Chem Lab midterm
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Strong Acids used on lab 3
Nitric acid (HNO₃)
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
Reaction of copper metal with aqueous solution of nitric acid produces a gas. formula of the gas is:___ and identify color of the gas ____
gas: NO₂ (nitrogen dioxide) color: reddish-brown
In theory, the percent recovery should be 100%. What does a percent recovery greater than 100% indicate?
Percent recovery greater than 100% indicates extra mass in the sample, usually due to:
Contamination (residues or impurities)
Moisture in the sample
Incomplete drying or leftover reagents
Percent Recovery Formula
mass recovered/inital mass x100
How to solve for theoretical percentage
mass of element in compound/total molar mass x100
At the end of the experiment, 0.350g of Cu(s) was recovered. How many moles of Cu recovered?
mass of Cu (g)/ molar mass of Cu (g/mol) 0.350g/63.55 g/mol =0.00551 mol Cu
1. When taking a mass on a balance, which of the following is true:
A. Close the door of the balance, before taking the measurement
B. Never weigh chemicals directly in contact with the balance pan; use vessels, weighing paper or filter.
C. Do not weigh hot or cold objects on the balance.
D. Report all digits given by the balance.
E. All of the above.
E. All of the above.
Which ones of the following statements is INCORRECT?
a) Density may be measured in units of kg/m3.
b) Density may be measured in units of g/cm2.
c) Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance.
d) Density may be measured in units of g/cm³.
b) Density may be measured in units of g/cm2.
4. What is the hottest part of flame?
A. Top of the outermost cone
B. Top of the innermost cone
C. Top of the middle cone
C. Top of the middle cone
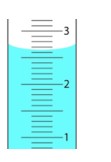
5. what is the value of liquid level in the cylinder?
2.65
6. A given sample of wood has a density of 0.8g/cm3. What will be the change in density of wood, if the piece of wood is cut into half?
A. It will be half of the initial value
B. It will remain unchanged
C. It will increase by a factor of two
D. Need volume of wood piece to answer.
B. It will remain unchanged
7. When 22.5 mL of liquid is poured into a 112 g beaker, the liquid+container mass is 135 g. The density of liquid is to correct no. of significant figures : A. 1.022 g/mL B. 1.02 g/mL C. 1 g/mL D. 1.0 g*/mL
D. 1.0 g*/mL
An irregularly shaped rock was lowered into a graduated cylinder holding a volume of water equal to 50 ml. The height of the water rose to 75 ml. If the mass of the stone was 250 g, what was its density?
10 g/mL
Is the empirical formula the true formula of a compound?
No, it is simplest whole number ratio of compound
Write empirical formula of Ethane gas (C2H6).
CH3
Is C3H6O7 an empirical formula?
Yes
To calculate mol, knowledge of _________ is required: A. Density B. Molar mass C. Volume D. None of the above
B. Molar mass
5. A sample of K weighs 0.39g. How many moles does it represent? Molar mass of K = 39 g/mol
0.010 mol
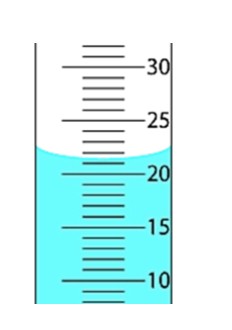
Read correct volume in the cylinder with correct no. of Sig Fig:
21.5
7. Sample was identified to contain 25g S and 30 g of Oxygen; calculate the empirical formula
S5O121
Calculate % composition of elements in a given formula H2O
1.2% H and 88.8% O
Formula for percent composition
mass of element/molar mass of compound x100
Given the masses of elements present in the formula, calculate the empirical formula As done in the calculation of MgO
MgO
Gases and Color Produced in Cu(s) + 4 HNO₃(aq) → Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2 NO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l)
Gas: NO₂ (reddish-brown)
Color change: Cu solid disappears → blue solution forms (Cu²⁺ ions)
Gases and Color Produced in Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Cu(OH)₂(s) + 2 NaNO₃(aq)
Gas: None
Color change: Blue solution → light blue solid (Cu(OH)₂)
Gases and Color Produced in Cu(OH)₂(s) → CuO(s) + H₂O(l)
Gas: H₂O vapor may rise (from heating)
Color change: Light blue solid → black solid (CuO)
Gases and Color Produced in CuO(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → CuSO₄(aq) + H₂O(l)
Gas produced: None color: black solid to blue solution
Gases and Color Produced in CuSO₄(aq) + Mg(s) → Cu(s) + MgSO₄(aq)
Gas produced: H₂ (hydrogen gas, colorless)
Color: reddish-brown solid to colorless
What type of reaction is Cu(s) + 4 HNO₃(aq) → Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2 NO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l)
Single Displacement and Redox
What type of reaction is Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Cu(OH)₂(s) + 2 NaNO₃(aq)
Double Displacement Reaction
What type of reaction is Cu(OH)₂(s) → CuO(s) + H₂O(l)
Decomposition Reaction
What type of reaction is CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) →CuSO4 (aq) + H2O(l)
Acid Base Reaction
What type of reaction is CuSO4 (aq) + Mg (s) → Cu(s) + MgSO4 (aq)
Single displacement/redox
What type of reaction is Mg(s) + H2SO4 (aq) H2(g) + MgSO4 (aq)
Single displacement/redox
Phosphate ions react with barium ions to produce barium phosphate:
3Ba2+(aq)+2PO43−(aq)→Ba3(PO4)2(s)3 Ba^{2+} (aq) + 2 PO_4^{3-} (aq) \rightarrow Ba_3(PO_4)_2 (s)3Ba2+(aq)+2PO43−(aq)→Ba3(PO4)2(s)
Extra PO₄³⁻ ions are added. Barium ions are: A. limiting reagent B. excess reagent C. spectator ions D. Acidifying agent
A. limiting reagent
In a synthesis experiment, a product was isolated, dried, and weighed: 10.5 g. Theoretical yield = 13.5 g. What is the percent yield?
77.8%
Percent Yield Formula
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
calculate moles of each reactant using 0.20 g Mg and 5.0 mL of 1.0 M CuCl. Molar masses: Mg = 24.31 g/mol, Cu = 63.5 g/mol.
Moles Mg ≈ 0.00823 mol
Moles CuCl = 0.0050 mol
What is the definition of a limiting reagent (LR)?
The reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, limiting the amount of product formed.
A student calculated % yield = 85.2%. Actual yield = 54 g. Find the theoretical yield.
63.4 g
What is the name of the compound (NH₄)₂CO₃?
Ammonium carbonate
What are the observations when (NH₄)₂CO₃ is heated?
White solid disappears; gases released; condensation forms on cooler surfaces
How do you test for NH₃ gas produced from heating (NH₄)₂CO₃?
Wet Litmus paper turns blue; pungent smell
What type of reaction is the heating of (NH₄)₂CO₃?
Decomposition
What are the observations when Mg reacts with HCl?
bubbling, Mg dissolves, H₂ gas released
What type(s) of reaction is Mg + HCl?
Single displacement, Redox
Write the half-reaction for Mg in Mg + HCl.
Mg → Mg²⁺ + 2 e⁻ (oxidation)
Write the half-reaction for H in Mg + HCl.
2 H⁺ + 2 e⁻ → H₂ (reduction)
How many electrons are transferred in the reaction of Mg with HCl?
2
What are the observations when Pb(NO₃)₂ reacts with KI?
Colorless solutions → bright yellow precipitate forms (PbI₂)
Write the balanced molecular equation for Pb(NO₃)₂ + KI.
Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2 KI(aq) → PbI₂(s) + 2 KNO₃(aq)
Write the complete ionic equation for Pb(NO₃)₂ + KI.
Pb²⁺(aq) + 2 NO₃⁻(aq) + 2 K⁺(aq) + 2 I⁻(aq) → PbI₂(s) + 2 K⁺(aq) + 2 NO₃⁻(aq)
What are the spectator ions in the reaction of Pb(NO₃)₂ with KI?
K⁺ and NO₃⁻
Write the net ionic equation for Pb(NO₃)₂ + KI.
Pb²⁺(aq) + 2 I⁻(aq) → PbI₂(s)
hat type of reaction is Pb(NO₃)₂ + KI?
Double displacement / precipitation
identify the LR in the experiment 2 done
KIO3