Tahany Final 2024
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Christian Scriptures
Collection of sacred texts in Christianity, including the Old and New Testaments. They serve as the foundation of Christian beliefs and practices.
Hellenistic
Period following Alexander the Great's empire, blending Greek, Egyptian, Persian, and Indian cultures. Marked by advancements in art, science, and philosophy.
Matthew
Book in the New Testament; presents the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ. Contains the Sermon on the Mount and the Great Commission.
Luke
Flashcard: Luke is one of the four Gospels in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, detailing the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ.
Covenant
a sacred agreement or pact between God and humanity, typically involving promises, obligations, and mutual commitments
Gospels
The four books in the New Testament that tell the story of Jesus' life, teachings, death, and resurrection: Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John.
Mary
Mary
Mother of Jesus in Christian tradition
Significant figure in the Bible
Known for her humility and faith
Celebrated as a symbol of motherhood and purity
Call
asked to do something by god
Fasting
A practice of abstaining from food and/or drink for a specific period, often for religious, spiritual, or health reasons.
Gentiles
Non-Jewish individuals, typically used in reference to those outside the Jewish faith or community.
Mark (bible)
Flashcard: Mark is the second book of the New Testament in the Bible. It is one of the four Gospels and focuses on the life, ministry, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ.
John (bible)
Who was the author of the fourth Gospel in the New Testament, emphasizing Jesus' divine nature and teachings?
Genealogy
Genealogy is the study of family history and lineage, tracing ancestry through generations to understand relationships and connections within a family tree.
John The Baptist
Flashcard: John the Baptist - A Jewish preacher who baptized Jesus in the Jordan River. He is considered a prophet and forerunner of Jesus in Christian tradition.
Joseph
Flashcard: Joseph was the husband of Mary and the earthly father of Jesus. He is known for his unwavering faith and obedience to God's will.
Demon (bible)
Evil Spirit
Polytheism
The Belief in more than 1 god
Pauline Letters
The Pauline epistles, also known as Epistles of Paul or Letters of Paul, are the thirteen books of the New Testament attributed to Paul the Apostle. Among these epistles are some of the earliest extant Christian documents. They provide an insight into the beliefs and controversies of early Christianity. As part of the canon of the New Testament, they are foundational texts for both Christian theology and ethics.
Revelation
divine guidance or inspiration
Jesus
the man who Christians believe is the son of God and whose life, death, and resurrection as reported in the New Testament of the Bible are the basis of the Christian religion.
Healing
a lifelong process which occurs by the sovereign grace of God, through faith in Jesus Christ and the empowerment of the Holy Spirit.
Miracle
an extraordinary event manifesting divine intervention in human affairs. the healing miracles described in the Gospels.
Disciple
someone who is following Jesus, being changed by Jesus, and is committed to the mission of Jesus
Salvation History
God's plan to save mankind from sin and lift the human family to the glory of Heaven
Acts Of the Apostles
the title now given to the fifth and last of the historical books of the New Testament. The author styles it a "treatise" ( 1:1 ). It was early called "The Acts," "The Gospel of the Holy Ghost," and "The Gospel of the Resurrection." It contains properly no account of any of the apostles except Peter and Paul.
Catholic Letters
As the history of the New Testament canon shows, the seven so-called Catholic Letters (i.e., James, I and II Peter, I, II, and III John, and Jude) were among the last of the literature to be settled on before the agreement of East and West in 367.
Evangelist
the one who proclaims the glad tidings. 2 In that sense, anyone who brings good news to another is an evangelist.
Ruah
wind representing God's Spirit
Twelve
it represents governing authority; b) completion or perfection. Governing authority: there were 12 sons of Jacob, thus 12 official tribes. Solomon had 12 administrators. There were 12 apostles of Jesus.
Messiah
the promised “anointed one” or Christ ; the Savior
Kingdom of God
the spiritual realm over which God reigns as king, or the fulfillment on Earth of God's will
Parable
an apparently simple story used to illustrate a moral or spiritual lesson, to teach a great truth or to challenge the hearers to change their own behaviour.
Why is Pentecost a good starting point for our study of Christian Scriptures
the Holy Spirit descended with power upon the Apostles, thus began the mission of the Church in the world.
Explain what we mean when we say that the Christian Scriptures are religious history.
documents that recount significant religious events, teachings, and experiences within the early Christian community, set within a specific historical and cultural context. These texts serve not only as sources of religious belief and practice but also as records of the community's understanding of divine revelation, the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, and the development of Christian theology and ethics. Through scholarly analysis and interpretation, they provide insights into the religious beliefs, practices, and debates of the early Christian movement, reflecting its evolving understanding of God's purposes in human history.
Explain what important event happened in the year 70 AD/CE.
the Romans reclaimed Jerusalem and destroyed the Second Temple with only a portion of the western wall remaining
List and explain the stages in the communication of the gospels
1st stage: The actual life teaching of Jesus Christ.
2nd stage: This is the oral tradition. The Gospels spread by word of mouth
3rd stage: The written tradition, over time the gospels were combined with other writings in the canon of Scripture, which forms the New Testament.
Explain what we mean when we say the scriptures are divinely inspired.
God Motivated people to write with their own words
Explain why the four gospels all begin differently.
each begin differently due to their unique theological emphases, audiences, and purposes. These different beginnings reflect the diverse theological perspectives and literary styles of the Gospel writers, as well as their intentions in writing their accounts of Jesus' life, ministry, death, and resurrection.
Explain the change from imminent to delayed eschatology and its impact upon scripture
People thought that the return of christ would happen soon ( within their lifetime) but as it did not happen as quickly as expected people begin to emphasize a more delayed and spiritual thinking.
Explain in what language the Christian Scriptures are written.
the Old Testament texts were written in Hebrew, and the New Testament was originally written in Greek.
Explain and diagram the two-source theory in the development of the Gospels.
In summary, the two-source hypothesis proposes that Matthew and Luke used Mark for its narrative material as well as for the basic structural outline of chronology of Jesus' life; and that Matthew and Luke use a second source, Q (from German Quelle, "source"), not extant, for the sayings (logia) found in both of them
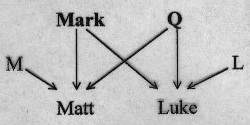
Explain who traditionally each evangelist was, and the modern scholarly opinion concerning this identification.
Matthew: Tax Collector Gospel of Matthew presents Jesus as the fulfillment of Jewish prophecy and emphasizes his role as the Messiah and teacher of the Law.
Mark: reflect Peter's teachings and eyewitness testimony, presenting Jesus as the suffering servant who came to serve and sacrifice for humanity.
Luke: presents Jesus as the compassionate Savior who came to seek and save the lost, with a particular emphasis on his concern for the marginalized and outcasts.
John: emphasizes Jesus' divinity and presents him as the Word made flesh, who came to reveal God's love and offer eternal life to those who believe in him.
List the three Gospels referred to as synoptic.
Matthew, Mark, and Luke
Explain why these Gospels are called synoptic?
because they can be “seen together.” What that actually means is that these gospels contain many of the same stories, and that those stories are sometimes even presented in the same sequence within each of the three different synoptic gospels.
Explain what were the benefits of the Pax Romana in the growth of the early Church.
The Pax Romana is Latin for roman peace. It is said that this era and the conditions of this time was perfect for spreading Christianity. There was a common language, and relative peace in this time period. Another major thing was the expanse of roads and sea travel that helped the spread of Christianity.
Compare and contrast the infancy narratives of Matthew and Luke.
Luke portrays Jesus' family observantly going to Jerusalem, but in Matthew they avoid the city. In Matthew's narrative the spotlight shines on Joseph. It is he who receives divine guidance in a series of dreams. In Luke's account it is Mary who shines, portrayed as the one who hears and keeps God's word.
Explain Jesus' method of calling disciples
The first four disciples that Jesus chose were two sets of brothers who were all fishermen. Jesus went along the shores of Lake Galilee. Seeing Andrew and Simon (Peter) he called them to discipleship. Jesus said he would teach them how to catch people, meaning that he would show them how to bring people back to God.
Explain the relationship of Jesus to his family during his lifetime.
While the Gospels do not provide extensive details about Jesus' family relationships, they highlight both moments of support and instances where his family struggled to understand his mission and teachings. These interactions underscore the complexities of familial dynamics amidst Jesus' ministry and the broader spiritual significance of belonging to God's family.
Explain Jesus' approach to the Law
According to Matthew 5:21–26 and 5:27–30, Jesus also held that observance of the law should be not only external but internal: hatred and lust, as well as murder and adultery, are wrong. The Jesus of Matthew in particular is a moral perfectionist (5:17–48).
Explain Jesus' issue concerning fasting and following certain ritual rules
Jesus clearly expected that His followers would fast (Matt. 9:14–15) and said that if they did so with proper motives, God would see and reward them (Matt. 6:16–18), just as He rewards those who pray with proper motives (Matt. 6:5–6).
Explain how ancient cultures explained mental illness.
Supernatural theories attribute mental illness to possession by evil or demonic spirits, displeasure of gods, eclipses, planetary gravitation, curses, and sin. Somatogenic theories identify disturbances in physical functioning resulting from either illness, genetic inheritance, or brain damage or imbalance.
Explain the parable of the sower and its meaning.
The man represents God and the seed is His message. Just as a planted seed starts to grow, the word of God starts to deepen and grow within a person. Some seed fell on the path and the birds ate it. The birds represent Satan. The seed on the path represents people who hear the message, but it is immediately lost.
Explain why Jesus spoke in parables.
In Matthew 13:10-16, Jesus tells us exactly why he spoke in parables. He says it has been given to some people to know the secrets of the kingdom of heaven, but not all. In other words, he does not reveal the truth of his kingdom to everyone. Though all can hear, not all are spiritually awake to understand
Explain what an apocalypse is.
a story representing the end of evil
Explain the unique role of James in the early church community.
As the head of the Jerusalem Church James obtained his most well-known role when he presided over the Apostolic council (Acts 15: 2-35). The issue that prompted this council was related to the entry of Gentiles into the Church.
Explain how and why the early Christians were expelled from Judaism.
the expulsion of early Christians from Judaism was driven by theological differences, social tensions, and historical circumstances that led to increasing hostility and separation between the two communities. ex. christians believing jesus was the messiah while jews did not, the argument of gentiles being followers of christ, adherence to jewish law.
Explain the relationship between the early church and the ancient synagogue.
the relationship between the early Christian Church and the ancient synagogue began with shared roots and common practices but evolved into a distinct separation as Christianity developed its own identity and theology. Despite this separation, interactions and tensions between the two communities persisted throughout the ancient world.
Explain the significance and resolution of the Jewish/Gentile Christian conflict.
The conflict arose in Jerusalem over the issue of table-fellowship with the Jewish Peter and the Gentile Cornelius (“You went into the house of uncircumcised men and ate with them” [11:3]) and concludes with the apostles' and brothers' affirmation that “God has granted even the Gentiles repentance unto life”
explain what was done at the “Council of Jerusalem.”
The council decided that Gentile converts to Christianity were not obligated to keep most of the rules prescribed to the Jews by the Mosaic Law, such as Jewish dietary laws and other specific rituals, including the rules concerning circumcision of males.
Explain the precedent set by the "Council of Jerusalem"
decreed that Gentile Christians did not have to observe the Mosaic Law of the Jews.
Explain the conflicts that Paul had with the Jerusalem community and James.
Paul had a conflict with the jerusalem community and james about gentile christians having to observe the rules of the jewish faith.
Explain the historical background to Revelation.
Christians faced persecution by emperor domition for refusing to participate in emperor worship. also The Jewish-Roman War (66-73 CE) and the subsequent destruction of Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE had a significant impact on Jewish and early Christian communities.
Explain what we mean when we say that we lack autographs of the Christian Scriptures.
we mean that the original manuscripts written by the authors of the biblical books are not available to us today. The term "autographs" refers to these original handwritten documents penned by biblical authors such as Moses, David, Isaiah, Matthew, Paul, and others.
Explain the importance of textual criticism.
Looks at how 2 texts say the same thing, is it important(word choice)? helps to get as close as you can to the original autographs
Explain how the cannon came to be.
the formation of the biblical canon was a dynamic and complex process shaped by historical, social, theological, and cultural factors. It involved the gradual recognition and acceptance of certain texts as sacred scripture within religious communities, ultimately resulting in the canonization of the old and new testament.
Explain the importance of variant readings.
variant readings in the Bible are important because they provide valuable insights into the textual history, transmission process, cultural context, theological implications, and literary aspects of the biblical texts. They remind us of the richness and complexity of the Bible as a collection of diverse documents shaped by centuries of interpretation and transmission.