Adrenergic Agonists and Antagonists
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What are the two parts of the autonomic system
parasympathetic and sympathetic
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Effects of the sympathetic nervous system
dilated pupils, increased heart rate, dilated bronchi
constricted blood vessels, inhibits digestion, decreases serotonin
effects of the parasympathetic system
Decreases heart rate, constricts pupils, reduces ventilation rate, increases digestive activity, sexual arousal
increases serotonin
what is the difference between the autonomic system and somatic system ganglia
the somatic does not have ganglia and is direct to the skeletal muscle
what is the basic setup of the ganglia in the autonomic nervous system
preganglionic neuron
ganglionic transmitter: ach
receptor
postganglionic neuron
neuroeffector
effector organ
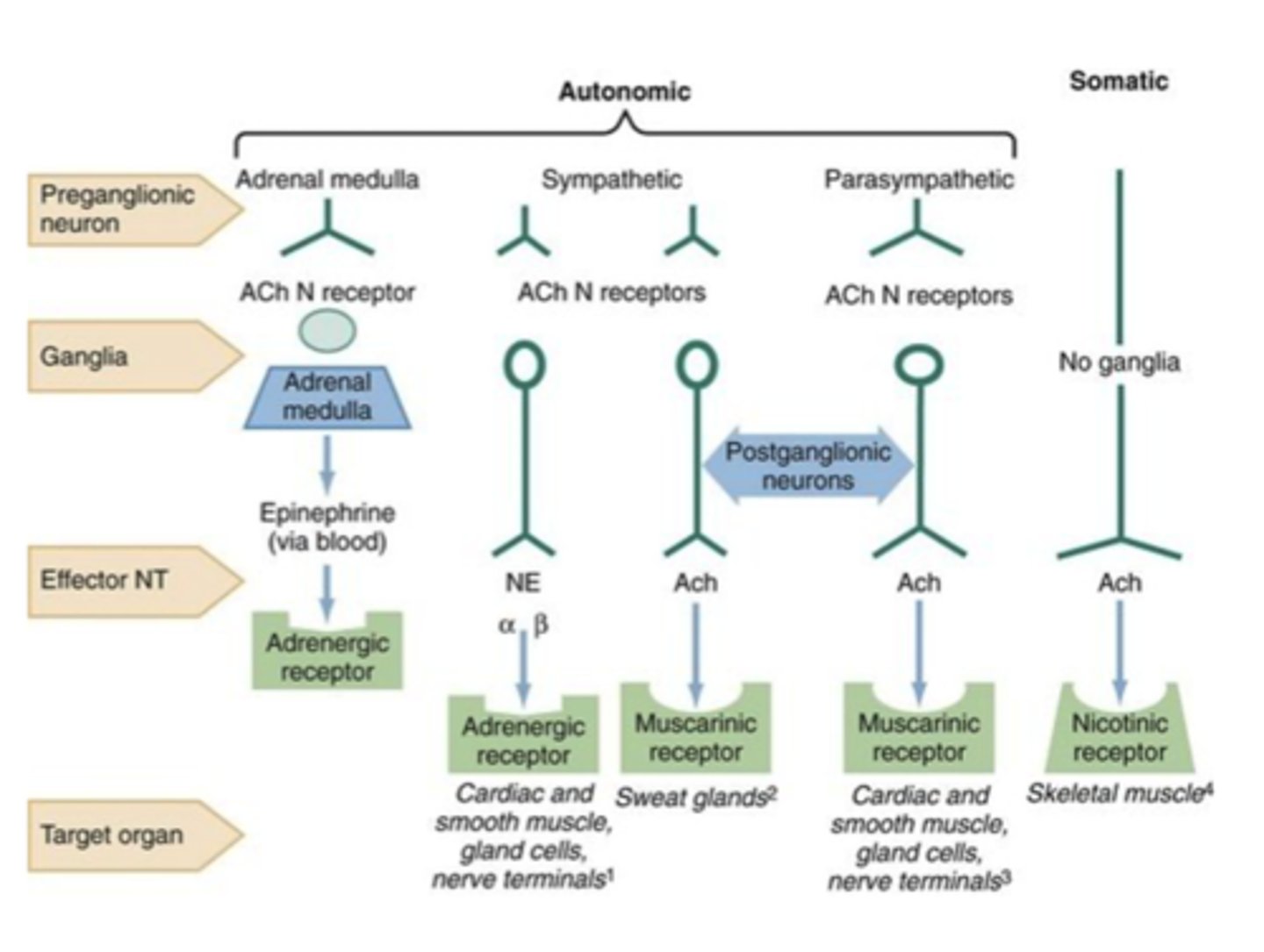
what does the sympathetic nervous system use to communicate with target orangs
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
what kind of receptor is on the effector organ for the sympathetic nervous system
adrenergic receptor
what kind of receptor is on the effector organ of the parasympathetic system
muscarinic
what kind of neuroeffector is the parasympathetic nervous system using
acetylcholine
What kind of receptors do norepinephrine and epinephrine have
use the same ones
metabotropic alpha 1/2 or beta-1/2/3
Basic mechanism of adrenergic effects
1. synthesis of norepinephrine
2. uptake into storage vesicle
3. release of neurotransmitter
4. Binding to receptor
5. Removal of norepinephrine
6. metabolism
synthesis of norepinephrine rate limiting step
hydroxylation of tyrosine is the rate limiting step
uptake into storage vesicles
dopamine enters a vesicle and is converted to norepinephrine
norepinephrine is protected
transport into the vesicle is inhibited by reserpine
what inhibits uptake into storage vesicles
reserpine
release of neurotransmitter
influx of calcium causes fusion of the vesicle with the cell membrane in a process called exocytosis
what promotes release of the neurotransmitter
amphetamines
removal of norepinephrine
released norepinephrine is rapidly taken into the neuron
what inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine
SNRIs cocaine and imipramine
metabolism
norepinephrine is methylated by COMT and oxidized by MAO
what are COMT inhibitors
entacapone and tolcapone
Modulation via Norepinephrine beta receptor upon its release
binds
G alpha activates adenylyl cyclase
conversion of ATP to cAMP
cAMP stimulates PK
phosphorylated K channel closes
cells more excited
what is a adrenergic receptor
GPCR receptors, primarily located in blood vessels, alpha and beta types whose primary ligands are epinephrine and norepinephrine
what is the function of alpha 1 adrenergic receptor
vasoconstriction
increase peripheral resistance
increased blood pressure
mydriasis
increase closure of bladder
Alpha 1 receptor has a greater affinity for
norepinephrine
Alpha 2 function
inhibits norepinephrine release
inhibits acetylcholine release
inhibits insulin release
alpha 2 receptors affinity is greater for
epinephrine
function of beta 1 receptor
increases heart rate, lipolysis, myocardial contractility
renin
beta 1 affinity is greater for
epinephrine and norepinephrine affinity is equal
function of beta 2 receptor
vasodilation
decreased peripheral resistance
bronchodilation
increased glucagon release and glycogenolysis
relaxes uterine muscle
Which organs does beta 1 associate with
heart and kidneys
Which organ(s) do beta 2 receptors associate with
lungs primarily
beta 2 has a higher affinity for
epinephrine (by a lot!)
How do a and beta receptors differ
affinity for various agonists
alpha highest for epinephrine and lowest for isoproterenol
beta highest for isoproterenol and lowest for norepinephrine
which receptor is not used clinically
alpha 2
What do selective beta blockers do and where do they act
used to decrease heart rate and blood pressure, on beta 1 receptors
where do nonselective beta blockers act and what do they do
block both B receptors, bronchoconstriction
What do direct acting adrenergic drugs do
act on postsynaptic receptors
what are examples of direct acting drugs
epinephrine
norepinephrine
isoproterenol
phenylephrine
what do mixed action drugs act on
direct stimulation of target and enhances release of NE from vesicles
Mixed action drug examples
pseudoephedrine
metaraminol
what do indirect acting drugs do
enhance the release of NE from the vesicles
examples of indirect acting drugs
amphetamines
cocaine
Affinity for B receptors increases as what gets larger
as the group on the amine nitrogen gets larger
Catecholamines
rapid onset of action
brief duration of action
not administered orally
do not pentrate the blood brain barrier
catecholamine drug examples
Epinephrine
NE
isoproterenol
dopamine
Non catecholamines
longer duration of action
orally administration or inhalation
How does epinephrine affect the heart
increases the rate and force of cardiac contraction
what is epinephrine's cumulative effect
increases systolic blood pressure
decreases diastolic pressure
respiratory effects of epinephrine
bronchodilation by acting directly on smooth muscle cells
epinephrine hyperglycemia effect
increased glycogenolysis in the liver increased release of glucagon and decreased release of insulin
what vessels does epinephrine constrict
arterioles in the skin
what vessels does epinephrine dilate
vessels to the liver and skeletal muscles
What is the onset of epinephrine
rapid onset with brief duration
what is epinephrine metabolized by
MAO and COMT
preferred route of epinephrine
intramuscular anterior thigh
Therapeutic uses of epinephrine
bronchospasm
cardiac arrest
anesthetics
duration of local anesthesia
topical
what kind of effect can a single cartridge of local at a 1:100,000 ratio with E have on plasma epinephrine concentration
doubling effect
CNS adverse effects of epinephrine
anxiety, fear, tension, headache, tremor
cardiac adverse affects of epinephrine
trigger cardiac arrythmias, especially if pt is using digoxin
Adverse effects of epinephrine in diabetic patients
release of endogenous stores triggered and may need to up the dose of insulin
Adverse effects of epinephrine in pits with hyperthyroidism
increased production of adrenergic receptors in vasculature leads to hypersensitive response
how can inhalation of epinephrine affect the heart
sensitive the heart to the effects of epinephrine
tachycardia
Why is there a risk of hypertensive episodes with nonselective B blockers
they prevent vasodilatory effects of epinephrine on B2 receptors leaving the A receptor stimulation unopposed
Which receptor blocker is responsible for vasodilation
alpha 1 blocker
Which receptor blocker is responsible for stopping norepinephrine release inhibition
alpha 2 blocker
What do Beta 1 blockers do
decrease in cardiac hyperactivity
What do B2 blockers do
lead to bronchoconstriction
why should you be cautious when using propranolol in diabetic patients
it can inhibit actions of catecholamines released in response to hypoglycemia and complicate therapy of diabetic patients and block warning signs of hypoglycemia and delay recovery
why should you be cautious when using bet blockers for pts with severe allergies
can be ineffective in patients taking beta blockers already
why should you be careful when moving a patient that is taking an adrenergic antagonist
lower blood pressure increases risk of fainting