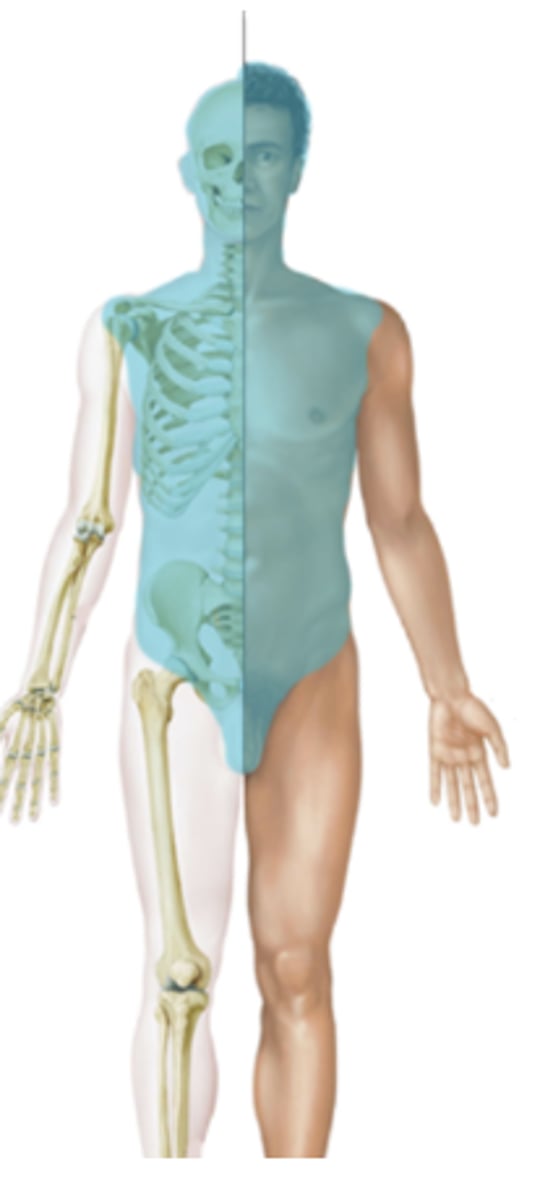
Appendicular (Body Divisions)
Includes limbs or appendages that attach to the axis
Integumentary System
- Makes up your body covering and includes our skin and associated structures such as our hair and nails
- Layers of skin and its accessory structures
Skeletal System
Includes the bones and joints of the body
Muscular System
- Contains your muscles
- Muscular and skeletal systems work together for movement and support
Nervous System
Includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that run throughout the body
Endocrine System
- Includes the glands that produce and secrete hormones
- Along with the nervous system, these two organ system function in the integration and coordination of the body to act as a unit
Digestive System
Starts at the mouth with a long tube and ends at the anus
Respiratory System
- Allows you to breathe
- Includes the nose, air passageways, and lungs
Cardiovascular System
- Includes blood, blood vessels, and the heart
- The circulatory system
Lymphatic System
Includes the lymphatic vessels, cells, and structures that can initiate an immune response
Urinary System
Respiratory, cardiovascular, lymphatic, and urinary systems function together in the processing and transportation of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products
Reproductive System
Provides the means for the sexual maturation and procreation of each individual
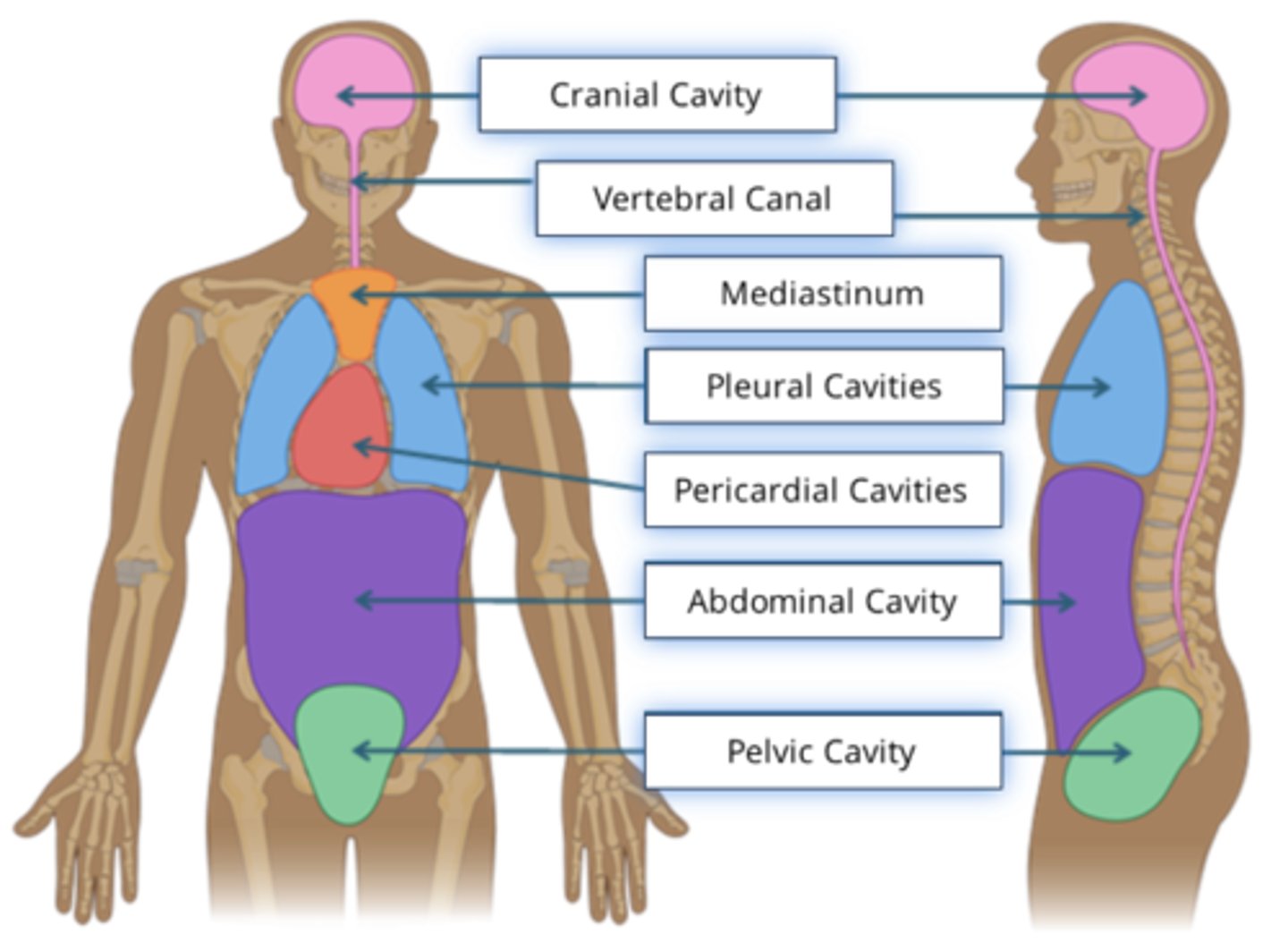
Body Cavities
- Organ systems are enclosed within distinct spaces, known as body cavities
- These spaces are important because they contain and protect our vital organs
- Anterior view = from the front
- Lateral view = from the side
Characteristics of Anatomical Positions
- Standing upright
- Feet parallel and on the floor
- Head level and looking forward
- Arms at the side of the body
- Palms facing forward and thumbs pointing away from the body
Directional Terms
- They provide precise descriptions of the location of structures relative to other structures in anatomical position
- Paired with an associated term that means the opposite
Superior (Directional Terms)
Above or over
Inferior (Directional Terms)
Below or under
Anterior (Directional Terms)
In front of / front
Posterior (Directional Terms)
after / behind / following / toward the rear
Medial (Directional Terms)
toward the midline / middle / away from the side
Lateral (Directional Terms)
toward the side / away from the middle
Proximal (Directional Terms)
near / closer to the origin
Distal (Directional Terms)
away from / farther from the origin
Superficial (Directional Terms)
closer to the surface of the body
Deep (Directional Terms)
father from the surface of the body
Parietal (Directional Terms)
indicating component of the body walls, which may include muscles, connective tissue, and tissue covering the organs
Visceral (Directional Terms)
Lines the outer surfaces of organs (viscera) that are located within the cavities
Sagittal (Sections of the Body)
- A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right parts
- When a sagittal plane passes specifically through the midline of the body, it is referred to as the midsagittal plane
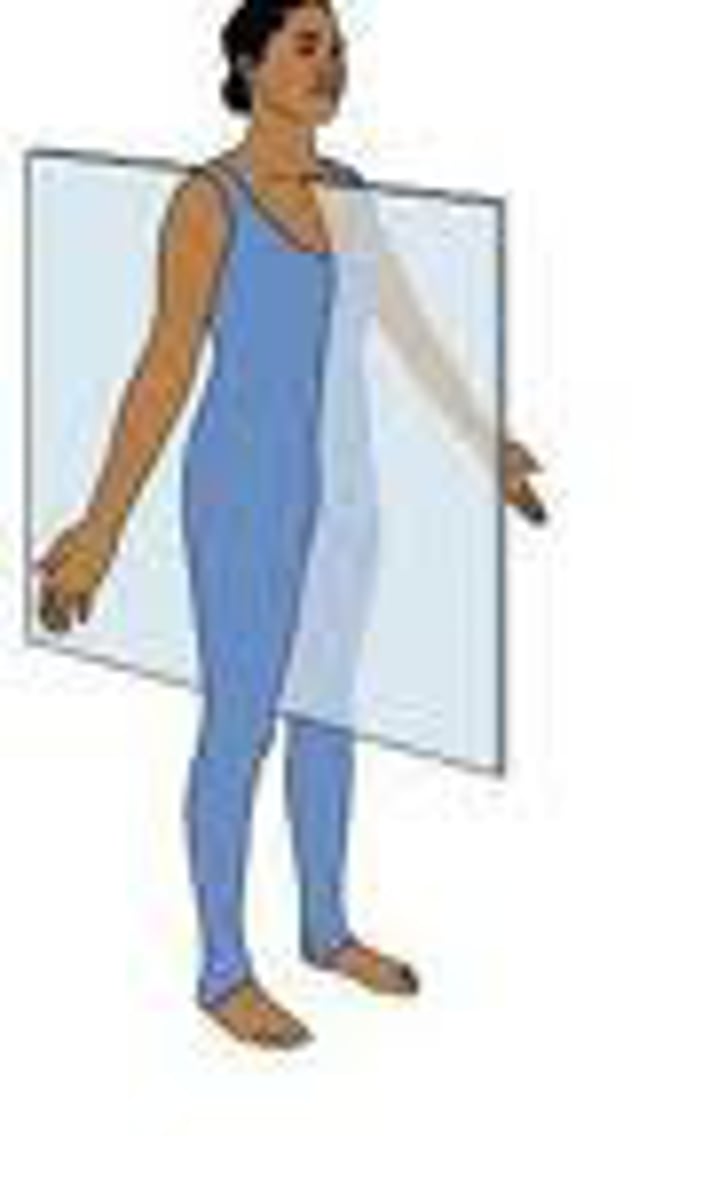
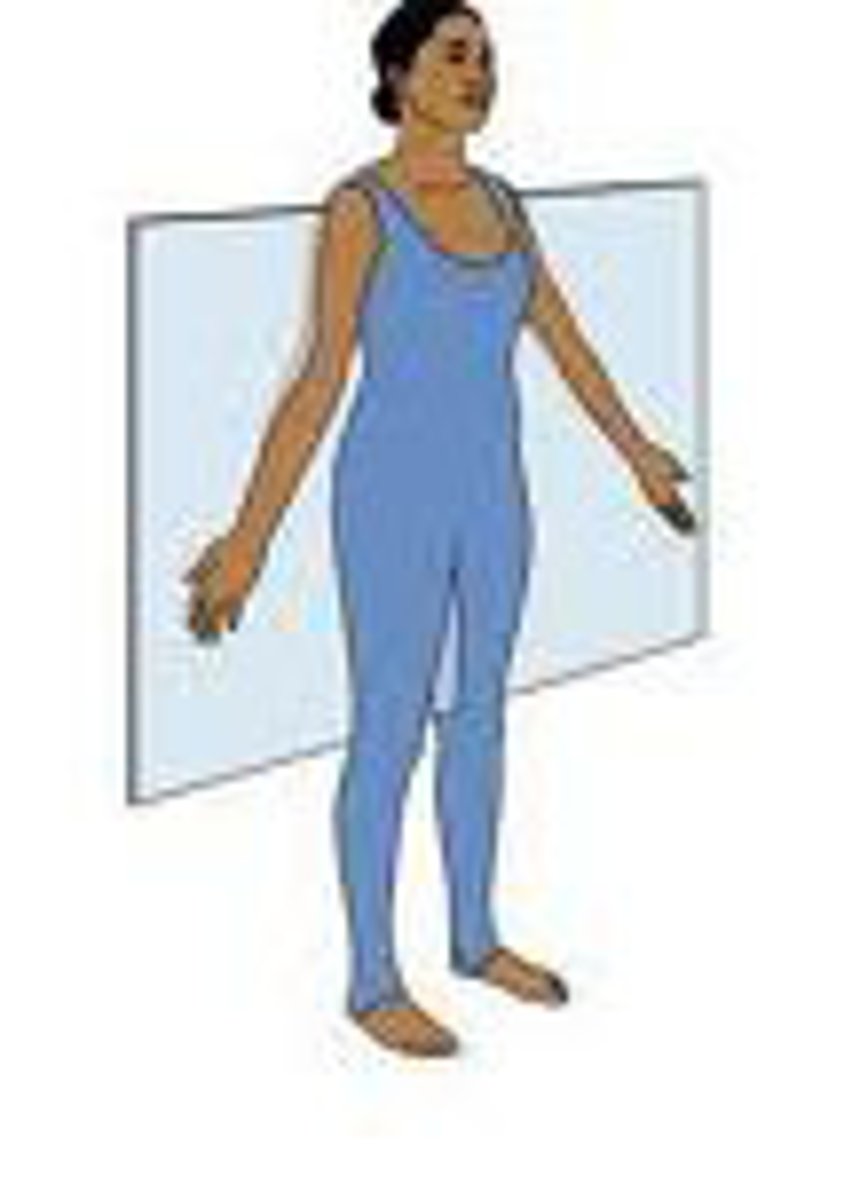
Coronal (Sections of the Body)
- Also known as frontal plane
- A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts

Horizontal (Sections of the Body)
- Also known as transverse plane
- The horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts
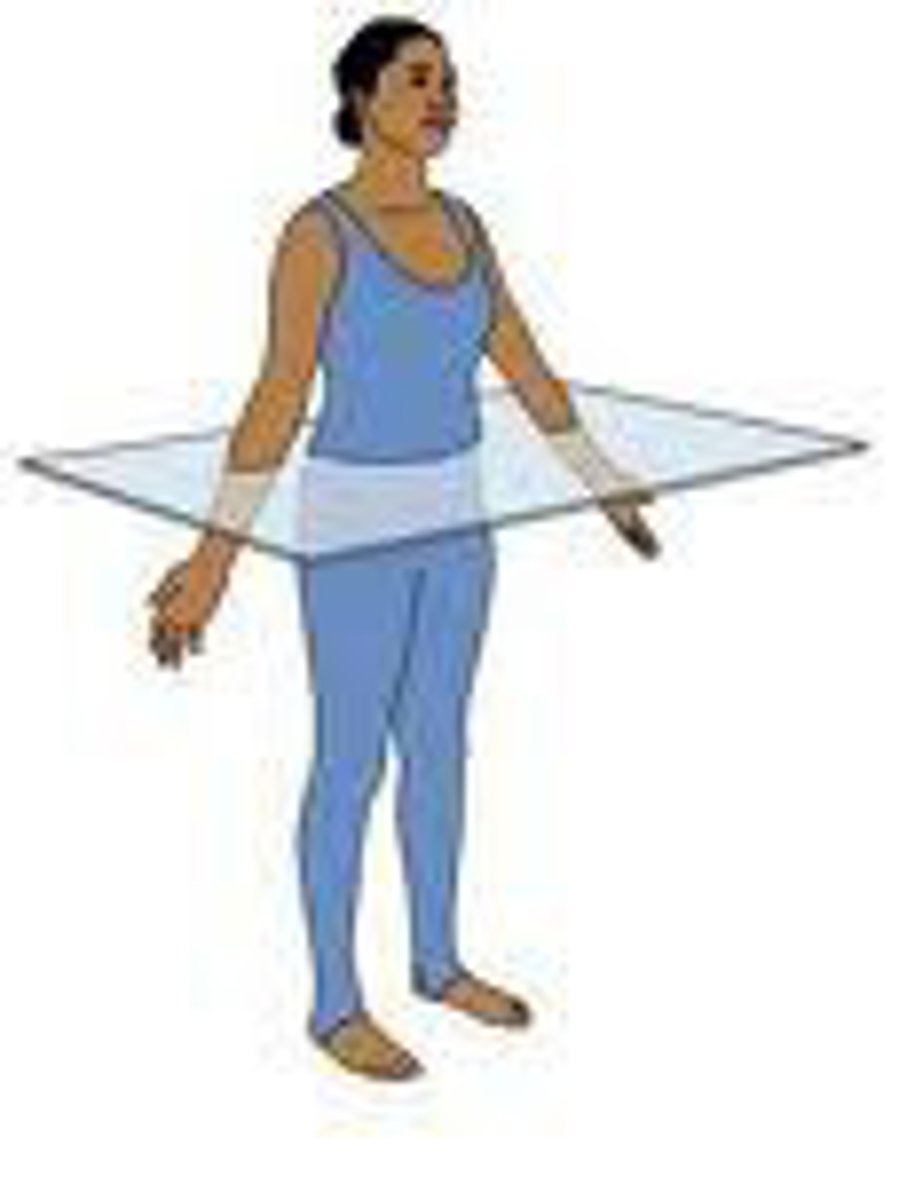
Oblique (Sections of the Body)
A plane that passes through the body at an angle
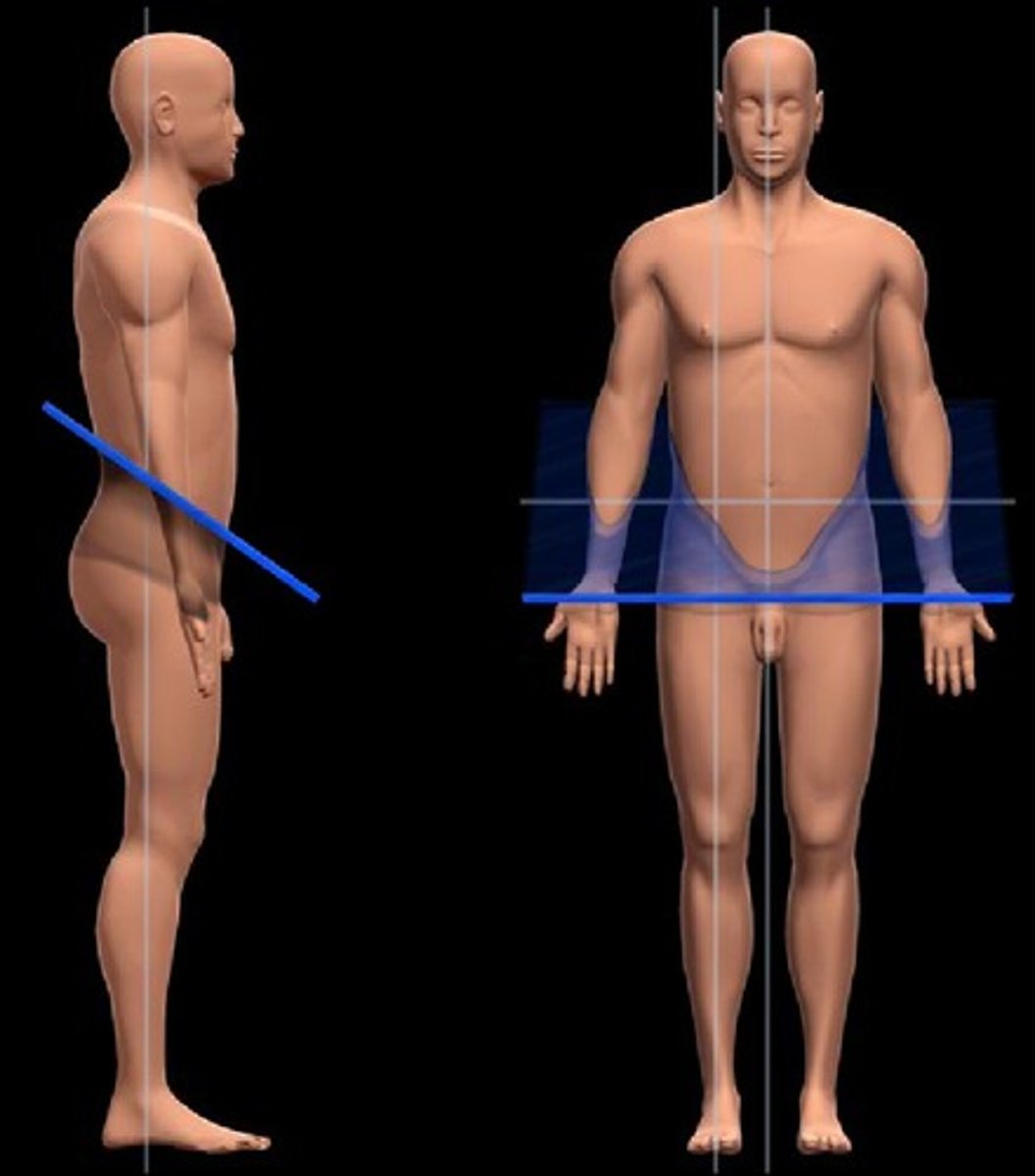
Longitudinal (Sections of the Body)
- Any plane that is perpendicular to the horizontal plane
- Both sagittal and coronal planes are examples of longitudinal planes
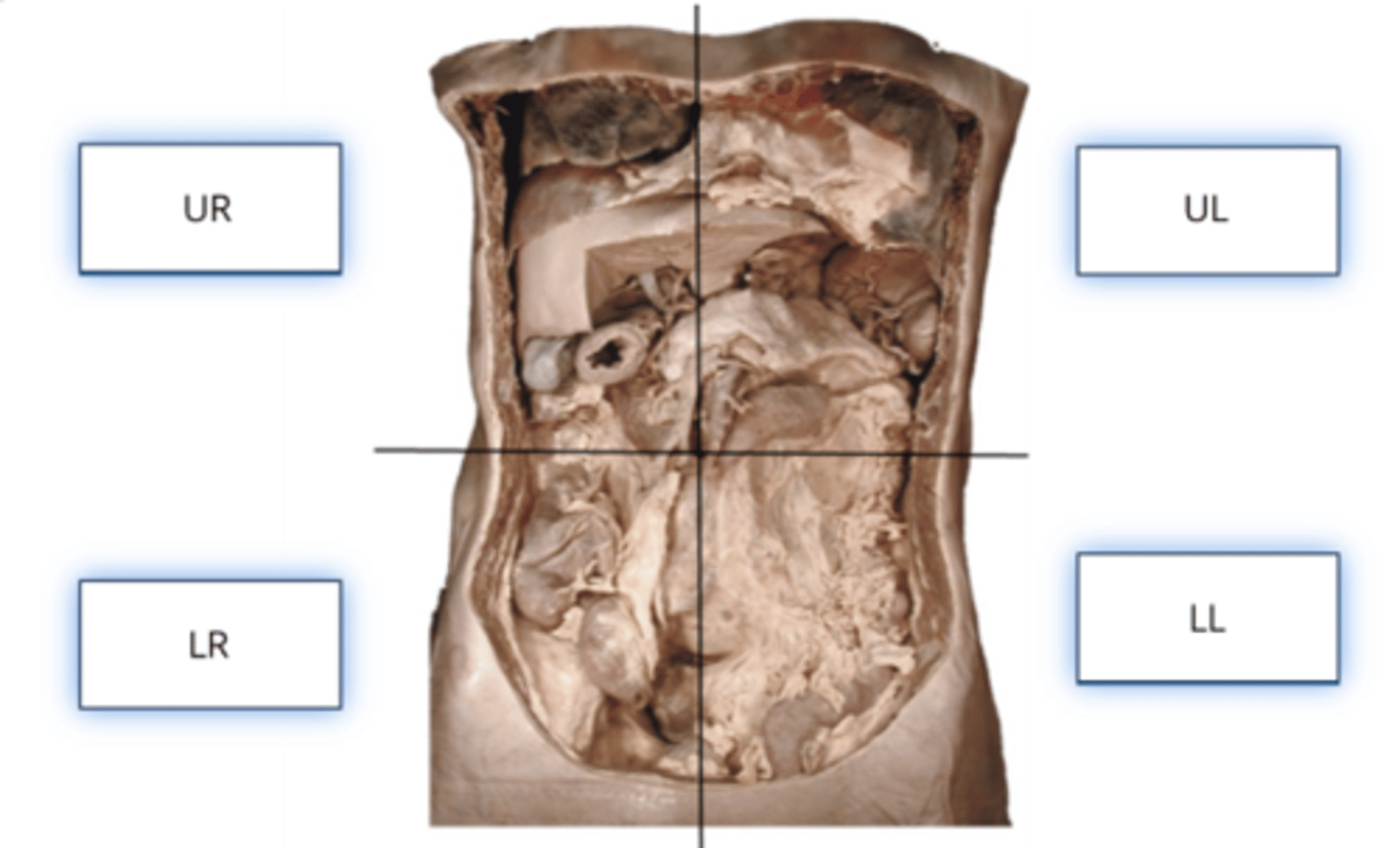
Body Quadrants
- Abdominal and pelvic cavities can be divided into four quadrants
- These quadrants are often used in medicine to describe the location of pain, dysfunction, or injury
Epithelium
- Tissue composed of closely apposed (side by side) cells with little to no intervening intercellular substance
- There are two types of epithelium:
Covering epithelium: cells that cover the external and internal surfaces
Glandular epithelium: cells that produce and secrete product, such as hormones
Characteristics of Epithelium
- Can be observed in various shapes and layerings throughout the body
- Regardless of shape, amount of layering, or location, epithelial tissue share similar characteristics
1. Cellularity
2. Polarity
3. Attachment
4. Avascularity
5. Regeneration
Cellularity (Epithelium)
- Adjacent epithelial cells are joined by specialized junctions
- There are 4 types of junctions: tight junctions, adhering junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
Polarity (Epithelium)
An epithelial cell has an exposed (apical) surface that faces the exterior of the body or internal space, and a basal surface where it is attached to the underlying tissue
Attachment (Epithelium)
Epithelial cells rest on and are attached to the basal lamina (basement membrane)
Avascularity (Epithelium)
- Epithelial tissue has no direct contact with blood vessels
- The epithelial cells retrieve nutrients from the blood vessels in the underlying tissue
Regeneration (Epithelium)
Epithelial cells are renewed continuously
Functions of Epithelium
Support and Protection
- Covers and lines external and internal surfaces of the body protecting the underlying tissue from injury, pathogens, and dehydration (e.g. skin)
Permeability
- Epithelium allows substances to be absorbed into the body (e.g. epithelium lining the digestive system absorbs nutrients from food)
Sensation
- Some epithelial tissues contain specialized cells that are able to detect sensory stimuli (e.g. skin senses touch, tongue senses taste)
Secretion
- Some epithelial cells are specialized to secrete specific substances (e.g. skin secreted lubricating oil, enzymes, and hormones are secreted by the digestive system)
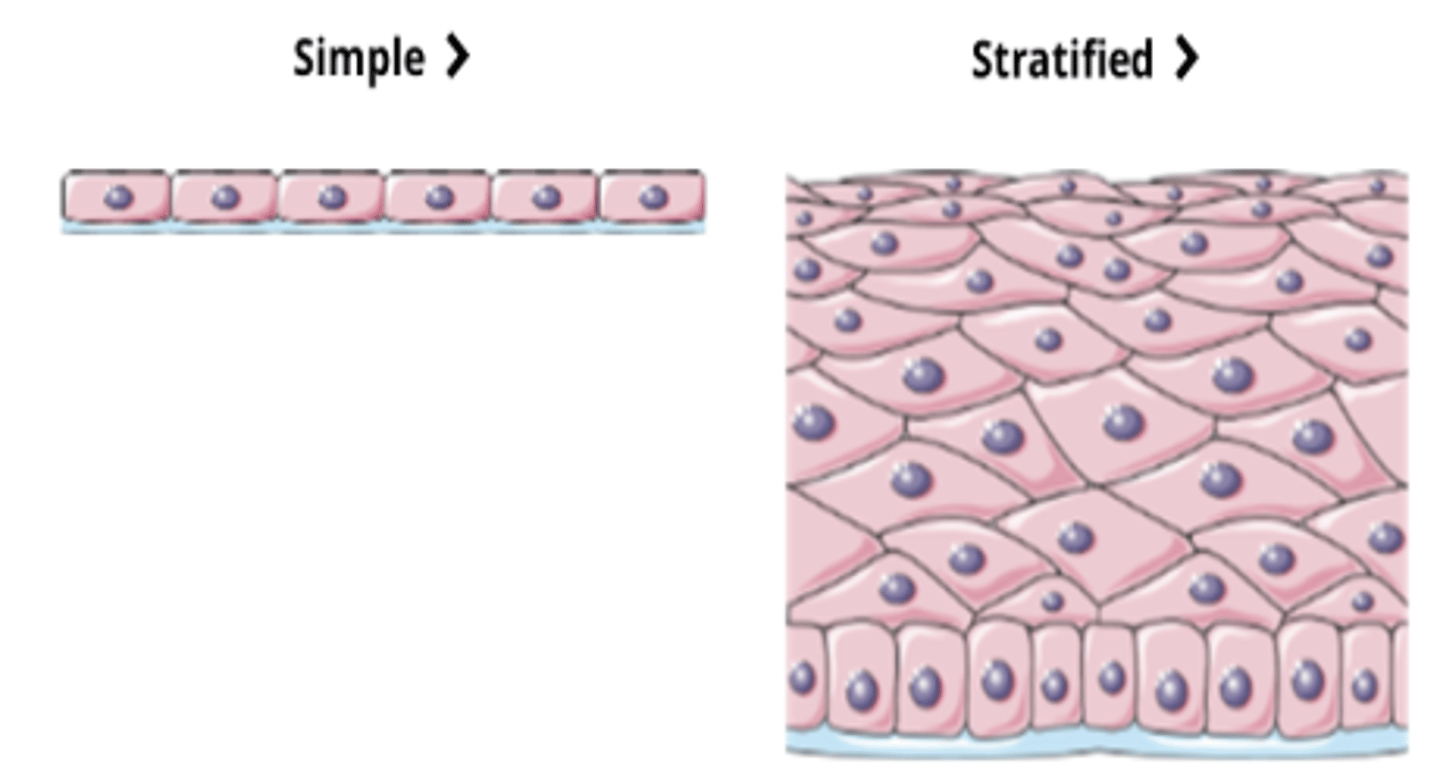
Cell Organization (Classifying Epithelium)
- Simple = Only one cell layer thick
- Stratified = Two or more layers thick, only the deepest layer of cells is in contact with the basal lamina
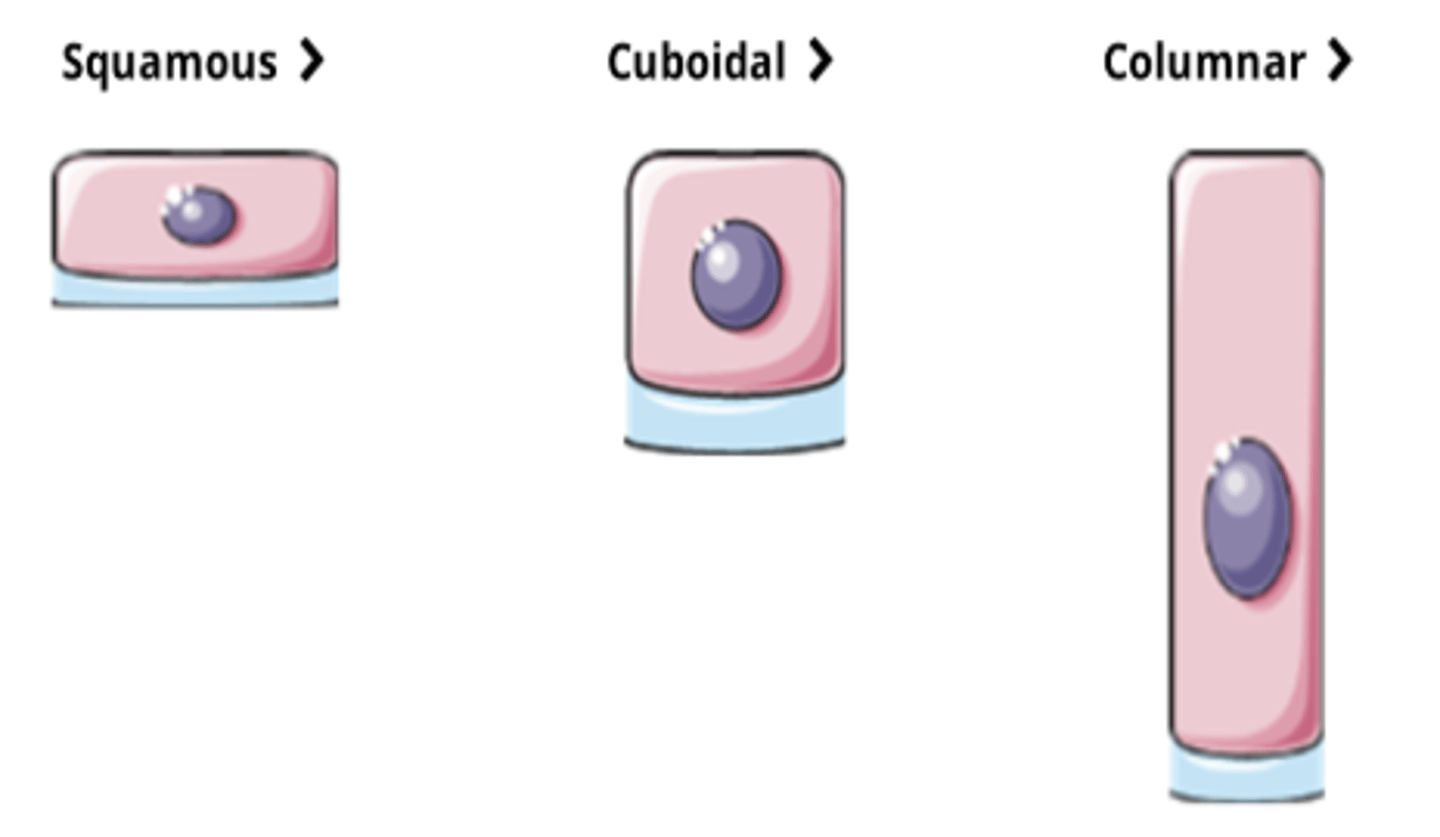
Cell Shape (Classifying Epithelium)
- Squamous = Flat (thin), wide, and somewhat irregular in shape
- Cuboidal = about the same size on all sides; the nucleus is usually centrally located
- Columnar = taller than they are wide; the nucleus is oval and located in the basal region of the cell
Transitional Epithelium
- Multiple layers of epithelial cells that allow for stretching
- Vary in shape
- Domed shaped surface cells, relaxed state
- In the bladder, cells are able to change shape as urine accumulates
Pseudostratified Epithelium
- Comprises only a single layer of cells and has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelium
- Hair-like projections on the surface help move mucous
Connective Tissue
- Most widespread and abundant type of tissue in the human body
- Most diverse of the four tissue types with a wide variety of functions
- Ranges in consistency from the gel-like softness of areolar connective tissue to the hardness of bone
Functions of Connective Tissue
- Primarily to support, anchor, and connect various parts of the body
Support and Protection
- Bones of the skull protect the brain
- Kidneys are surrounded by fat padding that protects it
Structural Framework for the Body
- Cartilage supports body structures such as the windpipe (trachea), ears, and nose
- Bones of the skeleton provide the framework for skeletal muscles
Medium for Exchange
Blood serves as a medium that carries gases, nutrients wastes, and blood cells to different parts of the body
Storage and Repair
- Bone stores minerals such as calcium; fat serves as a major energy reservoir for the body
Defence
- Connective tissue performs this function through a number of ways such as acting as a physical barrier, through white blood cells, antibody production
Components of Connective Tissues
- All types have three basic structural elements: cells, fibres, and intercellular substance
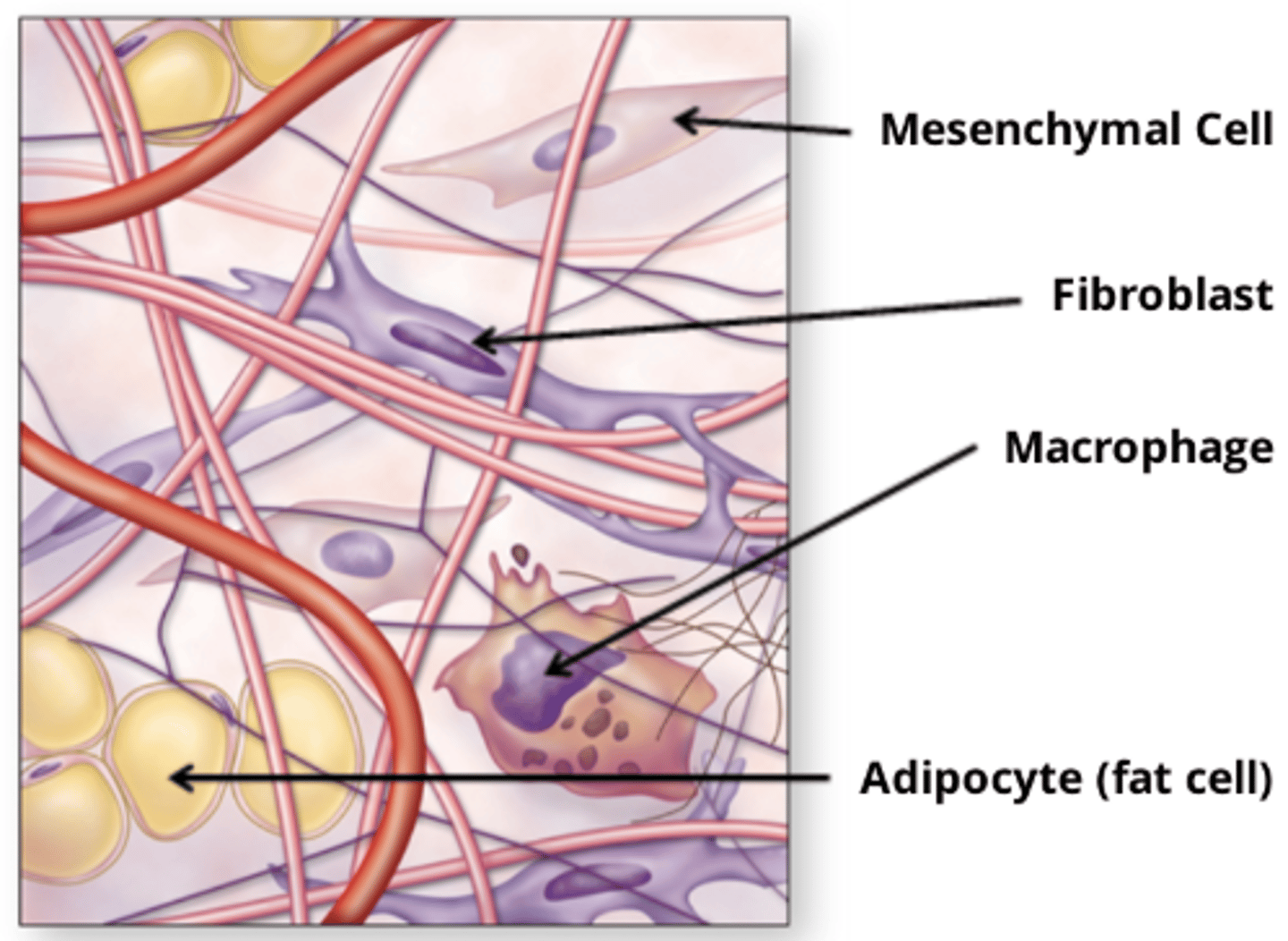
Cells of Connective Tissue
- Many different kinds of cells can be found in connective tissues (CTs)
- In some CTs, there is a large diversity of cell types, in others, the diversity is very low
- Some of the cells in CTs are fixed (permanent residents in the connective tissue
- Others are wandering (transient migrants who have entered the CT from the blood in response to specific stimuli)
Fibres of Connective Tissue
Three types of fibres secreted by fibroblasts:
- Collagen Fibres
- Reticular fibres
- Elastic fibres
Each type is formed by proteins made of long peptide chains
Ground Substance of Connective Tissue
- Occupies space between the cells and fibres of connective tissues
- High water content
- Transparent
- Colourless
- Viscous
Types of Connective Tissue
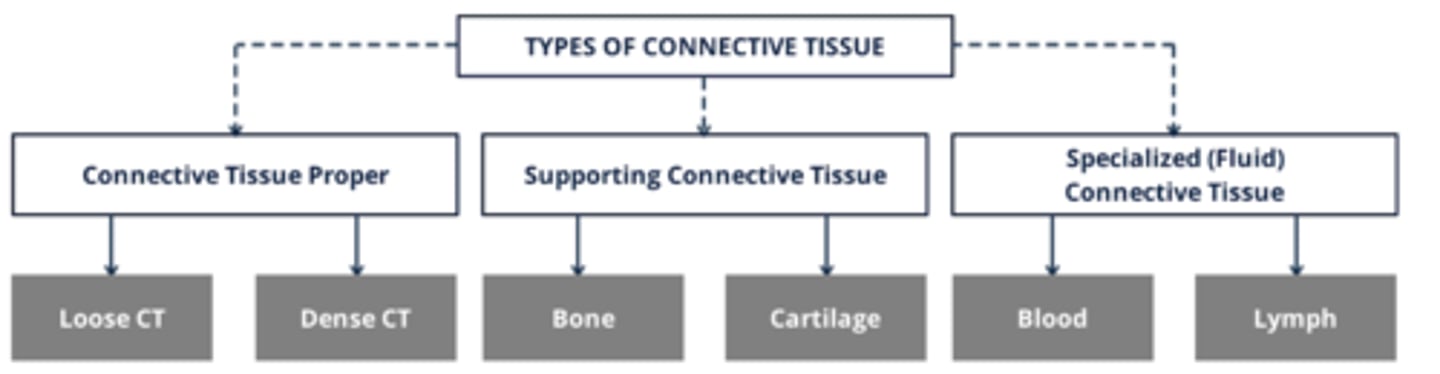
Loose CT (Types of Connective Tissue)
More ground substance with few CT fibres
Ex. Adipose tissue
Dense CT (Types of Connective Tissue)
Less ground substance with more CT fibres
Ex. elastic tissue
Bone (Types of Connective Tissue)
Important structural tissue that forms the framework of the body
Cartilage (Types of Connective Tissue)
A structural component of the body
Blood (Types of Connective Tissue)
- Fluid within blood vessels and the heart
- Contains various cells and proteins and performs a number of essential functions
Lymph (Types of Connective Tissue)
- Interstitial fluid (fluid that bathes cells)
- Collected into thin-walled lymphatic vessels and transported to the cardiovascular system
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome - Collagen
Connective tissue diseases are categorized into two groups:
- Rare genetic disorders
- Acquired disorders
- EDS is an example of a genetic disorder that can cause defects in collagen
- Without the proper form of collagen people with EDS have symptoms that affect functions of the muscular and skeletal systems
Components of Cartilage
- Cells
- Fibres
- Ground Substance
Perichondrium
- Dense, irregular connective tissue that envelops cartilage to provide nutrients to it
Lacunae
- Small space in cartilage that houses one or more chondrocytes (the major cells of cartilage)
Types of Cartilage
- Hyaline
- Fibrocartilage
- Elastic
Hyaline Cartilage
- wear resistant tissue
- designed to bear and distribute weight
- strong and flexible
- most common type of cartilage
Ex. joint surface of moveable joints, trachea, walls of nose, ribs
Fibrocartilage
- tough and inflexible form of cartialge
- durable and resistant to compression
Ex. intervertebral discs
Elastic Cartilage
- more flexible than hyaline cartilage
Ex. external ear, epiglottis